Based on the location and nature of pain in the eyes, an ophthalmologist can often suggest the likely cause of the symptom. What diseases may indicate pain that occurs when moving the eyes, we will talk in this article.
A healthy person does not experience painful sensations when he moves his eyeballs - looks down or up, watches moving objects. If your eyes hurt when you move, then there is a problem. This may be severe fatigue of the visual organs, an ophthalmological or general disease. A doctor can determine the exact cause.
Ophthalmopathologies in which it is painful to move the eyes
The cause of pain that occurs when moving the eyeballs is often directly related to diseases of the visual system.
- Blepharitis.
Usually, pain when moving appears in the late stages of inflammation, when the pathological process has spread from the eyelids to the entire eyeball. In this case, the patient can hardly move his eyes, which are very festered and look reddened.
- Neuritis of the oculomotor nerve.
The disease does not occur very often, but one of its characteristic signs is the difficult movement of the eyeballs and the resulting pain.
- Ocular myositis.
With this disease, the external eye muscles become inflamed, which naturally leads to pain when trying to change the direction of gaze. The inflammatory process in the extraocular muscles can be caused by infectious and inflammatory diseases, injuries, intoxications and a number of other reasons.
- Glaucoma.
Sometimes a patient who goes to the doctor with the complaint “it hurts to move the eyes” is diagnosed with “glaucoma.” With this disease, pain in the eye area can “radiate” to the head, accompanied by swelling of the eyelids, vomiting, decreased visual acuity, and changes in pupil size. If a person experiences such symptoms, one should not delay contacting a doctor. Glaucoma is dangerous, first of all, due to irreversible vision loss.
Treatment
In order to choose the most effective treatment, you need to visit an ophthalmologist . After examination and diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe therapy.
Stay up to date! The therapeutic course may include taking anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs, eye drops or ointments.
- Intraocular pressure is eliminated with medication . But in some cases, the doctor may prescribe laser coagulation.
- Glaucoma requires immediate medical intervention. Any delay may result in loss of vision. Exact therapeutic measures will be prescribed after a medical examination.
- Myositis – eliminated due to therapeutic exercises for the eyes.
Self-medication is only permissible as first aid. If you experience eye pain, do not rely on traditional medicine.
Be sure to seek medical advice from an ophthalmologist.
In most cases, treatment is prescribed individually based on the diagnosis and general clinical picture.
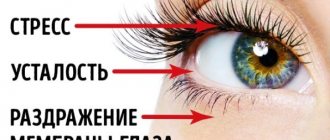
Need to know! If you feel that your eyes hurt from overwork or from the first signs of inflammation (after using low-quality decorative cosmetics, contact lenses, etc.).
You can try to eliminate eye pain yourself, using simple techniques or traditional medicine recipes , for example:
- Give your eyes a break from the computer and reading - if possible, take a bargain and spend it away from technology. A long walk in the fresh air will have health benefits.
- Do a head massage - massage your head starting from the temples, then moving to the back of the head, and from the back of the head to the forehead. You can use a special head massager. Stretch your neck with light, leisurely tilts of your head from side to side.
- Take a painkiller - drugs such as No-shpa, Citramon, Spazmalgon, Nurafen, Papaverine have proven themselves to be effective.
- Prepare a mint tincture - this remedy quickly relieves swelling and pain from the eyes. Take mint leaf powder and honey in a 1 to 1 ratio, and add water until you get a slurry with the consistency of liquid sour cream. Leave it to sit for 24 hours, then gently drop it into your eyes or lubricate your eyelash line, morning and evening.
- Rinse your eyes with chamomile solution - it has a disinfecting and soothing effect on the skin of the eyelids, and also removes redness of the eyes. To prepare it, pour 2 tablespoons of chamomile with 1 glass of hot water. After the herbs have brewed and the solution has cooled, soak a cotton pad in it and wipe your sore eyes.
Reference! Lotions made from infused black tea (brewed tea bags will do) will help quickly remove inflammation and relieve fatigue.
Other causes of the symptom
In addition to ophthalmological diseases, pain during eye movement can also be caused by general pathologies.
- Respiratory viral infections.
Any ARVI, cold, or flu contribute to the accumulation of toxins in the body. One of the forms of intoxication is pain when rotating the eyeballs.
- Sinusitis.
With sinusitis, the sinuses of the nose become inflamed, which are connected to the eye sockets by common walls. The inflammatory process that begins in the ENT organs can lead to compression of muscle tissue, which interferes with the free movement of the eyeballs and causes pain.
- Migraine pain.
Migraine headaches are often accompanied by pain in the eyeball. Since migraine is characterized by unilateral localization, eye pain is also concentrated on one side.
Why do my eyes hurt when I move them?
The eyeball is very sensitive to all kinds of external irritants, so many people may experience pain when moving their eyes. When the inside of the eyes hurt when moving, this may indicate the presence of certain problems with the eyes, some of which are quite serious. That is why, in case of prolonged painful sensations in the eyes, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
Causes of pain when moving the eyes and how to eliminate them
Pain in the eyes from the inside when they move down, to the side and up can be associated with various reasons, the exact one of which only a doctor can determine.
- Eye strain and general fatigue are often caused by prolonged work at the computer and other technical devices, reading, working with small objects or handicrafts. To avoid this, it is necessary to alternate work and rest so that the eyes can “rest.”
- The presence of certain infectious diseases of the eyes and brain, as well as general intoxication of the body, can cause pain in the eyes when they move. Among infectious eye diseases, the most common are conjunctivitis, blepharitis, uveitis, keratitis and iritis. All these diseases, in addition to pain, cause redness and itching, and also lead to dryness and swelling of the eyes. Consequently, when one of these diseases is diagnosed and treated correctly, the painful sensations in the eyes disappear.
The situation is similar with infectious diseases of the brain (meningitis, encephalitis, myelitis, etc.) - if any of these diseases is identified by a qualified specialist, then its subsequent treatment will help relieve the patient of pain in the eyes when moving. The main thing is not to self-medicate!
As for intoxication of the body, it cannot necessarily be caused as a result of some poison entering the body. Intoxication occurs even in the presence of viruses and fungi in the body (for example, with common flu).
- A foreign body entering the cornea also leads to eye pain. The foreign body can be metal shavings, sawdust, small stone chips, etc. In any case, the foreign body must be promptly removed from the eye by an ophthalmologist so that it does not cause a serious infection of the eye organs. Accordingly, after removing the foreign object from the eye, the pain disappears and the quality of life improves significantly.
- Dry eye syndrome is another disease that is accompanied by painful sensations when moving the eyes in different directions. In most cases, special moisturizing eye drops with artificial tears will help solve this problem.
- Glaucoma is one of the most severe eye diseases, which is characterized by rapid progression and leads to irreversible blindness. The main manifestation of glaucoma is considered to be an increase in intraocular pressure, and in the first stages of development this disease manifests itself in the form of minor pain in the eyes. That is why it is very important to visit an ophthalmologist at least once a year and undergo a complete examination.
Thus, there are many reasons for pain in the eyes. But in all cases, pain in the orbit that appears as a result of eye movement indicates that the eye muscles and nerves are involved in the inflammatory process. This situation can occur, for example, both during intoxication due to influenza or acute respiratory infections, and in fairly severe diseases (meningitis, encephalitis, glaucoma, etc.).
All of the above reasons that cause eye pain are the most common, but far from the only ones. Only an ophthalmologist after a thorough examination of the visual organs will help to identify the final cause of pain in the eyes during their movement.
Prevention of eye pain
The following are preventive measures for the occurrence of painful sensations in the eyes when they move:
– maintaining facial hygiene (wash your face regularly, don’t forget to remove makeup from your face, use only your personal towel, etc.);
– annual visit to the ophthalmologist;
– performing eye exercises to strengthen the eye muscles;
– frequent hand washing and a ban on touching your eyes with dirty hands;
– wearing special computer glasses while working behind a monitor screen;
– wearing sunglasses in bright sunshine, as well as wearing special protective glasses when working with chemicals, at a construction site or in dusty areas;
– strengthening the immune system and balanced nutrition.
All these seemingly simple tips will really help prevent the development of many eye diseases that cause not only painful sensations in the eyes, but also a number of other more serious consequences.
Take care of your eyesight! At the Clean View clinic you can undergo a full range of procedures for diagnosing vision and treating eye diseases. More details by phone.
Brief Summary of Eye Pain
Advertising:
Sharp pain, stinging, discomfort when moving the eyeballs is a common problem that can have both physiological and pathological causes. An unpleasant sign can accompany many diseases of an inflammatory or infectious nature, indicate incorrectly selected glasses or prolonged wearing of contact lenses.
Deterioration of vision and sharp pain when turning the head can be symptoms of coronavirus infection, malignant or benign neoplasms, as well as ordinary fatigue. Only an ophthalmologist can determine the exact cause, so in no case should you hesitate to visit a doctor.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure is often accompanied by a feeling of tension, tightness and pain in the eyeballs. High intracranial pressure also causes pain and discomfort when blinking. This problem develops as a result of the fact that the liquor environment affects the walls of the cerebral ventricles. It is impossible to measure the level of intracranial pressure at home; this can only be done in a hospital using special equipment.
An equally common cause is cerebral hypertension, which is accompanied by frequent migraine attacks, the formation of dark circles under the eyes and redness of the ocular conjunctiva. Many patients indicate additional symptoms - double vision, narrowing of the visual field, nausea and chills. Cerebral hypertension can have dangerous consequences for the human body, so at the first signs of pathology you should immediately seek medical help.
You are also worried about the question: “Why does my head hurt when I move my eyes?” What are the reasons for the trouble?
Headache that prevents you from moving your eyes due to increasing intensity is a common problem. It can be very acute, causing discomfort and limiting quality of life by reducing visual acuity.
There are different types of headaches that get worse in situations where you have to move both eyes or one, since it can be caused by different diseases with different causes, consequences and severity.
If a headache occurs or increases when there is a need to move the eyes (how could we not do this!), a rather unpleasant sensation arises. The main causes include glaucoma, stye, conjunctivitis. Given the importance of vision, no symptom should be underestimated.
Hordeolum (barley)
Hordeolum or stye (inflammation of the eyelid gland), surprisingly, can also cause headaches, which are localized on the side of the affected eye. Anyone who has suffered from this problem knows how painful it can be to move the eye. These sensations often occur in the area of the temples or, directly, the eyes.
Treatment is based on local application of antibiotics in the form of ointments or eye drops. Other inflammations of the eyelids can manifest in a similar way, which can cause situations where it is painful to move the eye/eyes. If they do not go away on their own or complications arise, you need to visit an ophthalmologist.
Neuritis
Typical pain behind the eye is inflammation of the optic nerve, which transmits image information from the eye to the brain. This is a serious disease, manifested by a sudden loss of visual function and pain behind the eye, especially when it moves.
Often, when you move your eyes, you also get a headache. Although most often it results in restoration of visual function, the disease can lead to nerve damage and thus to one-sided blindness.
The cause is viruses and bacteria, but the disease is also often the first symptom of multiple sclerosis.
The head often hurts during eye movements due to other diseases, for example, inflammation of the teeth, migraines, sinusitis.
Refractive errors (farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism)
Other causes include refractive errors, i.e. farsightedness, nearsightedness and astigmatism, for which unsuitable glasses are used; many people do not know about these defects at all. Along with eye pain, headache also occurs, usually aggravated by eye movement.
Ophthalmic migraine
Ophthalmic migraine is a temporary or permanent disorder of one eye that either accompanies a migraine attack or occurs independently in patients with a history of migraine.
Ophthalmic migraine occurs due to circulatory disorders in the retina. Patients complain of temporary loss of vision in one eye. Most patients under 40 years of age experience vision loss in one eye ranging from a few seconds to several hours.
Repeated attacks can cause permanent damage to the visual field. Ophthalmic migraine is not always accompanied by headache. Ophthalmic migraine is not always accompanied by headache.
If it is present, it is localized above or in the immediate vicinity of the affected eye and intensifies with eye movement.
Vision loss or disturbance may occur before, during, or after a headache attack. Ocular migraine is rare and therefore diagnosis is made by differentiation. It is necessary to exclude transient blindness, which is a secondary disease during microembolization of reticular arteries.
Source: //zen.yandex.ru/media/id/596a6a468146c12e34f9afda/597a44f8b2d0097284508b89
Prevention
In addition to drug treatment, doctors recommend doing eye exercises. During this period, you should observe restrictions on reading, watching TV and working on the computer. For the purpose of prevention, such restrictions will have to be observed for a long time.
It is worth noting that hygienic eye care is very important. For rinsing, you can use chamomile decoction. Compresses made from ordinary black tea will be useful. The main prevention is to visit an ophthalmologist once a year. This will help to detect the development of diseases in time. Timely treatment ensures a favorable result.
A healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition affect the condition of the eyes. Nutrition should be balanced with plenty of vitamins, fruits, and herbs. Blueberries and carrots are very good for the eyes. If the activity is related to computers, then during the working day you need to give your eyes a rest. Getting enough sleep will help your eyes relax and rest.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the patient's condition consists of several stages. The doctor prescribes two or more methods to identify the root cause:
- Anamnesis collection. This is data obtained from the words of the patient or his close relatives. Based on these, the doctor may prescribe further examination.
- General inspection. The condition of the mucous membrane of the eyes, conjunctival sac, and eyelids is revealed. You can detect signs of neuralgia visible to the naked eye (nervous tics, slurred speech).
- Measurement of arterial and intracranial pressure.
- Examination of the internal structure of the eyes. To do this, a solution is instilled onto the patient’s mucous membrane, disrupting the process of accommodation of the pupil. This condition occurs over time. Using special instruments, the doctor assesses the condition of the cornea, lens, eye chamber, retina, and microcirculation vessels.
- Laboratory research. A general blood and urine test and blood biochemistry are performed. If necessary, measure the amount of glucose. The doctor receives data on the basic parameters of the biological fluid, which indicate the condition of the internal organs.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball.
- CT, MRI of the head. The internal structure of the eyeball and brain is assessed layer by layer. The doctor identifies the integrity or damage of tissues, nerve fibers, and blood vessels.
Therapy is based on the cause that caused the patient's condition:
- an anesthetic that is used for 5-7 days to avoid the risk of addiction to the active substance;
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve inflammatory conditions in the outer tissues of the eyes;
- antispasmodics that eliminate excessive vasoconstriction;
- antihistamines that eliminate inflammation and swelling in the presence of allergies;
- antiviral and antibacterial drugs that eliminate the presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood;
- steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are used for inflammation of blood vessels and nervous tissue;
- drugs that lower blood pressure, which are taken in the form of tablets;
- a drug that reduces intraocular pressure, used in the form of drops;
- antipyretic drugs at temperatures above 38.5 degrees.
In addition to prescribing medications, the doctor describes to the patient the basic principles of dealing with this type of pain:
- long sleep;
- reducing eye strain by shortening the time spent at the computer, TV, tablet, phone;
- gymnastics for the eyes.
If all doctor's instructions regarding the prescribed medication and dosage are followed, the risk of complications from the disease is reduced. Complete recovery from diseases is possible.
For pain in the head and eyes due to diseases not related to the visual analyzer, no special treatment or diagnosis is needed. It is enough to eliminate the cause and the eye problem will disappear on its own. If pain when turning your eyes persists even after recovery from the underlying disease, you should consult an ophthalmologist for advice and, possibly, special treatment.
If symptoms of glaucoma appear, then an examination by an ophthalmologist is needed urgently; in case of an attack, it is urgent. To make this diagnosis, intraocular pressure measurement and follow-up are necessary.
For pain associated with myositis and other signs of overstrain, eye exercises are often prescribed, followed by visual rest. Often, a preliminary ultrasound of the eye area is performed in order to more thoroughly examine the tissues filling the orbit.
If you have any doubts about your eye health, you should consult a doctor for advice, since the earlier the diagnosis is made, the easier the treatment and the more favorable the prognosis.
To find out why it hurts to move your eyes, visit an ophthalmologist
If it hurts to move your eyes and the discomfort does not go away within a few days, consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will conduct an examination, find out the cause of the development of such a symptom, and only after that will prescribe the most appropriate course of treatment.
To treat myositis, you can use special health-improving exercises. To thoroughly examine the condition of the muscle fibers, the doctor may need ultrasound results. Do not delay visiting an ophthalmologist if you feel pain in your eyes. Identifying pathology at an early stage will allow you to quickly get rid of it and avoid complications.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of such signs:
- infectious lesion;
- sinusitis, sinusitis;
- swelling;
- excessive fatigue of the visual organs;
- allergic reactions, Quincke's edema;
- head and eye injuries;
- ophthalmic migraine;
- blepharitis;
- neuroses;
- inflammatory processes of the facial nerve;
- glaucoma;
- cataract;
- neoplasms in the brain;
- myositis.
The etiology of pain can only be determined after a thorough examination of the whole body. Each patient experiences such manifestations individually.
Diagnostic methods for eye pain
If it is painful for a person to look or roll his eyes, and there are other symptoms from the organ of vision, he should contact an ophthalmologist who will conduct the necessary studies:
- visual inspection;
- visual acuity test;
- slit lamp examination;
- conjunctival smear.
Based on the data obtained, a diagnosis is made as to why a person cannot move his eyeballs.
If the doctor sees that there is no pathology on the part of the organ of vision, but the person still feels pain when moving the eye socket, he will refer him to other specialists - a traumatologist, endocrinologist, neurologist.
First of all, the specialist will conduct a visual examination of the organs of vision and assess the condition of the cornea, eye socket and eyelids. The following diagnostic methods may also be prescribed:
- study of peripheral vision to establish the boundaries of the visual field;
- examination of the fundus of the eye using an ophthalmoscope. This method will allow us to study the retina, optic nerve disc, and blood vessels;
- biomicroscopy. Examination of ocular tissues with a slit lamp. Helps identify glaucoma, keratitis, iridocyclitis and other inflammatory phenomena in blood vessels;
- tonometry is used to measure pressure in the organs of vision;
- Ultrasound is used to assess the structure of the eye, the condition of the lens and retina;
- pathologies of the cornea can be detected using confocal microscopy;
- A fluorescein test will allow you to assess the condition of the lacrimal ducts, as well as detect dacryocystitis.