- Hemophobia in children and adults
- Why does a phobia occur?
- Causes
- Main symptoms
- Treatment of hemophobia
- Correct installation
- Drug treatment
- Exercises to calm down
- Meditation to treat hemophobia
You can often hear from a child: I’m afraid to donate blood from my finger. Such irrational fear of a medical procedure is accompanied by hysteria. Hemophobia, the fear of donating blood, affects adults who did not cope with the phobia in childhood.
Hemophobia - fear of donating blood
A progressive mental disorder harms a person: against the background of one phobia, other fears develop, and new symptoms appear. Treatment of fear involves correcting the thinking and behavior of the victim of the phobia.
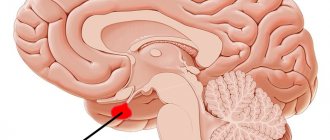
Hemophobia in children and adults
Hemophobia is the fear of the procedure of drawing blood from a finger or from a vein. The body's spontaneous defense reaction is accompanied by an acute reaction from the patient. The internal state of fear is born due to the inevitability of pain: from the first procedure, a negative experience is stored in the child’s memory. He knows that donating blood hurts.
Hemophobia arises against a background of false expectations. Before the procedure, the little patient is told that he will not experience any pain. Deception enhances the negative experience and in adulthood the person continues to be afraid of the procedure and avoid it. Hemophobia is accompanied by other fears: fear of medical institutions or fear of infections.
Why does a phobia occur?
For the development of fear, prerequisites are needed. People with good stress resistance are less likely to suffer from obsessive disorders. Environmental factors worsen personality resilience. Excessive stress on the psyche creates internal tension: problems at work or at home reduce defense mechanisms. As a result, physical and mental stress only intensifies the phobia, and the person experiences weakness, apathy, and becomes depressed.
Negative factors include the pace of life of a modern person. Without timely rest, mental disorders are inevitable.
Pessimism, which is another defensive reaction of the psyche, creates the preconditions for the development of fear. The more a person believes in the negative outcome of any event, the more susceptible he is to phobias.
I want to be a donor, but I don’t know anything about it and I’m afraid. Instructions on how to come for your first donation
Step 1: Stop being afraid
Blood transfusion stations (BTS) operate on the principle of “maximum benefit to the recipient and minimal harm to the donor.”
But I quite often meet people who did not donate blood not because of some illness or contraindication, but because of their own fears and prejudices. 1. “They will infect me with something through needles.”
Donating blood is completely safe for donors. SPCs are equipped with high-quality disposable sterile equipment. All syringes and needles are opened in front of you, so no one will inject you with a used needle.
2. “I will faint if they take so much blood from me.”
Of course, there is a risk that you may lose consciousness. Especially if you know about your intolerance to the sight of blood. But if you have a proper breakfast before donation, you will not lose consciousness because 500 ml of blood is taken from you. The donor's best breakfast is sweet porridge with water, sweet tea and simple cookies.
3. “Blood should be donated only in emergency cases when there is an urgent need”
Firstly, if you go to the Blood Service website in the “Donor traffic light” section, you will see that there is not enough blood in the Yekaterinburg SEC.
Secondly, you need to understand that all emergencies do not occur according to schedule, but completely unexpectedly. It is therefore important that blood transfusion stations have sufficient quantities of material at all times.
4. “Donation is long and painful”
The actual blood donation process takes approximately 15 minutes. You will spend approximately an hour and a half in the hospital, but this is due to the fact that you will be examined by a doctor before the procedure.
And to find out how you feel from the injection, just pinch yourself on the inner surface of the elbow area.
Step 2: Check yourself for donor eligibility
Now you are not afraid to donate blood and have decided to do so soon. But to become a donor, there are a number of rules that must be followed. The main ones:
- age - over 18 years old;
- weight - more than 50 kg;
- have no contraindications (we will discuss them below);
- be registered in the Sverdlovsk region for at least a year.
Doctors identify the presence of contraindications during examination. There is a map by which you can independently understand whether you can become a donor right today or not.
Step 3: Find a suitable SPC
There are not many places in Yekaterinburg where donations are carried out. The day before coming to the hospital, you must call in advance and make an appointment. Please note that all blood collection sites operate on different hours.
- St. Palmiro Togliatti, 8 - Regional blood transfusion station. Opening hours: Mon-Fri 08:00–13:00. Phone: +7 (343) 212–90–44 (donor department), +7 (343) 233–46–61 (reception).
- St. Solikamskaya, 6 - Blood transfusion station of the FMBA of Russia. Opening hours: Mon-Fri 08:00–12:00. Phone: +7 (343) 322–73–48.
- St. Repina, 1 - Blood transfusion department of the Research Institute of OMM. Opening hours: Mon-Thu 9:00–11:00. Phone: +7 (343)371–28–30.
- St. Volgogradskaya, 185 - Sverdlovsk Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1. Opening hours: Mon-Fri 08:30–12:30. Phone: + 7 (343) 240–35–35, +7 (343) 240–47–56.
- St. S. Deryabina, 32 - Regional Children's Clinical Hospital No. 1, blood transfusion department. Opening hours: Mon-Fri 09:00–12:00. Phones +7 (343) 240–57–80, +7 (343) 240–58–01.
Step 4: Prepare for the procedure
Before donation, you need to prepare your body:
- Do not take aspirin- and analgesic-containing medications within 72 hours;
- Do not drink alcohol within 48 hours;
- Eliminate fatty, spicy, smoked foods, as well as eggs and dairy products from your diet within 24 hours. You can eat boiled cereals, fruits and vegetables, bread and dried goods. For drinks, sweet tea, mineral water and juices are preferable;
- in the morning before the procedure, have a light breakfast (as mentioned above, sweet porridge with water is best);
- refrain from smoking one hour before donating blood.
Step 5: Come to the hospital and undergo the procedure
- You must come to the hospital with your passport. You may also be asked for SNILS, so I recommend taking that too.
- Upon arrival, you will immediately register.
- Afterwards there is an examination, which will take about an hour. During this time, you will fill out a questionnaire, a blood sample will be taken from your finger, and you will be examined by a therapist. Your doctor will tell you if you can donate blood that day. There is an important clarification here: if you come for a donation for the first time, you also need to undergo a preliminary examination - they will take a sample of blood from a vein. The results of the examination become known within a week . Only after this you can become a donor.
- When you come for your donation, you will be given sweet tea and cookies before the procedure.
- When you are ready, you will be called into the office and 500 ml of blood will be drawn from a vein.
Step 6: Recover After Donating Blood
- Immediately after the procedure, you need to sit for a while (5-10 minutes). If you feel dizzy, please notify staff immediately.
- Just like before donation, after donation you should not smoke for one hour.
- Do not remove or wet the bandage for 3-4 hours.
- For 24 hours after donating blood, it is not advisable to carry heavy objects or drink alcohol.
- Drink as much fluid as possible for the next 48 hours after the procedure.
- Do not vaccinate within 10 days after donating blood.
Step 7: Get the goodies
Donation is a free event. However, in addition to the feeling of fulfilled duty to society, you are also entitled to a payment “for food”: today it is 564 rubles (5% of the minimum wage) and two days off for recovery. You can reschedule one of them to any other time during the year.
Step 8: Make Blood Donation a Regular Habit
You can come back for a second blood donation after 60 days. But there is a limit on the maximum number of blood donations: men can donate blood five times per year, women - four times.
In addition to whole blood, you can also donate its components (plasma, platelets, leukocytes). After donating plasma, at least 14 days must pass before the donor can donate blood or plasma again.
You can also receive the title of “Honorary Donor of Russia.” According to Federal Law No. 125 “On the donation of blood and its components,” the badge “Honorary Donor of Russia” is awarded to citizens who donate free of charge:
- whole blood 40 or more times;
- plasma 60 or more times;
- whole blood 25 or more times and blood plasma in a total amount of 40;
- whole blood less than 25 and blood plasma in a total amount of 60.
Honorary donors have the right to:
- extraordinary treatment in state or municipal organizations;
- priority purchase at the place of work or study of preferential vouchers for sanatorium and resort treatment;
- provision of annual paid leave at a time convenient for him;
- provision of an annual cash payment: in 2021, the payment amount is 14,145.98 rubles.
Causes
The causes of hemophobia are always psychological in nature. If a person is afraid of pain, the reason for the fear is an exaggeration of the pain syndrome that the patient once experienced. It is common for a victim of a phobia to make a tragedy out of the procedure and exaggerate the discomfort during blood donation. Reasons why the patient is afraid of the procedure:
- fear of blood;
- negative experience;
- incorrect attitudes and associations;
- associated phobias.
A person is afraid to see his own or someone else’s blood - these are different phobias. Fear of the sight of your blood is a defensive reaction. Fear of the sight of someone else's blood is expressed in disgust towards people or fear of becoming infected. You need to understand the causes of fear by studying possible and additional causes of irrational fear.
The phobia is intensified by obsessive states: if the patient is afraid of needles, unsterile objects, or the smells of medical institutions, the future procedure causes panic fear. Over time, the phobia develops, and the patient avoids the test procedure to the detriment of his own health.
The reasons for the phobia may lie in the negative experience of donating blood.
Why is there a fear of donating blood?
This fear is caused by traumatic events in childhood associated with blood. For example, a baby breaks his nose, panics greatly, and receives psychological trauma. The traumatic memory of an unpleasant incident eventually turns into a phobia.
Fear of analysis:
- It affects not just any person, but impressionable people who tend to exaggerate possible troubles. In the minds of sensitive babies, a slight pain from a harmless medical procedure turns into true torture;
- appears in children with overly protective parents who are trying to protect their own child from the “cruel world.”
A similar phobia also occurs in people with a low pain threshold. In such individuals, even a minor scratch causes severe pain.
Hemophobia is “hereditary” and “contagious.” If the mother suffers from it, then soon you can hear the phrase “I’m afraid to donate blood from my finger” from the baby.
Main symptoms
A child and an adult perceive threat differently. The baby's first defensive reaction is hysteria. In adult patients, the phobia manifests itself differently: he deliberately ignores the procedure. A person stocks up with a whole arsenal of excuses why he won’t be able to undergo the procedure. Manifestations of hemophobia:
- uncontrollable panic attacks;
- loss of consciousness;
- confusion of thoughts;
- shortness of breath (a person is suffocating and cannot take a deep breath);
- cardiopalmus;
- tremor of the upper and lower extremities.
Manifestations of hemophobia cannot be controlled; spontaneous reactions occur when there is a need to take blood. The fear of blood makes you nervous.
A panic attack is accompanied by increased anxiety. This condition may last for several hours after the procedure.
Hemophobia causes increased sweating, chills and chest pain. During an attack, a person poses a danger to himself and others.
A progressive phobia affects the perception of reality: dizziness and headaches, temporary clouding of reason. An obsessive condition needs urgent treatment.
Treatment of hemophobia
Fear is a normal protective reaction of the body. The psyche senses a threat and immediately reacts to it. The fear of blood is not fatal, but it does affect human behavior. If the problem is a fear of blood, it is necessary to develop resistance to the sight of it. Habituation occurs along with establishing new affirmations.
Phobia with an acute reaction is less common. In most cases, the manifestation of fear is an anxious state. Psychotherapeutic techniques are used to help the patient: the level of fear is reduced, the true cause of the phobia is determined.
Emergency assistance to the patient if the fear of blood suddenly manifests itself:
- the patient sits in a comfortable position, the head tilts towards the knees (in this position, blood rushes to the head and the pressure decreases);
- breathing is restored (even breathing helps to calm down and reduce anxiety);
- After the exercise, you need to stand up and relieve tension from the muscles.
Such help is needed in cases where a panic attack interferes with diagnosis.
The primary task is to establish control over your own body. If a person cannot control the body's reactions, the phobia will only intensify over time.
Correct installation
Attitudes are internal beliefs that are formed in early childhood. After the first visit to the doctor, the baby forms an impression of the procedures completed. Negative experiences are the main cause of hemophobia in the future.
Impressionable people suffer from hemophobia. They are accustomed to react sharply to any environmental changes. It is difficult for hypochondriacs who are afraid of infection to cope with medical procedures.
Working with a psychoanalyst will help you get rid of the feeling of fear: a person works on his own thinking, gets rid of attitudes embedded in the subconscious.
Drug treatment
Hemophobia is not a dangerous irrational fear. In most cases, treatment is accomplished without drug therapy. A course of sedative tablets is prescribed for increased anxiety. Sedatives provide temporary relief and are not a cure. Tranquilizers are not prescribed in case of hemophobia.
Exercises to calm down
The best option for getting rid of hemophobia is physical exercise, which helps relieve excess stress. Adaptive responses are shaped by self-control skills. Breathing exercises will help you calm down in a short time. In a comfortable position (sitting or standing), it is necessary to restore breathing. Don't hold your breath. As soon as your breathing calms down, hold your breath for 2-3 seconds for every 5th breath. Then breathing is restored again. The exercise is repeated at least 3 times.
Meditation to treat hemophobia
Meditation is an effective calming technique. It does not fight the cause of the phobia, but helps to counter the spontaneous reactions of the body. Meditation calms anxiety, relieves stress and muscle tension.
Yoga classes are suitable for preventing the development of additional phobias. In combination with psychoanalysis, the relaxation technique allows you to get rid of the obsessive state.
Meditation is an effective calming technique