Vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by impaired tone of blood vessels, spasms of blood vessels, impaired circulation, and impaired vision. Attacks during VSD are often accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity; attacks occur during which a person sees only darkness and cannot see the outlines of objects. Decreased vision and pain may occur on one side or affect both eyes.
At the Yusupov Hospital, research into VSD is carried out in several areas: the state of the cardiovascular system, visual system, digestive system, respiratory system, endocrine system, nervous system.
Why do my eyes hurt with VSD?
If a patient with VSD has floaters in front of his eyes, this is a common visual disorder caused by a sudden narrowing of the blood vessels in the eye. Flashes of light, distorted images, pain in the eyes, a cloudy or dark background with partial vision or a complete lack of vision of objects may also be bothersome. Examination of the patient's systems and organs helps to identify diseases associated with neuroses; the doctor prescribes treatment for depression, neurosis, and prescribes medications to relieve panic attacks, pain, and anxiety.
Pain in the eyes with VSD is often accompanied by headache and pain in the heart area. Often, along with pain in the eyes, vision drops sharply, the image becomes blurred, the vision becomes dark, flashes and spots appear before the eyes. Visual disturbances can indicate not only VSD; if such symptoms appear, you should consult an ophthalmologist, who, if there are no ophthalmological problems, will refer the patient to a neurologist or oncologist.
About weakness, sweating and pain
There may be several reasons for feeling unwell. And it is not always clear which doctor to contact with a particular ailment. Our expert will help you navigate. In order to get a complete answer, in the comments to this article you need to:
- briefly outline the main symptoms;
- make the question as specific as possible;
- write a question in the comments under this article.
You will find answers to your questions in the next issue of the section “What kind of doctor do I need?”
Question: Weakness is combined with severe sweating. What could be the reason and which doctor will help solve the problem?
Sweating is a natural physiological process that is characteristic of warm-blooded organisms, including humans. The main function of sweating is to regulate heat exchange and maintain optimal water-salt balance in the body. However, severe sweating can be one of the symptoms of diseases. Excessive sweating – hyperhidrosis.
The causes of hyperhidrosis and general weakness may be the following:
- diseases of the thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism - increased production of thyroid hormones, can also be accompanied by rapid heartbeat - tachycardia, irritability, nervousness, sleep disturbances);
- diabetes mellitus (with elevated glucose levels, blood vessels and nerve endings are affected, especially with diabetes, the hands, neck, and scalp sweat);
- hypoglycemia (a decrease in blood glucose levels causes an increase in adrenaline levels, which provokes sweating);
- pathology of the adrenal glands (pheochromocytoma - a tumor of the adrenal glands stimulates the production of catecholamines: adrenaline and norepinephrine);
- ovarian dysfunction and menopausal changes in a woman’s body (the production of testosterone, the male sex hormone, increases, which increases metabolism and thereby causes increased sweating);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, coronary heart disease, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases;
- lesions of the central nervous system of various etiologies;
- benign and malignant neoplasms (as small signs syndrome);
- chronic infectious diseases;
- chronic stress and depression.
The patient needs to see a general practitioner. The specialist will give directions for the necessary laboratory and functional tests (general blood test, general urinalysis, biochemical blood test, TSH, free T4, free T3, ECG, etc.) and, depending on their results, for additional examination methods.
_____________________________________________________________________
Question: When I get up after lying or sitting for a long time, my heel starts to hurt. To the point of lameness. It lasts about five minutes, and then everything goes away. Tell me which doctor to contact?
Heel pain is one of the symptoms of inflammatory diseases of the heel area.
The calcaneus is the bony skeleton of the calcaneal region; it has a body and a calcaneal tubercle. The body participates in the formation of the transverse tarsal joint (the connection between the calcaneus, navicular and talus bones). The calcaneal tubercle is located slightly behind and downward from the body of the heel bone - it is a massive bony process, and it is on it that the bulk of the body presses when walking. It plays an important role in supporting the arch of the foot (the long plantar ligament is attached to it). The most powerful tendon in the body, which is formed as a result of the fusion of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles of the leg, is attached to the posterior surface of the tubercle - the Achilles tendon. It is surrounded by subcutaneous fatty tissue, which contains a whole network of vessels and nerves.
What can hurt in the heel area:
- calcaneus (with reactive arthritis, osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, osteochondropathy of the tubercle, crack or fracture);
- synovial bursae (with bursitis - inflammation of the mucous bursae);
- ligaments, tendons, fascia (for sprained Achilles tendon, plantar fasciitis, etc.);
- surrounding joints (with gouty arthritis, etc.);
- nerves, blood vessels (for polyneuropathy, angiopathy).
Heel pain in the morning, as a rule, can be associated with an inflammatory or degenerative-dystrophic disease of the foot and peri-heel area and can be characterized by plantar fasciitis, heel spurs, gout, arthritis, etc.
The patient needs to see an orthopedic doctor. The specialist will give directions for the necessary laboratory and functional studies (radiography of the foot, plantography, etc.), and if there are indications, he will refer you to other specialized specialists (rheumatologist, neurologist).
occupational therapist, head of the hospital “Clinics for the whole family 1 + 1”
answered your questions Photo depositphotos.com The author’s opinion may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Visual impairment due to VSD
There are several causes of visual impairment in VSD:
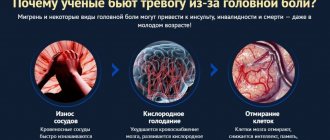
- disturbance of blood circulation in the blood vessels of the head. The small vessels of the eye become thinner, the blood circulation of the eye is disrupted, the image is distorted, and visual acuity decreases. Lack of blood circulation in the vessels of the brain and eyes causes image distortion;
- panic attacks, increased anxiety are accompanied by a feeling of constant fear, have a negative impact on thinking, mood, functioning of the nervous system and all organs and systems. This leads to disruption of the visual system;
- a person living in stress perceives the world in “black colors”, he loses interest in life, stops recording joyful and interesting events - this manifests itself in the form of detachment from everyone, the eyes turn red, hurt, the body is exhausted by stress, immunity drops, the patient sees the surrounding reality in dim, unclear images. Stress leads to loss of vision, exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- stress or neurosis often leads to loss of appetite, the patient is indifferent to the quality of his diet, and the daily diet lacks nutrients and vitamins. An unbalanced diet causes a lack of nutrients in the brain, brain tissue and blood vessels begin to suffer, the functioning of brain structures is disrupted, vision decreases, and memory deteriorates.
Clinical manifestations of the visual system in vegetative-vascular dystonia:
- flickering spots in the eyes are observed when overtired, changing position;
- a flash of light that may be accompanied by loss of balance;
- pain in the eyes occurs in bright light, when touched, blinking, the pain can become constant, aching, one-sided or two-sided;
- there is double vision, the image is distorted, the clarity of the image disappears;
- when looking at an object, the surrounding background loses clarity and becomes cloudy;
- it becomes dark in the eyes, for a certain time the patient sees only a dark background without the outlines of objects.
Prevention of VSD
Having found out why VSD is worsening, it is worth paying attention to preventive measures designed to prevent or weaken the development of the main phases of this condition.
Prevention of VSD includes:
- compliance with the work and rest regime;
- rejection of bad habits;
- balanced diet;
- positive thinking, liberation from negative emotions;
- protection from stress, physical and emotional fatigue;
- maintaining an active lifestyle;
- yoga, fitness, physical therapy classes;
- hydrotherapy (contrast shower, bath, bath procedures);
- stimulation of the autonomic nervous system through massage;
- Spa treatment.
Following all of the above rules will help avoid the development or prevent exacerbation of the disease.
How to eliminate vision problems with VSD
Problems with visual impairment and eye pain can occur with high intracranial pressure, high blood pressure, stress, and physical inactivity. When visiting an ophthalmologist at the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will undergo the necessary tests of intraocular pressure, blood pressure, and an examination of the condition of the visual organs. With VSD, the nervous regulation of all structures of the body changes, including those responsible for the position and movement of eye structures. Hypotonicity and hypertonicity of the muscles responsible for the condition of the lens of the eye, smooth muscle muscles of blood vessels leads to a change in the refractive function of the eye lens, affects the photoreceptors of the retina, and discoordination of the smooth muscles of the iris occurs. Spasm of the muscles of the walls of the small blood vessels of the eye leads to disruption of the nutrition of the cells of the eye structure, causing visual impairment.
The doctor will determine what diseases cause vision deterioration and what causes the pain in the eyes. During the examination, the main symptoms will be determined: different pupil sizes, changes in the fundus, swelling and bruising around the eyes, red eye syndrome, blurred vision. If a patient has VSD, prevention is of great importance. To avoid a decrease in visual acuity, you should maintain a healthy lifestyle, eat a balanced diet and avoid stressful situations. In the rehabilitation department of the hospital, dystonics will be able to take courses in physical therapy and breathing exercises. Dystonics will be able to undergo treatment of diseases against which VSD is diagnosed in a neurology clinic. You can make an appointment with a doctor by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Main provoking factors
Visual impairment with VSD is justified:
- Severe anxiety.
- Nutrient deficiency.
- Poor blood circulation.
Severe anxiety
The subconscious is beyond control. You can only follow your thoughts. According to many psychologists, the development of vegetative vascularity is provoked by the transition of accumulated negative thoughts from consciousness to the subconscious.
Foci of excitation in the brain responsible for processing negative information spread to other areas, including the visual system. The result of this is a distortion of the information that was received from the eyes.
Nutrient deficiency
The retina of the organ of vision may lack nutrients. The brain urgently needs:
- Carbon.
- Vitamins.
- Oxygen.
- Magnesium.
- Phosphorus.
- Calcium.
If the transport of these substances to it is blocked, it operates unstable. He incorrectly processes the information that is conveyed to him by his eyes. Therefore, it seems to a person that vision deteriorates with VSD.
Poor circulation
The main provoking factor is a decrease in the performance of capillaries. The transportation of blood to the organs of the visual system is disrupted. This leads to an incorrect perception of the world.
Causes of red eyes
Some people experience a combination of “red eyes and VSD”. The main reason is an imbalance between the parasympathetic and sympathetic systems. Red eyes are explained by dystonia of the vessels supplying the visual organs.
Another reason is an increase in blood pressure. Therefore, red eyes are observed in people with VSD of the hypertensive type. Pressure increases in the systemic circulation.
If a person is bothered by red eyes and there are accompanying symptoms, he needs to visit not only a neurologist, but also an ophthalmologist.
Causes of bruises
Some patients with VSD develop bruises under the eyes. Most often this is explained by a specific structure. Sometimes bruises under the eyes indicate that a person needs rest. In some cases, we are talking about kidney pathology.
In patients with dystonia, bruising under the eyes may be due to concomitant cardiac disease.