The process of speech restoration after a stroke
Content
The process of speech restoration is very long
Restoring speech after a stroke is a process that should begin immediately after the condition after the stroke has stabilized. You need to be prepared for the fact that it will take longer than the restoration of motor functions. Everything can drag on for up to six years, although even after such a period of time, speech may not fully resume. The patient must be reassured that the success of treatment primarily depends on his own efforts.
A speech therapist should monitor the improvement of speech functions. He may prescribe both medication and speech therapy exercises. If you try to treat a patient yourself, you can cause great harm, then the chances of recovery will be significantly reduced. It is worth noting that there are two types of speech disorders, each of which requires separate treatment.
Forms of disorders
Let us first consider the manifestation of each form, and then the treatment required in each form.
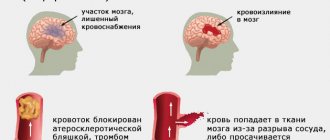
- Aphasia. The very phenomenon of speech as a manifestation of higher nervous activity is disrupted. The patient is unable to recognize written or spoken language, but he hears sounds and words. This is sensory aphasia. Due to the fact that the necessary impulse is not formed in the necessary parts of the neocortex, the patient cannot pronounce a word. This is the so-called motor aphasia or apraxia of speech. There is total aphasia, in which a person not only cannot speak himself, but also does not understand what is being said to him.
- Dysarthria. This is a defect in the pronunciation of words and sounds. A person understands perfectly well what is said to him, can write and read, but is not able to speak, since the work of the muscles that are responsible for the pronunciation of sounds is impaired. This is also called articulation disorder, which affects parts of the subcortical structures and frontal lobes.
Now is the time to discuss which treatments are used in each type.
Treatment of aphasia and dysarthria
- Speech therapy method. In this case, speech, reading and writing are restored by training and consolidation of linguistic skills. Melodic intonation therapy is also used, which is aimed at activating the functions of the right hemisphere of the brain. Cognitive functions and speech can be restored using computer technology. The speech therapy method is most beneficial when interacting with pharmacological methods that are aimed at bringing the damaged hemisphere back to normal. Although for severe aphasia other methods are still used.
Stroke: restoration of speech. Exercises
Patients diagnosed with aphasia and speech disorders are concerned with the following questions: is it possible to fully recover from a stroke and how long will it take?
First of all, it is necessary to take into account the irreversibility of the process of destruction of brain cells. To restore the patient’s ability to speak, specialists will need to select means of recovery after a stroke that will help switch speech functions to the closest areas of the brain not affected by the disease. And the timing depends, among other things, on the high inertia of brain cells - after all, it is necessary to switch them to functions unusual for them
Many methods have been developed for restoring speech after a stroke that can speed up this process - speech, melodic, visual, artistic, etc. These speech therapy methods are used along with drug therapy - the patient is prescribed drugs that can stimulate the formation of new neural connections.
The method of intonation (melodic) therapy is based on “singing”. The patient is asked to sing words that cannot be pronounced clearly. Visual therapy uses the ability to form associations between words denoting an object and their visual image.
The most common method of treating aphasia is speech therapy. Classes on the method are conducted with a speech therapist-aphasiologist and are included in the course of intensive rehabilitation of patients after a stroke to the extent necessary for a particular patient.
Exercises to restore speech after a stroke begin with a complex that is designed to gradually restore the patient’s articulatory skills. This could be pronouncing individual sounds, syllables or words, or pronouncing tongue twisters. The exercises are performed with a speech therapist, and the results are consolidated independently in your free time. The more intense the exercise, the greater the likelihood of recovery.
Folk Means.RU
Folk Remedies » Blood » Restoring speech after a stroke
Restoring speech after a stroke
More than a third of stroke patients experience speech disorders. I offer exercises to restore speech.
Start your classes with exercises that engage the muscles involved in pronouncing sounds. On the first day, it is enough to do the exercises 2 times, and then add one approach every 3 days. Bring the repetition of each exercise up to 5-7 times. Do the whole complex 5 times a day.
1. Pull your lips out with a tube for 3-5 seconds, then rest for 3-5 seconds, repeat the exercise.
2. With your lower teeth, grab your upper lip with tension for 3-5 seconds, then rest for 3-5 seconds, and then repeat.
3. With your upper teeth, grab the lower lip with tension for 3-5 seconds, then rest for 3-5 seconds, repeat.
4. Stick out your tongue as much as possible and at the same time slowly stretch your neck forward for 3 seconds, return to the starting position within 3 seconds.
5. Lick your lips: first from right to left the upper lip, then from left to right, and then lick the lower lip in the same order.
6. Lick your lips in a circle: first clockwise, then counterclockwise.
7. Try folding your tongue into a tube and stretching it out. Stay in this position for 3 seconds.
8. Open your mouth slightly, try to cup your tongue and hold it there for 3 seconds.
9. Lift the tip of your tongue up and reach the soft palate.
10. Teeth are open, lips are closed. Run your tongue between the upper gums and cheeks to the lower gums clockwise and in the opposite direction.
The next exercise is performed with an assistant. Have your assistant start saying a word and you finish it. For example, an assistant says: “Now a dog is running down the street...”, and you add: “ka.” Start with one syllable, then move to two syllables. For example, the assistant says: “Across the sky
white floats about...”, and you add: “varnish.”
Have your assistant sit next to you and sing the song quietly, in an undertone. Try to pick up the words and join in the singing.
Pronouncing tongue twisters gives a very good effect.
Tongue twisters with the sounds b-p: “The bull is blunt-lipped, the dumb-lipped bull”, “The bull had a white lip and was dumb.”
Tongue twisters with the sounds l -v: “The queen gave the gentleman a caravel, the queen and the gentleman retired to the caravel.” “The cap is sewn, but not in the Kolpakov style; the bell is poured, but not in the Kolokolov style. It is necessary to re-cap and re-cap. We need to re-bell the bell, and re-bell it.” “The butt is on the head, the cap is on the butt. A shock under the butt, a priest under the cap.”
Improve the articulation of tongue twisters with the sounds r and v. “There is grass in the yard, there is firewood on the grass, don’t cut wood on the grass in the yard.”
Alexander Vladimirovich Goyaovkov.
Types of pathology
Depending on the affected area, the following types of speech loss are distinguished:
- motor aphasia. This consequence develops due to improper functioning of cerebral structures in the area of Broca's area. The patient perceives and normally recognizes words addressed to him, but so far he cannot speak independently. If we talk about the development factor, it lies in the deformation of the brain structures responsible for the motor function of various muscles. As a result, nerve conduction is disrupted;
- sensory. Then the person loses the ability to understand the words of other people. The patient can speak, but at a partial level. The monologue then looks like it’s abrupt;
- sensorimotor. This type is mixed; the ability not only to speak, but also to understand others is lost. In this case, it is difficult to say anything about how quickly speech function can be restored;
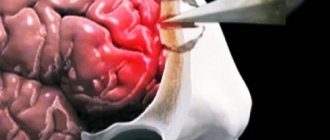
- total. Here the patient completely loses the functions associated with the generation and perception of speech. The corresponding pathology is observed in the case of massive disturbances of normal blood flow;
- semantic defeat. A person can perfectly understand the words spoken by the interlocutor and speak, but the ability to analyze complex written and speech structures is lost, he confuses endings, practically does not control word combinations, the meaning of some constructions is lost;
- amnestic. In this case, the patient does not remember the names of familiar objects, abstract concepts are mostly confused;
- afferent. There are difficulties with the pronunciation of several sounds;
- dynamic. Analytical skills related to the search and use of correct semantic structures change.
Important! There are other subtypes of violations. Sometimes the patient has a lively speech, but devoid of any meaning.
Is speech restored after a brain accident? Of course yes. But only with a systematic and integrated approach will it be possible to achieve a positive result.
Prognosis after speech loss
According to statistics, major strokes have the most severe consequences, one of which is speech disorder. On average, if you follow all the recommendations, recovery occurs:
- in 55% of cases after a severe phase of stroke;
- in 75% with moderate disease;
- in 92% if a mild form is diagnosed.
When rehabilitation measures are not carried out, you should not expect a positive result. The probability of recovery does not exceed 15%.
Rehabilitation program and its features
Recovery after a stroke is facilitated by a whole range of different activities:
- professional massage and special physical education;
- work to restore memory and speech;
- psychological and social assistance;
- prevention of possible complications that occur after a stroke.
According to the recommendations of doctors, the patient should be treated 1-2 times a day, provided he is in good health. To perform certain physical exercises and exercises aimed at restoring memory and speech, 35-40 minutes of exercise is sufficient. What to do if a person feels weak, has shortness of breath, dizziness, or high blood pressure? You don't have to give up classes altogether. It is enough to reduce them to 10-15 minutes.
Try to add variety to your workouts more often. If the patient is already getting up and moving around, encourage him to walk on grass, sand, stones and other uneven surfaces. After a while, you can move on to climbing a hill or even climbing stairs. The main thing is not to rush things. For walking, you should choose orthopedic shoes or high boots, in which the foot is well supported.
Every day, teach your loved one something new: hold a spoon, fasten a zipper, put on shoes, turn a faucet on and off, answer a phone call, and so on. It is very important to help him. But you shouldn't try to do the work for him if you don't want to interfere with the recovery process.
Important point! The rehabilitation period should take place in a calm atmosphere. Therefore, be patient and do not get nervous when a person tries to do something on their own. Spilled water? Broke a plate? No problem, solve the problem with a smile and continue learning. It is vital for people who have suffered a stroke to feel needed. Therefore, you can safely involve them in doing simple housework.
Features of motor function recovery after stroke
Movement disorders are rightfully considered one of the terrible consequences of a stroke. They are expressed in partial or complete immobilization of the legs and arms.
Among the main methods used to restore motor functions are:
- electrical stimulation is a physiotherapeutic method based on the effect of pulsed electric current on the body;
- therapeutic physical culture (physical therapy);
- massage;
- biofeedback is a method, the essence of which is to “return” the values of physiological indicators to patients (information is displayed on a computer screen).
The ideal solution is to combine several methods. With any approach, there is no need to tire the patient with lengthy procedures or intense training. The load should be increased gradually.
A little remodeling of the apartment wouldn't hurt. Specially equipped handrails, as well as chairs for support, will make life easier for the patient.