21.04.2017
Belkin Andrey Avgustovich
Director of the Brain Institute Clinic LLC, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor of the Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine of the Ural State Medical University, Chairman of the Supervisory Board of the Brain Clinical Institute ANO.
Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist, doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Lipovka Nadezhda Sergeevna
Head of the Department of Medical Rehabilitation, Physician of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Neurologist
Traumatic coma occurs as a result of the impact of some mechanical factor on the victim’s head area. Most traumatic brain injuries occur as a result of motor vehicle accidents. When the head hits a blunt hard object, enormous kinetic energy is transferred to the brain, which, by inertia, hits the inside of the skull, and then receives a counter-impact from the opposite side. As a result of injury, hemorrhages in the brain and ruptures of axonal connections can occur. Subsequently, cerebral edema occurs with its dislocation, which leads to traumatic coma.
Clinical picture and symptoms
When a traumatic coma occurs, consciousness may be lost immediately or may fade away gradually. In some cases, the victim has a clear period during which nothing bothers him. However, most often he talks about total brain damage. With the development of cerebral edema, compression of the brain stem occurs, which causes symptoms such as:
- Severe headache.
- Indomitable vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Double vision.
- Dizziness.
- Confusion.
- Difficulties with orientation in time and space.
- Memory loss.
Subsequently, loss of consciousness occurs and the victim gradually goes into a deep coma with the loss of all reflexes.
Traumatic coma: causes
The most important reason is a gross violation of the integrity of brain structures. A brain contusion may be accompanied by a violation of the integrity of its architecture and vascular bed, which leads to increased intracranial compression and herniation of the brain stem into the foramen magnum. In this case, irritation of the vital centers of the medulla oblongata occurs and respiratory and cardiovascular activity is inhibited.
Treatment
Due to a sharp and significant increase in intracranial pressure, it is imperative to immediately administer strong loop diuretics. Reducing blood pressure and removing fluid from the body slows down the development of cerebral edema and helps gain the necessary time. In case of severe cerebral edema, surgical intervention is performed - craniotomy with subsequent decompression. The Clinical Institute of the Brain has at its base a high-tech neurosurgical department that can cope with even the most severe cases of traumatic coma.
Impaired consciousness: mechanism of occurrence
After damage to the central nervous system due to a traumatic brain injury, a person loses the ability to respond to any external stimulus. The psycho-emotional state is completely disrupted, the victim cannot contact the people around him. Coma sets in.
Coma due to TBI is characterized by the immersion of a person in a specific state, which is associated with inhibition of certain areas of the central nervous system. The victim does not respond to pain, bright light and loud sound, and has no reflexes.
Consciousness is impaired when certain parts of the brain that are responsible for speech, thinking, wakefulness, and reasoning are damaged. Based on the degree of damage, loss of consciousness can have different durations:
- mild traumatic brain injury (for example, bruise): loss of consciousness does not occur or lasts no more than 5 seconds;
- moderate injury (for example, open head injury): duration of disturbance of consciousness – 2 hours-2 days;
- severe injury: deep coma and vegetative states occur.
Coma after TBI is not a separate disease, but only a consequence of damage to the central nervous system. If there is a severe general condition that threatens a person’s life, he may be placed in an artificial coma. This condition allows you to cause a controlled decrease in the activity of reflexes and vital functions.
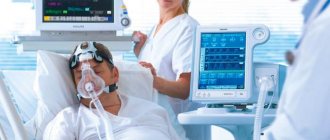
An artificial coma involves the introduction of special medications into the body. In this case, the respiratory function is performed by a ventilator.
First aid
If you find a victim in a traffic accident, immediately call an ambulance and rescue team. If possible, move the victim out of the danger zone, but do not forget about your own safety.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 5 votes
Share article on social networks
Treatment during coma
Once a diagnosis of coma due to traumatic brain injury has been made, appropriate treatment is begun. First of all, measures are taken to increase blood flow to the brain. Emergency treatment begins already in the ambulance.
Artificial ventilation is used and medications are introduced into the body to help normalize blood pressure. It requires the introduction of drugs that improve the functioning of organs such as the liver and kidneys.
In case of respiratory arrest, the emergency doctor inserts a special tube into the tracheal cavity, which is a conductor of oxygen air coming from the breathing apparatus.
Since, while in a coma, a person cannot eat on his own, nutrients are administered by tube. To prevent secondary infections of the urinary tract and lungs, powerful antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Programs:
Assessment of rehabilitation potential
Early (resuscitation) rehabilitation
Drug-free brain stimulation
Kinesitherapy with biofeedback
Restoration of the peripheral nervous system
Rehabilitation after a coma
Complications
If the central nervous system was affected at the time of the traumatic brain injury, complications are likely to occur. Coma is one of them. With severe TBI, the consequences can be so serious that the patient will no longer be able to care for himself, stand up, or sit. In such cases, outside help and special medical equipment will be required.
Coma is not always accompanied by such severe consequences. In some cases, a person quickly recovers from injury and impairment of consciousness, and basic functions and reflexes return to normal.
The most common consequences of coma include amnesia or incomplete memory loss, impaired concentration, loss of the ability to independently care (eating, taking water procedures, etc.).
Being in a lying position for a long time, a person may begin to suffer from bedsores, which require other specific therapy using medications.
Prevention of complications, rehabilitation
Only timely treatment can reduce the risk of negative consequences after a head injury. First aid is usually provided by medical personnel. But people who were close to the victim at the time of his injury can also help. You need to do the following:
- Turn the person over to a position in which the likelihood of hypoxia and asphyxia is minimal. If the victim is conscious, you should turn him on his back. Otherwise, you need to lay it on its side.
- Treat the wound with water or hydrogen peroxide, apply bandages and a bandage to it: this will reduce swelling and the risk of developing infectious complications with an open head injury.
- If signs of asphyxia, difficulty breathing, or heart rhythm disturbances appear, perform cardiopulmonary massage and provide the patient with access to air.
- Stop accompanying bleeding, treat other damaged areas of the body (if any).
- Wait for the ambulance to arrive.
From the editor: Types of intelligence according to Gardner and Buzan
Treatment of head injuries is carried out exclusively in a hospital, under the strict supervision of a doctor. Depending on the type and severity of the pathology, drug therapy or surgical intervention is used. The following groups of drugs may be prescribed:
- analgesics: Baralgin, Analgin;
- corticosteroids: Dexamethasone, Metipred;
- sedatives: Valocordin, Valerian;
- nootropics: Glycine, Phenotropil;
- anticonvulsants: Seduxen, Diphenin.
Typically, a patient's condition after an injury improves over time. But the success and duration of recovery depends on the measures taken during the rehabilitation period. Lessons from the following specialists can return the victim to normal life:
- occupational therapist. Works on renewing self-care skills: moving around the apartment, driving a car as a passenger and driver;
- neurologist. Deals with issues of correction of neurological disorders (decides how to restore the sense of smell, reduce seizures and what to do if you constantly have a headache after suffering an injury);
- speech therapist. Helps improve diction, cope with the problem of slurred speech, restores communication skills;
- physiotherapist. Carries out pain correction: prescribes procedures to reduce headaches after head injury;
- kinesitherapist. Its main task is to restore the functions of the musculoskeletal system;
- psychologist, psychiatrist. Help eliminate mental disorders due to brain injuries.
How to help in the first minutes
First aid is often provided by people who, by chance, find themselves close to the victim. And they are not always health workers. With TBI, however, it should be understood that loss of consciousness can last a very short time and therefore not be recorded. However, in any case, a concussion, as a complication of any (even seemingly mild) head injury, should always be kept in mind and, taking this into account, help the patient.
If a person who has received a TBI does not come to his senses for a long time, he needs to be turned over on his stomach and his head tilted down. This must be done in order to prevent vomit or blood (in case of injuries to the oral cavity) from entering the respiratory tract, which often happens in an unconscious state (absence of cough and swallowing reflexes).
If the patient has signs of impaired respiratory function (there is no breathing), measures should be taken to restore the patency of the airways and, before the ambulance arrives, provide simple artificial ventilation (mouth-to-mouth, mouth-to-nose).
From the editor: Causes, symptoms and types of neuroses
If the victim has bleeding, it is stopped with the help of an elastic bandage (a soft lining on the wound and a tight bandage), and when the victim is taken to the hospital, the surgeon will suture the wound. It’s worse when there is a suspicion of intracranial bleeding, because its complication is most likely hemorrhage and hematoma, and this is already a surgical treatment.
Due to the fact that a traumatic brain injury can occur in any place that is not necessarily within walking distance of a hospital, I would like to introduce the reader to other methods of primary diagnosis and first aid. In addition, among the witnesses trying to help the patient, there may be people with certain knowledge in medicine (nurse, paramedic, midwife). And here's what they should do:
The first step is to assess the level of consciousness in order to determine, based on the degree of response, the patient’s further condition (improvement or deterioration), and at the same time – psychomotor status, the severity of pain in the head (not excluding other parts of the body), the presence of speech and swallowing disorders; If blood or cerebrospinal fluid leaks from the nostrils or ears, assume a fracture of the base of the skull; It is very important to pay attention to the victim’s pupils (dilated? different sizes? how do they react to light? strabismus?) and report the results of your observations to the doctor to the arriving ambulance team; You should not ignore such routine activities as determining the color of the skin, measuring pulse, respiratory rate, body temperature and blood pressure (if possible).
With TBI, any part of the brain can suffer, and the severity of one or another neurological symptoms depends on the location of the lesion, for example:
- A damaged area of the cerebral cortex will make any movement impossible;
- If the sensitive cortex is damaged, sensitivity will be lost (all types);
- Damage to the frontal lobe cortex will lead to a disorder of higher mental activity;
- The occipital lobes will no longer control vision if their cortex is damaged;
- Injuries to the cortex of the parietal lobes will create problems with speech, hearing and memory.
In addition, we should not forget that cranial nerves can also be injured and give symptoms depending on which area is affected. And also keep in mind fractures and dislocations of the lower jaw, which, in the absence of consciousness, press the tongue against the back wall of the pharynx, thereby creating a barrier to the air flowing into the trachea and then into the lungs. To restore the passage of air, it is necessary to push the lower jaw forward, placing your fingers behind its corners
In addition, the injury can also be combined, that is, with a TBI, other organs can be damaged at the same time, therefore, a person who has received a head injury and is in an unconscious state must be treated with extreme care and caution
And one more important point when providing first aid: you need to remember about the complications of a TBI, even if at first glance it seemed mild. Bleeding into the cranial cavity or increasing cerebral edema increases intracranial pressure and can lead to compression of the brain (loss of consciousness, tachycardia, increased body temperature) and irritation of the brain (loss of consciousness, psychomotor agitation, inappropriate behavior, obscene language). However, let's hope that by that time the ambulance will have already arrived at the scene and quickly taken the victim to the hospital, where he will receive proper treatment.
Treatment
It is important to carry out treatment immediately after damage. If all manipulations are performed correctly, the chances of survival and recovery increase. After the ambulance arrives, the patient is hospitalized
After determining the nature and severity of the damage, therapy is prescribed
After the ambulance arrives, the patient is hospitalized. After determining the nature and severity of the damage, therapy is prescribed.
If a person has received a minor injury, he is prescribed medications to relieve pain and is recommended to get proper rest.
In severe situations, they begin with restoring respiratory function (if it is impaired). The patient may be placed on a ventilator. If the wound is small, then apply a bandage; in serious cases, stitches may be applied.
Subsequently, they resort to drug treatment, with the help of which they restore and maintain basic indicators, return or stabilize the patient’s consciousness. When it is possible to overcome the acute phase, they move on to further rehabilitation.
The duration of the recovery period and its success depend on the severity of the injury and the correctness of the selected treatment.
From the editor: Diagnosis and treatment of trigeminal neuralgia