Meningitis is a disease during which the membranes of the brain (meninges and subarachnoid space) become inflamed. It is caused by viruses and bacteria, depending on this the course of the disease occurs. In any case, this is a dangerous disease that requires medical treatment. It can lead to infection of the bloodstream or brain, as well as sepsis, which can be fatal.
Bacterial meningitis is believed to be more severe. If this form is diagnosed, the patient requires emergency medical care. In patients with viral meningitis, the symptoms and course of the disease are milder, but treatment is also in a hospital.
Meningitis in adults and children can have different symptoms, so next we will look at these two groups separately.
According to statistics, 90% of meningitis cases are children. In adults, those bacteria and viruses that can cause meningitis provoke the appearance of sore throat or tonsillitis. In some cases, the infection reaches the brain, affecting it and causing inflammation. Meningitis can also be a complication after sinusitis, tuberculosis and other similar diseases.
Meningitis in children: symptoms, signs and causes
The cause of meningitis in children can be viruses of different natures - polio, Coxsackie, enteroviruses, etc. The disease is also caused by bacteria: staphylococci, meningococci, Haemophilus influenzae, etc. A newborn can become infected during childbirth.
The risk of meningitis is very high in the following categories of children:
- premature babies with weak immune systems;
- newborns who were born with hypoxia, infections and severe pregnancy in the mother;
- young children (most often under three years of age) who have other foci of infection (ARVI, tonsillitis, otitis, etc.);
- children with brain and spinal cord injuries;
- children diagnosed with disorders of the nervous system.
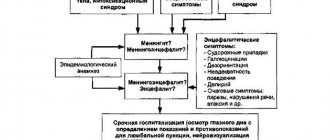
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
Classic symptoms of herpetic meningitis include intense headache with photophobia, fever with high fever and severe general malaise, hyperhidrosis, muscle pain, and repeated vomiting unrelated to food intake. The patient cannot tilt his head forward, loses significant coordination of movements, and becomes aggressive or depressed. Lymph nodes enlarge. One of the first signs is often a skin rash characteristic of herpes in the form of small multiple blisters.
In acute, severe cases, symptoms of cerebral edema quickly develop, mental disorders appear in the form of hallucinations, confusion, and disorientation in what is happening. Specific reflex disorders and signs (so-called meningisms, meningeal signs) are easily detected. Partial or complete paralysis and epileptic seizures may develop. With an adequate therapeutic response, acute symptoms are reduced within about a week, however, some severe and complicated cases lead to coma and death; if it is possible to avoid it, it leads to the development of endocarditis, secondary epilepsy, etc.
The diagnosis is assumed clinically and confirmed by laboratory-serological analysis of blood, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva and other biological fluids. Additionally, instrumental studies are prescribed as necessary (EEG, tomography, radiography, etc.).
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Symptoms of meningitis
Children who develop the disease have the following symptoms:
- high temperature: from 39 degrees and above, it is difficult to get rid of or impossible to do at all;
- severe headache, which intensifies with sudden body movements or bright light;
- tension in the neck, which makes it impossible to tilt your head to your chest;
- severe vomiting, prolonged action, which does not bring relief!;
- there are convulsions.
In principle, the symptoms are the same as in adults. Only for newborns the signs of the disease may not be so bright. Frequent regurgitation, lack of appetite, upset stomach, lethargy, abnormal sleep, and changes in crying are noted. Any such symptoms are a reason to consult a pediatrician. A clear, recognizable sign of meningitis is a star-shaped rash, which indicates meningococcal infection.
What are the types of meningitis?
The etiology of meningitis varies. Let's consider the main causes of the disease.
- Viral . Most often they are caused by enteroviruses, mumps virus, flaviviruses, varicela zoster virus, and herpes simplex virus. Less commonly, the cause of the disease can be cytomegalovirus, adenoviruses, lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, HIV, Epstein-Barr virus. Symptoms are similar to the flu; signs of meningitis in the form of a headache appear after a few days. The course of the disease is not very severe.
- Bacterial . This type of meningitis occurs when various bacteria enter the body: meningococci, Haemophilus influenzae, streptococci, and in rare cases, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella. The course of the disease is rapid and acute, all symptoms appear within one day.
- Purulent . Any bacterial infection of the body can develop into purulent meningitis. Most often, the development of the disease was preceded by infection with Haemophilus influenzae, meningococci and pneumococci. The appearance of purulent meningitis in newborns is often provoked by streptococcal infections, E. coli and salmonellosis.
- Tuberculous . The first symptoms are fever, after a few days vomiting and severe headache appear. The disease affects the brain only after two weeks.
- Meningococcal . It occurs due to the entry of the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis into the human body. Signs of this type of meningitis include hemorrhagic rash, fever and chills. Acute inflammatory changes occur in the blood.
Symptoms
The incubation period for viral meningitis usually lasts 2-4 days.
The disease begins acutely, with high fever and general intoxication. In patients with high body temperature, malaise increases, muscle and joint pain, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea appear. Slight drowsiness and stupor are often associated. More severe signs of meningitis (impaired consciousness, stupor and coma) are not typical for inflammation of the meninges caused by viruses and require a more in-depth examination of the patient. From the first or second day of the disease, doctors determine a clearly defined meningeal syndrome:
- severe headache;
- repeated vomiting;
- lethargy and drowsiness, sometimes agitation and anxiety.
Patients may complain of cough, runny nose, sore throat and abdominal pain.
Often, patients with viral meningitis develop skin hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity to various irritants). On examination, neck rigidity and signs of severe hypertensive cerebrospinal fluid syndrome are revealed. During a lumbar puncture, clear, colorless cerebrospinal fluid flows out under pressure. An increased content of lymphocytes is determined in the cerebrospinal fluid, while the levels of protein, glucose and chlorides are within normal limits. After 3-5 days, body temperature normalizes. Sometimes a second wave of fever appears. In patients with viral meningitis, the following meningeal signs are determined:
- Kernig's symptom - the patient cannot straighten the leg bent at a right angle;
- Brudzinski's symptom: lower (when trying to straighten one bent leg, a reflex flexion of the second leg occurs), and upper - when bending the head, involuntary flexion of the lower limb occurs;
- Babinski's symptom - dorsiflexion of the first toe occurs with streak irritation of the plantar surface of the foot.
In most adults, viral meningitis occurs without complications. Some recovering patients complain of headaches for several weeks or months. They have mild intellectual impairment, asthenia or impaired coordination of movements. The prognosis for newborns and infants is not clear. They may have persistent complications in the form of intellectual impairment, learning difficulties, and hearing loss.
Treatment of meningitis
Treatment of meningitis must be carried out in a hospital setting and depends on its type. Until the results of the study are received, the patient is prescribed Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxox. This is the so-called starting antibiotic therapy. After receiving the tests, targeted antibiotic therapy is prescribed, depending on the bacteria detected and their sensitivity to the drug.
Symptomatic treatment may include infusion therapy, enteral or parenteral nutrition, rehabilitation exercises, which are recommended after relieving cerebral edema, treatment of complications and their prevention.
1.General information
Meningitis is a serious neurological disease, an inflammatory process of the central nervous system that affects the soft membranes of the spinal cord and brain. Depending on the etiology, there are several variants of meningitis: bacterial, fungal, viral, medicinal.
Viral meningitis can be caused by various pathogens, but the term “herpetic meningitis” is most often used as a synonymous diagnosis, since this family of viruses is the most common cause of viral meningitis. To date, about 90 types of herpesvirus are known.
Of these, at least eight can parasitize the human body, characterized by extreme resistance and the ability to remain in a latent, inactive state for decades, only to suddenly become active with renewed vigor under unfavorable conditions. So, for example, in old age a person who had chickenpox in childhood and seemingly developed immunity to this virus, which in fact was not completely destroyed by the immune system, but “slept” inside the cells throughout his life, can get shingles. , patiently waiting in the wings.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Meningitis: which doctor treats it?
Since meningitis is most often an infectious disease, treatment is prescribed by infectious disease doctors . They also carry out diagnostics. Moreover, all this is done after the patient is hospitalized, i.e. in the infectious diseases department. Additionally, observation by a neurologist is necessary, since the infection affects the nervous system.
Even suspicion of meningitis requires immediate hospitalization until the causes are clarified . This disease has a very high mortality rate and an even higher rate of neurological complications. For prevention, you need to get vaccinated, maintain hygiene, and eat right. Be healthy!
Treatment
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors provide treatment for viral meningitis, aimed at preventing or limiting the formation of irreversible damage to the brain. To destroy pathogens of viral infection, patients are prescribed the following medications:
- recombinant α-interferon;
- inducers of endogenous interferon (neovir, cycloferon);
- RNase;
- intravenous immunoglobulins (intraglobin F).
Antiviral drugs are prescribed from 2 to 5 days of illness or in severe condition of a patient with viral meningitis.
In severe cases of the disease, glucocorticoids are used during the first 2-3 days of the disease: dexamethasone or prednisolone. If the patient develops complications, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. For serous meningitis caused by a virus or Epstein-Barr, acyclovir is prescribed. For immunocompromised patients, immunoglobulin is administered intravenously. To reduce intracranial pressure, furosemide, Lasix or acetazolamide are prescribed. With severe cerebral edema, treatment with mannitol is started. Detoxification therapy is carried out with glucose solution, rheopolyglucin, albumin, plasma. Crystalloid and colloid solutions are administered intravenously.
When the body temperature is above 38 degrees, antipyretics are used - paracetamol, ibuprofen. All patients with serous meningitis at the Yusupov Hospital are prescribed drugs that improve the metabolism of cells of the central nervous system: piracetam, nootropil, picamilon. To reduce the energy deficit of the brain and improve tissue metabolism in viral meningitis, ascorbic acid and riboxin are prescribed. In severe cases of the disease, antioxidants are prescribed - cytomol, cytochrome. From the first day of therapy, all patients with viral meningitis are prescribed drugs that improve cerebral circulation (Cavinton, dipyridamole).