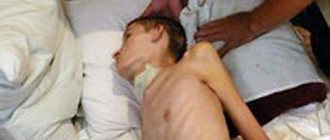
Meningitis is characterized by inflammation of the meninges of the spinal cord and brain. The disease is classified as infectious. Meningitis affects adults and children. In children, meningitis often occurs in a fulminant or acute form. Adults are more likely to suffer from meningitis caused by meningococcal infection; women are sick less often than men.
The Yusupov Hospital diagnoses and treats meningitis. In the laboratory you can undergo a number of tests for the causative agent of the disease, and experienced doctors provide consultations in the hospital. Meningitis can have a fulminant course, in which case qualified assistance should be provided immediately. With meningitis, it is very important that the diagnosis be made in the first days of the disease.
Causes of meningitis
Meningitis can be of infectious or non-infectious origin. The infectious form of the disease develops as a result of the penetration of microorganisms into the body: bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. Non-infectious meningitis develops in patients as a result of taking certain medications and the formation of tumors.
In medicine, classification is used according to the type of pathogenic microorganisms. It is important for a modern person to know how to recognize meningitis and what types of disease exist:
- bacterial meningitis is most often caused by streptococci, meningococci, pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae, which are transmitted by airborne droplets;
- viral meningitis. The most common form of the disease. This type is characterized by the least severity. The causative agents of viral meningitis are enteroviruses;
- fungal meningitis develops as a result of the activity of certain types of fungal microorganisms;
- parasitic meningitis.
The list of therapeutic measures for meningitis is determined by the factors that caused the development of the disease. Thus, when treating bacterial meningitis, antibiotics are prescribed, which are ineffective for viral meningitis. If a person knows how to recognize meningitis, then the likelihood of diagnosing the disease at the initial stage and the effectiveness of therapeutic measures are high.
To determine the causes of meningitis, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use modern diagnostic equipment. An important advantage of examinations at the Yusupov Hospital is that patients do not need to wait in lines, since appointments with specialists can be made in advance.
Expert opinion
Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
For several years in a row, infectious diseases have been among the causes of the development of pathologies of the nervous system. Meningitis accounts for 30-40% of cases. Modern drugs and high-quality diagnostics do not guarantee the absence of death. Mortality is explained by late seeking of medical help. Doctors associate this with the atypical course of meningitis, when the symptoms are not specific for a long time.
It is not possible to determine meningitis on your own. The clinical picture of the disease is varied. Signs differ according to the etiological factor. The initial symptoms of meningitis are often mistaken for cold symptoms. As the infection spreads, the condition worsens sharply. The high risk of death due to meningitis persists for 1-2 days from the onset of the first pathological symptoms. Delayed diagnosis and therapy lead to the development of severe, life-threatening complications. Therefore, it is important to immediately consult a doctor if you suspect the development of meningitis. At the Yusupov Hospital, the examination takes a minimum amount of time. The treatment plan is determined in accordance with the identified pathogen.
Methods of transmission of meningitis
There are a huge number of options for the virus to enter the body of another person, which is a characteristic feature of all infectious pathological processes. The most common ways:
- Airborne - when sneezing or coughing.
- Contact and household - in case of insufficient adherence to personal hygiene standards.
- Oral - with a kiss.
- Oral-fecal - eating dirty food or using unwashed hands.
- Hematogenous - entry through blood cells.
- Lymphogenic - affects the brain through the lymph.
- Placental - during childbirth.
- If contaminated liquid enters the body, swim in inappropriate places, drink poor-quality water.
Use the search portal to schedule an MRI of the brain for meningitis, which will help identify the extent of the inflammatory process and exclude other types of abnormalities. Using our website, you can independently fill out an application for an appointment at any metropolitan clinic, find out about the number of vacancies, and also familiarize yourself with the current price lists of medical organizations.
Risk group
Children and the elderly are at risk for meningitis. In addition, this disease is often diagnosed in people with an absent spleen and immunodeficiency.
The spread of meningitis, like all other infectious diseases, is more active in crowded places, closed groups, for example, in kindergartens, schools, student dormitories, barracks, since it is easier to get meningitis if you are in the company of asymptomatic carriers.
Most often, meningitis is transmitted by airborne droplets. This mechanism of infection transmission is considered the most common and characteristic of meningitis of viral origin. The infectious agent is transmitted through coughing, sneezing, kissing and sexual contact.
Newborn babies can become infected from an infected mother through the birth canal. The likelihood of infection is especially high in children born by caesarean section. Bacterial and viral meningitis can be transmitted this way.
Infection with meningitis can occur through the oral-fecal route: through dirty food or untreated water.
In addition, meningitis can develop as a result of the bite of an insect or animal that carries an infectious agent.
Expert opinion
Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
Meningitis of any origin is a dangerous infectious disease that affects adults and children. Without timely treatment, death occurs in 80% of cases. It has been proven that, despite the initiation of therapy, 10% of patients die within the first day from the onset of pathological symptoms. Meningitis most often affects children. Viral etiology accounts for 60–70% of cases. Fungal meningitis accounts for 1–3%. It is not possible to diagnose and treat an infectious disease at home. Therefore, it is necessary to seek medical help soon after the first signs of the disease appear.
The most informative method for diagnosing meningitis is lumbar puncture. The causative agent of the disease is sown in the cerebrospinal fluid. To identify the localization of the pathological focus in the brain area, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe MRI and CT. Etiotropic therapy is selected depending on the results obtained. Symptomatic treatment is aimed at alleviating the general condition. Vaccination is considered the only reliable means of preventing meningitis.
Varieties
Currently, in the modern field of neurology, experts have divided the described disease into several classes. Let's take a closer look at the differences at the childhood stage.
Meningococcal meningitis - such a deviation from the norm causes deformities in the convex and ball area. Symptoms of the disease in a child in this case are as follows:
- A sharp jump in body temperature that cannot be controlled by antipyretic drugs.
- Prolonged vomiting that does not bring relief.
- Serious pain in the head, resulting from increased blood pressure and migraines.
- The patient takes a characteristic pose: arches his back, bends his legs and pulls them closer to the abdominal area.
- A rash appears.
- Muscle cramps occur.
- Loss of consciousness.
A few days before the start of the active stage of progression, the baby exhibits all the symptoms of a common cold. This class of disease carries a serious danger in the form of bacterial shock, during which the development of pathology begins at double the speed.
The last stage of meningococcal meningitis - the appearance of necrosis on the skin indicates a severe degree, since as a result of infection an abnormality in the vessels begins, leading to the formation of blood clots and inflammation. In addition, children develop strabismus due to damage to the cranial nerves, uveitis and conjunctivitis.
Purulent meningitis - for the presented form, the characteristic factors of occurrence are considered to be:
- Rapid deterioration of the patient's general condition, accompanied by fever and chills.
- Repeated vomiting.
- Problems with knee flexion (Kernig and Brudzinski symptoms).
- Painful sensations in the lower extremities.
- Presence of tachycardia and bradycardia.
- Formation of rashes on the skin.
The purulent form is also divided into several subtypes: fulminant (affects exclusively newborn children), acute and chronic.
Serous meningitis is diagnosed in children between one and a half to six years of age. The development of the disease is provoked by the viral microorganism mumps, as well as enteroviruses. Typically, infection occurs at home, as it can be transmitted from house rodents whose secretions contain the pathogen. The described stage manifests itself in the form of fever, the usual standard symptoms of meningitis, as well as generalized disorders occurring in the internal objects of the body. The incubation period is up to 14 days. Problems that concern patients:
- Presence of weakness and weakness.
- Difficulty emptying.
- Heat.
- Inflammatory processes of a catarrhal nature, localized in the upper parts of the respiratory system.
- Headache.
- Nausea and gag reflexes.
- Congestion in the eyes, causing discomfort.
Tuberculous meningitis has three stages, each of which has its own individual manifestations. Symptoms:
- Prodromal - the gradual development of the disease, causing pain in the head, nausea and dizziness. In addition, in some cases, fever may develop.
- Irritation - rapid acceleration of previously formed symptoms, a significant jump in temperature. The pain is localized in the frontal lobe and occipital region. As the deviation progresses further, the child constantly sleeps and becomes quite lethargic in behavior, and consciousness is depressed. Patients often cannot tolerate loud noises and lights.
- Thermal - is distinguished by the formation of paralysis and paresis. Complaints arise 3-4 weeks after debut. All problems are very similar to encephalopathy (fever, formation of bedsores, tachycardia, etc.).
Viral meningitis - signs of the presence of this form have the same features as with the usual form of the disease, but in addition there is intoxication, Brudzinskogo and Kernig syndromes, as well as ARVI symptoms.
Symptoms of meningitis in adults
Meningitis usually has a sudden onset. The first symptoms of meningitis in adults are: fever, headaches, vomiting (the so-called meningeal triad). However, these pathological signs of meningitis also accompany other infectious diseases, so it is important to know the features of the manifestation of meningitis.
Meningitis is characterized by rapid development with pronounced signs of intoxication:
- headache;
- high fever and chills;
- confusion and loss of consciousness;
- convulsions;
- skin rash;
- muscle weakness;
- drowsiness;
- photophobia, increased skin sensitivity, reaction to sound;
- stiff neck;
- loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting;
- conjunctivitis;
- increased heart rate.
In patients with meningitis, the first sign of the disease is often a rash on the skin and mucous membranes. The rash is initially hemorrhagic in nature, sometimes spots and papules appear on the skin. The rash is considered an allergic reaction to medication.
Over the next few hours, hemorrhagic elements of various sizes and shapes appear. They may look like small spots or stars. Elements of the rash may merge and form spots.
Make an appointment
Headache
A severe headache should alert you. Headaches caused by meningitis feel different from other types of pain. Their intensity is much higher than that of headaches associated with dehydration or migraines. Taking over-the-counter pain medications does not provide relief.
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting that occur with a headache are not absolute signs of meningitis. These symptoms may accompany other diseases, such as migraine. Close attention should be paid to other conditions that occur along with vomiting and nausea.
Vomiting with meningitis rarely occurs once, most often it is repeated, repeated, and is not associated with food intake.
Heat
An increase in body temperature, like other symptoms, may indicate the development of meningitis. With this disease, the temperature is usually much higher than with acute respiratory infections. In addition, taking antipyretic drugs for meningitis is ineffective - it is very difficult and short-term to reduce the temperature.
Pain in the neck
Quite often, patients with meningitis complain of pain and a feeling of tension in the neck, and it is difficult for them to turn or raise their head. This is due to pressure from the inflamed membranes of the brain. This symptom can also be observed when the neck muscles are strained or injured from a sudden movement of the head.
The suspicion of meningitis can be confirmed by bending the patient's hips in a horizontal position - the occurrence of pain in the neck while performing this movement is a sign of meningitis.
Difficulty concentrating
Inflammation of the meninges during meningitis is associated with perception difficulties in patients. It is difficult for them to read an article to the end, concentrate on a conversation, or complete the task at hand. The degree of confusion may worsen as brain swelling increases. In addition to lethargy and confusion, patients experience a drop in blood pressure, shortness of breath, and noisy shallow breathing.
Lethargy, drowsiness
Patients become unable to act independently, they develop drowsiness and lethargy. This condition occurs as a consequence of general intoxication of the body or cerebral edema. Bacterial meningitis can be accompanied by a sharp depression of consciousness and even coma.
Photophobia
A manifestation of photophobia in patients with meningitis is severe pain that occurs in bright light. The appearance of pain and sensitivity of the eyes, as a reaction to light, is considered an alarming signal, as it is a characteristic sign of meningitis.
Convulsions
Convulsions, sometimes with involuntary urination and disorientation in space, are observed in 20% of patients with meningitis. Their course is similar to epileptic, or the appearance of tremor of individual muscles and individual parts of the body is observed. The occurrence of seizures (generalized and local) is associated with irritation of the cortex and subcortical structures of the brain.
Characteristic rash
A hemorrhagic rash on the skin and mucous membranes is not a specific symptom of meningitis. It appears in 25% of patients with bacterial meningitis and is most often observed in diseases of a meningococcal nature, since it is meningococcus that causes damage to the internal walls of blood vessels. The appearance of skin rashes is usually observed 15-20 hours after the onset of the disease. In this case, the rash is polymorphic - it can be roseolous, papular, in the form of nodules or petechiae. The rashes have an irregular shape and may protrude above the skin level.
Psychomotor agitation, anxiety
Anxiety, agitation and disorientation occur in patients with a form of the disease such as meningoencephalitis at the onset of the disease. With the bacterial form of meningitis, similar symptoms may appear 4-5 days after the onset of the disease. After psychomotor agitation, patients may experience loss of consciousness or coma.
At the beginning of the disease, as well as in later stages, patients with meningitis may develop symptomatic psychosis, manifested by agitation or, conversely, lethargy, delirium, visual and auditory hallucinations.
Delusions and hallucinations can occur in patients with lymphocytic choriomeningitis and meningitis, which is caused by the tick-borne encephalitis virus.
If you have at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor, since it is impossible to check meningitis yourself. To identify this disease and immediate treatment, qualified medical care is required.
The Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital offers high-quality diagnostics and treatment of meningitis of any form. The hospital's doctors use an individual approach in their work. Treatment tactics, developed individually for each patient, are explained to him in detail during the consultation process and are implemented as accurately as possible during therapeutic measures.
Expert opinion
Tatyana Aleksandrovna Kosova
Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, neurologist, reflexologist
Infectious diseases have been among the causes of death among the population for a long time. Meningitis is registered in 30–40% of cases. Unfortunately, despite the quality of the treatment, the possibility of death cannot be ruled out within the first 24 hours after the onset of clinical symptoms of the disease.
Among the etiological factors of meningitis, sinusitis is distinguished. The accumulation of purulent contents in the sinuses without proper treatment can lead to the spread of infection to the meninges. In such cases, meningitis is considered as a complication of sinusitis. The effectiveness of treatment for sinus inflammation depends on the quality of the diagnosis.
The Yusupov Hospital conducts a full range of examinations necessary to detect sinusitis and meningitis. The clinic’s doctors select the correct therapy based on the data obtained and the nature of the pathology. Doctors advise not to delay seeking medical help if symptoms of sinusitis develop and not to self-medicate. Without proper treatment, pus quickly spreads beyond the sinuses and penetrates into the brain area. An examination by a doctor will reduce the risk of a complicated course of the disease.
General information
According to the mechanism of occurrence, meningitis is divided into primary and secondary. Primary meningitis is spoken of when the disease begins directly with damage to the meninges. Secondary is a consequence of some other pathology, when the infection enters the nervous system from the primary focus in various ways. Tuberculous meningitis stands out separately - its clinical symptoms increase slowly, over several weeks or months.
The most dangerous form of the disease is reactive meningitis due to the high rate of development and transience of the clinical picture.
In a short period of time, purulent foci form on the surface of the brain, which lead to death. A favorable outcome is possible only if a correct diagnosis is made in the first hours after the onset of the disease and appropriate treatment is started.
Purulent meningitis in adults and children is expressed in the development of cerebral and meningeal syndromes, which are accompanied by symptoms of an infectious lesion and an inflammatory reaction of the cerebrospinal fluid. The first symptoms of purulent meningitis are similar to those of the flu, which after a few hours are supplemented by a severe headache, severe vomiting, impaired consciousness, tension in the neck muscles and pain when trying to pull the legs towards the stomach.
In conditions of timely and adequate treatment, the prognosis is good - in most cases, the disease is completely cured, leaving no negative consequences. Serious consequences of meningitis develop if medical care was not provided on time or the patient has a history of severe concomitant diseases. Complications are more common in children than in adults.
- Symptoms and signs of meningitis in a teenager
Sinusitis and meningitis: the relationship of diseases
Meningitis develops as an independent disease and can be a complication of pathological processes. Sinusitis and meningitis are interrelated, since the accumulation of pus in the maxillary sinuses can cause inflammation of the lining of the brain. It is important for people at risk to know how sinusitis turns into meningitis and what symptoms the patient experiences. The development of sinusitis by contact occurs against the background of an existing infectious process. Infection accumulated in the paranasal sinuses can cause inflammation of the meninges.
The development of complications with sinusitis is rare, since modern specialists use effective treatment methods. However, if treatment is untimely and ineffective against the background of reduced immunity, the patient may develop meningitis. If a patient suspects meningitis or their health has sharply worsened, it is necessary to consult a general practitioner or neurologist, who will prescribe an examination and determine the cause of the problem.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients are provided with a wide range of medical services, which include examinations, therapeutic measures, disease prevention and recovery after illness. If meningitis is suspected, patients are urgently hospitalized.
The most important and revealing test for suspected inflammatory processes in the membranes of the brain and spinal cord is a lumbar puncture. It is necessary to examine the cerebrospinal fluid to identify the cause of inflammation and prescribe adequate therapy.
Etiology and pathogenesis of meningitis
Etiological factors that trigger the development of meningitis can be:
- bacterial pathogens (pneumococcus, staphylococcus, meningococcus, E. coli, streptococcus, mycobacterium tuberculosis);
- mushrooms (cryptococci, candida);
- viruses (rubella, measles, Coxsackie, HIV, ECHO, herpes).
In some cases, inflammation of the meninges develops as a result of complications of helminthiasis and the introduction of protozoan microorganisms into the body.
Diagnosis of meningitis
The diagnosis of meningitis can be made based on the results of additional studies - laboratory and instrumental:
- detailed blood test;
- fundus examination;
- X-ray examination of the skull;
- heart electrocardiograms;
- electroencephalography;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital confirm or refute the diagnosis of meningitis using a study of cerebrospinal fluid. A lumbar puncture is performed immediately after examining the patient. Normal cerebrospinal fluid is transparent, colorless, and flows out under a pressure of 130-180 mm during puncture. water Art. It detects from two to eight cells in one microliter. In serous meningitis, the cerebrospinal fluid is colorless, clear or opalescent. During cerebrospinal puncture, it flows out under a pressure of 200-300 mm. water Art. at a speed of 60-90 drops per minute. In the cerebrospinal fluid, from 200 to 800 cells are determined in 1 μl, 80-100% are lymphocytes. The amount of protein and glucose is increased. After the puncture, the patients' condition improves significantly.
With serous-bacterial meningitis, the cerebrospinal fluid may be colorless or yellow, opalescent. During puncture, it flows out in a stream under a pressure of 250-500 mm of water column. The number of cells increases to 800-1000 in 1 μl, they contain the same number of lymphocytes and neutrophils. Protein levels are increased and glucose concentrations are significantly decreased.
The liquor in purulent-bacterial meningitis is cloudy, whitish or greenish-brown. Due to the high viscosity and blockage of the liquor pathways, it often flows out in rare drops under high pressure. The number of cells in one milliliter of cerebrospinal fluid exceeds 1000; they consist mainly of neutrophils. Protein concentration varies from 600 to 16,000 mg/l, glucose levels are reduced.
To confirm the diagnosis of meningitis, doctors use bacteriological examination of mucus from the nasopharynx and cerebrospinal fluid. During bacterioscopic examination of cerebrospinal fluid, smears are stained with Gram or methylene blue. To exclude fungal meningitis, the specimen containing cerebrospinal fluid is stained with ink. Laboratory assistants isolate a pure culture on media with the addition of normal horse serum or cattle serum and identify it by biochemical activity and antigenic structure.
In case of viral meningitis, in preparations prepared with Gram staining and ink, it is impossible to identify the causative agent of the infection. Cultivation of bacteria and fungi also gives negative results. By culturing cellular material with standard laboratory cell lines, a pathogen serologically identical to the measles virus can be isolated. Rubella virus is isolated using the co-cultivation method.
To identify oligoclonal immunoglobulins, the method of agarose gel electrophoresis or isoelectric focusing of cerebrospinal fluid gamma globulins is used. Immunoglobulins appear in a number of viral infections. As a result of immunological studies, viral antigens or antibodies are detected in the cerebrospinal fluid, and the nucleic acid of the virus is detected using the polymerase chain reaction method. The enzyme immunoassay method detects pathogen antigens in feces, urine or saliva. Express methods allow you to quickly and early determine the presence of the herpes simplex virus antigen in the cerebrospinal fluid and blood or the DNA of the virus (using the polymerase chain reaction method).
Laboratory diagnosis of meningitis using modern research methods can be performed at the Yusupov Hospital. According to indications, doctors determine changes in brain tissue using computer or magnetic resonance imaging. If the first signs of meningitis are present, adequate antibiotic therapy is started immediately after diagnosis.
Make an appointment
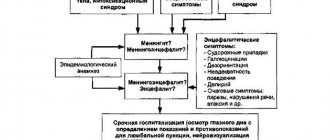
Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of meningitis
The main diagnostic method in the study of meningitis will be lumbar puncture, since the study of cerebrospinal fluid can detect meningitis even with minimal clinical manifestations. This study is performed only in a hospital setting and after preliminary diagnosis, which includes taking an anamnesis, palpation, percussion, identifying meningeal and cerebral signs, as well as excluding contraindications. In most cases, examination of the cerebrospinal fluid allows one to determine the etiology of the disease and prescribe appropriate treatment. The main task of differential diagnosis is to exclude other diseases with similar symptoms, in particular meningism. A distinctive feature of meningism is the absence of general infectious symptoms against the background of meningeal syndrome.
How is meningitis treated?
At the Yusupov Hospital, patients can receive a full range of medical services for the detection and treatment of meningitis, rehabilitation after illness and prevention. Patients with meningitis can contact the neurologist clinic of the Yusupov Hospital every day for 24 hours to receive emergency care.
The staff of the Yusupov Hospital follows the tradition of attentive and respectful treatment of each patient, therefore they approach the treatment of each case individually. Neurologists inform patients at risk about how to distinguish meningitis from other diseases and prevent its development.
When patients are admitted to the Yusupov Hospital, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, including a number of examinations to identify the causes of meningitis, collection of complaints and symptoms. Patients with meningitis need inpatient treatment, so the Yusupov Hospital has created comfortable living conditions and ensures interaction with qualified personnel.
How is an MRI of the brain performed for meningitis?
Magnetic resonance imaging is a modern technological assessment of the patient’s general well-being. The presented procedure has a number of advantages: painless, non-invasive, and capable of providing detailed photographs in several planes. If there is a suspicion of the disease described, the attending physician will issue a referral for this testing. Depending on the clinical manifestations, the expert will decide on the need for testing with a counter-reagent.
To undergo an MRI scan, the patient does not require any special preparation before the session. The main rule is to come to the medical facility at the appointed time in comfortable clothing without metal parts. If it is necessary to perform an analysis with a contrast agent, you need to stop eating for several hours. Stages of implementation:
- Entering the radiology room where a magnetic resonance imaging device is installed.
- Taking a “lying” position on a mobile couch (in case of urgent need, the doctor can fix the limbs and head with special fasteners).
- Placing the patient in the tomograph capsule.
The total time for the procedure is usually 15-20 minutes. During this time, you need to remain completely still and, at some points, at the doctor’s command, hold your breath so that the data obtained is reliable.
is a Russian search platform for the optimal selection of the nearest rated medical centers specializing in magnetic resonance analysis, CT, radiography and other examination options. On the company’s website you can read real reviews from past visitors to any clinic, which will make your decision easier when it’s difficult to choose a place. Special sections contain data on the current cost, promotional offers and location of all capital institutions.
Treatment of meningitis
Meningitis is a direct indication for hospitalization of the patient. Therapeutic tactics are etiotropic in nature and are aimed at eliminating the primary source of infection. The effect of etiotropic treatment must be assessed by analyzing clinical data and the results of microscopic examination of the cerebrospinal fluid.
In the treatment of bacterial meningitis, both in children and adults, the main emphasis in drug therapy is on the prescription of antibacterial drugs in large doses. The choice of antibiotic depends on the causative agent of the infection.
If the inflammatory process is of viral origin, it is important to use antiviral drugs, in particular Viferon. And with fungal etiology, meningitis is treated with antimycotic drugs.
Along with therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, the use of detoxification and restorative therapy is very important.
In order to prevent seizures, the use of lytic mixtures (pipolfen, aminazine, novocaine) is recommended. If the course of meningitis is complicated by cerebral edema or Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, it is advisable to use corticosteroids (dexamethasone). Also, if necessary, symptomatic treatment of pain and hyperthermia is carried out.
MRI for meningitis, what does it show?
The result of magnetic resonance imaging is a series of monochrome images of the brain matter, taken layer by layer in increments of 1 mm. The images alternate between dark and light areas of varying degrees of intensity. The shade transitions correspond to the contours of the internal fabrics. Knowledge of anatomy and experience in the field of radiology allows the doctor to distinguish one anatomical structures from others, assess the compliance of their boundaries and sizes with the norm.
With meningitis, inflammation develops in the meninges, accompanied by thickening of the latter, disturbances in the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, exudation, widening of the furrows and interhemispheric fissure and other nonspecific changes. A scan with contrast shows characteristic staining of areas of inflammation and pathological effusion. MRI after meningitis provides information about the presence or absence of complications and allows one to assess the completeness of the restoration of brain tissue.