Neurologist
SEMENOVA
Olga
5 years experience
neurologist, head of the office for diagnostics and treatment of cognitive disorders
Make an appointment
Polyneuropathies (polyneuropathies) are a group of pathologies affecting peripheral nerves. The clinical picture is determined by the form of the disease diagnosed in the patient. Specific signs are muscle weakness and atrophy, decreased tendon reflexes, sensory disturbances, and autonomic disorders. Treatment of polyneuropathy is carried out by a neurologist. The main task of the doctor is to determine the cause of the disease. Therapy is symptomatic.
Information about polyneuropathy
The word "polyneuropathy" is translated from Greek as "damage to many nerves." This term very accurately describes the essence of the pathology. All structures of the body are entangled in a network of thin nerve fibers, which are divided into three groups:
- motor: responsible for motor functions;
- sensory: provide tissue sensitivity;
- Autonomous (vegetative): necessary for the unconscious regulation of the activity of certain structures, for example, blood vessels or internal organs.
Damage to certain fibers inevitably leads to disruption of their functions. The most common is mixed polyneuropathy of the lower extremities, in which symptoms of dysfunction of the sensory and motor nerves appear.
Make an appointment
Treatment
Therapy for hereditary forms of polyneuropathy is symptomatic. Autoimmune disorders are brought into remission. Diabetic, alcoholic and uremic types of pathology require a combination of drug therapy and exercise therapy. Against the background of diphtheria polyneuropathy, patients are prescribed artificial ventilation.
Modern pharmacology cannot offer people suffering from polyneuropathies drugs that effectively eliminate damage to the cylindrical processes of nerve cells or myelinated nerve fibers. Palliative therapy includes vitamin complexes and neurotrophic agents.
Treatment of porphyritic polyneuropathies involves the use of glucose and painkillers. In the demyelinating form of the disease, patients are prescribed membrane plasmapheresis, supplemented by immunoglobulin injections. If they are insufficiently effective, doctors use glucocorticosteroids - prednisolone or its analogues.
Treatment of diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities is carried out not only by a neurologist - the patient needs to consult an endocrinologist. For severe pain, men and women receive tricyclic antidepressants, pregabalin and gabanetin.
The symptoms of toxic polyneuropathies become less obvious when contact of a child or adult with the toxin is excluded. In case of drug intoxication, the doctor adjusts the daily dose received by the patient.
Surgical intervention against the background of polyneuropathy is performed when there is deformation of the feet and the development of joint contractures. In this case, the patient will face a long period of rehabilitation. To treat uremic polyneuropathy, a child or adult may require a kidney transplant.
Causes
Damage to peripheral nerves can occur due to the following conditions:
- diabetes mellitus: the most common cause of polyneuropathy, resulting from metabolic disorders in the myelin sheath of nerve fibers; mainly the lower extremities are affected;
- severe and prolonged deficiency of B vitamins necessary for the full functioning of the nervous system;
- infectious diseases: HIV, tick-borne borelliosis, leprosy;
- renal failure;
- alcohol abuse;
- acute and chronic intoxication, including drugs;
- autoimmune diseases: damage occurs against the background of a malfunction of the immune system; the most common are chronic and acute inflammatory polyneuropathy (Guillain-Barré syndrome);
- long stay in intensive care, for example, with extensive injuries or serious illness;
- exposure to ionizing radiation;
- pregnancy: carrying a child can cause vitamin deficiency and autoimmune lesions.
In addition, there are hereditary forms of the disease, transmitted from relatives, as well as idiopathic polyneuropathy, the cause of which cannot be determined.
Autoimmune polyneuropathy
Autoimmune polyneuropathies include acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy Guillain-Barré. This is a disease of the peripheral nervous system, which is manifested by the acute development of peripheral paralysis and an increase in protein concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid.
The cause of the disease is unknown. Immunological disorders lead to segmental demyelination in the anterior roots and proximal (located closer to the body) parts of the nerves of the limbs and autonomic ganglia. In half of the patients, 1-3 weeks before the onset of neurological disorders, diseases of the upper respiratory tract, tonsillitis, and transient acute intestinal disorders are noted. The first neurological disorders are pain and a crawling sensation in the legs or partial paralysis of the lower extremities. In the future, movement disorders in the legs progress, and movement disorders of the upper extremities are added. Symptoms increase during the first 1-3 weeks of the disease.
Flaccid paralysis is detected, which often spreads in an upward direction, involving the muscles of the legs and pelvic girdle, torso, neck, and sometimes the respiratory muscles. Neurologists identify muscle hypotonia, decreased or absent reflexes, a slight decrease or increase in reflexes in the distal extremities, and symptoms of tension in the nerve trunks. Many patients with severe motor disorders develop autonomic disorders: a sharp decrease in pressure when getting out of bed, rapid heartbeat and paroxysmal arrhythmia. Spinal puncture reveals protein-cell dissociation—an increase in protein with a slight increase in cells in the cerebrospinal fluid. During electroneuromyography, neurophysiologists in 90% of cases detect a decrease in the speed of excitation along peripheral nerves.
Treatment of autoimmune polyneuropathy is aimed at preventing possible complications. The neurology clinic staff provides professional care. In case of respiratory failure, patients are artificially ventilated using expert-class ventilators; in case of swallowing problems, they are provided with parenteral nutrition. Recovery is accelerated by plasmapheresis started in the first 7 days of the disease. Intravenous slow administration of immunoglobulin is effective. Heparin is used to prevent thrombotic complications. Rehabilitators provide massage of the lower extremities and physical therapy classes.
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy is also an autoimmune disease. It manifests itself with symptoms similar to Guillain-Barré syndrome, but has a chronic course, characterized by repeated periods of weakening of symptoms, or a continuously progressive course. In most cases, the cause of the disease cannot be determined. Autoimmune polyneuropathy can occur with HIV infection and systemic lupus erythematosus. The disease is based on disorders of the immune system. If the nature of the disease is unclear, patients are prescribed prednisolone, azathioprine, plasmapheresis, and immunoglobulin is administered intravenously.
Kinds
Polyneuropathy is divided into several types depending on the type of fibers affected:
- sensory: the nerves that provide sensitivity are affected;
- motor: disturbances in the functioning of motor nerves are detected;
- motor-sensory: mixed form, in which motor disorders predominate;
- sensory-motor: mixed neuropathy, in which sensitivity disturbances are more pronounced;
- vegetative: first place comes to disturbances in the functioning of internal organs, changes in vascular tone and associated trophic disorders.
Significant differences in symptoms are noticeable only in the initial stages of the disease. Subsequently, all nerve fibers are involved in the pathological process, and the manifestations become mixed.
There are other types of classification of the disease:
- depending on the cause: alcoholic, diabetic, idiopathic, etc.;
- depending on the location of the lesion: polyneuropathy of the upper or lower extremities;
- depending on the type of course: acute, subacute, chronic;
- depending on the mechanism of occurrence: demyelinating (the sheath covering the nerve fibers is destroyed), axonal (formed by the death of nerve processes - axons), axonal-demyelinating.
Complications of radiculopathy
In the absence of a proper approach to the treatment and prevention of this disease, radicular syndrome quickly becomes chronic. As a result, changes such as sudden movement, exposure to cold, or stress can trigger an attack of pain.
Another complication may be a persistent impairment of the motor and sensory function of the affected limb and lead to disability. For example, a hernia in the lumbar spine without timely treatment causes peripheral paresis and parylysis of the lower limb, and disrupts the function of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms
Symptoms of polyneuropathy depend on its cause and the characteristics of the damage to the fibers. The most common signs of pathology include:
- decreased sensitivity of the feet and palms, leading to the subjective sensation of wearing socks or gloves;
- pain in the affected limbs (sharp or dull, short-term or nagging, usually worse at rest and at night);
- spasms and twitching of muscle fibers;
- pain when touching the skin or pressing on the affected limb;
- decreased reflexes;
- increased sweating of the extremities;
- trophic disorders: swelling, changes in skin color and dryness, trophic ulcers;
- weakness of the muscles of the arms and legs, slight tremors;
- paresthesia: pathological sensations of crawling, burning, coldness;
- muscle atrophy;
- restless legs syndrome.
Alcoholic polyneuropathy
This form of the disease most often affects the lower extremities. It develops with prolonged uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages and manifests itself primarily as a burning sensation and tingling sensation in the legs. With the further development of the pathology, the patient begins to feel numbness and muscle cramps, which develop due to the concomitant lack of B vitamins.
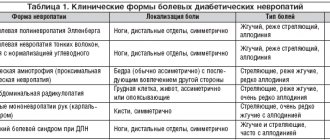
Diabetic polyneuropathy
Elevated sugar levels cause damage to the nerves of the feet (distal version) and the upper legs (proximal version). In the first case, a person experiences a characteristic set of symptoms:
- numbness and decreased pain sensitivity;
- periodic burning pain;
- muscle weakness;
- decreased reflexes;
- impaired coordination of movements, manifested by unsteadiness of gait.
The combination of polyneuropathy with damage to small vessels leads to the appearance of trophic ulcers in the lower part of the leg. The proximal version of the lesion is characterized by sharp pain in the buttock and upper thigh, as well as gradual muscle atrophy in this area.
Chronic polyneuropathy
The typical form of chronic demyelinating polyneuropathy is manifested by symmetrical weakness and sensory disturbances in all extremities. Symptoms of the disease develop over more than two months and are accompanied by the absence or reduction of tendon reflexes in all extremities. Sometimes cranial nerves are affected.
The atypical form of the disease occurs in the following variants:
- asymmetrical – sensory and motor disorders are not symmetrical or are located in the area of innervation of individual nerves;
- focal - motor and sensory disorders are localized in the area of innervation of the lumbosacral or brachial plexus, or one or more peripheral nerves in one lower or upper limb;
- isolated motor – exclusively movement disorders are determined;
- isolated sensory (including chronic immune sensory polyradiculopathy) - only sensory disorders occur.
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy has 4 main course options: chronic monophasic, chronic relapsing-remitting, stepwise progressive, steadily progressive.
Patients complain of weakness in the distal or proximal parts of the lower extremities, sometimes asymmetrical, numbness and a crawling sensation in the hands and feet, and instability when walking.
The lower extremities are usually affected first. Patients have difficulty walking, climbing stairs and out of a chair, and fall. When the upper extremities are involved in the pathological process, patients experience difficulty using kitchen utensils, grasping objects, and tying shoelaces.
Severe paresis is not accompanied by increasing atrophy. There is a diffuse decrease in muscle tone, a decrease and subsequent loss of tendon reflexes. The Achilles reflex is the one that most consistently fails. In most cases of the disease, vegetative disorders are observed:
- increased sweating of the skin of the torso, feet and palms;
- transient cardiac arrhythmia with the development of fainting;
- a progressive decrease in body weight by 10-20 kg over the course of a year at normal temperature, the absence of hypothyroidism and gastrointestinal dysfunction.
The distinctive clinical signs of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy include:
- predominantly distal or mixed (distal and proximal) nature of incomplete paralysis of the limbs;
- severe muscle hypotonia and limb wasting;
- more persistent and frequent autonomic and sensory disorders in the hands.
Respiratory and pelvic disorders are extremely rare.
Neurologists prescribe the following laboratory tests:
- general blood analysis;
- biochemical blood tests for sugar, creatinine, urea, AST, ALT, bilirubin, electrolytes;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for thyroid hormones;
- determination of antinuclear antibodies;
- polymerase chain reaction of blood for hepatitis viruses;
- blood test for HIV infection;
- Serum immunoelectrophoresis - blood testing for protein, protein fractions, monoclonal protein;
- immunoelectrophoresis of urine for monoclonal protein, Bence-Jones protein.
To exclude other types of polyneuropathies and diseases of internal organs that can cause damage to peripheral nerves, instrumental studies are performed:
- plain radiography of the chest organs;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs, thyroid gland;
- magnetic resonance imaging of the brain;
- radiography of flat bones;
- electroneuromyography (allows us to identify signs of myelin destruction and axonal degeneration);
- needle electromyography - in order to identify signs of the ongoing denervation-reinnervation process in polyneuropathy.
Outpatient treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy is aimed at stopping the process of autoimmune inflammation and nerve destruction, restoring nerve conduction, muscle strength and sensitivity, and preventing repeated attacks of polyneuropathy. Patients are prescribed glucocorticoids, immunoglobulin and undergo plasmapheresis. Symptomatic therapy for CIDP includes drugs for the relief of neuropathic pain (gabapentin, amitriptyline) and anticholinesterase drugs (neostigmine).
In a neurology clinic, doctors prescribe a low-salt, high-protein, low-fat diet for patients with chronic polyneuropathy. Medical personnel provide adequate care to prevent bedsores and contractures.
Drug therapy in a neurology clinic consists of pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment. Pathogenetic therapy involves the use of first- and second-line immunomodulatory agents. As first-line therapy, glucocorticoid hormones, normal human immunoglobulin for intravenous administration, and plasmapheresis are used. In case of insufficient effectiveness of first-line drugs, reserve drugs (second-line drugs) are used - azathioprine, cyclosporine, cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil.
Rehabilitation specialists conduct physical therapy classes, perform massages, and administer physiotherapeutic procedures to prevent the formation of contractures (electrical stimulation, heat therapy, medicinal electrophoresis). Effective methods of treating chronic polyneuropathy are acupuncture and hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of polyneuropathy requires a comprehensive examination, which includes:
- survey: identifying patient complaints, clarifying the time and circumstances of the occurrence of each symptom;
- taking an anamnesis: recording all past diseases, injuries, intoxications, chronic pathologies, hereditary risk factors, etc.;
- neurological examination: assessment of skin and proprioceptive (spatial) sensitivity, motor function, muscle strength, quality of reflexes;
- consultations with specialized specialists: endocrinologist, narcologist, toxicologist, nephrologist, etc.;
- general urine test, general blood test, blood biochemistry (determination of glucose levels, lipid spectrum, vitamins and microelements, kidney function indicators and other parameters);
- blood test for HIV and other infections;
- genetic and immunological studies according to indications;
- Electroneuromyography allows you to identify lesions of nerve fibers and exclude other diseases with similar symptoms;
- biopsy of nerve and muscle tissue;
- lumbar puncture (examination of cerebrospinal fluid) to exclude neuroinfections;
- Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the lower extremities.
The list of examinations can be adjusted depending on the form of polyneuropathy and concomitant pathology.
Treatment of polyneuropathy of the extremities
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the main cause of damage to nerve fibers, restoring their normal functioning, as well as eliminating symptoms that are unpleasant for the patient.
Depending on the cause of the disease, the following may be prescribed:
- drugs to correct blood sugar levels;
- antihistamines;
- immunoglobulins and glucocorticosteroids to eliminate inflammation and autoimmune damage;
- plasmapheresis and detoxification drugs;
- antibiotics for infections.
To restore nerve fibers, the following are used:
- B vitamins (milgamma, neuromultivit);
- drugs that improve blood circulation, metabolism and tissue regeneration: actovigin, cerebrolysin, berlition (especially effective for diabetes mellitus);
- angioprotectors: trental, pentoxifylline;
- means to enhance the conduction of nerve impulses to muscles: neuromidin.
Symptomatic therapy includes:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac, ketorolac), glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone, dexamethasone), analgesics (analgin, lidocaine) in the form of tablets, injections or local forms to relieve pain;
- anticonvulsants: tebantin, catena;
- antidepressants for chronic pain;
- sleeping pills according to indications.
Non-drug therapy is of great importance in the treatment of polyneuropathy. It includes:
- restorative and therapeutic massage to stimulate blood circulation in tissues, their nutrition and regeneration, as well as strengthen muscles;
- electrophoresis and phonophoresis with analgesics, B vitamins and other drugs (the use of electric current or ultrasonic waves facilitates the delivery of drugs to the affected area);
- electrical stimulation of muscles;
- magnetic therapy, UHF therapy, ultraviolet irradiation;
- darsonvalization: exposure to high frequency alternating current to improve metabolism and tissue regeneration;
- mud therapy: mud applications on the affected area;
- therapeutic baths with mineral waters or sea salt;
- physical therapy: dosed physical activity strengthens muscles and improves blood circulation in them; at an advanced stage of the disease, it is necessary to start with the easiest complex and gradually complicate it.
- classical acupuncture and electroacupuncture: stimulate the work of muscle tissue and nerve fibers;
- classes with an occupational therapist: necessary when it is not possible to fully restore the function of the limb; exercises are aimed at developing new movements adapted to the capabilities of the arm or leg.
For full treatment, a long-term complex effect on the affected area is required. Only if the patient thoroughly fulfills all the doctor’s instructions can success be achieved, but even in this case, full restoration of the functions of the nerve fibers is not guaranteed.
Treatment of radiculopathy
A neurologist treats herniated discs. Medical specialists have extensive experience in treating such diseases. You can go through all stages of treatment under the supervision of your attending physician, who will answer all your questions.
In most patients with radicular pain, conservative treatment is effective; however, in 2% of patients there are absolute indications (progression of sensory and motor disorders, cauda equina syndrome) for surgical treatment.
In general, we can say that conservative tactics for managing patients with this disease are favorable in most cases and should be considered as a priority in the absence of a verified compressing substrate.
The first stage of treatment is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Corticosteroid (CS) injections may be considered as an alternative to NSAIDs for the treatment of radicular pain. Perineural injections (translaminar, epidural, transforaminal or selective root block) should be performed only after neuroimaging (MRI) of a clinical topical diagnosis. To influence the neuropathic component of radicular pain, some drugs from the group of anticonvulsants (carbamazepine, gabapeptin, pregabalin, lamotrigine) can be used.
According to studies conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of systemic local analgesic drugs lidocaine, mexiletine, tocainide and flecainide showed good results.
Complications
If you do not consult a doctor in time and do not eliminate the cause that caused the damage to the nerve fibers, neuropathy will steadily progress. Complications of the disease include:
- a significant decrease in muscle tone with subsequent muscle atrophy;
- loss of limb performance;
- development of extensive trophic ulcers requiring surgical intervention;
- loss of ability to move and self-care;
- chronic insomnia due to pain and the development of restless legs syndrome;
- depression and neuroses.
You can avoid complications if you consult a doctor for help in a timely manner and also follow preventive measures.
Make an appointment
Prevention
Polyneuropathy is a condition that can be effectively prevented long before the first symptoms appear. To do this you need:
- visit a doctor in a timely manner and undergo comprehensive diagnostics in order to promptly identify and eliminate diseases that can cause damage to peripheral nerve fibers;
- eliminate bad habits: smoking and drinking alcohol, prevent toxins from entering the body;
- eat well, include a sufficient amount of macro- and microelements, vitamins in the diet; For the proper functioning of nervous tissue, polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are found in vegetable oils, olives, nuts, and fatty sea fish, are especially important;
- control blood sugar and cholesterol levels;
- provide the body with regular physical activity without striving for records (walking, swimming, cycling, etc.).
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will provide assistance with any form of polyneuropathy. Specialists will conduct a full diagnosis to accurately identify the extent and location of the lesion, and then prescribe treatment and rehabilitation in accordance with the individual characteristics of the body. We use comprehensive methods that include:
- drug therapy in accordance with indications and modern recommendations for the treatment of polyneuropathy, including courses of infusions;
- various types of physiotherapy: magnetic therapy, laser and ultrasound exposure, phonophoresis and electrophoresis;
- physical therapy under the supervision of an experienced instructor, training in exercises to restore limb function at home;
- massotherapy;
- sessions with a psychotherapist if you have depression, insomnia, or increased anxiety;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment for complete rehabilitation.
Advantages of our clinic
The multidisciplinary clinic “Energy of Health” has experienced staff and the most modern equipment for diagnosing and treating various diseases. We provide each client with high quality medical services, which include:
- detailed examination to accurately determine the cause of complaints;
- consultations with narrow specialists directly in the clinic, as well as communication with foreign doctors if necessary;
- comprehensive treatment, selected in accordance with the indications and individual characteristics of the body;
- minor surgical operations directly in the clinic;
- own day hospital for maximum convenience;
- drawing up rehabilitation programs;
- affordable prices and services within the framework of voluntary health insurance.
Polyneuropathy is a dangerous complication of many conditions and diseases. You should not hope that the symptoms are limited to a simple tingling sensation; over time, the condition will worsen. Don’t delay seeing a doctor; sign up for a consultation with neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic.