Erased dysarthria
A child with mild dysarthric status has impaired motor sphere, sound pronunciation, and prosodic aspect of speech. However, all these defects are minimally expressed, in an erased form, and therefore are detected only with a careful neurological and speech therapy examination. Typically, erased dysarthria is diagnosed at 5-6 years of age. Before this, speech disorders were regarded as polymorphic dyslalia, and only the extraordinary persistence of sound pronunciation defects forces specialists to take a deeper look at the problem.
In general physical development in children with MDD there is a slight lag behind the age norm. Patients may be short, underweight, or have a narrow chest. They are clumsy, quickly tire during physical activity, and have difficulty performing movements in a synchronized manner. Along with the general motor sphere, fine motor skills suffer. Due to the fact that differentiated movements of the fingers are disrupted, children have difficulty mastering self-care skills (fastening buttons, tying shoelaces), feel awkward during creative work (drawing, appliqué, modeling), and do not like toys with small parts (puzzles, construction sets). Schoolchildren's graphomotor skills suffer: illegible handwriting and low writing speed.
Damage to the facial and articulatory muscles is indicated by hypomimicness of the face, laxity of the lips, pareticity of the tongue, asymmetry of the nasolabial folds and corners of the mouth. When performing articulation tests, hyperkinesis, synkinesis, slight cyanosis and deviation of the tongue appear. During speech activity, hypersalivation is noted. It is difficult to perform articulatory movements, hold a pose, and smoothly switch from one articulation to another. The neuropsychic status of children with erased dysarthria reveals vegetative disorders (sweating and cyanosis of the extremities, persistent dermographism). The child may be easily excitable, fussy or inhibited, lacking initiative. Characterized by reduced performance, poor switching ability, instability of attention, and decreased memory capacity.
Violation of sound pronunciation is multiple in nature - phonetic defects affect two or more groups of sounds (usually whistling, hissing and sonorant). Abnormal pronunciation in most cases is represented by sound distortions (interdental and lateral sigmatism, throat rhotacism), often combined with the absence and replacement of sounds, defects in voicing/voicing and softening. Even having achieved the normative isolated sound of a phoneme, it is difficult to automate the disrupted sound and introduce it into speech. Along with sound pronunciation, the prosodic aspect is disrupted: the voice is fading, intermittent, unmodulated, nasalized, and the intonation expressiveness of speech is reduced. In general, the child’s speech is “smeared” and poorly intelligible.
Treatment in Moscow
For many years, the Yusupov Hospital has specialized in the treatment of dysarthria in children and adults. The high professional level of specialists allows us to accurately determine the type of pathology, which eliminates the possibility of incorrect prescription of therapeutic measures. An individual approach to each patient guarantees a favorable atmosphere throughout the entire course of treatment and rehabilitation. The main directions of the clinic:
- Treatment of complex neuralgic pathologies - multiple sclerosis, major stroke and other dangerous diseases that cause the death of certain groups of brain cells.
- Help for patients with cancer - chemotherapy, therapy that eliminates pain syndromes and painful symptoms.
- Treatment of progressive brain diseases - Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia, Pick's disease and other rare forms of dementia.
- Rehabilitation of patients after severe operations, chemotherapy, traumatic brain and spinal injuries, major stroke and radiation therapy.
- Effective treatment and correction of speech disorders. The range of measures includes constant monitoring by specialists, physiotherapeutic measures, therapeutic exercises and classes with a speech therapist who has extensive experience in the successful treatment of dysarthria.
By contacting the Yusupov Hospital, the patient receives a guarantee of a speedy recovery and the most favorable outcome. You can make an appointment for a consultation with specialists by phone.
Make an appointment
Classification
The classification is made according to three types of characteristics - according to the location of the problem in the nervous system, according to the syndrome of cerebral palsy (each of them manifests its own type of deviation) and according to how difficult or easy it is to understand the patient’s speech (the latter is the classification of speech therapists). Let's look at each in order.
Depending on where the source of the problem is located, only 5 types can be distinguished:
- Bulbar dysarthria - in the medulla oblongata there are nuclei of several important cranial nerves that are necessary in the formation of speech: hypoglossal, glossopharyngeal, vagus; when these nerves are affected, speech problems arise. The most pronounced signs are disorders of chewing, swallowing, areflexia, nasalization, and lack of differentiation of sounds among themselves.
- Pseudobulbar – requires differentiation from bulbar; one of the signs is violent crying or laughter. In this case, the corticonuclear pathways are affected. This type of disease is characterized by slurred speech, sonorant, whistling and hissing sounds are pronounced incorrectly. It is difficult for the patient to control the tip of the tongue.
- Cerebellar – the cause is damage to the cerebellum/conducting pathways, as the name implies. There is slow and slurred speech, sounds produced using the lips and the front of the tongue are poorly produced, and isolated cries are observed.
- Cortical – lesions in the cerebral cortex. In this case, only articulatory apraxia is observed.
- Subcortical – similarly associated with damage to the subcortical nuclei. This type can be combined with the first, second and third; it is characterized by articulatory spasms, disturbances in timbre and strength of the voice, and involuntary cries.
According to the leading clinical symptom of cerebral palsy, the following forms of dysarthria are distinguished:
- spastic-rigid,
- spastic-paretic,
- spastic-hyperkinetic,
- spastic-atactic,
- atactico-hyperkinetic.
According to severity, 4 degrees of dysarthria are differentiated, where the first is erased dysarthria (its signs can only be determined by a speech therapist), the second is when speech is understandable, but others notice defects, the third is only relatives who often communicate with the patient can understand him, the fourth (anarthria ) – there is no speech, or it is completely incomprehensible.
Diagnostics
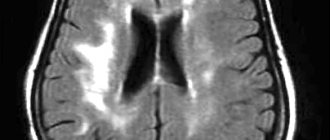
Treatment of dysarthria begins with diagnosis, which may involve neurologists and speech therapists. Based on the examination and conversation, a decision is made on the depth of the neurological examination and its plan is formed. The neurological examination is complemented by speech therapy, which includes diagnostics of oral and written speech.
Forms of dysarthria are identified and diagnosed using the following methods:
- electroencephalography;
- electroneurography;
- MRI of the brain;
- electromyography;
- transcranial magnetic stimulation.
The speech therapist, for his part, evaluates non-speech and speech disorders - the structure of the speech organs, the range of possible movements of the tongue, larynx, lips, the condition of the muscles, the nature of breathing. When testing oral speech, a specialist identifies the development of speech according to classical parameters - tempo, intelligibility, synchronization of the three components of a conversation (voice formation, articulation, breathing), sound pronunciation, etc. The written speech test allows you to differentiate the disease you are looking for from several types of speech disorders - dyslalia, motor alalia, motor aphasia.
Features of moderate dysarthria
The average severity of dysarthria is already characterized by gross defects in pronunciation, facial expressions, chewing and swallowing. Speech with this degree of dysarthria becomes inarticulate, blurred, and incomprehensible.
Children with moderate dysarthria are educated in specialized schools. After a certain time, relatives get used to it and begin to understand the patient’s speech. The facial expressions of a patient with moderate dysarthria are poor. In most cases, drooling is observed. Eating is difficult due to defects in chewing and swallowing.
Definition and general information
Dysarthria is a speech therapy disorder. Its frequency is only 3-6% of all children, but there is a tendency for this indicator to increase. The disease is among the three most common speech disorders, along with dyslalia (speech defects not associated with damage to the central nervous system) and alalia (serious disturbances or complete absence of speech in children). Dysarthria occurs due to disruption of the central or peripheral nervous system, which affects the innervation of the muscles of the lips and tongue, larynx, palate, larynx and respiratory muscles.
Features of severe dysarthria
What is grade 3 dysarthria, and what its manifestations are, is easy to understand, since in severe dysarthria, the sound production function is completely or almost completely absent.
Level 3 dysarthria is characterized by the absence of speech function, mask-like facial expression, drooling, and severe disorders of chewing and swallowing. The patient's mouth is constantly open, the tongue does not move. Children are educated in special schools, where they master general education subjects according to an individual program.
Features of mild dysarthria
With a mild degree of dysarthria, there are no gross violations. With 1st degree of dysarthria, articulatory motor skills are inaccurate and slow. The speech is understandable, but a certain defect is still noticeable. Due to the defect, communication is disrupted. Patients prefer to speak using short words and sentences. Neurotic disorders often occur due to speech impediments. In children in whom speech function is just beginning to develop, a diagnosis of mild dysarthria should be immediately treated to avoid general underdevelopment of speech function in the future. Untreated dysarthria will lead to impaired written speech in the future. If speech disorders in childhood are not corrected, in the long term this will lead to a delay in the child’s mental development. Children with mild dysarthria receive education in secondary schools.
There are no gross defects in chewing and swallowing, but choking and coughing are sometimes observed. The patient's facial expressions are usually not impaired.
Correction
Correction of dysarthria by a speech therapist is carried out in conjunction with all procedures and treatment prescribed by a neurologist.
Treatment of dysarthria in terms of neurology consists of a set of measures and procedures, which are selected individually depending on the severity of the concomitant disease. The patient may be prescribed:
- drug therapy;
- segmental reflex and acupressure massage;
- acupuncture;
- acupressure;
- exercise therapy;
- medicinal baths;
- physiotherapy;
- mechanotherapy;
- hirudotherapy.
In addition to standard hospital procedures, activities with creative elements (sand therapy, isotherapy), as well as touch therapy, finger exercises and dolphin therapy are well suited for the rehabilitation of patients.
Correction of the disease by the efforts of a speech therapist is carried out in parallel and includes speech therapy massage and gymnastics (breathing, articulation), orthophonic exercises, practicing and automating correct sound pronunciation. The list of procedures and techniques that will be included in the treatment of pathology depends on the cause of the defect and its severity.
To make an appointment, call us at the numbers on the website or use the special form. Neurologists and speech pathologists-speech pathologists from our network of Nearmedic clinics will provide comprehensive support to both children and adults. The frequency of visits to a speech therapist is 2-4 sessions per week.