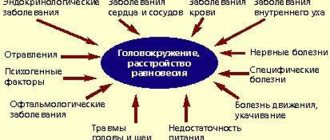
Causes of headaches, nausea and dizziness
Headache and dizziness are often accompanied by nausea. The centers of these sensations are located close to each other in the brain. Acute pain often leads to loss of balance, loss of coordination, and nausea. It is important to determine what caused these symptoms - information will allow you to prescribe the correct and most effective treatment.
Migraine
Migraine is an acute headache that occurs in attacks and occurs without a specific reason. Its characteristic feature is the “migraine aura”, which is felt several hours before the onset. Most patients who regularly suffer from migraines can determine the imminent onset of an attack by characteristic precursor symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness, sudden loss of balance;
- increased sensitivity to bright light and sounds;
- in some cases - speech impairment, memory loss.
If you often feel dizzy, dizzy, or feel nauseous, this may indicate a migraine. The disease is often hereditary, and in some patients it occurs after injuries and bruises. For treatment, specific drugs are prescribed to strengthen blood vessels and relieve acute pain.
Metabolic disorders
Symptoms such as headache, nausea, dizziness can occur with systemic diseases. They are accompanied by other symptoms or occur independently. A more detailed diagnosis may reveal the following disorders:
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, including its inflammatory diseases and neoplasms;
- diseases of the stomach and intestines: ulcers, inflammation of the mucous membrane.
A thorough examination is important for prescribing the correct treatment. Taking medications that only relieve symptoms will not help you feel better, but will only make the situation worse. If a patient often has a headache, and dizziness and nausea appear as accompanying symptoms, the cause may lie in dysfunction of the internal organs.
Hearing diseases
Diseases of the inner ear are accompanied by severe headaches, nausea, dizziness, and deterioration of well-being. They pose a great danger because they progress quickly. If treatment is incorrect or untimely, there is a risk of complete hearing loss.
- Meniere's disease is a specific pathology in which an increased amount of endolymph is produced in the inner ear. The liquid puts pressure on the structures of the hearing organ, which is manifested by nausea, headache, dizziness, and impaired coordination of movements. Characteristic symptoms are a sharp decrease in hearing in one or both ears, auditory hallucinations.
- Vestibular neuritis is inflammation of the vestibular nerve. Most often, the disease is of viral origin, less often associated with a bacterial infection or allergy. Neuritis is manifested by an acute headache, but there is no hearing impairment.
- Labyrinthitis is an inflammation of the inner ear. The disease is a complication of otitis media and develops if it is not treated in a timely manner. Labyrinthitis causes symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, weakness, headache, as well as hearing loss and tinnitus. Purulent discharge from the ear canal may be observed.
- A perilymphatic fistula is a damage to the septum between the middle and inner ear. The liquid contents of the inner ear penetrate into the middle section. The condition is very dangerous and can lead to unilateral hearing loss.
It is important to understand that diseases of the inner ear are not always accompanied by hearing impairment. Often the patient simply has a headache and dizziness, nausea, weakness and fever. When diagnosing, one should not exclude the possibility of damage to the organ of hearing, even if there are no typical complaints of pain and tinnitus.
Arterial hypertension
High blood pressure is a common disorder for both older and younger people. Its causes include weakness of blood vessels, a decrease in the strength and elasticity of their walls. The disease is chronic and manifests itself in attacks. At home, you can always measure blood pressure using a tonometer if the following symptoms occur:
- nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache;
- deterioration in coordination of movements;
- redness of the skin and mucous membranes;
- heart rhythm disturbance.
Attacks of arterial hypertension can be triggered by stress, high tension, physical exertion, as well as sudden changes in weather conditions. If they are moderate, they go away after a long rest. If your health suddenly deteriorates, it is important to immediately seek medical help, since hypertension in combination with weakness of the vascular walls can cause a stroke.
Vertebro-basilar insufficiency
Vertebro-basilar insufficiency is a dangerous syndrome in which brain function is disrupted due to insufficient blood flow in important arteries (basilar or vertebral). Blood does not flow to the nerve cells, so they cannot function normally.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency is manifested by the following symptoms:
- headache, nausea, dizziness, weakness;
- short periods of vision loss, the appearance of black dots and circles before the eyes;
- sudden hearing loss, tinnitus;
- constant weakness and fatigue, possible fainting.
The disease can be congenital or acquired, and is often hereditary. Its causes in adulthood include damage to the cervical spine, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and inflammatory vascular pathologies. An accurate diagnosis can only be made on the basis of MRI or CT data, since the clinical picture resembles other diseases that are accompanied by cerebral circulation disorders.
Other reasons
The causes of headaches, dizziness, nausea and weakness can be associated with various conditions and diseases. These symptoms occur in diseases of the internal organs, endocrine and cardiovascular systems. They can indicate a huge number of disorders, which can only be distinguished based on the results of diagnostic data:
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine - a disease of intervertebral cartilage, in which they are destroyed, deformed and compress the blood vessels carrying blood to the brain;
- increased intracranial pressure - this value cannot be measured accurately, but headache, dizziness and nausea are typical symptoms;
- Tension headache is one of the most common causes and is associated with stress, physical fatigue, and prolonged exposure of the neck to an uncomfortable position;
- The cause of dizziness, nausea, and headaches in women can be early pregnancy.
Doctors at the Clinical Institute of the Brain warn that such symptoms are a reason for a more detailed examination. They may not occur frequently in a healthy person, even due to high fatigue and tension. Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache and weakness may indicate hidden pathologies of internal organs that progress and cause dangerous complications.
What is dizziness?
True dizziness or vertigo is a condition during which patients have a feeling of rotation of surrounding objects around them or a false sensation of their own movement or rotation.
An example of true dizziness, but not in any way related to the disease, is the dizziness that appears in people after riding a carousel, when, after an abrupt stop, they continue to see the movement of surrounding objects relative to themselves, as if the carousel were still in motion.
In most cases, the occurrence of true dizziness is a symptom of diseases of the system of control of balance and body position in space. This system includes the eyes, the vestibular apparatus of the inner ear, and sensory receptors in the human muscles, joints, and bones. Very often, dizziness, which is caused by a disruption in the balance system, is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Diagnostic methods
To understand why the patient feels sick, sick, and dizzy, a full examination should be performed. Various techniques are aimed at identifying hidden pathologies that require specific treatment. During the initial examination, the doctor collects medical history data. It is important to describe in as much detail as possible under what conditions the headache begins, how often attacks occur and how long they last. To confirm the diagnosis, the following techniques may be needed:
- first of all, measuring blood pressure; the patient is also recommended to monitor it at home;
- tests to check balance, including the Romberg test (deterioration in coordination of movements is manifested by staggering in a standing position, with eyes closed, feet shifted and straight arms extended forward);
- a general blood test will indicate inflammatory processes, as well as various types of anemia;
- blood test for glucose levels;
- heart examination, which includes ultrasound diagnostics and electrocardiogram;
- tests to assess hearing and visual acuity;
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- study of blood flow in the vessels of the neck and head - a contrast agent is used for this;
- electroencephalography - analysis of the bioelectrical activity of brain cells;
- computer or magnetic resonance imaging is the most accurate, informative way to examine the brain, including soft tissues and blood vessels, which allows you to obtain a complete image of the affected area.
At the Clinical Institute of the Brain, you can undergo a complete diagnosis and determine the causes of nausea, dizziness, and headaches. The regimen is selected individually, based on the results of the initial examination of the patient. An experienced doctor will prescribe only those studies and tests that will determine the nature of the pathology. This is the most important stage in solving the problem, since the diagnostic results allow you to select the most effective treatment regimen.
How does the human balance system work?
In most cases, true (central, systemic) dizziness is a manifestation of various diseases of the system that provides balance and control of body position in space. This system consists of the following 3 components:
- The vestibular apparatus, which is located deep in the skull, where sensitive receptors are located that respond to the angular or linear acceleration of the body in space.
- Eyes that provide visual information about the location of the body and its parts in space, as well as in relation to other objects.
- Sensitive receptors (proprioceptors) that are found in human bones, joints, muscles and ligaments. They provide reliable information about the position of body parts in space, as well as relative to each other.
All these 3 components of the balance system simultaneously send information to the brain, where it can be analyzed and processed into a person’s idea of his position in space and relative to other objects.
If for any reason the data that comes from one of the sources is distorted (for example, irritation of the receptors of the vestibular apparatus by an inflammatory reaction when there is no movement and acceleration), then an incorrect idea is created in the brain about the position and movement of the human body in space . Then an illusory sensation of movement or rotation arises, when in reality the body is motionless.
The causes of a disorder in a person’s balance system can be very different. Nowadays, more than 80 diseases are known that can cause dizziness. Below we describe the most common causes of dizziness.
Treatment methods
It is important to start treatment promptly if attacks occur frequently or are of high intensity. The regimen includes several steps aimed at eliminating the cause and symptoms of headaches and dizziness.
- The first stage is relief of an attack of acute pain. For this purpose, analgesics, antiemetics, and antihistamines are prescribed.
- The second stage involves systemic treatment of the underlying cause of the attacks. The doctor will select a suitable regimen to support the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, heart and blood vessels, and endocrine glands.
- For pathologies of the cervical spine, non-drug methods are effective. Treatment methods such as massage, gymnastics, and physiotherapy may be prescribed.
- For migraines, conventional painkillers do not provide relief. After confirming the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe medications from the triptan group (sumatriptan).
- To restore balance, a set of exercises that can be performed at home is effective. It includes turning the head while stopping the gaze at a certain point, walking with eyes closed, and standing on one leg.
If you have a headache, feel sick, feel dizzy, or feel weak, you should definitely consult a doctor and start treating the problem. The Clinical Brain Institute offers comprehensive programs for diagnosing and treating headaches. Here you have the opportunity to undergo a full examination by experienced specialists and receive the most effective recommendations. Treatment takes place under the full supervision of general and specialized doctors, using new techniques and modern equipment.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 16 votes
Share article on social networks
Symptoms other than dizziness
As can be seen from the above, the term “dizziness” has a rather narrow medical interpretation (a false sensation of rotation of surrounding objects or one’s own rotation). But, despite this, people also use this term to refer to other symptoms that are not actually dizziness. So, most often “dizziness” is called such phenomena as:
- darkening in the eyes after abruptly rising to your feet from a sitting or lying position;
- a veil before the eyes;
- feeling of imminent loss of consciousness (fainting);
- weakness, nausea, feeling of confusion and unsteadiness in the legs;
- feeling of unsteady gait and impaired balance.
When a person suffering from dizziness comes to see a doctor, he should describe his condition, how he is feeling and the symptoms he is experiencing as accurately as possible, and not simply say that he suffers from “vertigo.” The further examination and treatment plan will depend on the accuracy of the description of the existing symptoms.
In contrast to true dizziness, which appears due to a disruption in the functioning of a person’s balance system, false dizziness, which patients describe as a feeling of weakness, instability, darkening in the eyes, blurred vision, etc., can most often be a sign of anemia, chronic fatigue , hypovitaminosis, hypotension and vegetative-vascular dystonia. In addition, fainting, episodes of lipothymia (a sharp decrease in muscle tone with great physical stress) and short-term attacks of epilepsy can also be confused with dizziness.
We pay special attention to attacks of sudden dizziness and weakness in people who have diabetes. In this category of patients, dizziness and weakness may indicate a dangerous decrease in blood glucose levels.