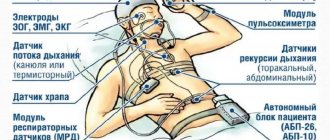
Hypochondria is a human psychopathological condition that manifests itself in constant and continuous concern and worry about one’s health. A person is afraid of getting sick with some disease, perceives his sensations as unpleasant or threatening his normal functioning.
Often hypochondriacs diagnose themselves and believe that they suffer from some incurable pathology. In other words, a person with hypochondria turns into a kind of machine that records all his sensations and interprets them into diseases and symptoms.
Causes of hypochondria
There are many hypotheses and assumptions about the causes of hypochondria. But researchers are unanimous on one thing: hypochondria occurs against the background of a depressive disorder. Scientists have shown that patients suffering from depression experience a significant increase in any complaints for which there is no physical reason.
Hypochondria also contributes to:
- disturbances in the functioning of the cerebral cortex; - distorted perception by the cortex of impulses from internal organs; — initial manifestations of delusional disorders; - a disturbance between the work of the autonomic nervous system (responsible for the autonomous functioning of organs) and the cortex.
Symptoms
The main symptom of this phobia is the obsessive fear of getting cancer and dying from it. It is common to pay increased attention to one’s internal sensations; any discomfort provokes the thought that this is a manifestation of cancer. Much attention is also paid to searching for information about cancer on the Internet and available literature.
Often unnecessary examinations and tests are carried out to exclude cancer; at the initial stages, good research results and the doctor’s conclusions about the absence of oncology calm down for a while and remove the influx of fears. But, over time, the conviction that cancer has begun grows stronger and cannot be dissuaded.
Isolated cancerophobia is rare; in this case, they speak of cancerophobia syndrome. Most often, obsessive fears of cancer are accompanied by other phobias, increased anxiety, asthenic phenomena, and vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD).
Cancerophobia can be observed as one of the symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic attacks, neurasthenia, depression, schizotypal disorders, consequences of organic damage to the nervous system, psychosomatic diseases and other diseases.
Symptoms, complaints and course of the disease
Every practicing doctor has encountered hypochondriacs in his practice. People with this pathology often present all sorts of complaints, look for many diseases, and do many additional examinations. However, their results are usually absolutely normal.
Hypochondria is divided into 3 types:
1. Obsessive. 2. Super valuable. 3. Delusional.
Patients with the obsessive form are anxious and suspicious, overly concerned about the state of their health, and constantly analyze all the processes occurring in the body. An attack of hypochondria can be triggered by viewing medical advertisements or an ambiguous phrase from a doctor. Patients with the overvalued form have similar symptoms, but they are characterized by an acute psycho-emotional reaction to the slightest physical discomfort (for example, a runny nose). The most complex and severe form of hypochondria is delusional.
It is characterized by: confidence in the presence of an incurable disease, attempts to dissuade are interpreted as “even the doctors have given up on me,” there are attempts to commit suicide, as well as depression, delusions and hallucinations.
Diagnosis and treatment
Any obsessive fear, including cancer phobia, deprives a person of the opportunity to live fully and puts him in constant dependence on existing fears. In addition, being under constant stress is of little benefit to health and actually increases the risk of getting not an imaginary, but a very real disease. A classic example is a stress-related disease such as gastric ulcer. And long-term stomach ulcers, as is known, can become malignant. So is cancerophobia treatable and how to get rid of it?
Talking about treatments for cancer fear in general is quite difficult. Thus, reactive syndrome can be dealt with using psychotherapy methods, sometimes with the addition of antidepressants or sedatives, and severe cases require hospitalization in a psychiatric hospital. However, a psychotherapist in our reality is an exotic figure, and few people will go to a psychiatrist of their own free will. Of course, first of all, cancerophobes turn to their local therapist with their fears.
Patients who have suffered from this disorder for several days are usually well known by doctors and are frequent visitors to the clinic. If such a patient comes to the appointment for the first time, the idea of a diagnosis may be prompted by an emotionally expressed statement about the presence of a malignant neoplasm.
It is better to treat a patient with such fear carefully. Sometimes complaints are actually caused by the presence of a tumor, so first of all you need to make sure that the patient’s suspicions are unfounded. A clear understanding of the sequence and scope of the examination aimed at excluding cancer pathology in organs and systems of the body will help.
In relation to patients who have undergone a course of radical treatment for a malignant neoplasm, even a non-oncologist in general should have an idea of the terms of follow-up. If there is a pain syndrome, it is necessary to find out its nature - whether the pain is associated with any disease or is it somatized depression. What to do if, during the examination, no evidence of the presence of a malignant neoplasm was obtained, but the patient is still convinced that he has cancer and continues to harass himself, and at the same time the doctor? Psychotherapists in the treatment of phobias use the techniques of rational (information, persuasion) and suggestive (suggestion to patients in a state of hypnosis) psychotherapy. Of course, suggestive psychotherapy should be carried out by specialists. The local doctor has methods of persuasion in his arsenal. Firstly, it is possible to documentally prove to the patient that he does not have cancer. If there are no medical indications for any specific examinations within the framework of compulsory medical insurance, the patient can have them performed at his own expense. The cost of the issue, as a rule, does not stop the cancerophobe. He will donate blood for all existing tumor markers and do a computed tomography scan of the whole body to make sure everything is normal.
Secondly, when communicating with such a patient, it is necessary to constantly convey the idea that in our time an oncological diagnosis is not a death sentence, cancer is a serious disease, but at the present stage it is curable. Positive examples work well - stories about those who had cancer, but were cured.
It makes sense to ask the patient about his professional and family history. As a rule, it turns out that everything is not very good there. And, along with recommending taking antidepressants, visiting a psychotherapist and personal growth courses, you can try to get the patient to think about what is really bothering him (problems in family life, lack of fulfillment in his profession, etc.) and what he is afraid to admit himself. to yourself. Of course, this will not cure a carcinophobe instantly, but it can point in the right direction.
If a person believes that following certain rules and recommendations will help him avoid cancer, there is no need to convince him otherwise. Constant actions that are monotonous and obligatory replace the obsession of the phobia. Careful adherence to a diet, a daily jog, a shower in the morning, even reading the evening prayer and going to church can calm him down and create the illusion that he is in control of the situation.
In addition, those suffering from cancer phobia should be oriented not towards the probable future, but towards the present and be encouraged to live for today. There is even some benefit that can be derived from cancerophobia. Sufferers are usually examined from head to toe. They continuously donate blood for tumor markers, do a variety of X-ray examinations, ultrasound, computed tomography and nuclear MRI of all areas of the body. Such a patient does not need to be referred for examinations; he already has all the latest results on hand. If, despite a comprehensive examination, the patient’s doubts cannot be dispelled, and he is still convinced that he has cancer, he can be sent to oncologists. After all, the cancer clinic is the final authority in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. And if this stage has already been passed, all that remains is to recommend a course of treatment with a psychotherapist.
Treatment of hypochondria
The tactics for correcting disorders are determined by the type of hypochondria. As a rule, treatment begins with various types of psychotherapy (Gestalt therapy, art therapy, psychoanalysis).
Medications are also used - antidepressants, tranquilizers, antipsychotics. If the patient’s symptoms are manifestations of schizophrenia, powerful antipsychotics should be used. In severe cases, hospitalization is required. Sometimes the use of alternative medicine is justified. Most often it acts as a “placebo” effect. However, if decoctions and infusions of herbs help the patient, they can and even should be included in the treatment regimen for hypochondria.
We also recommend reading the article about Haloperidol.
Treatment of cancerophobia
In more severe and long-lasting cases of cancerophobia, dissuading oneself is not enough. Treatment required. The first step is a consultation with a psychotherapist or psychiatrist. During the consultation, the doctor will clarify the condition and, if necessary, prescribe therapy. The following techniques are recommended that have a therapeutic effect for obsessive fear of getting cancer:
- Psychotherapy. The most effective are cognitive-behavioral and psychodynamic directions. The former teach you how to manage your anxiety, the latter help you get rid of your phobia by identifying the unconscious causes of fear.
- Biofeedback therapy. Advanced technology that combines elements of psychotherapy and computer technology. Helps reduce anxiety and fear-related thinking disorders.
- Pharmacotherapy. Some antidepressants and antipsychotics have an antiphobic effect and are used in courses. Tranquilizers can quickly relieve symptoms of fear and panic.
- Physiotherapy: electro-sleep, electro-analgesia. By reducing overexcitation of the subcortical structures of the brain, it reduces the severity of anxiety.
About hypochondria (excessive concern for one's health), which often accompanies cancerophobia, see HERE. You can read about other phobias HERE.
Where does pathophobia come from?
Due to the characteristics of a person’s psychotype, his early childhood experiences and a certain amount of psychological immaturity, fears of contracting some disease may arise. Usually these are people with an anxious accentuation of character, prone to rapid asthenia and indecisiveness. During preschool age, they may have had the experience of emergency hospitalization due to injury or serious physical condition, as well as being raised by parents prone to excessive anxiety and overprotection. Such childhood traumas, superimposed on parental overprotection, cemented in the child’s memory the emotional reactions of adults to their state of health. And over time, they became components of the character of an adult.
When they talk about pathophobia, most often we are talking about fatal infections, cancer and diseases that disfigure the appearance and psyche of the patient. This includes the fear of being bitten and getting rabies, cancerophobia, fear of dirt, germs and infection, fear of going crazy, getting heart disease and some others.
Why am I a hypochondriac
Obsessive fears can be easily dissuaded. Hypochondriacs are diligent people and gladly listen to all the recommendations of people they consider competent. Therefore, some fears may go away, others may come, replacing each other. Nowadays, this is well facilitated by the Internet, from where anxious people get “useful” information, often completely far from reality, about a wide variety of ailments.
Over time, the tendency to phobic reactions is consolidated, acquiring an obsessive neurotic character.
What is HIV
The human immunodeficiency virus was first isolated from the lymphocytes of a patient in 1983. Almost simultaneously this was done by an American laboratory and a group of scientists led by Luc Montagnier. The virus received its familiar name for HIV infection a little later.
This infection is a systemic human disease, which results in a rapid decline in immunity. As HIV infection progresses, it reduces the body's defenses so much that it ceases to resist pathogenic microorganisms and the patient is diagnosed with AIDS. Its symptoms:
- the appearance of a rash on the mucous membranes and skin;
- rapid weight loss;
- enlarged lymph nodes, their pain;
- fever;
- frequent diarrhea;
- the spleen and liver become larger;
- pharyngitis, cough and other catarrhal manifestations;
- the appearance of permanent secondary diseases - herpes, pneumonia, intestinal and other infections, cancer, fungi, etc.
HIV is an incurable disease because the virus constantly mutates after entering the body. Once the immune system begins to produce antibodies, the virus changes at the genetic level. This same circumstance explains the fact that so far no one has been able to create a vaccine against HIV infection.
HIV infection is transmitted through blood and other biological fluids (sperm, breast milk, vaginal secretions). It is impossible to become infected with the virus by other means, such as airborne droplets or touch.
How to stop being afraid of getting sick
Fear of diseases is a rather insidious phobia that alternates from finding symptoms of one disease to another. A suffering person is aware of the cause of his anxiety, but cannot do anything about it. In the light intervals, when the level of general anxiety decreases, obsessive fears go away and he feels absolutely healthy. But as soon as you find yourself in a difficult life situation again or see/hear something frightening, the phobia makes itself felt again.
Hypochondriacs are impressionable people, so the first thing you need to do to loosen the grip of fear is to stop reading about terrible diseases. Instead, try to fill your life with calm and pleasant emotions as much as possible.
You can’t just get rid of nosophobia. What is needed here is an integrated approach, with the prescription of sedatives and medications that stabilize the emotional background and relieve obsessiveness in thoughts and behavior. Therefore, you need to contact not a psychologist, but a psychiatrist-psychotherapist.
Psychotherapeutic techniques include psychological desensitization, cognitive behavioral and gestalt therapy.
Doctors at the Preobrazhenie Clinic deal with the fear of illness in their patients every day and have extensive experience in treating such conditions. With due diligence of the patient, these phobias can be cured within a few months.
The dangers of fear of tests and how to get rid of it
A person who has any phobia is almost always unhappy. He feels lonely because it seems to him that those around him do not understand him. A depressive state leads to the development of mental and psychosomatic disorders, which further aggravate the condition. Therefore, you should not ignore phobias, especially if the fear is associated with visiting a doctor and taking tests.
If you have discovered a number of symptoms characteristic of HIV infection, or someone close to you has said: “I am afraid that I have become infected with HIV,” then you need to immediately undergo testing. To overcome fear, you will need to do the following:
- turn to loved ones for help. Their support will help overcome uncertainty and fear. A person must understand that regardless of the test results, he will be loved and supported;
- make maximum volitional efforts to decide to visit specialists;
- get acquainted with the latest developments in the field of detecting HIV infection. When a person understands that he will get the result instantly, and he will not have to suffer waiting for several days, then the fear becomes less.
It will be useful to study information about the characteristics of the disease. People suffering from any form of speedophobia avoid contact with sick people in every possible way, considering them a potential threat. They do not trust information about the routes of transmission of infection, sincerely believing that they can become infected with HIV in other ways that doctors are silent about. If you cannot convince such patients of the irrationality of their fears through your own efforts, then you should consult a psychotherapist.