Headaches vary in intensity and nature. Most often, this condition does not cause people to worry about their health - after all, everyone gets migraines from time to time. Everyone has had this condition at least once in their life. However, migraine does not bring any significant health consequences. The majority of the population thinks so. This is a mistake - some headache symptoms should alert the patient and cause a visit to a neurologist. Diagnostics is necessary to exclude the appearance of neoplasms. Point pain in the head in one place is a serious symptom that cannot be ignored.
Types of migraine and their causes
Migraine is a neurological disease. We talk about it if the patient complains of recurring headaches. They can be different in nature and intensity. Migraine can be either an independent illness or a symptom of a disease. In order to find out what disease caused the development of migraine, many diagnostic studies should be carried out. These are CT, MRI, checking the condition of the cervical spine, assessing the functioning of blood vessels, etc. If your head hurts in one point, this is also one of the manifestations of migraine.
Neurology identifies the following types of migraine:
- Classic (with aura). This type of migraine is characterized not only by a severe headache in the temples or forehead, but also by a so-called aura. It seems to the patient that he sees flickering on the left and right, but when he shifts his gaze, it turns out that there is nothing there. This effect is called “visual aura”, and all patients suffering from classic migraine are familiar with it.
- Regular migraine without aura usually occurs in people aged twenty years and older. The cause of this condition is often osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, and mental disorders. A typical migraine is not characterized by pinpoint pain in the head. It is encircling in nature. often the back of the head, the forehead, and the temples hurt at the same time. Or the temple on one side and the back of the head. The top of the head almost never hurts during a regular migraine.
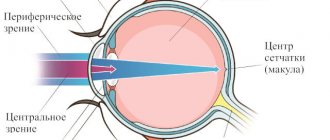
- Ophthalmoplegic migraine is a condition in which the muscles of the visual organs cease to function completely or partially. As a result of this, double vision, ptosis or mydriasis are observed in the developing pain syndrome. This diagnosis is quite rare, and it is treated not only by a neurologist, but also by an ophthalmologist. If the patient notes that pain on the right side of the head (in rare cases, on the left) or in the forehead is accompanied by visual impairment, he may have ophthalmoplegic migraine.
- The retinal form of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of “blind” spots. The patient suffers from the appearance of black areas in the field of vision. This process is accompanied by shooting pain in the back of the head. in some cases, the pain may not be sharp, but aching. For an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment, the patient will have to undergo an MRI of the brain and an electroencephalogram. In some cases, diagnosis may require checking the condition of blood vessels.
- Complicated migraine is characterized not only by headache, but also by visual, auditory, and vestibular disorders. In some cases, an attack of this disease can provoke loss of consciousness. If the condition is complicated by seizures, the patient may have an epileptic seizure. To identify the exact cause of the disease, you should undergo an electroencephalogram and a number of other studies.
Causes of pain in the occipital region of the head. Self help
Often, we rarely run to the doctor if something doesn’t hurt us too much; we only decide to visit an aesculapian when it’s already too hot. When experiencing pain in any part of the body, we sometimes do not even suspect that the cause of pain in one place may be the ill health of a completely different organ. This is what we will talk about today.
The most common causes of neck pain
Spine.
The presence of diseases of the spine in the cervical region, such as spondylosis, osteochondrosis, neck dislocations, spondylitis, can cause pain in the back of the head. Head movements are accompanied by neck pain.
Mental stress.
Stress is the main cause of a nervous state, and, accordingly, occipital pain. People, especially women, over 25 years of age should beware of stress, as they are at risk.
Overstrain of a physical and mental nature.
Excessive stress on the cervical spine also often causes discomfort in the back of the head. However, overstrain can also be mental. Concentrating on something, staying in one position for a long time, or an uncomfortable position also has unpleasant consequences.
High blood pressure.
This is the case when you need to see a doctor as soon as possible. The first sign of this condition is constant headaches in the back of the head in the morning.
Poor blood circulation in the muscles.
Poor blood circulation in the neck muscles leads to the appearance of compactions in them, which is called myogelosis. The reasons for its appearance are:
- stress;
- drafts;
- staying in one position for a long time and, as a result, muscle stiffness;
- problems with posture.
In this case, occipital pain is not the only sign of the disease. Dizziness, pain in the shoulders, and difficulty moving also appear.
Problems with peripheral nerves.
Neuralgia is the most common cause of pain. If you have neuralgia, a person also experiences pain in the jaw, neck, back, and ear. It hurts the patient to even cough or sneeze. In order to avoid the development of hypertension, you need to consult a specialist in time.
Migraine.
Migraine occurs not only in the head, but also in the neck. The pain, in this case, affects not only the back of the head, but also the temples. There may also be pain in the eyes, dizziness, a feeling of a white veil before the eyes, and hearing loss may develop.
Poor blood circulation in the brain.
Due to disturbances in the circulatory system of the brain, its functioning deteriorates. In this case, a person may experience, in addition to pain in the back of the head, dizziness, a sensation of tinnitus, visual and hearing disturbances. In some cases, nausea, fainting, vomiting may occur, and coordination of movements may be impaired.
First aid
If right now you cannot visit a doctor, and the pain does not go away, then you need to know first-aid techniques in order to experience relief at least for a while.
- Massage. It is done on the neck, shoulders and back of the head. You can do it yourself, but it is not very convenient, so it is better to ask someone for help. The main thing is not to make sudden, strong movements, and when pressing on any areas, do not apply force. It is better to stretch it a little and stroke it with relaxing movements.
- Change your body position, stretch, do exercises and be sure to ventilate the room.
- It is allowed to take medications that relieve spasms. In some cases, medications are taken that reduce muscle tone. But you can do this only if you are sure that the cause of pain in the back of the head is precisely the tightened neck muscles.
When and which doctor should I contact?
Of course, it is undesirable to engage in self-diagnosis and self-medication, therefore, when the first signs of pain in the back of the head appear, it is better to consult a doctor in order to accurately determine their cause.
This problem is dealt with by specialists such as a traumatologist, a neurologist and a massage therapist.
First, visit a neurologist, and he will redirect you to the right specialist. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Point headache
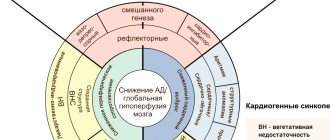
A piercing headache that suddenly appears at one point is an extremely dangerous syndrome. This condition, depending on the frequency of occurrence and intensity of the sensation, may indicate the following diagnoses:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature;
- intracranial pressure;
- surges in blood pressure (hypertension or essential hypertension);
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine.
These are the main reasons why a headache occurs at one point. The more often discomfort and pain occur, the more likely it is that the patient is dealing with a serious illness.
Localization and causes of headaches in various areas
Therefore, only a specialist can accurately determine the cause of pain and prescribe competent treatment.
Based on the localization of pain in different areas of the head, the following are distinguished:
- pain in the temples;
- pain in the back of the head;
- pain in the frontal region;
- a girdling headache that covers the entire head and feels like it comes from inside or outside;
- pain inside the head;
- pain in the neck area.
Sometimes it is difficult for patients to determine the area of localization of pain, since the unpleasant sensations often spread to neighboring areas. But each type of headache has its own characteristic causes:
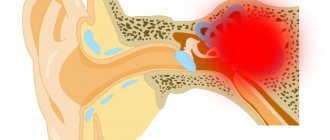
Pain in the temples.
Refers to vascular pain and occurs due to excessive stretching of the walls of the intracranial arteries. A classic example of such temporal pain is migraine, which occurs on average 1-2 times a month with a maximum attack duration of up to 3 days. Attacks of migraine-like pain can occur in people who drink a lot of coffee when they suddenly stop drinking it.
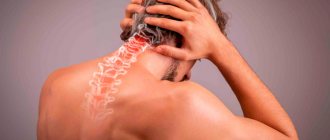
Pain in the back of the head.
Appear during a hypertensive crisis and are accompanied by nausea and vomiting. This pain syndrome indicates a sharp increase in blood pressure and the need to seek medical help.
Pain in the frontal region.
Associated with various pathologies of the respiratory system (sinusitis, sinusitis) and the visual apparatus. They can also occur due to low blood pressure.
Girdle pain.
The nature of this pain is external, dull and compressive; there is a feeling that the head is being squeezed by a hoop. Most often they are caused by spasms of the head muscles, so their second name is muscle tension headaches. They arise due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the patient’s work habits, and mental stress. They can also be caused by intoxication of the body with waste products of viruses or bacteria during infectious diseases: measles, ARVI, tuberculosis.
Pain inside the head.
Slowly increasing dull pain inside the head without clear localization. Their causes are increased intracranial pressure due to brain tumors, aneurysms, and hematomas. When such symptoms appear, a full examination and consultation with a neurosurgeon is required, since this is the most dangerous type of pain.
Pain in the neck area.
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis for neck pain based on the results of the examination.
Acute burning pain can occur due to local inflammation of one of the cranial nerves (occipital or trigeminal), as a result of cervical osteochondrosis, herniated disc, etc. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Feelings experienced by the patient
Before consulting a neurologist, the patient should listen to himself so that during the appointment he can describe as accurately as possible exactly how his head hurts at one point. Feelings may be as follows:
- Sharp and sudden pain, reminiscent of a puncture with a sharp needle.
- Localization of the problem: headache in one point - on the top of the head, in the back of the head or in another place.
- The vision becomes dark when an attack occurs, or perhaps the patient lost consciousness during an exacerbation of a migraine.
- During an attack, the patient observes any shadows, flickering on the left or right, darkening of some areas in the field of vision.
It will also be necessary to clarify how long the attacks last - a few seconds or minutes? The more detailed the patient describes the symptoms to the neurologist, the easier it will be to draw up a clinical picture for prescribing appropriate treatment.
Treatment
When a headache occurs at one point, most people prefer to take a tablet of a potent analgesic. This approach is fundamentally wrong: the attack of pain will return again and again. Stopping it every time with pills is wrong. It is better to undergo a full diagnosis once, find out the cause of the pain and take a course of medications that will cure the cause of the disease and prevent recurrent pain.
- If the cause lies in impaired cerebral circulation, taking nootropics and vasodilators will help. “Cinnarizine” has proven itself to be excellent, which, although it belongs to the old generation of drugs, is still actively used in modern neurology and psychiatry. This drug is cheap, and within the first week of use it can have a significant vasodilating effect, which will contribute to the complete disappearance of migraines of any etiology, regardless of the location of the pain - on the right side of the head, the back of the head, the crown.
- If a patient is diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis, headache is not uncommon. His forehead often hurts, and there are point pains in the temples and crown. In this case, it is useless to simply relieve the pain - you need to treat osteochondrosis first. The course of intramuscular injections of “Kombilipen” and “Milgamma” must be repeated every three months. A therapeutic massage of the cervical-collar area is necessary. Moderate exercise therapy will also be beneficial. In no case should the patient overexert himself or lift more than five kilograms, or engage in weightlifting or traumatic sports.
- Point cephalalgia in the head area is often one of the manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia. In this case, taking vasodilators and sedatives will help. You can often get by with taking sedative infusions. For example, “Fitosedan” has a fairly powerful sedative effect. You can also use nootropics. In some cases, the doctor may prescribe drugs that have a mild tranquilizing effect - for example, Afobazol.
Headache: causes
Every person, one way or another, has encountered headaches throughout their lives.
Unpleasant sensations are not a disease in themselves, but they can be used to diagnose a number of other diseases. Headaches can come in different ways. It can be classified according to the type of sensation - pressing, pulsating, sharp. Pain is also differentiated based on its cause – whether it is an independent disease or a symptom. Primary headache is an independent disease. Unpleasant sensations are the main and often the only symptom. Such cases account for approximately 90% of all visits to a therapist. This category includes:
- Tension headache.
- Migraine.
- Cluster headache.
- Pain during physical activity, sexual tension, etc.
Symptomatic (secondary) pain is a manifestation of pathologies and diseases of the brain and other structures that are located in this area. Secondary headaches also include drug-induced headache (MIH), which usually develops if the patient has already had migraines.
Women are more susceptible to migraines. It manifests itself most intensely at the age of 35-45. Diagnosed as an intense attack that occurs 2-4 times a month.
Migraine is a pain of a pulsating nature, the focus is on one side of the face, in the forehead, at the temple and around the eyes. At the beginning of the attack, unpleasant sensations appear in the back of the head and “crawl” forward. When moving, the discomfort becomes stronger. A well-known symptom of migraine is photophobia, as well as a strong reaction to sound. The disease is often accompanied by nausea, and in young people - drowsiness.
Migraines are usually caused by stress. This category also includes lack of sleep and vice versa, excessive sleep, hunger. In women, the onset of menstruation can trigger an attack.
People also regularly visit a therapist for tension headaches. TTH is divided into episodic and chronic. Both types are characterized by the same clinical picture; they differ only in the duration and frequency of attacks.
With TTH, the sensation is pressing, not pulsating, and can be described as a “hoop” squeezing the head. It is bilateral in nature and can spread to the back of the head, neck and trapezium. Unlike migraines, they are less intense and are rarely accompanied by additional symptoms, although some patients report mild nausea or dizziness.
TTH is usually caused by nervous tension, fatigue, or muscle spasms in the neck and shoulders. Usually starts in the afternoon after hard work. However, the patient remains able to work.
Most often, tension-type headache provokes prolonged forced holding of the head and neck muscles in one position, for example, when working at a computer or driving a car. Discomfort also occurs with anxiety and negative emotions.
Cluster pain combines the features of primary headache and neuralgia. This is one-sided severe pain, the focus of which is in the eye area, in the superciliary or temporal region. All attacks usually occur in the same place. Severe pain causes the eye to water, the eyelid to swell, and nasal congestion and sweating to occur.
Cluster pain is characterized by seasonality of exacerbation and alternation of attacks and periods of remission. The exact cause of the disease has not been established, but doctors associate the pain with the work of the hypothalamus. Its rhythmic activation leads to dilation of the vessels of the dura mater and the release of pain neuropeptides. Which creates a spasm similar to a migraine attack.
The only way to get rid of the problem is to start a course of medications as early as possible, after the first signs of exacerbation, and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. If the patient's attack can be predicted, then treatment begins in advance.
Cluster headache: symptoms
A rarer and more complex manifestation of point headache is cluster cephalgia. Doctors also call it cluster, histamine or Horton’s, depending on the location and nature of the pain. It manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- pain in the temporal artery during the next attack;
- discomfort and pain only on one side (not always), in the temple area;
- cephalalgia can develop at night - and often the patient is forced to wake up from the intensity of the painful sensations;
- the duration of the attack varies - most often it is five to six minutes, but in rare cases it can last for hours before taking the anesthetic;
- swelling of the nasopharynx and lacrimation;
- constriction of the pupils.
What is myofascial syndrome?
This is a chronic painful condition characterized by the formation of trigger or pain points in the muscles. Triggers are areas of spasmodic muscle tissue. These localized lumps can appear in muscle tissue and fascia in any part of the body. They are small in size, up to 1-3 mm. They can unite in a group, forming trigger zones with a diameter of up to 1 cm.
Main signs of the disease:
- local musculoskeletal pain, which is aching or cramping in nature, persists for more than a month;
- numbness;
- reflected pain sensations to distant areas of the body;
- feeling of "crawling";
- increased muscle tone due to tension;
- muscle fatigue;
- painful palpation of trigger points;
- disruption of normal muscle functioning, limitation of mobility.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
Myofascial pain can occur in any skeletal muscle. Provoking factors for its occurrence include diseases of the spine, excessive one-time or frequently repeated physical activity, sudden movements, hypothermia, stressful situations, and prolonged immobility.
Trigger points are found in skeletal muscles
The likelihood of triggers occurring is high in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle. As well as patients with pain in the affected internal organ or joint, causing muscle tension.
People over 35 years of age are most susceptible to the disease; it is rare in young people. Men get sick 2.5 times more often than women, because due to excessive stress on their back they have spinal diseases.
Depending on the pathogenesis, myofascial pain syndrome can be of several types:
- primary – occurs due to muscle strain, injury;
- secondary - appears against the background of diseases of the spine, joints, and internal organs.
Pain syndrome can be acute, subacute and chronic. Chronic pain weakens at rest and is activated under the influence of provoking factors.
There are 3 stages of disease development:
- I – hidden flow is inherent, pain in triggers appears only when you press them;
- II – pain occurs during physical activity and movement;
- III – the pain is constant, does not go away even at rest.
The mechanism of formation of trigger points and their types
There are 3 types of trigger zones:
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
- active – are very painful, pain occurs even at rest;
- hidden – do not cause significant discomfort, pain appears after the action of provoking factors;
- reflected – pain occurs after pressing on the trigger.
Their type is determined by a neurologist during diagnosis.
Trigger points appear in the muscles of the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine
Myofascial syndrome is a neurological disease, so the formation of trigger points occurs due to disturbances in the functioning of the central or peripheral nervous system (not without the participation of provoking factors). As a result, the nervous regulation of muscle tissue is disrupted, spasm and pain occur. Trigger zones are formed, which increases muscle tone and reduces their contractility. Pain sensations radiate to other areas along the innervation of muscle fibers.
Since the disease significantly worsens a person’s quality of life and reduces performance, it must be treated promptly. In the fight against this disease, injection therapy is effective, which involves blocking trigger points. It reduces pain and restores mobility.
A harbinger of serious illness
Cluster cephalgia, in which the patient constantly experiences pinpoint throbbing pain in the right side of the head, may indicate the development of the following diseases and conditions:
- brain tumors of various origins;
- withdrawal state;
- aneurysms;
- hematomas due to traumatic brain injuries and concussions;
- poisoning with certain drugs;
- taking vasodilators (for example, nitroglycerin) or histamine.
Pain points on the head
Pain points on the head
There are about 36 points on the head.
The “2M” pain point is the anterior fontanel, used to relieve constrictive headaches.
The point is located directly on the anterior fontanel (where the soft spot is felt, in the front upper part of the head).
Impact on the “2M” point is recommended for headaches of a compressive nature, with a feeling *’as if the head is being torn into pieces’*, “2M” is responsible for the condition of the cranial fluid.
Pain point “35” is somatic, having a restorative effect on the entire body. Controls the function of the cerebellum,
The paired point is located on both sides of the “1B” point at a distance of approximately 2.5 cm by 2.5 cm behind this point,
Together with point “1B” they resemble a pyramid (triangle) in shape. Acupressure of these points eliminates some types of eye diseases.
Pain point “1B” – controls the nerve plexus of the heart and the pyloric zone of the stomach.
Located in the center of the upper part of the crown, in front of the posterior fontanel, where the soft spot on the head is felt, at a distance of approximately 2.5 cm.
Promoting this point relieves spasms in the abdominal cavity, eliminates bloating (flatulence) and indigestion.
In some cases, in sensitive patients, when this point is applied, a tingling sensation is felt throughout the body from head to toe.
Pain point “9M” - posterior fontanel, controls brain functions, energy movement, eliminates puffiness.
The unpaired point, located directly on the posterior fontanel, harmonizes the energy between the pituitary gland and the pineal gland, controls the movement of energy down to the spinal cord. The effect on this point has a healing effect for brain disorders, removes excess fluid from the body, eliminates swelling of the legs and puffiness. Heals the colon. One of the important acupressure points.
Pain point “5M” – controls the emotional center of the brain. The paired point is located below the Sylvian fissure (see diagram), at the junction of the parietal and frontal bones, on both sides of the head. The “5M” point levels out the emotional background.
Impact on this point eliminates headaches localized in the frontal areas of the head.
Acupressure of this point should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Pain point "1M" - heals! diplopia (double vision). Paired points located at the junction of the temporal and frontal bones (see diagram) on both sides of the front of the head. Sensitivity or pain at this point indicates disorders of the cranial nerves. Impact on this point treats double vision and also regulates intestinal functions.
Pain point “2B” is a very important area (see diagram). The point located on the Sylvian fissure has a healing effect on the capillary system and coronary arteries of the heart. Points located behind the left ear and above, on this groove, treat the coronary arteries of the heart and the capillaries of the lungs. In front of the ear - used in the treatment of the eyes and vocal cords.
Pain point "3M" - eliminates dizziness, treats the stomach and trachea. It is located on the midline of the head, in front of the anterior fontanel, approximately 5 cm. Impact on this point treats the stomach, trachea, as well as the pons, located in the brain stem and responsible for supplying the brain with oxygen.
Acupressure of the “ZM” point eliminates dizziness.
Pain point “18” is a very important point responsible for the function of the pituitary gland.
Located between the “10B” points in the very center of the forehead.
Severe pain at point “10B” indicates a disorder in the pituitary gland, which is an important endocrine gland.
If there is a violation at point “10B”, it is necessary to simultaneously influence pain point 21.
Pain point “10B” is psychosomatic, used in eye treatment for blurred vision.
An unpaired bony prominence that stretches from temple to temple, passing through the center of the frontal bone and then rising up to a distance of about 5 cm above the temporal bone. This five-centimeter area represents an important area.
Two “10B” points located on the bone, directly above the beginning of each eyebrow - when exposed to them, the eyes are treated.
The central bone across the forehead is responsible for the state of the psyche, and is also general somatic.
Pain point “14M” is unpaired, associated with the eyes, stomach, and lower legs. Point “14M” is located in the center between the armor, at the root of the nose, and has a pineal shape. Impact on this point can eliminate some problems associated with visual impairment, stomach dysfunction, and pain in the lower legs.
Information about the work “Painful points on the head”
Section: Medicine, health Number of characters with spaces: 4491 Number of tables: 0 Number of images: 8
Similar works
Emergency care in neuropathology
524428
0
0
... laryngospasm. The pain radiates to the ear and is provoked by eating and swallowing. The pain point is determined on the lateral surface of the neck, slightly above the thyroid cartilage. Giving help. Emergency care is similar to that provided to patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Glossalgia. Clinic. Glossalgia is caused by damage to the peripheral somatic formations of the oral cavity, but mainly...
Characteristics of headache and headache of vascular origin
25772
0
0
... intoxication, lumbar puncture, cranial arteritis and ophthalmological disorders. 2. Headache of vascular origin Migraine headache Classic migraine is the most striking example of a headache that has clear temporal, spatial and qualitative characteristics. Although the timing of migraine attacks is highly variable,...
Cervical sciatica
109388
8
7
... "of the cervical spine, increase muscle tone (interspinous, intertransverse and rotator muscles), improve microcirculation processes in key regions. An approximate set of exercises for cervical radiculitis in the subacute period is presented in Appendix 3 [18]. The method of plastic breathing exercises: qi gong and taz chi tsuan must also be included in the structure of complex restorative…
Pediatrics
902914
1
0
... rheumatism caused a significant reduction in incidence - to 0D8 per 1000 children. Domestic pediatricians V. I. Molchanov, A. A. Kisel, M. A. Skvortsov, A. B. Volovik, V. P. Bisyarina, A. V. Dolgopolova and others made a great contribution to the development of the problem of childhood rheumatism. A connection has been established between the onset of the disease and the previous streptococcal infection, mainly in ...
Therapy for cluster headaches
Drug treatment may be prescribed by a neurologist after receiving the research results. For an accurate diagnosis, it is often necessary to undergo an MRI of the brain and electroencephalography. If the exact cause of beam cephalgia is not known, until the exact diagnosis is determined, the pain can be relieved with the following medications:
- Ketorol is a powerful prescription pain reliever that relieves even the most severe pain ten to fifteen minutes after administration.
- "Moment". The active ingredient of the drug is ibuprofen. It is a fast-acting, effective anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicine. Sold at any pharmacy without a prescription.
- "Citramon" is the most popular and cheapest analgesic, which also contains caffeine. Gives vigor and has a stimulating effect.
With a sharp point pain in the head, most people prefer to take a tablet of a potent analgesic. This approach is questionable: the attack of pain will return, and more than once. Stopping it every time with pills is wrong. It is better to undergo a full diagnosis once, find out the cause of the pain and take a course of medications that will eliminate the cause of the disease and prevent recurrence of pain.
Which doctor treats migraines?
In order to permanently get rid of attacks of cluster cephalgia or point migraine, to find out why the back of the head hurts, you should undergo a full examination. By influencing the source of the problem, long-term remission can be achieved. You can make an appointment with a paid neurologist. But then all the research will be paid. As a result, the total amount that the patient will have to spend to find out the cause of the pain will be at least twenty thousand rubles (you will need to pay for an MRI of the brain, an electroencephalogram, and a decoding of the result).
You can go a different route and not spend a penny on diagnostics. But this will take more time. The patient must take his medical insurance card and go to the district clinic, where he will be given a coupon for an appointment with a local physician. He, in turn, will issue a coupon for a consultation with a neurologist. Already there, after all the complaints have been stated, further treatment will be prescribed and a referral for the necessary research will be issued.
Methods for diagnosing myofascial syndrome
An experienced neurologist can easily identify trigger zones. During the examination, the doctor discovers the following:
- pain reaction when pressing on the affected area;
- the presence of a painful lump;
- limited range of motion due to pain and muscle spasm;
- muscle asymmetry.
During a visual examination, the doctor must determine the type of points and listen to all the patient’s complaints. To make a final diagnosis and find out the cause of the disease, the doctor conducts an instrumental examination. This may be an MRI, CT scan or x-ray of the spine.
At the SmartMed clinic you can undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the spine using the new Siemens Symphony 1.5 Tesla tomograph.
During a neurological examination, reflexes and muscle condition are assessed
Since activation of trigger zones is sometimes caused by somatic diseases, the neurologist prescribes further examination and consultation with specialized specialists.
Additional examination methods:
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
- Ultrasound of internal organs;
- CT or MRI;
- X-ray examination;
- electrocardiography;
- clinical and biochemical blood and urine tests.
Based on the diagnostic results, the neurologist draws up an individual treatment regimen for myofascial syndrome.
The relationship and difference between point pain and regular migraine
Point cephalalgia is often a component of other types of headaches:
- “Tension pain” is a concept in neurology that arose a long time ago and is still relevant today. It occurs in both men and women due to severe nervous and physical fatigue. It is expressed not only in point cephalgia, but also in the fact that the forehead and back of the head hurt (the localization and nature of the pain changes on average once an hour). At the same time, the patient feels nausea, dizziness, and may lose consciousness. A good night's sleep is often enough to stop these symptoms. If the patient is unable to fall asleep on his own, he should resort to taking a sleeping pill.
- Histamine pain. In 40% of cases it is associated with pain of a primary nature. One type of migraine can act as a harbinger of another and change the patient’s condition. For example, the condition begins as a migraine with aura, and after an hour it develops into an ophthalmoplegic form.
- Cranialgia is a condition that occurs when the trigeminal nerve becomes inflamed. This is a common reason why the back and top of the head hurt. Cranialgia is characterized by lumbago in the form of short-term impulses. Most often, this condition does not require any special treatment and goes away after the inflammatory process of the trigeminal nerve stops.
Venzo - what is it?
You won’t be able to find the word “crown” in the way it is written on the Internet, since the error correction program will throw you at the word “crown,” but this word fits the description very well, since there is such a phrase:
- The crown of creation is an epithet
And if there is a Ventsom, then there must be a Ventsos. I think that this is what the girl’s headdress was called, which we now know better as the Crown. It is this word that fits the description of the hidden word, since the Venzo (crown) is put on the head and one can hit one with it, but it is not clear why 2 times a year. By the way, the word crown is used in other variants, like crown (Under the crown).
Also the word Crown, which in our opinion is also Venzo, is several logs or beams connected into a single horizontal row of a wooden frame. It turns out that if the dacha is made of logs or timber, then there will be one of the crowns above the door, it turns out that you can hit your head on it (knock on the crown).
Advice from neurologists: how to avoid the development of cluster and point pain
A list of simple recommendations that will help prevent the development of migraines of any etiology and diseases that provoke them:
- You need to sleep at least eight hours every night. no matter what problems the patient may be experiencing, no matter what stress he may be experiencing, a good night’s sleep should be a must.
- Good nutrition is the basis of a healthy nervous system. Under no circumstances should you adhere to strict diets and starve yourself - even if the consequences do not appear immediately, they will come over time (the nervous system exhausted by fasting does not forgive such an attitude).
- A sufficient amount of amino acids, vitamins and microelements in the diet.
- The correct reaction to stress is to remain calm in any situation, so that later you don’t think about why your head hurts (the back of your head, the crown or your forehead).
- Moderate physical education - do not exhaust yourself with exercises, do not provoke overwork.