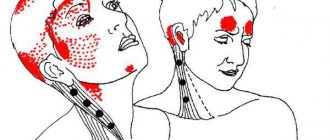
Why do my head and hands shake?
3 Cervical osteochondrosis or neuritis
A simple but effective way to get rid of headaches! The result will not be long in coming! Our readers have confirmed that they use this method successfully. After carefully studying it, we decided to share it with you.
February 12,
A person is capable of productive activity if he feels good and nothing bothers him. Well, if something constantly starts to hurt, you don’t want to do anything. The most common problem is a headache. The back of the head is throbbing with pain and seems to be shooting.
The relationship between headaches and vertebral pathologies
Often the pain moves to the neck. There are a number of reasons that cause such feelings, and it is very important to establish the true one in order to be able to get rid of the problem. Self-medication can only cause harm, so the best solution would be to go to the hospital.
Causes of trembling head and hands
Clinicians identify possible causes of trembling of the head and hands:
- drug use and alcohol abuse, other types of pathological addiction;
- tremor of a hereditary nature (the so-called essential tremor, usually appears after 25 years);
- diseases and damage to the cerebellum;
- a consequence of taking certain medications;
- consequences of stress, prolonged or sudden fear;
- physiological tremors after severe fatigue, overexertion.
As you can see, there are quite a few reasons for trembling. Tremors can be caused by any psycho-emotional stress, for example, a student session or public speaking. Often, emotional tremors disappear on their own and do not require treatment. However, a consultation with a neuropsychiatrist will not hurt.
As for addictions, tremors can appear after consuming large doses of coffee, alcoholic beverages, drugs and medications.
I'll start with the main thing - HEADACHES CANNOT BE TOLERATED. See a doctor immediately.
Next, several times a day, when the condition or nature of the pain changes, write down the date, data and type of pain. This will help you understand and control yourself, and correctly describe the symptoms to the doctor.
Further. The reasons may be very simple, but very common.
1. You sit a lot in the wrong position, which causes the neck muscles to be overstrained and the blood supply to the brain to be disrupted.
2. Physical inactivity.
Start moving immediately, walk outside, ventilate the room more often, and CHARGE, effortlessly, but regularly. 3.
A lot of strain on the eyes and, as a result, overload of the brain. Yes, this is primitive, but it is what most often causes pain.
the system chose this answer as the best
add to favorites link thank
Analostank [25.9K]
Oh, mommies, part of the sentence fell out!! Several times a day you need to measure your blood pressure, and then write down the data and the condition in which it was measured! Sorry - 4 years ago
The best thing to do is consult a neurologist. It is possible to do an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging of the head), it shows cerebral circulation disorders. Perhaps some nerve is pinched, so in a certain position the head hurts, but in another it does not hurt.
I myself am sometimes very worried about headaches, sometimes there is a throbbing pain in a certain part. And my mother suffered from acute cerebrovascular accident, suffered several strokes, and died from this. But the neurologist said that the headache due to poor circulation is constant and severe.
Therefore, the direct route to the doctor is better to be safe than sorry!
In most cases, the systematic appearance of occipital pain or its constant presence signals disorders occurring in the vascular, nervous or spinal system, as well as the formation of tumors or hematomas in this area.
Also, a headache in the back of the head can be provoked by non-pathological factors: weather dependence, air travel, uncomfortable sleeping position, nervous overstrain.
Severe headache in the back of the head
Severe occipital pain is evidence of acute inflammatory processes occurring in this area. It can develop in the presence of the following pathologies:
- Neuralgia of the nerve located in the occipital region - intense burning and paroxysmal pain covers the entire back of the head and can spread to the cervical region, muscles of the upper back, ears, and lower jaw. In most cases, pain syndrome develops from the inflamed nerve.
- Meningitis is a severe infection accompanied by very severe head pain, including the back of the head. Associated symptoms of the disease include high fever, vomiting, convulsions and, in severe cases, unconsciousness.
Headache in the back of the head and nausea
Diagnosis of noise in the head and weakness in the legs
Diagnosis of neurosis is difficult. Patients may complain not only of drowsiness, weakness and noise in the head, but also of incomprehensible pain in different parts of the body. However, during the examination it is not possible to detect any inflammation or infections.
With neurosis, the patient may attribute non-existent illnesses to himself, since the true cause of the noise in the head cannot be detected
In the somatoform form of neurosis, physical symptoms such as muscle cramps, numbness of the limbs or weakness in the legs are quite real. But they appear not because of problems with the body, but against the background of disorders of the nervous system.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
Diagnosis of noise in the head and weakness in the legs caused by neurosis includes: initial consultation and instrumental examination.
Examination, communication with the patient
During a personal conversation, the doctor tries to understand why the patient has noise in his head. He asks about the conditions under which the noise occurs, the frequency of its occurrence, and learns about the accompanying symptoms. With neurosis, in addition to noise in the head, the following symptoms occur:
- prostration;
- headache;
- drowsiness during the day and insomnia at night;
- mood swings;
- increased heart rate;
- apathy;
- irritability, increased anxiety;
- dizziness;
- breathing and digestive problems;
- pain in the body, arms and legs;
- "floaters" before the eyes.
To make an accurate diagnosis and exclude cardiovascular diseases, ear and thyroid diseases, the doctor prescribes a differential examination. With neurosis, the existing signs are the only clinical manifestation of the disease. The results of most tests are normal; no problems with internal organs or blood vessels are detected.
Differential diagnosis
A complete examination allows you to exclude organic pathologies that can cause loss of strength, weakness in the arms and legs, tinnitus and headaches.
You need to remain calm during the electroencephalogram
Differential diagnosis includes:
- Laboratory examination. To exclude inflammatory processes, hormonal disorders, and identify abnormalities in the functioning of internal organs, the doctor prescribes a clinical and biochemical blood test, a hormonal study, and a general urine test.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, heart. Depending on the clinical manifestations, ultrasound diagnosis of other organs may be required.
- MRI of the brain, cervical spine. It is the most informative method for diagnosing any pathological processes occurring in the head and neck area. With its help, you can detect areas of ischemia, cysts, tumors, hematomas, inflammatory processes, increased intracranial pressure, and any disturbances in the tissue structure. An MRI using a modern high-precision MRI machine can be performed at the SmartMed clinic.
- EEG. An electroencephalogram of the brain can detect epilepsy, encephalopathy, conditions after a stroke, trauma and neoplasms. It is an effective method for diagnosing neuroses in men and women and helps assess existing changes. A neurologist interprets the results.
- Angiography of blood vessels. Shows atherosclerosis, arterial aneurysm, ischemic stroke and other pathological disorders of vascular origin.
- Audiogram. Allows you to identify hearing problems that may cause noise or ringing in your head.
- ECG. Shows heart rhythm disturbances, ischemia, angina pectoris.
If necessary, other specialists may be involved in the diagnosis. These include a psychotherapist. His help may be required in case of a severe mental condition of the patient.
Kazieva Aminat Ziyavovna
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University
Experience since 2012
Other reasons
Headache is both one of the signs of an illness and an individual disease. Often you can cope with this problem on your own, with the help of a painkiller, or you can wait until the pain goes away on its own after a while, and there is no need for hospitalization.
The causes of shooting pain on the left side can be very different. Shooting pains in the head are always associated with nerves.
And since a person’s nerves are scattered throughout the body, the cause may be completely unrelated to brain disease, as many ordinary people believe. Most often, a headache in one or another part of the head is only an indicator that somewhere in the body there has been a failure of some organ.
It is worth listening to the characteristic symptoms.
Very often, a person who suddenly experiences a headache cannot determine the exact location of the pain in the head. Maybe just show the side of the shooting pain in the head - right or left, frontal or temporal.
When a certain part of the head hurts, it is a symptom of some disease. Therefore, it is always important to determine the location of the pain in the head.
Most often, the cause of shooting pains in the left side of the head is due to the fact that there is air in the head.
You can blow your head in a certain part of your head anywhere, even when it is not very cold. Such cases most often occur in warm weather, around summer or spring, and also in autumn.
A person is always a little naively confident that nothing will happen to his health in the summer or autumn, that is, in the warm season. But when a person loses his vigilance, his health can deteriorate. And in the warm season, people wear open and light clothes, and the wind is often too cool.
There are often cases when people can catch a cold even in their own home. This happens especially when the weather is warm outside.
People are starting to rejoice at the warming, especially after a long winter and cold weather. They begin to open the vents and windows, but the wind may still be cold.
But this is not what affects people; on the contrary, when a cool breeze flies into a warm room from under a small hole, it can blow through a sweaty person, even in his sleep. .
The draft affects the back of the head on the left side more. A person detects a shooting pain when he simply turns his head to the side, then a sharp pain is felt in the back of the head, as if someone is shooting in the head.
During physical activity, headaches are not always due to the development of diseases or any vascular disorders. This may be due to increased loads and improper exercise performance.
To get rid of such attacks, you need to take a warm shower and massage your head. If the sensations become constant after and during physical activity, you should consult a doctor.
Regular head shaking can be associated with both neurological problems and the development of very dangerous diseases. If a person’s head is shaking, the reasons must be found out as soon as possible, because the future state of health depends on this.
Causes of head tremors
What causes your head to twitch is one of the most common questions with which people turn to their doctor. Head tremors can indicate the development of a number of diseases, and making an accurate diagnosis at home is very difficult.
The first thing you should pay attention to is the nature of the shaking. With benign shaking, strange muscle contractions occur only at times of stress or extreme excitement. If a person is faced with malignant shaking, the head will be constantly in motion, interfering with normal life.
If your head is shaking, the cause can be either hereditary or physiological. Most often, this problem occurs in people suffering from alcohol or drug addiction. When the body is severely poisoned with alcohol or medications, the head begins to shake all the time, and the person is simply unable to control these contractions.
Such disturbances in the functioning of the body can also occur if a person has recently experienced severe stress or encountered physical fatigue. Usually, head shaking after stress stops as soon as the person manages to calm down.
If this symptom recurs, and in those moments when the person is not experiencing anxiety, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps the cause of the disease is much deeper than one might expect.
Why does an old man's head shake? Most often, this symptom manifests itself during the development of Parkinson's disease. This dangerous disease most often torments older people, and head shaking intensifies during rest and disappears completely during sleep.
Parkinson's disease, although considered very difficult to treat, is still manageable. With the help of medications, you can control the development of the disease and reduce the impact of negative symptoms.
If you ignore the disease, then it can easily affect the intellectual activity of an elderly person, his memory and conscious behavior.
If a person’s head shakes for no apparent reason, then it’s worth thinking about a hereditary influence. Often this symptom manifests itself in several generations, and at retirement or pre-retirement age. You can cope with the problem using a series of medications prescribed by your doctor.
Problems in the functioning of the nervous system are quite capable of causing the development of this negative symptom. If the cause of the tremor is a dysfunction of the nervous system, then the head will shake periodically, and every year the symptom will continue to actively progress.
Treatment of head tremors
Now that the reasons why the head is shaking have been clarified, all that remains is to find out how to recover from such a scourge. Typically, if the disease does not progress, doctors prescribe a series of anti-anxiety medications that help reduce the progression of the symptom.
If the tremor recurs more and more often, and the person is simply not able to control it, more effective medications are used, such as propranolol and primidone. By the way, primidone is most often prescribed to elderly people if they develop involuntary head shaking.
Before guessing about the disease and making a non-existent diagnosis, you should learn to distinguish headaches. A pulsating type headache is characteristic of vascular diseases.
Most often it is experienced by patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, in whom it is bilateral. Unilateral headache is characteristic of migraine.
This disease does not go away for a long time and intensifies in bright light, loud noise and other irritating factors. If a person has a headache that gets worse when lying down and his face swells, then he may have venous cephalgia.
Other causes of persistent headaches:
- protrusion of intervertebral discs, scoliosis;
- intracranial hypertension or hypotension;
- tumor of the base of the skull;
- brain tumors;
- other neurosurgical diseases;
- gynecological diseases;
- neurological diseases;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- lack of vitamins or oxygen;
- increased fatigue;
- neurosis;
- incorrect sleeping position or working posture;
- The pillow is too hard or too high.
In fact, in addition to the above list of reasons why a headache can be chronic, there are many more provoking factors. Diseases of the kidneys, liver, eyes, ears, smoking, hazardous work and other factors can always cause chronic headaches.
2 How the behavior of cerebrospinal fluid affects a person’s condition
If you suppress a headache with pills, after a while it comes back again. Even stronger and, as always, at the wrong time. Without taking proper measures, the pain becomes chronic and interferes with life. Find out how site readers cope with headaches and migraines using a cheap remedy.
When a person consults a treating neurologist or a neurosurgeon, the doctor usually asks a question about when the pain is unbearable: when you are lying down or when you are in an upright position. In some cases, the patient reports that with such headaches it is better for him to lie down, then he begins to feel much better.
Provided that this condition is caused by CSF effects, most likely the patient suffers from intracranial hypotension. If the headache intensifies in a supine position, then in this case there is pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid on the walls of the skull, i.e. there is intracranial hypertension.
Normally, the uniform distribution of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out under a pressure of 7 to 17 mm Hg. Art. (although some experts believe that the maximum value of normal intracranial pressure is no more than 15 mm Hg.
Art.). This ensures excellent brain function without headaches.
If a person has hypertension, his high blood pressure provokes vascular changes in the brain, resulting in an increase in intracranial pressure and, as a result, a prolonged headache.
With hypotension, the lack of cerebrospinal fluid affects the brain in such a way that this organ performs not only nutritional, but also shock-absorbing functions. In this case, cephalgia, which intensifies when walking or simply being in an upright position, goes away only during rest, when the patient is lying down.
The danger of this disease is that the lack of cerebrospinal fluid has an extremely negative effect on the functioning of the brain and blood vessels of the head, which can ultimately lead to death. This is due to the fact that hypotension severely damages blood vessels and can provoke hemorrhage, dislocation of the structures of the hemispheres and brain stem.
As a result, cerebral edema, damaged brain stem substance and hemorrhage lead, at best, to a stroke, at worst, to death.
Often, headaches are eliminated with conservative therapy aimed at restoring water and electrolyte balance.
In this case, they often resort to therapy using isosmolar solutions. If a patient has liquorrhea, most often he requires hospital treatment.
3 Why do hypertension and tumors cause headaches and how to treat them?
February 20,
People who experience headaches in the occipital part describe its effect as if something were pressing, pushing the back of the head. Painful sensations are accompanied by burning, pulsation, and crawling. Such manifestations are chronic, periodic or acute in nature and can have varying intensity.
Tension and overwork
There are certain situations in which the appearance of pain in the back of the head is not considered a symptom of a serious illness. Sometimes it is caused by stress, hunger, smoking and caffeine consumption. In other cases, acute pain always has a number of causes, which are very important to establish.
Causes of head tremors
Cervical dystonia
A characteristic sign of cervical muscular dystonia associated with impaired neck muscle tone is isolated head tremor. It occurs when maintaining a stationary position or at the beginning of a motor act (postural-kinetic), has a frequency below 7 Hz and varying amplitude. In some patients, tremors are present at rest. Dystonic tremor intensifies when turning and tilting the head in the direction opposite to the affected muscles. The patient's performance of reverse movements or corrective gestures (touching the chin) leads to the disappearance of trembling.
Essential tremor
Among the causes of head tremor, one of the main places is occupied by the essential process. Benign tremors, the mechanism of which remains unknown, can begin at any age. The disease debuts with tremors of the hands, the head is involved later. Symmetrical trembling with essential tremor is postural in nature or increases during movement, especially at its end point (terminal). Head tremors intensify with excitement and take the form of nodding (“yes-yes”) or rocking (“no-no”) movements.
The tremor frequency varies from 6 to 10 Hz in different patients. Over time, a resting tremor may develop, which is especially pronounced in a sitting position, but does not disappear with the onset of movement, being a continuation of the postural one. Other neurological disorders in essential tremor are usually absent, sometimes minor symptoms of ataxia, plastic hypertonicity (the “jackknife” phenomenon), and weakened facial expressions are observed. Some patients are diagnosed with mild cognitive impairment.
Parkinsonism
Classic parkinsonian tremor is a tremors at rest when the muscles are completely relaxed. Its source is recognized as the central oscillators in the basal ganglia. The neck muscles are involved simultaneously with the arms or a little later. Parkinson's disease is characterized by a “yes-yes” or “no-no” head tremor that disappears with movement. The picture is complemented by slowness, a shuffling gait, and a “supplicant pose.” Muscle tone changes (the “gear wheel” symptom), and the cognitive sphere suffers.
Multiple sclerosis
Tremor is considered a typical and common symptom of multiple sclerosis. Usually it is bibrachial, that is, it affects adjacent segments - one or both arms and the head. Trembling is explained by damage to the cerebellum and its connections, therefore it usually has an intentional nature, occurs during movement and intensifies when a goal is achieved. But people with multiple sclerosis may also experience other types of it, for example, head tremors at rest, caused by the presence of a focus of demyelination in the thalamus, basal ganglia or frontal lobes.
Multiple sclerosis, accompanied by tremors, has a number of clinical features. It is characterized by an earlier onset and a predominance of cerebellar disorders at the onset. The advanced stage of the pathology is manifested by imbalance in the form of static and dynamic ataxia, and oculomotor disorders. Pyramid symptoms (muscle weakness, spasticity) and sensory disorders are much less pronounced.
Metabolic encephalopathies
As a symptom of metabolic disorders, head tremor is included in the picture of generalized trembling hyperkinesis, involving the muscles of the arms, neck and torso. It is observed at the stage of subcompensation and progresses as the brain is damaged. Hypoxic-ischemic perinatal encephalopathy in children is caused by complicated pregnancy and childbirth (asphyxia, intrauterine infections, injuries). It can manifest itself as low-amplitude tremors, pathological head positions, clonic convulsions, which are combined with suppressed reflexes.
The symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy are quite varied. With chronic intoxication, tremors of the head and hands (including “flapping”) and spasms of facial muscles develop. The pathology is characterized by slow convulsive and fast intermittent movements (choreoathetosis), ataxia, and cognitive impairment. Severe uremia in chronic kidney disease is manifested by postural-kinetic tremors, rapid muscle twitching (myoclonus), and convulsive attacks. Any metabolic encephalopathy occurs against the background of impaired consciousness.
Paraneoplastic syndromes
In the clinic of opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome, tremor of the head, trunk and limbs is a sign of a fairly advanced process. This is an autoimmune paraneoplastic syndrome associated with the development of malignant neoplasms. Trembling is caused by damage to the cerebellar system, combined with decreased muscle tone, dysarthria, and drooling, but the most typical signs of the disease are opsoclonus and myoclonus.
Opsoclonus is understood as chaotic multidirectional eye movements, which are accompanied by convulsive twitching of the muscles of the limbs and trunk, static or dynamic ataxia. The second pathognomonic sign of the syndrome is polymorphic myoclonus, which takes the form of short muscle twitches of varying amplitude. Their predominant localizations are lips, eyelids, trunk and limbs.
Hereditary diseases
The cause of head tremors can be hereditary diseases of a neurodegenerative or demyelinating nature. Hyperkinesis is caused by changes in cerebral structures that control voluntary movements and maintain muscle tone and posture. Damage to the cerebellum, extrapyramidal system and corticospinal connections is observed in the following conditions:
- Olivopontocerebellar atrophy.
The first sign of the disease is cerebellar ataxia. It is accompanied by intention tremor, head tremors, and dysarthria. In later stages, Parkinson-like syndrome, paresis of facial muscles, and mental disorders are observed. - Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease.
The disease is characterized by a triad of symptoms - horizontal, vertical and rotational eye movements (nystagmus), head tremors, and coordination problems. Subsequently, muscle tone increases, speech slows down, and intelligence decreases. Late stages are characterized by hyperkinesis, parkinsonism syndrome, and profound dementia. - Ataxia with vitamin E deficiency ( AVED ).
Patients present with progressive cerebellar ataxia with absent tendon reflexes. Head tremor, pyramidal insufficiency, and dysarthria often occur. Characterized by polyneuropathy, skeletal deformities and sleep disorders. - Wilson-Konovalov disease.
The trembling form is manifested by static and postural tremor of the head, similar to rocking, and the upper extremities. Choreiform hyperkinesis and bulbar disorders (impaired speech, swallowing) may be detected. The progression of the disease leads to an increase in rigidity or muscle hypotonia, and mental disorders.
Prion diseases
Head tremor in those suffering from kuru, a rare prion disease, a type of spongiform encephalopathy, is a fairly characteristic symptom. It manifests itself as severe trembling or intermittent movements, often combined with spasm of the facial muscles (“sardonic smile”). The pathology begins with dizziness and fatigue; as the neurodegenerative process progresses, the ability to control voluntary motor acts is lost, ataxia, hyperkinesis (choreoathetosis), and myoclonus appear.
Types of headaches
There are two types of headache: primary and secondary.
- Primary headache is an individual disease, and out of 10 cases it can be encountered in 9.
- Secondary headache is a sign of another illness. It can be the result of fifty diseases.
Primary headache
- Inflammation, compression or irritation of the trigeminal nerve. A very common disease, especially among women over 40. Attacks last for about a couple of seconds. The disease is characterized by stabbing pain in the head, as well as in the crown area, sometimes spreading to the face and even the jaw.
- Cluster headache. Shooting strong painful sensations, mostly noticeable only on one side. The face swells and turns red, and the eyes water.
- Tension headaches mainly affect the entire skull as a whole, in some cases they are separately transferred to the areas of the back of the head, forehead, and crown. With this disease, the headache is moderate. It’s not uncommon to hear from a patient: “It gets worse when I shake it, but there are no strong unbearable attacks, the illness can last for a week of daily pain.” And basically, it is the result of severe emotional shock, or excessive physical exertion.
- Migraine. Women are more prone to migraines than men. Very often, attacks begin after sleep. The degree of pain ranges from moderate to unbearable, it hurts even when you touch it. It can last from several hours to 3 days.
Secondary headache
Headache during exercise
Some people experience headaches during exercise.
Many patients associate their appearance with an increase in blood pressure, which actually turns out to be slightly elevated with physical effort. However, it is known that blood pressure always rises during activity; this is a normal reaction of the body, but its increase does not always cause headaches. Both primary and secondary headaches occur during exercise. In primary cases, there is no connection with structural changes in the body; in secondary cases, diseases are identified, as a result of which pain occurs.
Primary exercise headache
Unpleasant sensations appear during physical stress and disappear after some time, usually 15-30 minutes after stopping the exercise. Occasionally, such pain can last up to 48 hours. They are most often pulsating in nature, bilateral. The onset of primary headaches associated with physical stress occurs at the age of 18-20 years, and they appear mainly in men.
Some experts associate their appearance with pain impulses from overstrained muscles and ligaments of the cervical spine. Others believe that pain during physical activity is caused by obstruction of venous outflow from the cranial cavity. If, during examinations of the brain and its vessels, no pathology is detected, then the patient is recognized as having primary headaches associated with physical activity. This variety is benign and does not pose a danger to humans.
Primary headaches that occur during physical activity do not always require treatment. It can go away on its own if you increase the load gradually so that the body adapts.
The drug indomethacin is effective for treatment and has a positive effect on many primary headaches. The daily dosage of the medicine is selected by the doctor; it ranges from 25 to 150 mg per day. In this case, it is necessary to take drugs that protect the stomach (omeprazole), since indomethacin can disrupt the protection of its mucous membrane from gastric juice. In many cases, these headaches go away on their own after 3-6 months.
Secondary exercise headache
Often headaches with physical effort make themselves felt by brain tumors, hematomas, and Arnold-Chiari anomaly (a congenital structural feature in which the size of the foramen magnum is larger than normal, so the cerebellum begins to descend through it). With these pathologies, during physical activity, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the cranial cavity becomes difficult, which causes pain.
When sharp headaches occur for the first time during physical exertion, it is necessary to exclude intracerebral or subarachnoid (blood flows under the arachnoid membrane of the brain) hemorrhage. With physical overexertion in people with atherosclerosis and arterial hypertension, the risk of rupture of cerebral arteries, vascular malformations (pathological additional vessels), and aneurysms (congenital protrusions of the vessel wall) increases.
In such cases, an urgent examination by a doctor and an MRI/CT scan of the brain are necessary. However, you should not decide to perform research on your own; this should be done by a doctor. If the diagnosis of hemorrhage is confirmed, the patient is sent to hospital on an emergency basis.
If an Arnold-Chiari anomaly is detected, decongestants that reduce the formation of cerebrospinal fluid are prescribed, or, in case of severe prolapse and compression of the cerebellum, the patient is referred to a neurosurgeon. When a tumor is detected, treatment tactics vary depending on the type and size of the tumor.
Where can I find a competent doctor who can help with headaches?
Residents of Saratov and the Saratov region can contact the Pain Treatment Clinic, which is located in Saratov at the address: st. Bakhmetyevskaya 26/28. You can contact the administrator by phone +7.
Self-medication at home
Painful bending and turning of the head can be treated by a physiotherapist, osteopath, or vascular surgeon. These doctors will prescribe a course of medications and, most importantly, a massage. Only massaging the cervical spine with the hands of a professional will help get rid of excruciating pain when the diagnosis is cervical osteochondrosis. Sometimes the pain goes away on its own. But massage of the scapular muscles and neck will eliminate them faster.
You shouldn't lead a sedentary lifestyle all the time. Managers, programmers - people in these professions are susceptible to osteochondrosis, as they are limited in movement. Loaders and people whose work involves lifting heavy objects are no less at risk of slipping intervertebral discs and, as a result, headaches.
To strengthen the muscles of the cervical and other parts, it is necessary to do special gymnastics.
Even at work, you can perform a number of simple exercises. Among them are circular movements of the head, slow bends, and turns.
- You suffer from occasional or regular headaches
- Presses the head and eyes or “hits the back of the head with a sledgehammer” or knocks in the temples
- Do you sometimes feel nauseous and dizzy when you have a headache?
- Everything starts to irritate me, it becomes impossible to work!
- Do you take out your irritability on your loved ones and colleagues?
Stop putting up with this, you can’t wait any longer, delaying treatment. Read what Elena Malysheva advises and find out how to get rid of these problems.
Head pain is a common ailment, and no matter how it seems that it cannot be cured, these pains can be cured. Treatment can be very modern, or it can take place in the old way - folk remedies that were used a very long time ago, and by the way, successfully.
Prescribing treatment without a full examination and careful study of the main causes is unacceptable. The appearance of any symptom leading to pain in the back of the head requires the attention of a therapist and other specialists.
It is not possible to completely cure the disease at home, but it is quite possible to improve the condition for a while. Stress in this case is considered an exception. On the recommendation of a doctor, the use of sedatives will be completely justified.
Pain in the back of the head should not be underestimated. When symptoms appear, it is better to immediately seek help from the appropriate doctors. Timely assistance can prevent a serious course of the disease.
After taking medications
Headaches happen if you take medications carelessly. This is especially true for drugs aimed at eliminating cardiac symptoms, which include Nitroglycerin and other drugs like it.
They contain special substances designed to increase blood flow to the heart and are often prescribed for symptoms of angina pectoris. After taking which, many patients may feel pain in the head due to a sharp dilation of the blood vessels in the brain.
However, not only heart medications, but also excessive use of other medications, including hormonal pills, can cause headaches. Based on this, they should only be taken under the supervision of a doctor.
Prevention
And, of course, we must not forget about the prevention of headaches:
- correct lifestyle;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol;
- balanced diet;
- reasonable alternation of sleep and rest;
- physical activity;
- walk outdoors.
In order to reduce attacks, or reduce the likelihood of their occurrence, prevention should be carried out, take care of the head and help it, namely
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Eat properly.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Drink plenty of fluids, about 2 liters per day.
- Sleep at least 7 hours a day.
- Don't be nervous, try not to give in to stress.
- Play sports: swimming, running and yoga.