Description of the phenomenon
Tinnitus or ringing in the ears is a very common condition, affecting approximately one in five adults. Usually it is only an inconvenience, but sometimes it can interfere with the ability to concentrate and sleep well. As a result, the patient experiences constant stress, which has a negative impact on his personal relationships and work.
This condition often accompanies hearing loss, although it does not cause deafness in itself. Many people with tinnitus have excellent hearing. Sometimes they develop increased sensitivity to sounds - hyperacusis, so they are forced to take measures to limit external noise.
In some cases, the pathology disappears after eliminating its cause, for example, otitis media or ear plug. However, often even after treatment, ear noise persists.
Why is there noise in my ears?
The causes of tinnitus may be associated with damage to parts of the auditory system - the outer, middle, inner ear or brain. There are several theories explaining what happens in the body with this pathology:
- spontaneous electroacoustic emission, that is, the spontaneous generation of electrical signals in the cochlea of the inner ear, which are perceived as tinnitus;
- damage to the organ of Corti with dysfunction of the auditory cells of the cochlea;
- dissonance between healthy and damaged cells of the organ of Corti, which can be caused by the normal aging process;
- increased activity in the posterior cochlear nuclei of the brain caused by exposure to too much external noise;
- auditory plasticity, that is, activation of nerve centers in response to hearing loss due to damage to the cochlea;
- the formation of new connections between the neurons of the auditory nerves when they are damaged, compressed by a tumor or hemorrhage, and the generation of impulses in them in the absence of external sound;
- damage to the trigeminal, facial, glossopharyngeal and other cranial nerves, activating the so-called oto-somatic interaction;
- increased activity of the limbic and autonomic nervous systems due to increased sensitivity to the first episode of tinnitus.
Thus, tinnitus is a complex process that requires accurate diagnosis using modern equipment and competent treatment.
Treatment
The therapeutic course carried out for this pathology takes a long time. Much depends on the causes of this problem, as well as the characteristic symptoms. The individual resistance of the patient’s body plays a big role in this matter, since treatment is carried out through the use of drug therapy. From the point of view of qualified specialists, in folk medicine there are effective ways to combat buzzing in the ears, which are definitely worth using. Let's consider both options.
Medication
The prescription of medications depends on the disease that provoked this phenomenon. Medicines are selected individually.
Let's consider what medications are prescribed for buzzing in the ears:
- First of all, medications that normalize blood circulation in the brain. The group of drugs that stimulate blood circulation includes Telektol and Betarex;
- Often this phenomenon occurs against the background of an acute allergic reaction, which causes severe swelling inside the ear. To eliminate this problem, Claritin or its derivatives are prescribed;
- Therapy with drugs that are necessary to restore the full supply of oxygen to the brain is also practiced. Trimectal or its analogues are prescribed;
- as a preventive measure, as well as to increase the effectiveness of the therapeutic course, the patient needs to use antispasmodics, which help eliminate excess tension inside the ear;
- if the cause lies in an infectious or viral disease, and there are also clear signs of the development of acute inflammatory processes, antibacterial agents are prescribed - Ceftriaxone or Augmentin, as well as their analogues;
- if the initial problem is psychological troubles in the patient’s life, then antidepressants and tranquilizers are used. It is worth remembering that they are prescribed exclusively by a psychotherapist!
Self-medication will cause irreparable damage to health. Therefore, to avoid this, it is recommended to visit a medical facility to undergo a full diagnostic series of procedures, as well as the correct and competent prescription of drugs.
Folk
Most experts believe that traditional medicine is effective in combating buzzing in the ears, but you should resort to it only after consultation with a therapist.
- It is recommended to use onion juice. Pass a large onion through a juicer. Using the liquid, make a compress on the ear. .
- Garlic tincture. Take a large peeled head of garlic, finely grate and add 50 ml. vegetable oil. Leave for several days. Use as a compress.
- Warming compresses made from potatoes and honey. Grate several potatoes (300 grams) on a fine grater. Mix the final product with three tablespoons of honey, mix and place in a bag or bandage. Apply to the ear and keep on the affected area for at least two hours.
Kinds
There are the following types of noise in the ear:
- subjective: the patient hears noise that does not come from the external environment, it is associated with irritation of the auditory nerve;
- pulsating: the patient hears a buzzing, ringing, clicking or other loud sound that coincides with his heartbeat;
- objective: a rather rare phenomenon associated with the patient’s increased sensitivity to external sounds or vibration of various parts of the body.
Depending on the cause of the noise, it is divided into the following types:
- associated with damage to the vascular system;
- caused by damage to the outer or middle ear;
- muscular;
- neurosensory (peripheral and central), associated with the pathology of auditory cells and pathways.
Additionally, doctors distinguish 3 degrees of noise: with the first, the patient notes sound sensations only upon active questioning, with the second, he considers it not the main problem with hearing, and with the third, tinnitus becomes the main complaint.
Certain states
Tinnitus, what to do? If you are tormented by constant tinnitus, then you should not hesitate to contact a specialist - an otolaryngologist for advice and medical help. In some cases, tinnitus can be a manifestation of serious illnesses and even brain damage. Let's look at the most common forms of tinnitus and what they are associated with.
- Constant tinnitus - this form is characteristic of atherosclerotic damage to the cerebral vessels, as well as the arteries of the neck. This kind of tinnitus does not go away on its own and is characterized by a long course that is not amenable to drug therapy. The patient quickly gets used to the constant noise, and it slightly reduces the person’s ability to work.
- Noise and pain in the ear - this symptom is a manifestation of inflammatory processes localized in the area of the inner and middle ear. Inflammatory diseases of the inner ear are quite rare, but otitis media is common. Otitis media occurring with the formation of pus can lead to a change in the anatomical shape of the auditory ossicles, which can ultimately manifest itself in the form of a sensation of various noises. The noise is also constant, but its intensity and shape change periodically.
- Pulsatile tinnitus – this noise is a characteristic symptom of hypertension. With high blood pressure numbers, the pulse wave increases, which leads to the appearance of rhythmic pulsating noise in the ears. When the pressure returns to normal, this noise disappears on its own. Another, but rare, cause may be erythrocytosis, a condition in which there is an excessive amount of red blood cells in the blood, which in turn leads to a violation of the rheological properties of circulating blood.
- Tinnitus and dizziness are the downside of hypertension. With low pressure, a similar noise in the ears is often observed, but it is always accompanied by dizziness, since there is not enough oxygen in the brain tissue. Another cause of noise with dizziness can be severe atherosclerosis with the blocking of most of the lumen of the vascular wall by an atherosclerotic plaque.
- One way noise. Noise localized in the right or left ear occurs when the vascular wall is damaged on only one side. This can happen if the patient has systemic autoimmune diseases or atherosclerotic disease.
Causes of tinnitus
The causes of tinnitus are usually associated with some kind of disease of the hearing organs or nervous system.
- The most common cause of tinnitus is hearing loss. Due to age-related changes, injuries, and the effects of medications, the sensitive cells of the cochlea are damaged. They do not send electrical signals to the brain, and it begins to produce its own impulses, as if compensating for the lack of external stimuli.
- Diseases of the outer and middle ear can cause noise: cerumen plug, otitis media, narrowing of the ear canal, tumor of the tympanic cavity.
- Exposure to loud noise is a very common cause of not only hearing loss, but also tinnitus. Every person should be aware of the damaging effects of loud music and the noise of operating machinery and protect themselves from such influence. Another cause of pathology is barotrauma.
- More than 200 medications can cause this symptom, most often aspirin, aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin, kanamycin) and quinine derivatives. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ethacrynic acid, platinum derivatives, ACE inhibitors and other drugs can cause noise. Exposure to methyl alcohol and benzene is also dangerous.
- Meniere's disease is a disease accompanied by transient dizziness, ringing and congestion in the ears, and temporary hearing loss.
- Acoustic neuroma is a tumor that affects the nerve pathway leading from the cochlea to the brain centers, and causes noise and hearing loss on one side.
- Pulsatile noise is usually associated with pathology of the circulatory system. It is observed during pregnancy, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, arteritis, and also with increased intracranial pressure; In addition, vascular murmur appears with heart defects, vascular development anomalies, and stenosis of the ear arteries.
- The causes of objective tinnitus may be diseases of the temporomandibular joint, pathology of the muscles of the soft palate, middle ear, or gaping of the eustachian tube in the nasopharynx.
- Diseases that can cause tinnitus: hepatitis, diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, instability or osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, as well as various hereditary anomalies (Chiari, Gardner-Turner, Klippel-Feil, Pence, Hunt, Konigsmark-Hollender-Berlin syndromes).
The causes and treatment of this pathology are complex, and only a highly qualified otolaryngologist can understand the problem comprehensively.
Medical certificate
Tinnitus can be an independent nosological entity, i.e. disease, but much more often we are part of a syndrome complex of some other disease. In the field of otorhinolaryngologists, tinnitus is usually called the term tinnitus. Problems with the ears, or more precisely with the sensation of tinnitus, are not uncommon in the practice of otorhinolaryngologists. According to statistics, more than 8% of the population of developed countries experiences this unpleasant symptom, and even more people live with it without seeking qualified medical help.
Tinnitus is a complex symptom and difficult to assess objectively, since it often does not have any external stimulus. Almost all people suffering from tinnitus notice a noise in the form of a high-pitched ringing. The high-pitched sound may resemble the characteristic ringing of a bell. The causes of this symptom or disease can be very diverse, from the banal formation of cerumen plug in the cavity of the external auditory canal, to complex nervous electrochemical disorders in the central nervous system of the brain.
Symptoms
Manifestations of tinnitus include a variety of sounds heard by the patient. It could be ringing, buzzing, the sound of a roaring aircraft engine, hissing, whistling, clicking. It may be constant or appear only occasionally.
If you experience noise in the ear, you should consult a doctor. This may be associated not only with pathology of the hearing aid, but also be a manifestation of hypertension, hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, anemia and other diseases.
With infectious diseases of the ear, noise may be accompanied by pain and discharge from the ear canal.
When noise is combined with dizziness, urgent medical attention is required, as this may be a manifestation of Meniere's disease or cerebrovascular accident.
With brain tumors, this complaint intensifies at the height of a headache attack. With a tumor located in the posterior cranial fossa, the noise increases with changes in body position.
Pathologies of sound perception
The most common is labyrinthitis, an inflammatory process affecting the structures of the inner ear. Due to the structure and physiology of a person, the inflammatory process often negatively affects the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, which leads to the appearance of additional symptoms such as dizziness and nausea.
Another possible cause is a pathological condition in which too much fluid collects in the inner ear. As a result, the functioning of receptor structures is disrupted. Associated symptoms: hearing loss in one ear, dizziness, which occurs and goes away spontaneously.
Hearing loss caused by damage to nerve pathways or auditory receptors also falls into the category of sound perception pathologies. Accompanied by severe hearing impairment in combination with noise.
Diagnostics
To identify the causes of ear noise, the following diagnostic tests are used:
- complete physical examination, medical history, examination of the head and neck, determination of cranial nerve function;
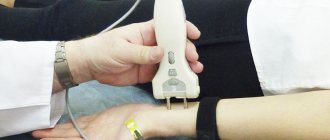
- hearing test (subjective audiography);
- objective audiological examination: method of studying the auditory brainstem response (ABR) and extratympanic electrocochleography;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the skull;
- endoscopic nasopharyngoscopy to identify the causes of muscle noise;
- microotoscopy;
- in some cases – diagnosis of hypertension, hyperthyroidism and other therapeutic diseases;
- according to indications - spinal puncture with determination of intracranial pressure.