Acoustic neuritis (another name is cochlear neuritis) is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the auditory nerve and sensorineural hearing loss develops.
Our expert in this field:
Lashch Natalia Yurievna
Neurologist of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences, associate professor. Laureate of the Moscow City Prize in the field of medicine.
Call the doctor Reviews about the doctor
Some facts about the disease:
- Hearing is impaired to varying degrees in 6–8% of people.
- There are two types of hearing loss: conductive hearing loss is associated with a violation of the conduction of sound vibrations to auditory receptors, sensorineural hearing loss is associated with damage to nerve structures. Neurosensory is 3 times more common.
- Women get sick more often than men.
- Cochlear neuritis is a polyetiological disease, that is, it can be caused by various reasons.
- There are acute and chronic forms of hearing loss.
- In approximately 3–6% of patients, the disease leads to communication difficulties.
How is the auditory nerve structured?
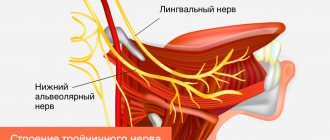
The vestibular-cochlear nerve is the eighth pair of cranial nerves, which consists of two parts: the vestibular nerve transmits information about the position of the human body to the brain, and the cochlear (cochlear) nerve is responsible for hearing. It collects information from receptors in the organ of Corti, which is located in the inner ear. It is here that sound vibrations are transmitted from the external auditory canal and the tympanic cavity.
When the cochlear nerve is damaged, its function is impaired, which manifests itself in the form of hearing loss and tinnitus.
What is neuritis, nerve neuritis?
Neuritis is a lesion of the spinal or cranial nerves, manifested by syndromes of irritation and (or) loss of their functions in the corresponding area
innervation.
Neuritis occurs during acute and chronic viral and bacterial infections (influenza, pneumonia, dysentery, focal infections). Nerve damage is relatively rarely inflammatory in nature; various degenerative changes are more often found.
Treatment of acoustic neuritis
Depending on the nature of the course of cochlear neuritis, treatment can pursue one of two goals:
- In acute illness, as a rule, they strive to restore hearing.
- In chronic cases, they try to stabilize the process so that hearing does not decline further.
In the acute form, hospitalization of the patient in a hospital is indicated.
Drugs for the treatment of acoustic neuritis
Medications used:
- Vasodilators - help normalize microcirculation and improve the nutrition of nerve fibers.
- Antiplatelet agents - reduce blood viscosity, thereby improving blood flow in small vessels.
- Neuroprotectors - stop and prevent damage to nerve tissue.
- Nootropics - improve the functioning of the nervous system.
- Antibiotics - used if the disease is caused by a bacterial infection.
- Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs - help reduce inflammation.
- Infusion therapy - intravenous infusions of various solutions through a dropper help remove toxins from the body that have led to damage to the nervous tissue.
Physiotherapy procedures are prescribed: electrical stimulation, phonophoresis with medications. Sometimes they resort to acupuncture. Sometimes surgical treatment is required for cochlear neuritis:
- Installation of a cochlear implant - a prosthesis that helps partially restore hearing.
- Removal of hematoma, tumor and other formations that compress nerve fibers and cause neuritis.
- Removal of a neuroma , a benign tumor of the auditory nerve.
- Constant painful tinnitus , recurring severe dizziness.
If treatment is started on time, hearing can be restored in approximately 50% of patients, and in another 40% significant improvements can be achieved. In the chronic form of the disease, hearing restoration becomes impossible; the doctor tries to prevent its further deterioration.
Take care of yourself, book an ENT consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Acoustic neuritis leads to a condition called sensorineural hearing loss.
Symptoms of the disease
Acoustic neuritis manifests itself in two main symptoms:
- Hearing loss: the perception of sounds deteriorates, a person understands other people’s speech worse. Over time, complete deafness may occur.
- Noise in the ears: it can vary in pitch and is caused by inflammation and poor circulation.
Causes of neuralgia
The causes of neuralgia are inflammatory, traumatic, toxic, infectious-allergic, and metabolic effects. Compression of nerves in the bone, musculoskeletal and osteoarticular canals, prolonged microtrauma, especially in combination with hypothermia, and foci of focal infection also play an important role.
In the mechanism of pain syndrome, irritation of peripheral nerve fibers and central changes are important. In various suprasegmental parts of the nociceptive system, a generator of pathologically enhanced excitation may arise, which causes paroxysmal pain of a central nature.
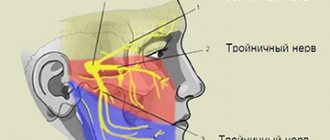
There are neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve, its ganglia and main branches (nasociliary, auriculotemporal nerves, pterygopalatine ganglion), glossopharyngeal nerve, occipital neuralgia, neuralgia of the facial nerve.
Trigeminal neuralgia is clinically manifested by short-term attacks of excruciating pain, most often in the area of the 2nd and 3rd branches of the trigeminal nerve. It is characterized by the presence of trigger zones on the skin and mucous membranes. Touching them provokes attacks of pain. In most cases, an attack of pain is accompanied by severe local and general autonomic disorders: facial hyperemia and swelling on the affected side, lacrimation, rhinorrhea, hypersalivation, possibly increased blood pressure, chill-like tremors, difficulty breathing. Detailed information on trigeminal neuralgia.
There are primary (idiopathic, essential, typical) and secondary (symptomatic) trigeminal neuralgia.
With primary neuralgia (mainly of central origin), attacks occur for no reason or are provoked by any movements of the facial muscles. Secondary neuralgia is usually a complication of the primary disease, has a predominantly peripheral genesis and is often caused by pathological processes in the dentofacial area. The pain is almost constant, periodically intensifying in the form of attacks lasting up to several hours.
How do symptoms of acoustic neuritis occur? How does the disease progress?
In the sudden form of the disease, hearing loss increases very quickly - within 12 hours. In this case, hearing decreases very strongly, right up to complete deafness. The disorder usually occurs on only one side—right or left. With a sudden form of hearing loss, hearing often disappears during sleep, which can cause a person to wake up. There is a feeling as if “the telephone wire has broken.” It is believed that most often this condition is caused by circulatory disorders in the inner ear, as well as viral infections: herpes, mumps, measles.
If similar manifestations begin to bother you, do not hesitate to visit a doctor. The medical center International Clinic Medica24 employs experienced neurologists and ENT doctors; we can undergo all types of diagnostics using modern equipment.
Unexpected deafness can be very frightening, but in about half of patients this form of the disease goes away on its own in the coming days.
If symptoms increase over the course of a day or longer, this form of auditory neuritis is called acute. If the disease is not treated, over time its course becomes subacute and chronic.
In addition to hearing loss, symptoms such as dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and impaired balance may be bothersome. This indicates damage to the vestibular nerve, which, together with the auditory nerve, is part of the vestibular-cochlear nerve.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Neuritis symptoms
The clinic of neuritis is characterized by dysfunction of the innervated structures. Since most nerves are mixed, when they are damaged in the innervation zone, flaccid paresis (paralysis), muscle atrophy, decreased and loss of reflexes, impaired sensitivity and autonomic disorders (swelling, cyanosis, increased sweating, depigmentation, hair loss) occur.
With neuritis of the facial nerve, damage to the root or trunk of the facial nerve occurs at various levels, manifested by homolateral paresis or paralysis of the facial muscles.
Why do you need to start treating the symptoms of auditory neuritis as early as possible?
The success of treating the disease directly depends on how quickly it is started. If the patient goes to the clinic on time, the chances of hearing restoration will be best. With chronic neuritis, there is no longer any talk of recovery - the doctor’s efforts are often focused only on preventing deterioration. The only way to at least partially restore hearing is to install a cochlear implant - a device that perceives sound vibrations through a microphone and transmits them in the form of electrical impulses to the brain.
What symptoms of cochlear neuritis should you see a doctor for?
If symptoms increase gradually, it may go undetected for some time. Check yourself: do you have hearing problems from this list:
- When you talk with 2-3 people, you have problems, you perceive what you hear worse and ask again.
- You can hear your interlocutor less well in a noisy room.
- You understand speech worse if it is uttered in a high-pitched female voice, and better if it is spoken in a lower-pitched male voice.
- You have difficulty distinguishing high frequency sounds from each other.
- The speech of others began to seem less intelligible and intelligible to you.
- Your hearing becomes impaired if there is background noise during a conversation.
To consult a doctor
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
There are many different reasons that can lead to the development of cochlear neuritis and sensorineural hearing loss.
Neuralgia treatment, how to treat neuralgia, intercostal neuralgia treatment, neuritis treatment
Complex treatment of neuritis and neuralgia (Saratov, Russia) includes a variety of effective techniques. Sarklinik knows how to treat and cure neuralgia neuritis !
Sign up for a consultation. There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Photo: Jabiru | Dreamstime.com\Dreamstock.ru. The people depicted in the photo are models, do not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Asthenia, asthenic syndrome, treatment, symptoms, causes, how to treat in children, adults
Trigeminal nerve, inflammation, treatment, trigeminal neuralgia, symptoms, how to treat
Memory loss, treatment, amnesia, short-term, partial, temporary memory loss
Polyneuritis, treatment of polyneuritis, alcoholic polyneuritis, polyradiculoneuritis
Urinary incontinence, treatment of women, men, children, adults, postpartum, neurogenic bladder, spina bifida
Comments ()
Infections
During infectious diseases, inflammation and swelling develop in the tissue surrounding the nerve fibers. In the best case, the process ends here, and after some time recovery occurs. If this does not happen, the nervous tissue begins to break down and is replaced by connective tissue.
The most common infectious cause of auditory neuritis (about 1/3 of all cases) is influenza. Other infections that can lead to cochlear neuritis: mumps, measles, rubella, scarlet fever, herpes, malaria, typhus, meningitis.
Trauma as a cause of acoustic neuritis
Various injuries can cause cochlear neuritis:
- Common mechanical head injury.
- Barotrauma caused by a strong pressure difference. It occurs in people who are near the source of the explosion, in pilots, and submariners.
- Acoustic trauma is damage to the hearing organ caused by loud sounds.
- Vibration injury is most often caused by occupational hazards among workers in enterprises that are constantly exposed to vibration.
Especially often, a combination of vibration and acoustic trauma leads to damage to the inner ear.
Poisoning with drugs and toxic substances
Some medications have ototoxicity, the ability to cause toxic effects in the inner ear. These drugs include some antibiotics (gentamicin, streptomycin, kanamycin, etc.), diuretics, antimalarials, and antitumor drugs. When poisoned by drugs, degenerative processes develop in the auditory nerve.
The risks are increased if two medications that have ototoxicity are taken at the same time. Treatment is safe only if it is carried out according to indications and as prescribed by a doctor, all drugs are used in optimal dosages. Among other substances, mercury and arsenic have a toxic effect on the ear.
Other causes of acoustic neuritis
Cochlear neuritis can occur as a result of the following reasons:
- Impaired blood flow in the vessels supplying the inner ear and brain.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Some metabolic disorders.
- Heredity.
- Neuroma is a benign tumor of the auditory nerve.
- Hematomas and tumors that compress nerve fibers.
In some cases, the cause of the disease remains unclear.
The main manifestation of cochlear neuritis is hearing loss, or hearing loss. It can be caused by various reasons.
There are two types of hearing loss:
- Conductive - associated with a violation of the passage of sound to the inner ear through the external auditory canal and the tympanic cavity.
- Neurosensory – caused by disorders of the nervous system. Sound perception suffers.
In order to determine the type of disorders and understand their causes, the doctor must carefully question, carefully examine the patient and prescribe all the necessary diagnostic methods. With neuritis of the auditory nerve, hearing loss is sensorineural in nature.
Take care of yourself, book a consultation now
Message sent!
expect a call, we will contact you shortly
Symptomatic picture
Characteristic symptoms are attacks of vegetation. They occur in the ear, parotid area, or in front of the opening of the ear canal on the side of the affected area. The pain is intense or burning. It radiates to the neck, back of the head, lower jaw and shoulder girdle. Due to the mechanism of pain irradiation, it spreads to the upper part of the thoracic region and the arm on the affected side. The duration of the attack ranges from several minutes to an hour or more.
Occasionally, paroxysm is accompanied by clicking or congestion in the ear. They are caused by reflex muscle spasms of the auditory tube. Also, during an attack, hypersalivation is noted, while at rest increased salivation does not occur.
Neuralgia can be triggered by:
- Hypothermia;
- Consumption of hot food and drinks;
- High physical activity;
- Psycho-emotional stress.
Since the autonomic nervous system depends on external factors such as temperature changes, changes in daily patterns, barometric pressure, etc., the autonomic system has a rhythmic character. It occurs most often at night and in the evening. In spring and autumn, neuralgia may worsen.
Hearing function remains unchanged during the period of illness.
Diagnosis of acoustic neuritis in the doctor's office
The diagnosis and treatment of the disease is carried out by ENT doctors and neurologists. During the conversation, the doctor may ask you the following questions:
- When did you notice that your hearing was getting worse? How exactly did this manifest itself?
- Are you bothered by ringing or tinnitus?
- What preceded the onset of symptoms? Have you had any infections? Have you had a head injury?
- Did your close relatives suffer from similar disorders?
- Are you worried about dizziness or nausea?
- Does hearing loss worsen over time?
Examination by a doctor: diagnostic methods that help assess hearing status
The following tests are used to diagnose cochlear neuritis and can be performed in a doctor's office:
- Otoscopy. The doctor examines the external auditory canal and eardrum using a special device - an otoscope. This helps rule out other conditions that could cause hearing loss.
- Acumetry. A test that helps identify the difference in the perception of normal speech and whispering.
- Weber's test. The doctor places a ringing tuning fork in the forehead or crown area. The healthy ear hears the ringing, but in the affected ear it is felt weaker or not heard at all.
- Rinne's test. The doctor brings a ringing tuning fork to the patient's ear and waits for it to quiet down. Then a ringing tuning fork is placed on the temple. With hearing loss caused by acoustic neuritis, the patient hears ringing worse in both cases.
- Tympanometry. The doctor examines the mobility of the auditory ossicles and eardrum by changing the pressure in the ear canal.
- Audiometry. Study of the perception of sounds of different frequencies using a special device - an audiometer. Helps determine the degree of hearing loss.
Diagnostic methods
When the first suspicious symptoms appear, the patient is recommended to consult a doctor for diagnosis.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor studies all the symptoms and manifestations of the disease, the patient’s complaints, collects anamnesis, and examines the affected area. To make an accurate diagnosis, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out , including specialized tests.
The essence of specialized tests is to carry out laboratory manipulations in order to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis. The manipulations are aimed at identifying the body’s specific reaction to external stimuli (physical, chemical effects). Such tests are used in all branches of medicine, including neurology.
To diagnose Frey's syndrome, the following special test is used: iodine and starch are applied to the painful area . Then the salivary glands are stimulated. The test is considered positive if the treated area turns purple.
Another special test is based on the use of novocaine. The patient is injected intradermally with a 2% solution of novocaine. If the attack of pain stops, the test is considered positive.
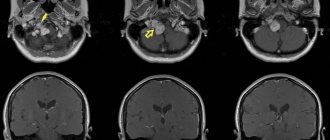
Instrumental diagnostic methods include x-rays, ultrasound, and MRI of the affected area. All these studies are carried out to clarify the diagnosis if special tests and clinical manifestations do not provide a clear picture and confirm the disease. Such methods allow doctors to differentiate auriculotemporal neuralgia from other similar diseases.