Noise in the head is a symptom that occurs in 10-15% of the population. A person hears sounds in the absence of a source of irritation. The noise is heard only by the individual himself. Patients suffer for years because they do not receive an adequate solution to the problem. Tinnitus disrupts the usual way of life, affects the ability to work, makes it difficult to pay attention, and impairs sleep. In some cases, the lack of timely assistance leads to disability.
Kinds
The work of the body is accompanied by the appearance of somatic or vibrator sounds. They appear during breathing, heartbeat, muscle contraction, and blood circulation. Somatic sounds become perceptible under certain conditions:
- heightened perception;
- noticeable increase in vibrations;
- the appearance of nonspecific noises.
In otolaryngology, the following groups of sounds are distinguished:
- vascular;
- noises of the external and middle ear;
- muscular;
- peripheral;
- centrally sensory.
Noises have a number of characteristics. They can be unilateral and bilateral, constant and periodic, monotonous and pulsating, high-frequency and low-frequency, intense and mild.
The severity of discomfort varies. According to the classification of A.P. Velitsky, there are 3 degrees of noise:
- weak;
- average;
- strong.
At the initial stage, the patient may not notice the discomfort, but only pays attention to it during the examination. That is, this is not the main symptom that led to seeking help.
The average degree of severity manifests itself in complaints of noise, but the patient does not pay attention to it. In severe cases, noise in the head and ears is the main symptom. A person feels constant discomfort, which worsens the quality of life.
In clinical practice, there are several classifications. According to E.R. Fowler, there are 2 types of tinnitus:
- vibrator (objective, related to the work of organs and systems);
- non-vibratory (subjective, resulting from irritation of the auditory nerve).
Objective noise occurs as a result of vascular and muscular pathology.
Vascular murmurs are characterized by a number of signs:
- permanence;
- synchronization with the pulse;
- changes in intensity depending on the degree of compression of blood vessels and the position of the head.
Increased discomfort is associated with increased blood pressure.
Muscle noise is not constant. The sounds that a person hears are similar to the chirping of a grasshopper. Some describe them as clicking.
Subjective noise is perceived as more painful. The sounds that the patient hears do not carry any information. The brain tries to decipher them, but to no avail. As a result, a person feels fear and anxiety.
Symptoms of Tinnitus
The main symptom of tinnitus is tinnitus of any type - whistling, ringing, rustling, buzzing, clicking, crackling, squeaking.
If the noise is accompanied by a sharp headache or severe dizziness, call an ambulance immediately. This may be a symptom of a cerebrovascular accident or hemorrhage.
If the noise is accompanied by pain in the ear, purulent discharge, or partial hearing loss, consult an ENT doctor. Most often these are symptoms of ear infections.
Causes
Noise in the head appears against the background of the development of many diseases. In some cases, it is not a harbinger of any dangerous condition. Endogenous sounds appear as a result of contraction of muscles and ligaments, crunching of joints, and blood pulsation.
Objective noise occurs due to several reasons:
- neuromuscular;
- muscular-articular;
- vascular.
Tinnitus is the result of the development of the following pathologies:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- hepatitis A;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypoglycemia;
- hypo- and hyperthyroidism;
- diseases of the outer, middle, inner ear;
- sulfur plugs;
- otitis;
- otosclerosis;
- Meniere's disease;
- hearing loss;
- acoustic and barotrauma;
- malignant neoplasms of the cerebellopontine angle, brain;
- intoxication;
- pathologies of the cervical spine;
- psychoneurological diseases;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- stress.
Subjective noise in some cases is the result of industrial factors, exposure to a sharp loud sound.
Elderly people more often suffer from noise in the head due to cardiac dysfunction, high blood pressure, and age-related changes.
Causes of tinnitus
Acoustic trauma
The appearance of noise is provoked both by a single sound impact of prohibitive volume (shots from large-caliber weapons, fireworks, rock concerts), and by the constant influence of sounds, which is often found among people listening to loud music through headphones, workers in factories and sewing workshops. In case of acute injury, a person temporarily loses hearing, which causes a monotonous ringing or squeaking in the ears. May cause severe throbbing pain in the temporal part of the head and dizziness.
With chronic exposure to sound stimuli, symptoms increase gradually. First, complaints appear about short-term noise (within 1-2 hours), which begins after being in a room with loud sounds or using headphones. As the condition progresses, the ringing in the ears becomes constant and is accompanied by hearing loss. The frequent occurrence of noise, which disrupts performance, is combined with headaches and hearing loss, is an indication for seeking medical help.
Age-related changes
Among people 55-65 years old, every fifth person periodically notes the appearance of extraneous sounds; after 65 years, the number of people suffering from humming and ringing in the ears increases to 40%. Typical complaints are bilateral noise, which at first feels very quiet and practically does not interfere with everyday activities. Then the sounds seem more intense. Due to the intensification of symptoms at night, patients usually suffer from insomnia. Tinnitus in the elderly is caused by degenerative changes in the inner ear and is combined with decreased hearing, which requires consultation with a doctor.
Hypertonic disease
The appearance of tinnitus is typical for patients suffering from high blood pressure, and the intensity of auditory sensations depends on blood pressure levels. Extraneous sounds are caused by the turbulent movement of blood through narrowed vessels with thickened walls. Hypertensive patients periodically hear a slight hum, which usually occurs against the background of a headache and a deterioration in their general condition. Increased noise, accompanied by painful nausea, flashing “spots” before the eyes, is a symptom of an incipient hypertensive crisis.
Pathological processes in the ear
Ear noise may indicate damage to the auditory analyzer, which is caused by disturbances in the perception and analysis of sounds, and discoordination of the work of different parts of the hearing organ. These reasons often cause temporary sensations of humming or ringing, which cease to bother you after the underlying pathology is relieved. With some lesions of the inner ear that are difficult to treat, the noise becomes constant. Tinnitus is caused by:
- Inflammatory diseases
: external and otitis media, eustachitis, labyrinthitis. - Blockage of the ear canal
: wax plugs, foreign bodies, water ingress. - Inner ear diseases
: Meniere's disease, otosclerosis.
Vascular disorders
Most often, the symptom occurs with atherosclerosis: the deposition of lipid plaques on the walls of the vessels of the inner ear disrupts the normal movement of blood, which is felt as a moderately intense “pulsating” noise. In most patients, the hum is more pronounced on one side, which is associated with the degree of damage to the vascular wall. Unilateral loud ear noise is observed in patients suffering from temporal artery aneurysm. In this case, uncomfortable auditory sensations are combined with periodic headaches and dizziness.
Tumor causes
Tinnitus is most characteristic of a benign formation—acoustic neuroma. With this neoplasia, unilateral tinnitus becomes the first symptom. A person notices the appearance of a weak constant hum in one ear, which does not disappear even at night. As the disease progresses, hearing on the affected side gradually deteriorates, and sound sensations become more intense. Pulsating one-sided noise in combination with swallowing disorders and asymmetry of the palpebral fissure occurs with glomus tumor of the ear.
Cervical osteochondrosis
In case of problems with the spine, the occurrence of ringing or humming in the ears is associated with sharp turns or tilts of the head, or prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position. The causes of noise are compression of individual vessels that go from the neck to the ear and brain. The symptom is observed periodically, the intensity of the sounds is low, so the performance of most patients does not suffer. With severe deformation of the cervical vertebrae, a monotonous strong ear noise is possible, combined with dizziness, fainting, and sharp pain in the neck.
Traumatic brain injuries
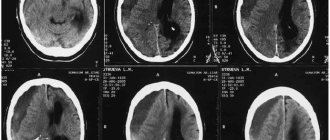
Mild head injuries may be accompanied by a short-term noise or ringing in the ears, which does not cause severe discomfort. With more significant damage, unusual auditory sensations are detected against the background of severe nausea and vomiting, intense headaches. Sometimes the symptom does not appear immediately after the injury, but several days later. The noise that occurs after hitting the head is grounds for an urgent visit to the doctor, since with a traumatic brain injury there is a risk of destruction of bone structures and intracranial hemorrhages.
Complications of pharmacotherapy
Tinnitus most often develops 1-2 weeks after the start of etiotropic treatment of severe bacterial infections, which is due to the strong ototoxic effect of drugs. The symptom also occurs in patients with hypertension who are forced to take medications from several groups daily. Side effects from the auditory analyzer are provoked by such groups of medications as:
- Antibiotics
: aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, macrolides. - Diuretics
: furosemide, ethacrynic acid, hydrochlorothiazide. - NSAIDs in high doses
: indomethacin, diclofenac, aspirin. - Tranquilizers
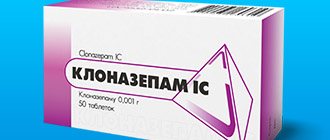
: flurazepam, tranxene, phenazepam.
Rare causes
- Malformations of the auditory analyzer
: Goldenhar syndrome, microotia, congenital sensorineural hearing loss. - Endocrine pathology
: hypothyroidism, pituitary adenoma. - Diseases of internal organs
: digestive system, kidneys. - Neurological causes
: multiple sclerosis, age-related degenerative processes in the brain. - Damage to the temporomandibular joint
. - Allergy
.
Which doctor treats
Since noise in the head is a symptom of ear diseases, as well as neurological pathologies, if an unpleasant symptom appears, you should contact an otolaryngologist or neurologist.
Why suffer from noise in your head if you can turn to a specialist at the Kuntsevo Medical and Rehabilitation Center to solve the problem?
IMPORTANT! You should not self-medicate, because noise in the head is a neurological symptom that may indicate the development of serious pathologies.
Our neurologist and otolaryngologist will conduct a detailed study of the causes of the symptom and indicate a direct path to solving the problem and getting rid of noise in the head. You just need to make an appointment with our doctor, who will not only help you get rid of the symptom, but will also describe a detailed course of rehabilitation.
Sign up
Consequences of lack of treatment
Ignoring a symptom such as tinnitus can ultimately lead to partial or complete hearing loss. If the cause of tinnitus is a tumor, then the worst result of lack of treatment can be death. Tinnitus is most often a symptom whose causes should be investigated by a doctor.
Don't delay visiting a specialist. Pay attention to symptoms and get diagnosed promptly. After 40 years, doctors recommend checking the condition of the hearing organs annually in order not to miss the onset of age-related changes and to prevent hearing loss.
Be healthy!
Treatment methods
A patient who seeks help undergoes an examination, on the basis of which he is prescribed treatment. There are 2 groups of methods: conservative and surgical. Preference is given to measures that include medicinal, physical, and psychotherapeutic methods of influence.
To reduce noise, patients are prescribed vasoactive, nootropic drugs, vitamins, antidepressants, tranquilizers, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants, anesthetics, antihistamines, vasodilators, diuretics, homeopathic remedies, etc.
Physical methods include:
- phototherapy;
- electrotherapy;
- faradization;
- iontophoresis;
- ultrasound;
- mechanotherapy;
- reduction;
- reflexology.
Tinnitus Retraining Therapy (TRT) and cognitive behavioral psychotherapy are used as psychotherapeutic techniques.
Surgical tactics are used in case of significant pathological changes in the auditory organ.
Rehabilitation and lifestyle restoration
Sound therapy is the main form of supportive treatment. Experts use audio maskers that reproduce environmental sounds. They distract from the main noise and improve the process of falling asleep.
Listening to musical works with certain acoustic characteristics has a beneficial effect on the body.
Some patients note an improvement in their condition after listening to the sounds of a departing train, rain, dripping water, or a washing machine.