- Location and functions of the facial nerve
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
- Folk remedies
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Pathology of the facial nerve is registered annually in 2–3 people out of 10 thousand people. It occurs due to various reasons, the nature of which largely determines the treatment of facial neuritis. Taking into account the anatomical connection of this formation and the ENT organs, with neuritis of the facial nerve the patient needs to consult not only a neurologist, but also an ENT doctor.
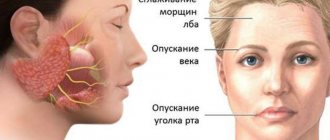
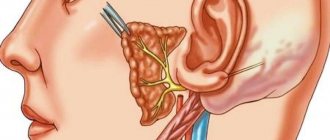
Location and functions of the facial nerve
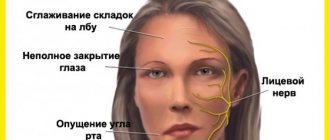
The facial nerve controls muscle movements in this anatomical region. This gives a person the opportunity to smile, express emotions with facial expressions, cry, and wink. Facial neuritis can lead to severe physical disability that is poorly tolerated psychologically. Although in most cases the symptoms of the disease gradually disappear, this requires long-term rehabilitation.
The facial nerve is the seventh of 12 paired cranial nerves. Each person has 2 facial nerves, corresponding to the right and left halves of the face. This nerve is adjacent to the eighth nerve, the auditory nerve, and passes through the structures of the middle ear, the mastoid process, and the parotid salivary gland, where it splits into many small branches.
2. Reasons
Cochlear neuritis can develop under the influence of many factors:
- infectious diseases (flu, measles, ARVI, herpes, scarlet fever, etc.);
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals, industrial hydrocarbons, drugs (antibiotics, chemotherapy, antiarrhythmics, diuretics, etc.);
- industrial hazards (vibration, noise);
- acute and chronic conditions associated with cerebrovascular disorders (blood supply to the brain);
- traumatic brain, acoustic, radiation, birth injuries;
- cancer;
- neurodegenerative processes and age-related changes.
As can be seen from the above, in most cases, cochlear neuritis is acquired. However, there is also congenital sensorineural hearing loss, which is usually caused by hereditary factors and is one of the elements of one or another chromosomal syndrome.
Visit our Otolaryngology (ENT) page
Causes
Facial neuritis occurs under the influence of the following etiological factors:
- in 15% of patients this is damage to the branches of the nerve during surgical interventions on the middle ear, mastoid process, and also associated with otitis media and other lesions of the hearing organ, for example, cholesteatoma;
- in rare cases, the disease is caused by infection - herpes virus (Hunt syndrome), mumps, polio, influenza, as well as Lyme disease, transmitted through tick bites;
- in 75% of cases, the cause of neuritis of the facial nerve cannot be determined; in this case, they speak of Bell's palsy, which worsens after hypothermia and colds.
Other causes include head trauma, surgery on the salivary gland, and removal of an acoustic neuroma.
Symptoms of the most common neuritis
Facial neuritis is characterized by facial pain, loss of control over the muscles of the mouth and eyes, disturbances in facial expressions, and distortion of facial features. The patient may shed tears or suffer from dry eyes. Often, facial neuritis occurs against the background of viral infections and hypothermia.
Trigeminal neuritis is accompanied by severe paroxysmal pain at the exit points of the nerve. The sensation may intensify when washing with cool water.
Acoustic neuritis is manifested by hearing impairment and tinnitus. If the nerve connecting the brain and the vestibular apparatus is damaged, symptoms such as nausea, dizziness, and unsteady gait may appear.
1 ENMG
2 Reflexology
3 Massage
Optic neuritis (or retrobulbar neuritis ) is expressed by pain when moving the eyeball, narrowing of the field of vision, partial loss of visual acuity, disturbances in color and light perception and other disorders of visual function.
Solar plexus neuritis (or solaritis ) is characterized by severe, burning abdominal pain, tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, flatulence and loose stools, accompanied by chills and cramps. Symptoms are relieved with potent drugs (conventional anti-inflammatory drugs do not help).
Ulnar nerve neuritis is characterized by pain in the affected area and impaired motor function, which is manifested by the inability to clench all the fingers on the hand into a fist, especially the little finger. Sometimes a person has problems bending his arm.
Radial neuritis is manifested by a decrease in the ability to flex and extend the forearm and wrist, difficulty deviating the thumb, and loss of sensation in the back of the hand.
Neuritis of the sciatic nerve is manifested by weakening of the flexors and extensors of the foot, pain covering the back surfaces of the thigh and lower leg, numbness of the gluteal muscles, and decreased sensitivity in the limb. The main cause of the disease is considered to be pinched sciatic nerve.
Neuritis of the femoral nerve is characterized by difficulties with flexing the hip and straightening the leg at the knee joint, decreased sensitivity and muscle strength of the anterior surface of the thigh, etc.
1 Laboratory diagnosis of neuritis
2 X-ray
3 MRI
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease occur acutely, within a few hours, for a maximum of 3 days. The gradual appearance of signs is most typical of compression of the nerve by a tumor growing from the surrounding tissue.
Depending on the severity, neuritis of the facial nerve is accompanied by the following symptoms:
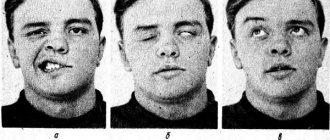
- movements of the facial muscles are weakened, up to barely noticeable, disruption of conjugate contractions of symmetrical areas of the face;
- facial asymmetry, even disfiguring;
- difficulty closing the eyes; in severe cases, the palpebral fissures do not close completely;
- disorders of swallowing, chewing, speech;
- when the disease is complicated by keratitis, vision loss gradually develops;
- taste disturbance, weakening or strengthening of sound sensations;
- lacrimation;
- with simultaneous damage to the trigeminal nerve - severe pain in the facial area.
Signs of intoxication and fever are uncharacteristic and usually occur due to the infectious nature of neuritis of the facial nerve.
Diagnostics
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is prescribed after an examination, which includes:
- general blood and urine tests, blood glucose levels;
- if the infectious nature of the disease is suspected (Lyme disease, HIV infection, syphilis and others) - appropriate serological tests;
- if sarcoidosis or brucellosis is suspected, chest X-ray;
- in the case of a prolonged course (more than 3 weeks), if damage to the brain stem or cerebellopontine angle is suspected, MRI is prescribed, and if the pathological process is localized in the area of the temporal bone, computed tomography is more informative;
- Electroneuromyography is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment;
- If a nerve tissue infection is suspected, a lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination are performed.
If the patient has already been diagnosed with ear diseases, or has discharge from the ear canal or hearing loss, he should definitely consult an ENT doctor.
Facial neuritis is differentiated from Lyme disease, Ramsay Hunt syndrome, Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome.
MDM therapy is the fastest way to cure facial neuritis without side effects
MDM therapy (mesodiencephalic modulation) is an innovative method of transcranial electrotherapy, which acts not on the peripheral, but on the Central nervous system, activating the main regulatory systems of the body (nervous, immune and endocrine) at the level of the control centers of the brain.
MDM therapy restores the mechanism of regulation of physiological processes disrupted as a result of hypothermia, infection and/or nervous stress, i.e. the ability of nerve structures to regenerate nerve impulses, improve redox reactions, activate blood flow and metabolic processes in cells and tissues.
Under the influence of MDM therapy, the brain begins to produce more than 40 biologically active substances, most of which have not yet been synthesized artificially. These substances have many times the therapeutic effect of all existing drugs and do not have side effects, because are endogenous (internal, produced by the body itself).
The MDM therapy program “Facial nerve neuritis” relieves inflammation of the nerve in 1-2 days, and completely cures the disease in 10 days (13 sessions) : facial asymmetry, numbness and other symptoms are eliminated, muscle motor activity is restored.
Since MDM therapy has a powerful immunostimulating effect, this can reliably protect the patient from the possibility of relapse of the disease.
The MDM therapy technique has been certified and approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Treatment
Treatment of facial nerve neuritis is carried out on an outpatient basis. The exception is cases of illness associated with ear pathology that require surgical intervention.
- At home, it is necessary to spare the organs of vision. Due to incomplete closure of the eyelids, the cornea of the eye quickly dries out, so it must be constantly moistened with special drops, wear dark glasses during the day, and cover the eyes with a bandage at night.
- The basis of treatment for facial neuritis is glucocorticoid preparations (prednisolone), which are often supplemented with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
- If facial neuritis is caused by damage to the part of the nerve that runs in the labyrinth, middle ear or mastoid process, then only surgery will bring the best results.
- In severe cases, accompanied by paralysis of facial muscles, microsurgical neurological operations are performed to stitch or transplant nerves.
Reconstructive surgeries that are performed on patients with severe cases of facial neuropathy:
- movement of the branches of the hypoglossal nerve to the distal end of the facial nerve;
- transposition of the temporal muscle to the corner of the mouth, which allows you to learn how to raise its corner;
- transplantation of a muscle flap from the thigh while preserving the nerve branches;
- plastic surgery – brow lift, face lift, partial lip resection, eyelid correction.
Electrical stimulation
Determination of current parameters for electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation is a therapeutic method of using pulsed currents of various shapes and frequencies to restore the function of the damaged neuromuscular system. Various injuries, wounds, bone fractures, infectious diseases, intoxication, degenerative-dystrophic diseases often lead to damage to the nerve fiber with the development of a degeneration reaction in the neuromuscular system with clinical manifestations of flaccid paralysis. Under the influence of electrical stimulation, the contractile function of the denervated muscle is preserved, blood circulation and energy potential in it increase, the activity of enzyme systems increases, oxidative processes and the transformation of glycogen in the muscles are stimulated. Favorable conditions are created for nerve regeneration. With preserved muscle innervation, the use of electrical stimulation prevents the development of muscle atrophy due to physical inactivity, increases performance and quickly increases muscle strength. In case of central paralysis, most often caused by impaired cerebral circulation, electrical stimulation creates centripetal afferentation, which promotes the disinhibition of blocked brain centers around the intensified area of the brain, improves nutrition and trophism of paralyzed muscles. Prevents the development of contractures.
Determination of current parameters for electrical stimulation is based on electrodiagnostic data and is carried out strictly individually, since under pathological conditions the excitability of the neuromuscular system varies widely.
Pulse shape. Modern devices for electrical stimulation can generate impulses of rectangular, triangular, trapezoidal shape. The selected impulse shape must correspond to the functionality of the muscle. During the degeneration reaction, the trapezoidal shape of the impulse will be more physiological.
Pulse duration. In the presence of quantitative changes in the neuromuscular system, an impulse with a duration of 1-5 ms will be optimal, with a partial degeneration reaction - 10-50 ms, with a complete degeneration reaction - 100-300 ms.
Pulse repetition frequency. With preserved muscle innervation, an alternating current of a carrier frequency of 2-10 kHz, modulated by a low-frequency voltage (50-100 Hz) or a neofaradic current (unipolar) of a frequency of 50 Hz, is used. A series of impulses alternate with pauses for muscle rest. With electrical stimulation, tetanic muscle contraction occurs.
With a partial degeneration reaction, a correctly selected combination of pulse duration and frequency can provide tetanic muscle contraction. The most rational combination is proposed: pulse duration 3-5-10-20-30-60-100 ms, pulse repetition frequency 80-60-40-25-10-8-5 Hz.
With a denervated muscle, electrical stimulation is carried out only with single impulses with pauses of 3-20 s. The more pronounced the degeneration reaction is, the longer the pause should be.
Polarity. The active electrode is selected in accordance with the polar Pfluger-Brenner formula. It can be a cathode or anode. With preserved innervation, the cathode is, as a rule, active, and with a severe degree of degeneration, the anode is active.
When stimulating skeletal muscles with impaired innervation, both electrodes (cathode and anode) with hydrophilic pads, the optimal area of which is 4 cm2, are applied to the stimulated muscle. When innervation is preserved, the anode is placed on the motor point of the stimulated nerve, and the cathode is placed on the motor point of the muscle it innervates. When stimulating smooth muscles, electrodes with hydrophilic pads with an area of 200-300 cm2 are placed over the area of the stimulated organ (stomach, intestines, uterus, ureter) using the transverse technique.
For peripheral paralysis with impaired muscle innervation, only single impulses are used with a repetition frequency of 1-0.25 Hz or less and a duration of 100-200 ms. The pulse repetition rate, as well as the duration and shape (triangular, trapezoidal, rectangular) are selected individually.
For electrical stimulation of skeletal muscles with preserved innervation, an alternating current of 2-5 kHz is used, modulated by a voltage with a frequency of 50-100 Hz, which follows in an intermittent mode (current sendings alternate with pauses) or a neo-faradic (half-wave) current with a frequency of 50 Hz.
To stimulate the smooth muscles of internal organs, alternating current with a frequency of 2-5 kHz with low-frequency amplitude modulation of 5-30 Hz is used.
Indications:
- flaccid paresis and paralysis associated with nerve injury, toxic damage, nerve inflammation, degenerative diseases of the nervous system and spine;
- central paresis and paralysis associated with impaired cerebral circulation;
- muscle wasting due to physical inactivity and immobilization bandages;
- hysterical paresis and paralysis;
- postoperative intestinal paresis, hypomotor dyskinesia of the stomach, intestines, biliary tract;
- atony of the sphincters of the bladder and rectum;
- ureteral stones, chronic prostatitis, dysfunctional diseases of the female genital organs;
- metabolic disorders: obesity, cellulite.
Contraindications: contracture of facial muscles, bone fractures before immobilization, joint dislocations before reduction, bleeding (except for uterine dysfunction), acute inflammation, purulent diseases (abscess, phlegmon, carbuncle, furuncle), thrombophlebitis, cholelithiasis, the first 3-4 weeks. from the moment of development of acute cerebrovascular accident, epilepsy, implanted pacemaker, loose metal bodies in vital organs, which, with oscillatory movements, can cause damage to the blood vessel.
Some methods of conducting electrical stimulation procedures with pulsed currents
Electrical stimulation of the peroneal nerve and the muscles innervated by it in peripheral paresis (paralysis)
Plate electrodes with an area of 4 cm2 are used. The anode is located in the upper third of the leg on the outer posterior side at the motor point of the peroneal nerve. During the procedure, the cathode is periodically moved to the motor muscles: tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum communis, peroneus longus, peroneus brevis, extensor pollicis intrinsic. Current parameters: pulse current shape - rectangular or trapezoidal, pulse duration 100-200 ms, pulse repetition frequency 0.5-0.25 Hz or less, current strength 10-15 mA in amplitude value. Duration of exposure is 15-20 minutes daily or every other day. The course of treatment is 15-20 procedures. Courses of treatment can be repeated many times.
Electrical stimulation of limb muscles for central paresis (paralysis)
For afferent stimulation of the cerebral cortex of patients who have suffered an ischemic stroke, electrical stimulation is prescribed after 2-3 weeks. from the onset of the disease (the appearance of limb paresis). One pair of plate electrodes with an area of 4 cm2 is located: the cathode - in the middle third of the shoulder on the outer side at the motor point of the radial nerve, the anode - in the middle third of the outer surface of the forearm. The second pair of the same electrodes is placed: the cathode - on the inner surface of the middle third of the shoulder on the ulnar and median nerves, the anode - on the inner surface of the forearm.
Current parameters: rectangular pulses with a duration of 1 ms with a repetition rate of 0.5 Hz (two pulses per second) are sent to the group of muscles innervated by the radial nerve (extensors), and after 1 s - to the ulnar, median nerves and the muscles of the flexor group innervated by them; amplitude current value 3-5 mA, duration of exposure 5-8 minutes.
Next »
Otogenic neuritis of the facial nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve, which occurs secondary to serious diseases of the middle ear, requires urgent surgery. During the intervention, the doctor relieves excess pressure on the nerve (decompresses it) by removing part of the bone wall of the nerve canal that runs in the middle ear. Subsequently, treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed, as a result of which the function of the affected facial nerve is also restored.
If the pathology develops at an early stage of acute otitis media, a decision may be made on conservative treatment of facial neuritis:
- vitamin therapy with ascorbic acid and group B preparations (Milgamma);
- decongestants (furosemide);
- glucocorticoids for rapid relief of inflammation and pain;
- after acute manifestations subside, actovegin, solcoseryl, and other drugs that affect the metabolism of nervous tissue are prescribed;
- If conservative treatment is ineffective, different types of surgical interventions are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic methods are included in the complex of restorative treatment measures:
- therapy with UHF, quartz radiation, laser;
- electrophoresis with B vitamins, lidase;
- acupuncture and massage, especially performed on the inside of the cheek;
- applications of therapeutic mud, ozokerite, paraffin;
- physical therapy aimed at restoring the activity of the muscles of the lower part of the face.
Treatment of neuritis
The approach to treating neuritis should be comprehensive.
Drug therapy for neuritis is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the disease, restoring nerve function, relieving inflammation and pain, activating blood flow and metabolic processes, improving nerve conduction, strengthening the body's defenses, etc.
Common non-drug treatment methods include therapeutic exercises, acupuncture, manual techniques and massage (in the absence of contraindications).
A special place in the treatment of neuritis is given to physiotherapy: treatment with waves and currents, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, radon and mud baths, etc.
Surgical treatment (suturing or plastic surgery of the nerve) is resorted to in the absence of a positive effect from conservative therapy.
Prevention of neuritis
Simple and effective measures will help to resist the development of the disease:
- avoiding hypothermia;
- proper balanced nutrition;
- timely treatment of viruses and infections;
- strengthening the immune system (vaccination, hardening, vitamin therapy);
- regular examination of the body.
At the MedicCity clinic, the professional experience and knowledge of doctors from 30 medical specialties is at your service. With us you can undergo a complete diagnosis of the body and get advice from the right specialist at a time convenient for you, without wasting time and nerves. Don't give diseases a chance!
Folk remedies
At home, you can use traditional medicine recipes to warm up and relieve inflammation:
- three times a day for 20 days, warm the sore side with a bag of warm table salt;
- massage your face with essential oil of fir or cedar twice a day for two weeks;
- 3 times a day for 2 weeks, make warm compresses with linden blossom infusion or gruel from fresh black elderberries;
- 3 times a day for 15 days, rub with a composition consisting of equal parts of horseradish juice and olive oil;
- before going to bed, make compresses from fresh wormwood leaves for 30 minutes;
- make compresses from cottage cheese and honey: mix 4 parts of low-fat cottage cheese and 1 part of linden honey, wrap in gauze and apply to the affected half of the face for 1 hour, wrap with a scarf; do 2 compresses a day for 2 weeks.
Of course, folk recipes cannot replace drug therapy, much less surgery. However, they are not prohibited from being used to speed up recovery in complex treatment.
Possible complications
Treatment of facial neuritis cannot be delayed. The later therapy is started, the greater the likelihood of developing complications:
- With a long course of the disease, the patient develops a persistent contracture of the facial muscles on the affected side: the muscles are involuntarily tense, contracted, and involuntary movements are possible. Recovery from such a complication is extremely difficult.
- The appearance of the face can change greatly: immobile muscles create a significant cosmetic defect.
- Persistent disturbances of taste.
- Corneal ulcers, infection, cataract formation, blindness.
- Constant spasm of the muscles of the face or eyelid.
Tests and diagnostics
A neurologist makes a diagnosis based on the patient’s complaints and clinical picture. The neurologist may ask you to make movements with your facial muscles - close your eyes, bare your teeth, raise your eyebrows, puff out your cheeks or whistle, and wrinkle your nose. Such tests allow the doctor to determine the presence of neuritis. If the diagnosis is in doubt, the doctor may prescribe the following tests:
- CT, MRI;
- Electroneuromyography (ENMG);
Additionally, the neurologist may recommend consultation with a neurosurgeon and otolaryngologist.
Prevention
Taking into account the main causes of the disease, its prevention includes protection from colds, hypothermia, as well as timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. It is useful to harden the body, treatment in sanatoriums on the seashore, and a diet rich in B vitamins.
After suffering from facial neuritis, self-massage of the face with essential oil of fir or cedar is useful to prevent recurrence of the disease. It can be done at night during the cold season.
The paid services department of NIKIO invites patients with neuritis and neuropathies of the facial nerve for treatment. The patient is examined by an experienced doctor; a consultation with a candidate or doctor of medical sciences is possible. The clinic uses modern physiotherapy equipment. If necessary, the patient undergoes surgery to quickly restore the function of the damaged nerve.
Nerve neuritis, treatment
Adequate treatment is impossible without identifying and eliminating the cause of the disease. If it develops due to an infectious infection, the neurologist prescribes antiviral and antimicrobial drugs. When the cause of the disease is a violation of tissue nutrition, vasodilating medications are used. If inflammation develops after an injury, it is necessary to immobilize the affected limb.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are actively used; B vitamins and decongestant therapy are prescribed to normalize the functioning of the central and peripheral NS. Treatment of neuritis also involves physical therapy - ultraphonophoresis, UHF, electrophoresis using special compounds, etc. If tunnel syndrome is detected, medications are delivered to the diseased canal.
Rehabilitation for neuritis is of great importance. It includes not only drug therapy, but also massage and exercise therapy. All activities are aimed at restoring normal muscle function. If necessary, electrical stimulation is prescribed.
Sometimes treatment of nerve neuritis is only possible through surgery. If compression of the nerve is observed, it is decompressed (dissection of the compressing tissue, most often tendons).
If after drug treatment there is no improvement, the nerve is not restored or degeneration is observed, it is stitched together, and sometimes plastic surgery is performed.