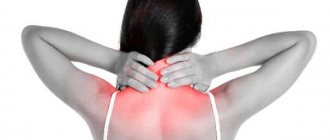
The scalp becomes numb most often due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, when the nerve fibers are pinched by bony protrusions. The cause may be compression by tense neck muscles due to an uncomfortable posture during sleep or work, or muscle spasm due to neck pain.
The frontal part of the head becomes numb with trigeminal neuralgia, and numbness of the ear and half of the face occurs with neuritis of the facial nerve. Unilateral damage is typical for migraine attacks and strokes, and the vertex loses sensation when the occipital nerve is pinched.
Dangerous symptoms include sudden numbness with general weakness and lack of sensation in half of the head, arm or arm and leg on one side, then you need to call an ambulance.
For a routine examination, you need to contact a neurologist. He conducts a study of the neurological status (skin tests, reflexes), prescribes x-rays of the cervical spine, MRI, and blood tests. To treat radicular syndrome (the most common cause), painkillers (Diclofenac), vitamins (Milgamma), improving blood circulation (Trental), muscle relaxants (Sirdalud), exercise therapy, massage, and physiotherapy are prescribed.
Head goes numb: causes, sign of what disease
If your head goes numb, this is due to a deterioration in the sensitivity of the scalp, the causes being diseases:
- cerebral vessels - inflammation (vasculitis), blockage with deterioration of blood supply (stroke or temporary ischemic attack);
- traumatic origin - cranial, cervical spine;
- hereditary - for example, narrowing of the openings through which the spinal cord root passes;
- with compression of the nerve fiber - by muscles (with spastic contraction or prolonged tension), bone outgrowths with osteochondrosis, space-occupying formation (tumor, blood accumulation, inflammatory compaction, aneurysm);
- neuritis of the facial nerve;
- trigeminal neuralgia;
- infectious (herpes, meningitis);
- metabolic – diabetes mellitus, lack of vitamin B12, B1;
- against the background of lead poisoning, other toxic compounds, and medications.
Most diseases occur with concomitant symptoms, the patient feels severe weakness, dizziness, speech, vision, and movements may deteriorate. If the general condition is normal, but only, for example, the scalp under the hair becomes numb, then this is usually a manifestation of prolonged muscle tension. This happens with sedentary work, incorrect body position during sleep, headaches and after a long trip on a bus, train or plane.
The location of the numbness zone is also important. In neurological and vascular diseases, it has clear and permanent outlines; by its location, a neurologist can determine the location of nerve damage.
If there is a variety of symptoms (tingling in different parts of the face, burning, heat, numbness), then a suspicion of neurosis or neurocirculatory dystonia arises. They often occur against the background or after stress overexertion.
Leather
If the scalp becomes numb, then most often you need to look for the cause in the cervical spine. Osteochondrosis is the most common cause; it causes irritation of the spinal cord roots by bone outgrowths (osteophytes), which patients call “salt deposition.”
If the size of the osteophytes increases, then compression begins with pain during movements and impaired sensitivity. Usually the numbness spreads to the head, neck, and sometimes extends to the arm.
If it shrinks (squeezes) the scalp, this sensation may be confused with a decrease in sensitivity. This is especially common in the setting of tension headaches. Patients describe it as tension, tightening or squeezing. Most often it is symmetrical, sometimes bringing the head and face together on one side. This disease is characterized by the appearance of symptoms after the action of a provoking factor:
- stress, lack of sleep;
- incorrect static posture;
- visual strain;
- long break in meals;
- staying in a stuffy room, heat, cold;
- anxiety, depression;
- high blood pressure;
- infection;
- hormonal disorders (usually premenstrual syndrome, menopause).
Forehead, frontal part
Trigeminal neuralgia
Numbness of the forehead (frontal part of the head) is possible with trigeminal neuralgia. This disease is characterized by painful attacks of the type of electric discharges, after which the sensitivity of the facial skin is impaired. Since the forehead is innervated by the superior orbital branch of this nerve, when it is damaged, skin numbness, tingling, and a feeling of cold occur. Causes of neuralgia include:
- vascular diseases - congenital tortuosity, aneurysm (expansion of the area), arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis;
- tumors of the brain, skull bones;
- sinusitis;
- traumatic brain injury;
- changes in bite, dental procedures;
- herpes.
Neuralgia can be suspected if pain occurs after touching the skin of the face or contraction of facial muscles when eating or talking.
Right side or left
If the right or only the left side of the head hurts and goes numb, then the cause may be neuritis of the facial nerve. It is also called Bell's palsy, since one of the manifestations is weakness of the facial muscles. The patient experiences pain behind the ear, then half of the face goes numb, on the affected side the nasolabial fold is smoothed, the corner of the mouth is drooping. Then a skew of the facial part of the head occurs on the healthy side, and on the affected side, movements of the facial muscles become impossible.
Unilateral numbness and asymmetry of the face also occurs with acute cerebrovascular accident. Then, when trying to smile, one half lags behind the other (a crooked smile), the eyebrows rise to different heights, and if you ask the patient to stick out his tongue, it deviates to the side. There may be loss of vision in one eye. Speech becomes slurred. Usually, with a decrease in sensitivity, weakness is felt in the arm or arm and leg on one side, the patient will outgrow the sensation of touching half of the upper lip.
Symptoms may disappear within a day, then a diagnosis of transient (transient) ischemic attack is made. If symptoms persist for more than 24 hours, a stroke develops. The causes of deterioration of cerebral circulation include atherosclerosis, hypertension, and osteochondrosis.
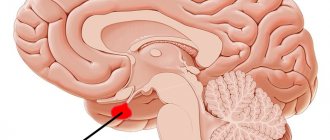
Crown, upper part of the head
Numbness and tingling in the crown and upper part of the head can be associated with pinching (neuralgia) of the occipital nerve. This disease is provoked by:
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- infectious diseases (sore throat, mumps);
- inflammation of the lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) of the occipital, behind-the-ear group;
- neck injuries, surgeries;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged muscle tension.
Painful shooting sensations from the back of the head to the crown, from the neck to the shoulders and shoulder blades are typical. Most often they are one-sided, but they can spread to both sides.
Ear and head part
Numbness that starts from the ear and then covers half of the head is typical of neuritis of the facial nerve.
The most common cause is hypothermia and inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media). Similar signs may also appear against the background of herpes, mumps, or after an injury. Less commonly, such symptoms occur due to an acute cerebrovascular accident (ischemic stroke), a tumor, or an infectious lesion of the brain (encephalitis).
Half head, whiskey
Numbness of half the head or a predominant deterioration of sensitivity in the temples is typical for a migraine attack with aura. At the same time, there may be tingling in the fingertips.
Sometimes numbness spreads to the entire arm, part of the neck and body. You may experience ringing in the ears or unusual sounds or smells. Half of the head also goes numb in patients with an epileptic attack, a transient disorder of cerebral circulation.
Also hands
Numbness of the head and arms is a typical sign of cervical osteochondrosis, and can also be caused by:
- trauma, especially vertebral subluxations;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the spine;
- curvature of the spinal column;
- scoliosis.
In older people, the height of the intervertebral discs may decrease (spondylosis).
Damage to the cervical and upper thoracic roots occurs with herpes zoster. Impaired sensitivity of the scalp and hands is caused by circulatory disorders (for example, diabetes mellitus, vasculitis). Less commonly, tumors of the spinal cord or brain are found in the patient.
Numbness in various parts of the body is typical of the onset of multiple sclerosis. This is a disease of autoimmune origin. When it occurs, the body produces antibodies to the nerve sheath, an inflammatory reaction develops, followed by damage to the nerve fiber, replacing it with scar tissue.
Most often, the patient is initially concerned about weakness in the legs, back pain, tingling in the limbs, blurred vision, and dizziness are also possible. As the disease progresses, muscle spasms are observed, making it difficult to walk, the functioning of the intestines and bladder is disrupted, and problems with swallowing food arise.
Causes
In modern medicine there are physiological and pathological provoking factors. The first are related to:
- Staying in one position for a long time. This worsens blood circulation, pinches nerves, and causes spasm.
- Incorrect body position in sleep. If the pillow is too high or completely absent, the blood supply to the brain is worsened. As a result, dizziness begins and the back of the head goes numb.
- The position of the body in space changes sharply. For this reason, vascular spasms occur.
- Hypothermia.
- Stressful situations.
When signs of numbness and tingling do not disappear within 15 minutes and recur from time to time, you need to contact a specialist to determine the cause.
Pathological factors affecting the development of this condition include:
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Trauma.
- Pinched nerves.
- Problems with blood supply.
- Tumors.
In 80% of examples, numbness is caused by the following diseases:
- Osteochondrosis.
- Hypertension.
- High ICP,
- Neuralgia.
If the back of the head goes numb: reasons
When the back of the head goes numb, most often the cause should be sought in the cervical spine. This is typical for infringement and/or irritation of the 2nd and 3rd roots of the spinal cord. They exit through a narrow intervertebral foramen, pressure is exerted on it by bony protrusions or congested veins due to obstruction of blood outflow. The most common disease with radicular syndrome is osteochondrosis.
Prerequisites for infringement also become:
- decreased height of intervertebral discs and their hernial protrusion;
- violation of the shape of the arcuate processes (congenital or after injury);
- vertebral displacement due to instability;
- excessive stress on the spine;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- obesity;
- hypothermia;
- bone abnormalities (for example, an accessory growth or a narrowed foramen).
Numbness in the back of the head can also be caused by rarer causes:
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- infectious inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord (spinal meningitis);
- osteomyelitis (bone suppuration) of the spine;
- tumor of the spinal cord or root, vertebra.
Some patients experience headaches due to high blood pressure. This can be explained by the fact that the arteries become tense, compress the veins and venous outflow becomes difficult. This leads to irritation of the spinal root. Typically, such symptoms develop with a long course of hypertension and widespread atherosclerosis.
What diagnostic methods will help determine the cause of numbness in the back of the head?
Numbness in the back of the head (the causes of the disorder must be determined to select the correct treatment), which occurs rarely and goes away quickly, should not be a cause for concern. But if the attacks are frequent and last more than 15 minutes, you need to visit a doctor and undergo an examination.
To make a diagnosis, it is recommended to:
- blood test. The study helps identify iron and vitamin B12 deficiency, which is the cause of poor circulation;
- X-ray, MRI in order to identify spinal deformities and other pathologies in which nerve endings are pinched;
- electroneuromyography , which allows you to determine the location of damaged nerve fibers and identify neuropathy;
- Ultrasound and Dopplerography to detect vascular pathologies.
Other tests may be needed depending on the presence of associated symptoms. If a person has suffered a skull injury, he will have to contact a surgeon and traumatologist. In case of pathologies of internal organs, a complete diagnosis of the body is necessary.
Why does my head go numb and dizzy?
Ready to go numb and dizzy with vascular diseases of the brain (for example, with dyscirculatory encephalopathy).
It is most often associated with atherosclerosis, hypertension, and diabetes, but in every third person with such symptoms, osteochondrosis and spinal instability in the cervical region are detected.
Risk factors include abnormal development of the vertebral artery, systemic vasculitis (inflammatory damage to blood vessels), heart rhythm disturbances, persistent or frequent hypotension (low blood pressure).
A pre-fainting state with darkening of the eyes, dizziness, ringing in the ears and a feeling of numbness in the scalp, hands and face occurs during panic attacks. They are one of the manifestations of neurosis, neurocirculatory dystonia. Sudden loss of sensation on only one side of the face and weakness of the limbs is dangerous, as it can be a harbinger of a stroke.
When urgent help is needed
Numbness of the head goes away on its own and quickly enough if it occurs after being in an uncomfortable position, but there are also symptoms for which you should immediately consult a doctor:
- sudden severe weakness;
- inability to move an arm or arm and leg on one side of the body;
- slurred speech;
- lag in movements on one half of the face;
- unbearable headache;
- sharp fluctuations in blood pressure;
- increased body temperature;
- loss or deterioration of vision and hearing.
Causes of headaches from cold
This type of headache occurs as a reaction to exposure to cold temperatures and can appear in the following situations:
- a significant decrease in air temperature;
- windy or frosty weather;
- swimming in cold water;
- cold (or contrast) shower;
- consuming cold foods and drinks that affect the palate and back of the throat (so-called “ice cream pain”).
Since the attack is caused by a change in vascular tone, it can be more protracted if you try to warm up with alcohol. Smoking also has a negative impact on the patient’s condition, provoking further development of headaches.
Diagnosis of the condition
To make a diagnosis, you need to contact a neurologist, he will conduct an examination and determine the localization of numbness using skin tests, then identify the circumstances of the complaints (for example, previous trauma, infection, hypothermia). Information about concomitant diseases (hypertension, diabetes) will be important. The rate of increase in symptoms allows you to narrow the direction of the diagnostic search. For example:
- instant numbness occurs with stroke and injury;
- during infection, symptoms increase from several hours to 2-3 days;
- weeks and months covering an increasingly larger area are typical for the tumor process, multiple sclerosis.
To clarify the affected area and the cause of numbness, the following is prescribed:
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- Ultrasound of head and neck vessels;
- neurophysiological testing (electroneuromyography) – determining the speed of propagation of a nerve signal;
- MRI of the brain;
- blood tests: general, biochemistry (renal tests, glucose, glycated hemoglobin, magnesium, calcium, potassium, sodium), level of vitamin B12, folic acid;
- test for thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland;
- immunological tests (for antibodies if infection is suspected, plasma protein electrophoresis).
The patient may need to consult an infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, oncologist, or surgeon.
Treatment methods for loss of sensation in the head
The scope of treatment for loss of sensation in the head completely depends on the disease. For example, for the most common disease – osteochondrosis, the following is prescribed:
- painkillers from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Diclofenac, Ketonal, Ibuprofen;
- relaxing muscles: Mydocalm, Sirdalud;
- decongestants: Hypothiazide, Lasix;
- stimulating metabolic processes: Rumalon, Actovegin;
- improving nerve functions: Milgamma, Berlition;
- facilitating venous outflow: Troxevasin, Aescusan;
- normalizing microcirculation (Trental, Xanthinol nicotinate);
- activating the transmission of nerve impulses: Neuromidin.
The required group of drugs is selected based on the prevailing symptoms. In addition to medications, it is recommended to wear a Shants collar to relieve the load on the spine. Physiotherapy helps well - in the acute stage, UHF, the introduction of Hydrocortisone with ultrasound, acupuncture, and during the recovery period massage and physical therapy are indicated.
A similar approach is used in the treatment of neuritis and neuralgia. If there is a tumor process, a herniated disc, or spinal instability, surgery is needed. It is also recommended if the full course of drug therapy is ineffective.
If the cause of numbness is cerebral vascular disease, then the following drugs are used:
- cholesterol-lowering drugs (Vasilip, Roxera);
- calcium channel blockers (Corinfar, Nimotop);
- improving cerebral blood flow (Pentilin, Bilobil);
- reducing blood viscosity (Curantil, Aspirin);
- protecting against lack of oxygen (Nootropil, Ceraxon);
- B vitamins (Neurobion, Milgamma).
Causes of numbness and methods of their treatment
Numbness of the head in the occipital area, which occurs regularly and does not go away for a long time, can be caused by certain diseases, for example, multiple sclerosis, neoplasms, osteochondrosis, arterial hypertension and others.
Depending on what caused the discomfort, the patient may be advised to:
- wearing a corset;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics;
- application of compresses;
- carrying out massage procedures.
Sometimes the rehabilitation process takes a long time, but it is necessary to complete the full course of treatment to avoid the development of complications, in some cases life-threatening. Situations that provoke discomfort should be avoided, as the intensity of symptoms may increase under the influence of external factors.
Migraine
Numbness in the back of the head can occur with migraine. It affects approximately 18% of women and 5% of men. The disease manifests itself as intense unilateral pain in the head.
The attacks are accompanied by additional symptoms:
- increased fatigue;
- nausea;
- feeling of squeezing of the head.
With physical activity, the condition worsens, relief occurs in darkness and peace. In a woman, the pathology may be associated with the cycle. Drug therapy can be targeted and preventive.
For short attacks of low intensity, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs will help relieve the condition:
- Naproxen;
- Ibufen;
- Ibuprofen.
If such drugs do not help or cannot be used due to the need for frequent use, then the use of triptans (Sumatriptan, Rizatriptan) is recommended. These drugs are distinguished by vasoconstrictor properties, relieve swelling and compression of brain tissue. It is recommended to alternate drugs from different groups, taking into account the severity of the attack. This prevents addiction and the development of complications.
For frequent, intense attacks that interfere with daily activities, a course of preventive therapy is prescribed. This will not get rid of the disease, but it will greatly improve the quality of life.
It is recommended to take drugs with different mechanisms of action:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (short-term, due to the risk of side effects);
- antidepressants that relieve stress, which can cause migraines.
It is important to improve your lifestyle. You should eliminate bad habits, stop eating certain foods that can provoke an attack, get enough sleep and avoid emotional overload.
High pressure
Arterial hypertension is a pathology that may not manifest itself for a long time. A person may suffer from increased fatigue, headaches, dizziness, and numbness in the back of the head. Some patients experience swelling in the face and legs that become numb to the touch.
A long-term disease, left unattended, leads to the development of various complications, for example:
- coronary heart disease;
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic stroke;
- narrowing of the renal artery;
- vascular dementia.
You can prevent further development of pathology by changing your lifestyle. The patient should lose excess weight, stop drinking alcohol, reduce salt intake, avoid stress, and move more. If such measures do not help, it is necessary to take antihypertensive drugs (Berlipril, Captopres, Anaprilin). Folk remedies (motherwort, lemon balm, peony, hawthorn) will help improve your condition.
You will have to take medications for high blood pressure for life. But in some cases, even high doses of drugs do not give the desired effect, so when diagnosing pathology, it is important to establish the specific cause of the disorder. After its elimination, the condition returns to normal without the use of drugs.
VSD
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is not an independent disease. This is a multi-symptom syndrome that manifests itself as malfunctions in various organs.
Signs of the disease are varied. They can appear alone or in combination with other disorders. A person may suffer from dizziness and ear congestion. Blood pressure often increases or decreases, blood flow is disrupted, and the head goes numb, including in the back of the head.
There is no general treatment plan for VSD. To improve a person’s condition it is recommended:
- avoid stress;
- take vitamins;
- attend physical therapy sessions;
- swimming, walking, doing exercises.
Meningeal syndrome
This pathology is characterized by the appearance of a complex of symptoms indicating damage to the cerebral membranes of the brain. The patient may have numbness on both sides of the head or the back of the head.
In addition, the patient suffers from:
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- photophobia;
- brief unconsciousness.
Stiffness is felt in the cervical region, and it is difficult for the patient to tilt his head. But at the same time, the movement to the sides is not disrupted.
Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of the disease. After this, all clinical manifestations disappear. If the pathology is caused by bacteria, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used. If the disease is of viral origin, the patient is prescribed antiviral drugs, and if it is fungal, antimycotics are prescribed. To prevent the development of cerebral edema, the use of diuretics and glucocorticosteroids is recommended.
Symptomatic therapy:
| Symptom | Group of drugs | Titles |
| Hyperthermia | Antipyretics |
|
| Arterial hypertension | Antihypertensive drugs |
|
| Vomit | Antiemetics |
|
| Psychomotor agitation | Psychotropic drugs |
|
Fever
At high temperatures, in addition to headaches, other symptoms appear. The patient may have numb skin in the back of the head and muscle stiffness.
An increase in temperature may be caused by:
- infectious diseases;
- autoimmune pathologies;
- tumors;
- increased activity of the thyroid gland;
- tissue damage;
- heat stroke.
To eliminate the symptom, it is necessary to cure the underlying disease. Antipyretics (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen) are used as symptomatic therapy.
Osteochondrosis
With this disease of the cervical spine, the functionality of the intervertebral discs is lost. Due to the fact that nerve endings and vessels are pinched, blood flow and innervation of the nervous system are disrupted.
The disease manifests itself:
- numbness in the back of the head;
- dizziness;
- pressure surges;
- blurred vision;
- headache.
Numbness in the back of the head, the causes of which are associated with osteochondrosis, can be easily eliminated with the help of means that normalize blood flow.
Patients are also recommended to use:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They can be used topically (ointments, gels) to eliminate pain and inflammation (Diclofenac, Finalgon);
- steroid drugs in the form of intramuscular injections;
- muscle relaxants to eliminate muscle spasms (Mydocalm);
- B vitamins to improve metabolic processes;
- novocaine blockades for severe pain.
Stroke
Acute cerebrovascular accident occurs as a result of blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain. In this case, the patient may experience numbness not only in the back of the head, but also in the entire head and limbs.
The condition may also be accompanied by:
- motor disorders;
- loss of sensation in some areas of the body;
- speech disorders;
- severe headache;
- vomiting;
- confusion, loss of consciousness;
- complete or partial paralysis.
If you have at least several of the listed symptoms, you must call an ambulance. Before her arrival, the patient should be placed comfortably so that the head is slightly elevated. Treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting, where the patient must be taken as quickly as possible.
Atherosclerosis
Numbness of the back of the head can also be observed with atherosclerosis. This is a pathology characterized by the deposition of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels that interfere with normal blood circulation. Due to insufficient blood supply, the nutrition of body cells is disrupted.
The plaque can break away from the wall of the vessel, which leads to blockage. In this case, blood stops flowing to the brain, the patient suffers from tinnitus, dizziness, loss of sensitivity in the back of the head or other parts of the head. Vision may decrease, memory may deteriorate, and in the most severe cases, dementia may develop.
For the purpose of treatment, it is necessary to adjust your lifestyle. The patient must adhere to a diet limited in fat, be physically active, give up bad habits, avoid stress and cure chronic diseases.
Among medications, doctors usually prescribe lipid-lowering, antiplatelet, antihypertensive and antioxidant drugs, and drugs that improve microcirculation. The treatment is long-term, success depends on the stage at which it began. In some cases, surgical therapy is necessary.
Avitaminosis
Another reason for loss of sensitivity in the back of the head is a lack of B vitamins and some minerals (calcium, magnesium, potassium). Due to a deficiency of such substances, nerve cells and fibers are damaged, which leads to muscle spasms and a feeling of numbness.
Self-massage of the cervical region or a light warm-up helps to get rid of unpleasant sensations. To make up for the lack of necessary components, you first need to take an analysis to determine their level. After this, the doctor will recommend taking vitamin complexes, as well as probiotics for better absorption of nutrients. The patient will have to give up alcohol and smoking, sweets, fried foods and include more vegetables and fruits, dairy products, vegetable oils, and nuts in the diet.
Traumatic brain injuries
A common cause of head pain and numbness in various parts of the head is traumatic brain injury. You can get hurt in an accident, at a sports competition, or in an emergency at work.
In addition to throbbing pain and numbness, injuries are accompanied by other symptoms:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- vomiting;
- darkening of the eyes.
To eliminate pain, the patient is recommended to take painkillers, for example, Analgin, Sedalgin.
Multiple sclerosis
In multiple sclerosis, nervous tissue is replaced by connective tissue. This leads to a feeling of numbness in the head, including in the back of the head, loss of sensitivity in the limbs, decreased muscle tone, and impaired coordination of movements.
To make a diagnosis and select a treatment regimen, you must contact a neurologist. In the acute stage of the disease, the doctor will recommend taking Cortisone to reduce inflammation. During the period of remission, immunosuppressive drugs (Azathioprine, Methotrexate) are prescribed.
Brain tumors
When tumors of the head or spine grow, nerve endings and blood vessels are compressed. The patient suffers not only from numbness, but also from intense pain.
The condition is aggravated by other symptoms:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- impaired coordination;
- memory impairment.
Oncologists and neurosurgeons treat such pathologies.
The fight against neoplasm is carried out with the help of:
- surgical intervention;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy.
Pinched nerves of the head
In addition to numbness, pinching of the occipital nerve is accompanied by sharp pain when turning the head, pain in the neck, and intolerance to bright light. The cause of the disease is inflammation of surrounding tissues. If discomfort occurs, you should contact a neurologist. After the examination, the doctor will prescribe glucocorticoids Kenalog and Metipred. For severe pain, novocaine blockades are prescribed.
Hypothermia
Hypothermia is more likely to affect children or older people. Due to slow blood circulation, numbness occurs in the back of the head or another area of the head. Unpleasant symptoms are aggravated by hunger or overwork, in patients with weak immunity, vascular diseases, mechanical damage, bleeding.
First of all, in case of hypothermia, it is necessary to stop the loss of heat. The victim must be covered with a blanket, warmed with a heating pad or with your own body, and rub the frostbitten areas. Using a hot bath or shower, rubbing the patient with snow, or giving alcohol to the patient is strictly prohibited. After tissue sensitivity returns, the person needs to be given pain medication. In case of severe hypothermia, you should seek medical help.
Stress
Under the influence of stress, the body tenses, which can lead to numbness on the right or left side of the head, back of the head, lower jaw, and lips. In addition, with severe emotional shock, the brain suffers due to vascular spasm and insufficient blood supply, which can also cause unpleasant symptoms.
To prevent unpleasant consequences, the stress factor should be eliminated first. You can also improve your condition with the help of physiological procedures, psychological correction, taking sedatives (Persen, Alora, Novopassit), and sedative decoctions. In extreme cases, antidepressants and tranquilizers are prescribed.
Numbness in the occipital area sometimes indicates the development of some disease in the body. It is necessary to be wary if the discomfort does not go away for a long time and is accompanied by additional symptoms, for example, lightheadedness, nausea, impaired motor functions or speech.
Such signs are a reason to seek medical help to determine the cause of the deterioration of the condition. You cannot delay your visit to the doctor, as some diseases and conditions can even threaten the patient’s life.
Prevention measures
To reduce the risk of spinal diseases, it is recommended:
- monitor your posture while working, change body position;
- do therapeutic exercises daily;
- If you have pain or discomfort in the neck, consult a doctor immediately;
- undergo preventive courses of massage, physiotherapy, and take medications if necessary;
- Avoid hypothermia and sudden movements.
Vascular complications occur less frequently in patients who maintain blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol within normal limits. It is also important to quit smoking, alcohol abuse, and reduce body weight if you are obese.
The scalp becomes numb most often due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The cause may be inflammation, pinched nerves, blockage or spasm of the artery supplying the brain (stroke, migraine). Numbness can be a consequence of injury, infection, and less commonly a tumor or multiple sclerosis.
Diagnosis of cold headaches
Diagnosis of this disease involves differentiating headaches associated with cold stimuli from other types of headaches. This diagnosis is established in the presence of the following symptoms:
- the pain is acute, non-pulsating and short-term;
- the effect of the cold stimulus was confirmed;
- pain occurs immediately and only under the influence of an irritant;
- the attack stops within a few minutes after the stimulus is removed.
It is also recommended to undergo examination by an allergist, who will conduct the necessary research to determine the presence or risk of an allergy to cold.