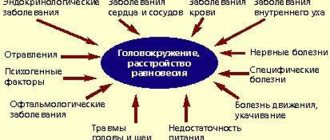
Causes of the problem
“There are a number of major nerve clusters that connect your brain to different parts of your face and head. When nerves are inflamed, compressed, or damaged, numbness can occur. Reduced or blocked blood supply can also cause numbness,” says Irina Ryabokon.
The reasons why numbness of the head may develop, says the neurologist, are varied. So, for example, if such a symptom appeared due to a cold, headaches or because of an uncomfortable sleeping position, then there is no need to worry. But if a person suffers from some illness, takes a number of medications, or has suffered an injury, you need to be wary. Head injuries or concussions can cause numbness if nerves are damaged.
“By the word “numbness,” which actually means loss of sensitivity, patients often understand various sensations, such as crawling, burning, tingling (so-called paresthesia). To find out the cause of such sensations, it is extremely important to determine what exactly is meant - a decrease, lack of sensitivity or paresthesia,” explains Ryabokon.
Sclerosis, but not that one. By what signs are multiple pathologies recognized? Read more
The neurologist notes that with paresthesia, sensitivity can be preserved, sometimes even enhanced. Less common are situations where paresthesia is combined with a violation of sensitivity in this area (sense of touch, pain sensitivity - injection, feeling of vibration, etc.).
“Paresthesia (without loss of sensitivity) can have numerous causes, and the cause cannot always be determined. For example, they may be side effects of certain medications or associated with severe anxiety or anxiety. Especially when the localization of sensations changes,” notes the neurologist.
But impaired sensitivity in a certain area of the head or face requires a detailed examination. “The cause may be vascular disorders, nerve damage, or brain diseases. The unilateral and persistent nature of the disorders requires seeing a doctor and a detailed examination,” she says.
Quite serious illnesses can also cause this symptom. “Diabetic neuropathy can cause permanent nerve damage. Numbness is also a common symptom of multiple sclerosis, a chronic condition that affects the central nervous system,” says the specialist.
In addition, in the list of what numbness in the head may indicate, the following items:
- allergic rhinitis;
- cold;
- sinusitis;
- brain tumor;
- arterial hypertension;
- stroke;
- epilepsy attacks;
- use of prohibited substances;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking anticonvulsants.
“You should see a doctor immediately if head numbness occurs after starting medication,” says the neurologist. The specialist also notes that the list of reasons for the feeling of numbness in the head can be supplemented with headaches and cluster pains (severe pain syndrome), tension pain, migraines, encephalitis, Lyme disease, shingles, as well as dental infections.
“Numbness in the head sometimes occurs only on one side. Or only the temple or back of the head may suffer. Typically, such conditions signal the following diseases: Bell's palsy, infections, acute migraine,” the doctor notes.
My head hurts! When to take your child to a neurologist Read more
Diagnostics
What should a doctor do when determining your problem? First, they will take a general blood test. This will help determine if you have iron deficiency anemia or Addison-Birmer disease caused by a lack of vitamin B12.
The next possible analysis is electroneuromyography
. It will help identify which nerve is damaged. Also, with the help of such diagnostics, it is possible to identify diseases such as neuropathy and carpal syndrome.
X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging are also used to detect bone displacement, which in turn can cause pinched nerves and, as a result, numbness of the head.
The doctor can also use ultrasound to detect abnormalities in the vascular system and circulatory disorders of the vertebrobasilar and carotid arteries.
In some cases, other tests may also be needed, as well as consultation with other doctors. For example, if the cause of hypoesthesia is a traumatic brain injury, you will be referred to a traumatologist and surgeon.
The choice of treatment method depends on the underlying causes of hypoesthesia. Treatment is carried out only after a comprehensive diagnosis and full confidence in the diagnosis. Complete rehabilitation of the body can take a long time, but it is better to complete the full course of treatment in order to avoid serious complications that are dangerous to your life.
If the facial part of the head is numb, you should be careful when eating and near heat sources, since sensitivity is impaired and you can accidentally injure the oral cavity or get burned.
It would be a good idea to think about in what situations numbness occurs most often. And try to avoid this, since external factors can also influence the appearance of hypoesthesia.
If the back of the head goes numb, then most likely it is caused by a common cold and does not pose a serious danger if treated correctly. It can also appear due to nervousness. And if you are sure that you just got a cold, then you can deal with this problem at home. You can make a warm compress or use a cream or ointment with a warming effect.
And remember that self-medication can sometimes harm your health.
. Be careful and very attentive to some recipes from your friends or found on the Internet. You may be allergic to some products, and some may worsen your condition. Also, various conspiracies and similar procedures will not be able to help you; you will only waste your time and money.
In any case, in order to correct the problem and not harm yourself even more, the best solution would be to seek help from a specialist. If you notice symptoms of a serious illness, immediately go for examination. Don’t be afraid, as modern diagnostic methods are completely harmless. A disease detected in time is much easier to eliminate without much harm to the body and at minimal cost. Good health to you!
Various unpleasant sensations that occur during the day can interfere with your ability to perform your work duties, household or household chores. One of the common phenomena is when your head hurts and goes numb.
In some cases, this manifestation may be harmless
. For example, at moments of awakening from sleep, when the sleeper’s head was in an uncomfortable position. This leads to numbness in part of the head, with a characteristic aching pain. This condition is harmless and is transitory as soon as blood circulation normalizes. In this case, it is easy to quickly get out of a painful state; it is enough to massage the numb area, accelerating the normalization of blood circulation. However, the painful condition of the head with numbness does not always have harmless causes.
If this condition occurs almost every day, then you should think about going to the doctor.
. What if this is some kind of pathology that threatens the body with serious problems.
Physiological state
“Often a feeling of numbness in the head occurs during sleep. When you wake up with a numb head, it may be a sign that you are sleeping in a position that restricts blood flow to your head,” notes the neurologist. Here you can try to cope with the problem of sleep correction. “In this case, try sleeping on your back or side, placing your head and neck in a position that will not cause discomfort. If you are lying on your side, try putting a pillow between your knees, this will help straighten your back,” advises Irina Ryabokon.
If the back of the head goes numb: reasons
When the back of the head goes numb, most often the cause should be sought in the cervical spine. This is typical for infringement and/or irritation of the 2nd and 3rd roots of the spinal cord. They exit through a narrow intervertebral foramen, pressure is exerted on it by bony protrusions or congested veins due to obstruction of blood outflow. The most common disease with radicular syndrome is osteochondrosis.
Prerequisites for infringement also become:
- decreased height of intervertebral discs and their hernial protrusion;
- violation of the shape of the arcuate processes (congenital or after injury);
- vertebral displacement due to instability;
- excessive stress on the spine;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- obesity;
- hypothermia;
- bone abnormalities (for example, an accessory growth or a narrowed foramen).
Numbness in the back of the head can also be caused by rarer causes:
- syphilis;
- tuberculosis;
- infectious inflammation of the membranes of the spinal cord (spinal meningitis);
- osteomyelitis (bone suppuration) of the spine;
- tumor of the spinal cord or root, vertebra.
Some patients experience headaches due to high blood pressure. This can be explained by the fact that the arteries become tense, compress the veins and venous outflow becomes difficult. This leads to irritation of the spinal root. Typically, such symptoms develop with a long course of hypertension and widespread atherosclerosis.
How can a neurologist help?
If you have such a symptom and exclude physiological reasons for its development, you should visit a specialist. You should contact a neurologist. He will examine you and ask about your symptoms and medical history. He may also order one or more of the following tests to help determine the cause of the numbness in the head: blood tests, nerve conduction studies and electromyography, MRI, CT scan, nerve biopsy.
Since quite a few conditions cause numbness in the head, it may take some time to determine what exactly is causing the characteristic symptoms. You should not leave the situation unattended, because you can waste time, and then you will have to undergo treatment longer and more difficult.
There are contraindications. Be sure to consult your doctor.
A brain tumor
Description
Pathology is
a neoplasm of constantly dividing cells
.
Such tumors are malignant and cause problems for other organs. Localization of headaches
The syndrome is characterized by a compressive effect. The location of the pain is determined by the location of the tumor.
Additional symptoms
- Dizziness.
- Numbness of the occipital region due to increasing compression of the cerebellum by the growing tumor.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Loss of coordination.
- Significant memory impairment.
Which specialist will help?
You should contact an oncologist and neurosurgeon.
Diagnostics
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Positron emission tomography.
- CT scan.
Treatment course
There are several directions in the fight against tumors. Among them, the most effective methods stand out:
- Surgical intervention.
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy.
Prevention measures
To reduce the risk of spinal diseases, it is recommended:
- monitor your posture while working, change body position;
- do therapeutic exercises daily;
- If you have pain or discomfort in the neck, consult a doctor immediately;
- undergo preventive courses of massage, physiotherapy, and take medications if necessary;
- Avoid hypothermia and sudden movements.
Vascular complications occur less frequently in patients who maintain blood pressure, blood sugar and cholesterol within normal limits. It is also important to quit smoking, alcohol abuse, and reduce body weight if you are obese.
The scalp becomes numb most often due to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. The cause may be inflammation, pinched nerves, blockage or spasm of the artery supplying the brain (stroke, migraine). Numbness can be a consequence of injury, infection, and less commonly a tumor or multiple sclerosis.
When urgent help is needed
Numbness of the head goes away on its own and quickly enough if it occurs after being in an uncomfortable position, but there are also symptoms for which you should immediately consult a doctor:
- sudden severe weakness;
- inability to move an arm or arm and leg on one side of the body;
- slurred speech;
- lag in movements on one half of the face;
- unbearable headache;
- sharp fluctuations in blood pressure;
- increased body temperature;
- loss or deterioration of vision and hearing.
Possible diseases
Numbness of the nose can be a symptom of serious diseases. Let's consider the most common pathologies that manifest themselves as paresthesia (sensory dysfunction).
Vascular diseases
Impaired local circulation can occur when the diameter of the vessel is reduced by atherosclerotic plaques, as well as due to compression of the vessel from the outside, for example, by a tumor. An aneurysm (local dilation of a vessel with thinning of its wall) is also a serious threat.
Depending on the location of the area with impaired blood flow, a person may be concerned about:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- numbness of parts of the body, face;
- movement disorder;
- changes in speech, auditory, visual function;
- swallowing disorder.
Therapeutic tactics are determined exclusively by the doctor based on the clinical picture and instrumental examination data (computer, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound).
Drug treatment may include vascular, neurometabolic, and decongestant drugs. Do not forget about physiotherapeutic procedures that enhance the effect of medications and restore lost functions.
According to indications, surgical intervention may be performed.
Osteochondrosis
The development of osteochondrosis is based on degenerative processes in the intervertebral discs, as a result of which their shape changes and the ability to perform physiological functions is lost. There are several forms of the disease. Paresthesia in the nasal tip is observed when the cervical vertebral zone is affected. Among the causes of the disease it is worth highlighting:
- traumatic injury;
- genetic predisposition;
- heavy weight;
- metabolic disease;
- chronic infectious diseases;
- age-related processes;
- heavy physical labor with stress on the spinal column.
Intervertebral disc degeneration is predisposed by:
- poor nutrition;
- "sedentary work;
- poor posture;
- frequent stress.
The disease manifests itself symptomatically:
- soreness in the back of the head, cervical area. The pain syndrome is characterized by an aching character;
- muscle weakness, which makes it difficult for a person to turn his head;
- neck crunch;
- headache;
- dizziness;
- paresthesia in various parts of the body, face, from which a person may notice that the tip of the nose is numb. The symptom appears as a result of compression of the nerve.
You can often notice a decrease in visual acuity, disruption of the heart and respiratory organs.
With cervical osteochondrosis, a violation of blood flow in the vessels of the brain is often diagnosed.
Untreated osteochondrosis can be complicated by impaired blood flow in the cerebral vessels, due to which:
- migraine occurs;
- blood pressure increases;
- Vascular dystonia develops.
Compression of the spinal cord increases the risk of death. In this case, surgical intervention is required.
Therapeutic tactics for the disease include:
- bed rest;
- medicinal assistance;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- dietary nutrition;
- gymnastics;
- folk recipes.
Drug therapy involves prescribing drugs to improve microcirculation, reduce pain, provide nutrition to nerve endings, and slow the progression of degenerative processes. From the table below you can get an idea of the effect of the drugs.
Treatment
Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of the numbness.
Diagnosis of pathology may require computed and/or magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, and possibly some other methods.
If the tip of the nose becomes numb due to the fact that the person slept in an uncomfortable position, after waking up and restoring blood circulation, the numbness goes away on its own.
After being in the cold for a long time and returning to a warmer room, it is recommended to stop smoking and drinking alcohol for a while, and you should not try to warm frozen and numb areas of the body with hot water or intense rubbing. In such a situation, you can apply a warm towel (for example, heated with an iron) to your nose.
If you have an allergic reaction to cold, before going outside in the cold season, it is recommended to apply a protective cream to exposed areas of the body and avoid hypothermia.
For the treatment of pathological conditions that may be accompanied by numbness of the tip of the nose, the following can be used:
- decongestants;
- neurometabolic stimulants;
- anticoagulants;
- beta blockers, etc.
Patients are often prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, exercise therapy, diet, bed rest may be required, and some patients may require surgical treatment.