MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast is a magnetic resonance examination of the most important endocrine gland of the human body, due to its small size, the use of contrast agents is required. Contrast agents for MRI contain nanoparticles of gadolinium, a metal that can increase the sensitivity and information content of the method. Once in the blood, gadolinium is evenly distributed throughout all tissues of the human body. Inflammatory processes, tumors and other anomalies, on the contrary, lead to local accumulation of contrast, which is why this area stands out in the images, facilitating diagnosis.
Where is the pituitary gland located?
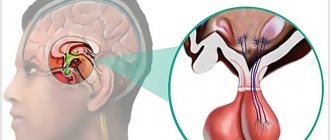
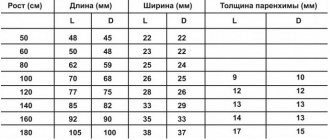
The pituitary gland is the most important organ of the endocrine system (gland), which produces a number of biologically active substances (hormones) that regulate the balance of energy, nutrients and minerals, cell division, sexual functions and reproduction, metabolism and many other aspects of the normal functioning of the human body. This is hard to believe, especially considering the small size of the pituitary gland - only 13 mm in length, 5-6 mm in thickness (the size of a pea or bean). The mass of the pituitary gland does not exceed 0.5 grams.
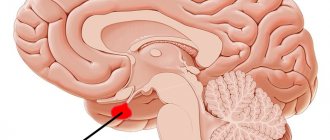
The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, inside the skull, in an area called the sella turcica (due to the shape of the bones, which actually resemble a saddle). The only method for diagnosing pituitary gland diseases that allows obtaining detailed and high-quality images is magnetic resonance imaging. MRI of the pituitary gland is always performed with contrast - this allows to increase the accuracy of diagnosis and the information content of the images, which is important, given the miniature size of the organ.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the pituitary gland
Make an appointment
The pituitary gland is a small gland weighing less than a gram, which is located on the lower surface of the brain, on a special bony process shaped like a sella turcica. The hormones that the pituitary gland secretes are at the very top of the hierarchical ladder of hormones, leading the entire work of the body’s endocrine system. Therefore, clinical symptoms when the function of the pituitary gland deviates from the norm are as diverse as the functions performed by the endocrine system are diverse.
- Identified hormonal disorders: changes in the level of hormones secreted by the pituitary gland - prolactin, somatotropic hormone (growth hormone), ACTH, which determines the functioning of the adrenal glands, TSH, which controls the thyroid gland, as well as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulate the production of sexual hormones.
- Menstrual irregularities and infertility in women, milk production outside the period of breastfeeding (galactorrhea).
- Deterioration of sexual function and enlargement of the mammary glands (gynecomastia) in men, suspicion of testicular tumors.
- Sharply increased urine output, suspicion of diabetes insipidus, “unreasonable thirst”
- Very small, or vice versa, very tall, obese. Noticeable enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, and lower jaw.
- The appearance or intensification of headaches, severe dizziness
- Decreased visual acuity, especially if vision cannot be corrected with glasses, narrowing of visual fields, often detected when obtaining a driver’s license; This occurs because the enlarged gland can put pressure on the optic nerves.
If you have any of the symptoms, your doctor (neurologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, andrologist, ophthalmologist, therapist) will prescribe an examination for you. The most common pathology of the pituitary gland is an adenoma - an enlargement of the gland by more than 10 mm in vertical size and, as a result, increased production of regulatory hormones. With proper management, pituitary adenoma is benign and does not require surgical treatment. When diagnosed in time, the disease is successfully cured. The function of the pituitary gland is easy to assess using hormones, but determining the size of the gland through a dense skull is difficult, so studying the condition of the pituitary gland presents significant difficulties. The absolute method of choice for making a correct diagnosis is MRI of the brain and pituitary gland. This study allows you to clearly see the pituitary gland, determine its size and connection with other parts of the brain.
MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast.
When performing MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast, the information value of the study increases many times. The use of contrast allows not only to clarify the location and size of the formation, its intimate relationship with other structures, but also to obtain objective information about its blood supply, which is often a key point in deciding the nature of the pathology and the need for surgery. Contrast is injected into a vein immediately before the examination procedure. A study without contrast does not require special preparation.
The duration of an MRI study of the brain and pituitary gland does not exceed 25 minutes on a high-field MRI of 1.5 Tesla; when using contrast - no more than 40 minutes. If the fullness (power) of the MRI machine is below 1-1.5 Tesla, then the image quality may not be sufficient to see subtle changes; if above 1.5 T, then the examination time increases significantly without a clear advantage in quality. The current opinion about the harmfulness of MRI is unfounded - for more than a quarter of a century of the history of the use of magnetic resonance, no negative effects on the body have been identified. The absolute harmlessness of the method allows it to be used repeatedly and control the treatment process.
Indications and contraindications for MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast
Indications for the use of contrast-enhanced MRI of the pituitary gland:
- pituitary tumors/cysts of various origins;
- metastases to the pituitary gland;
- empty sella syndrome;
- hypofunction of the pituitary gland (decrease in the levels of pituitary hormones - prolactin, somatotropin, TSH, LH, FSH, etc.);
- hyperfunction of the pituitary gland (increased levels of pituitary hormones);
- apoplexy (hemorrhage) in the pituitary gland, pituitary necrosis (Sheehan syndrome);
- Itsenko-Cushing's disease;
- other endocrine disorders associated with the functional activity of the pituitary gland.
Symptoms in which an MRI of the pituitary gland is recommended:
- headache;
- decreased visual acuity (loss of visual fields, double vision, distortion of visible objects);
- excessively short or high stature inappropriate for age, delayed physical development;
- constant thirst with increased fluid consumption and frequent urination;
- infertility, both male and female;
- impotence in men, irregularities or absence of the menstrual cycle in women;
- obesity.
Indications for the study
As a rule, pituitary adenoma is detected on MRI during a comprehensive diagnosis of the brain. In most cases, this type of study is prescribed in the following cases:
- Suspicion of a concussion after previous injuries;
- Unreasonable headache that does not go away even after taking medications;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Disorientation in space;
- Loss of consciousness, presyncope;
- Vomiting and nausea;
- Facial asymmetry;
- Impaired oculomotor function (ophthalmoplegia) and double vision (diplopia);
- Decreased visual acuity for no apparent reason;
- Loss of body weight;
- Increased irritability.
Also, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain may be prescribed if surgical intervention is necessary.
Contraindications to contrast-enhanced MRI of the pituitary gland
MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast is contraindicated:
- patients who have metal foreign bodies in their bodies (iron filings in the eyes, steel clips on blood vessels, orthopedic structures, etc.) – the metal heats up and can move from its place under the influence of magnetic fields;
- patients with pacemakers, defibrillators, neurostimulators, cochlear implants, insulin pumps - magnetic fields can damage complex electronics;
- pregnant women in the first 13 weeks of pregnancy - MRI is not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy without good reason;
- children under 5 years of age - MRI in children under 5 years of age is performed in specialized hospitals under anesthesia and medical supervision;
- patients with severe claustrophobia - people with a fear of closed spaces often cannot remain calm and still during an MRI examination.
In addition, MRI diagnostics may be hampered by excess weight (more than 130 kg) and circumference (more than 150 cm in girth) of the body. Patients with such data do not physically fit in the magnetic resonance imaging machine.
Contraindications
The doctor may refuse to conduct the study in the following cases:
- If the patient has a pacemaker installed or there are non-removable metal structures in the body.
- During pregnancy, especially in the first trimester. In this case, experts recommend other diagnostic methods.
- In case of deviations that prevent the patient from controlling his own body and maintaining a motionless state.
- With a severe form of claustrophobia.
Often, brain diagnostics using magnetic resonance imaging is carried out with additional contrast. However, contrast agents are prohibited for pregnant and lactating women, those with renal and liver failure, and those who are allergic to the substances used.
Before the examination, you should definitely consult with your doctor and exclude contraindications.
Preparing for MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast
Magnetic resonance imaging of the pituitary gland with contrast agents is performed without any preliminary preparation. The study can be carried out at any time convenient for the patient. The main condition for safe MRI is the absence of foreign metal objects on the patient’s body. Magnetic fields generated during the examination can lead to heating of jewelry, piercings, and metal clothing fittings, with the risk of burns. It is strictly prohibited to carry mobile phones, electronic gadgets, credit and other magnetic cards, storage media, external batteries, etc. Otherwise, injury or burns may occur. The patient can leave anything unnecessary in the storage room.
Contrast drugs very rarely cause side effects - the most common of them is a mild allergy in the form of a small rash and itching on the skin. Severe allergic reactions to contrast are rare and also serve as a contraindication for its administration. In such cases, the study is performed without contrast.
How often can I have an MRI with contrast?
When the patient did not have allergies or other reactions when the dye was injected, then brain tomography using contrast can be performed many times. Often, only one session is enough to provide a medical report. Repeat testing is usually necessary to monitor the effectiveness of therapy. The clinics presented on our search service use various contrast amplifiers: “Gadovist”, “Primovist”, “Omniscan” and others. Individual intolerance to the presented remedies is rare, so scanning with an additional booster is harmless.
How does a contrast-enhanced MRI of the pituitary gland work?
Magnetic resonance imaging is performed on an outpatient basis, using special equipment - an MRI scanner. The research setup is a large cylindrical block with a tunnel equipped with a special bed on which the patient lies during the examination. A lattice structure resembling a helmet is installed around the patient’s head - this is an additional coil that increases the quality and clarity of images of the brain and pituitary gland.
Before the examination, the patient is asked to wear special headphones - they protect the ears from the noise that occurs during the operation of the tomograph. Headphones can transmit music, which helps the patient relieve stress, and also serve to communicate with the operator. To make an emergency call to the operator, the patient can press a pear-shaped button, which is in his hands at all times during the examination.
The duration of an MRI of the pituitary gland is approximately 30 minutes. In the first half, the study is performed without contrast. Then, 15 minutes after the start of the procedure, the nurse administers an intravenous contrast agent, after which the study is repeated with contrast enhancement.
All that is required of the patient during diagnosis is to lie down, remaining calm and still. MRI is an absolutely safe and painless procedure that is not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations. Slight discomfort may occur in people prone to anxiety and panic attacks due to the limited space of the tunnel.
After completing the examination, you must wait for the images to be decrypted (usually this takes a maximum of 15-30 minutes). The images themselves are recorded free of charge on a CD and sent to the patient along with a written report from the radiologist. If desired, you can record pictures on a flash drive or print them on film.
MRI of the head with or without contrast?
The differences between diagnostic procedures are the quality of the images and the information content of the data, since when using a coloring component, the level of detail in the image increases, which allows you to carefully examine the anomalous area. MRI according to the native protocol is performed without contrast agents. Before a routine tomography, the patient does not need to undergo special training. An examination with an additional amplifier takes longer than a classic MRI due to the fact that after completion of the survey screening, another 15 minutes are needed to carry out the procedure in “contrast” mode.
Another difference between diagnostics with and without contrast is pricing. Conventional tomography will cost less. The final cost of a scan with contrast agent depends on the amount of contrast agent injected. Its dosage is calculated for each patient individually. Doctors focus on the patient’s weight. Contrast is indispensable when diagnosing oncological pathologies.
Interpretation of the results of MRI of the pituitary gland with contrast
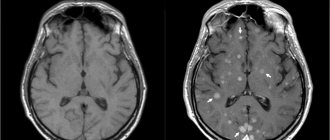
MRI results of the pituitary gland - a series of thin layer-by-layer images of the sella turcica area. Since the pituitary gland is the size of a pea, each section has a minimum thickness of 1 mm. The radiologist carefully examines each image, looking for deviations from the norm. Normal MRI picture of the pituitary gland: dimensions do not exceed 1-1.3 cm, absence of cysts, tumors and other heterogeneous inclusions, the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland are clearly distinguishable. When administered, the contrast is evenly distributed throughout the pituitary gland. In addition, the condition of the tissues surrounding the pituitary gland - nerve fibers, blood vessels and other anatomical structures - is described.
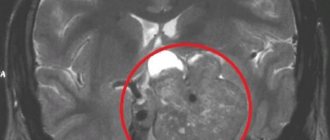
Local accumulation of contrast is the main sign of the presence of a pituitary tumor. Most often, doctors deal with so-called pituitary adenomas - these are hormonally active tumors that secrete pituitary hormones. An excess of certain hormones leads to endocrine diseases with corresponding symptoms.
Adenomas in the photographs look like formations in the pituitary tissue of arbitrary size, intensively accumulating a contrast agent. Moreover, in the absence of contrast, the tumor may not be visible - very small tumors or microadenomas can hardly be detected without contrast. This is why MRI of the pituitary gland is almost always performed with contrast enhancement.
Why is an MRI of the brain with contrast prescribed?
Tomographic diagnostics allows you to assess the condition of the head with high accuracy, as well as identify deviations of the central nervous system. Screening has high sensitivity, specificity and provides the most informative information about the diseases present in the patient. However, there are abnormal reactions, the diagnosis of which can be difficult even with tomographic examination. Usually these are neoplasms of a different nature or inflammatory lesions, represented by multiple or amyotrophic sclerosis. In such situations, scanning must be carried out in a special mode - with a contrast amplifier.
The mechanism of action of the coloring component lies in its ability to accumulate in areas of the brain where inflammation, tumors or other abnormalities are present. In this case, healthy structures practically do not absorb the additional amplifier. The contrast is based on the rare earth metal gadolinium. It is presented in the form of nanoparticles and is able to enhance the vibrations received by the MR device from soft tissue areas of the body. Areas with a high content of the coloring element, corresponding to a specific deviation, are highlighted in the images, accurately indicating the location, volume and shape of the violation.
The contrast agent highlights the characteristic features of the tumor or lesion, which facilitates evaluation and increases the accuracy of screening. Tomographic testing of the head is necessary if the doctor suspects the development of a tumor and demyelinating pathology. Some types of tomography are performed only with an additional intensifier, including MRI of the pituitary gland. But usually the patient is referred for a dye scan as part of a classic MRI brain scan.
What is MRI of the pituitary gland?
The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland located deep in the brain in an area called the sella turcica.
Despite its small size (on average 7-10 mm), the pituitary gland is a very important organ that produces a huge amount of hormones. This important endocrine gland produces substances that affect other glands, causing them to produce their own hormones. The pituitary gland can be compared to the command post for controlling the entire body.
Location of the pituitary gland
How is the examination carried out?
The CT machine consists of a sliding table and the tomograph itself. Before the procedure, the patient lies down on the table. Special belts and pillows are used to secure the body and provide comfort. Next, the work table is pushed into the tomograph ring. The radiologist leaves the room, turns on the machine and monitors the patient through a special window. The patient can report his feelings and well-being to the medical staff using voice communication. The CT procedure lasts approximately 15-20 minutes. After this, the radiologist evaluates the received images and begins to interpret them.
CT pituitary gland with contrast
If bone tissue is visualized quite well on CT images, then the structure of the soft tissue surrounding the pituitary gland can only be correctly assessed using contrast enhancement. To do this, before the CT scan, the patient is given intravenous auxiliary iodine-containing drugs. It is also possible that contrast is supplied to the patient’s blood throughout the entire scanning procedure (bolus injection). For this purpose, special devices called injectors are used.
There are a number of contraindications to the use of contrast enhancement:
- allergy to iodine-containing drugs;
- renal or liver failure;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diabetes.
CT pituitary gland
CT scan of the pituitary gland (with or without contrast) is a non-invasive diagnostic method for studying one of the glands of the endocrine system of the human body, as well as the tissues surrounding it. The pituitary gland is located in the brain. Its size varies from 15 to 17 mm in cross section, and its weight is approximately 1 g. Despite such a modest size, the pituitary gland secretes a huge amount of hormones, and a failure in its work always affects a person’s well-being.
What does a CT scan of the pituitary gland show?
With the help of CT, the pituitary gland can be seen in cross-section in various projections. The images assess the condition and structure of bone formations (for example, the sella turcica, located in close proximity to the gland), as well as soft tissues. The altered structure of bone formations indirectly indicates the occurrence of a space-occupying formation (tumor) in the area of the pituitary gland.
There are several options for changing bone structure:
- the sella turcica has increased;
- the processes and the back of the sella turcica were destroyed;
- The sella turcica was destroyed, as well as the bone tissue of the base of the skull.
The larger the tumor, the more clearly the destruction of bone tissue is visualized on CT images. In addition to the size of the tumor, it is important to determine its density, shape, number of nodes and exact location. All this can be assessed using computed tomography images of the pituitary gland.