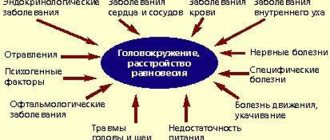
Causes of dizziness
- Overeating after a long break, leaving a strict diet or fasting.
- Food allergies can be caused by food additives, which are abundant in most foods, as well as sweets or protein foods.
- Reaction to foods containing the amino acid tyramine - chocolate, gourmet cheeses, overripe fruits, marinades, citrus fruits.
- Hypovolemia is a decrease in blood volume in the body. This condition is characterized by constant thirst, weakness, rapid heartbeat, blue skin, and dizziness.
- Dumping syndrome is a pathological condition caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain and heart, hyper- and hypoglycemia.
There are early and late dumping syndromes.
How does tachycardia manifest?
The state of the heart can be quickly determined by the heart rate (HR) - through the pulse, which can be easily felt in large peripheral arteries. Normally, its frequency coincides with the heart rate, since the pulse is the response of the arteries to the ejection of blood from the heart when it contracts. Indicators for a healthy person are 60–80 beats per minute. If your heart begins to beat faster, it may physically feel like it is jumping out of your chest.
However, this does not always happen, and then the presence of tachycardia can be suspected based on a number of other symptoms.
Different pacemakers (sources of impulse generation) are responsible for different types of tachycardia.
Clinical signs of tachycardia
- Pain or discomfort in the chest.
The chambers of the heart contract alternately: while some parts are filled with blood, others are resting. The stronger the tachycardia, the shorter the periods of myocardial relaxation. Working without rest causes pain in the heart.
- Dizziness and general weakness.
In the pulmonary circulation, blood oxygenation (oxygen saturation) occurs. With tachycardia, the time required for complete gas exchange decreases. Rapid contractions of the heart release blood into the vascular bed with a reduced content of O2, which is why the tissues do not have enough of it. To make it easier for organs to receive it, vascular resistance decreases. This results in a compensatory decrease in pressure in the blood vessels, accompanied by dizziness and general weakness. Sometimes it can lead to loss of consciousness.
- Dyspnea.
It occurs both during movement, since during physical activity the body requires more oxygen, and at rest - if tachycardia persists for a long time. The same oxygen starvation leads to the development of shortness of breath: increased breathing is an attempt to restore oxygenation.
- Cyanosis, or blueness of the skin.
With hypooxygenation (decreased oxygen concentration in the body), the blood contains a large amount of reduced hemoglobin, a substance responsible for binding oxygen. Low oxygenation leads to cyanosis of the lips, tips of the ears, or fingers.
Tachycardia can be expressed by less significant symptoms: cough, headache, nausea, sleep disturbances, decreased appetite and performance. These complaints are not typical for an increase in heart rate, but you should mention them when visiting a doctor
Early dumping syndrome
It appears immediately after eating, most often in people who have undergone surgery on the stomach or duodenum, but can also occur in non-operated people who have impaired stomach function.
Milk, carbohydrate products, liquid foods, and eating large portions contribute to the development of dumping syndrome.
The essence of the pathology is that food is not digested in the stomach, but immediately passes into the intestines, where increased pressure occurs and irritation of the mucous membrane occurs. As a result, a large volume of blood flows to the intestine, and a shortage of blood occurs in the heart and brain. Carbohydrates quickly pass into the blood, and blood sugar increases. As a result, blood pressure sharply decreases or increases, hormones are released into the blood, and symptoms of hyperglycemia—high blood sugar—appear: dizziness, nausea to vomiting, severe weakness, cold sweat.
Ear congestion
Fungus
Allergy
20020 04 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Ear congestion: causes, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Congestion in the ear or ears occurs as a result of a violation of sound perception and is characterized by various sensations, which may include deafness, a feeling of squeezing and heaviness, and the sound of one’s own voice being too strong. Ear congestion, regardless of the causes of its occurrence, is difficult for the patient to tolerate and, as a rule, requires the help of a specialist.
Types of ear congestion
Blockage in one or both ears may be accompanied by pain, tingling, noise or ringing in the ears, and dizziness. In some cases, congestion disappears after swallowing.
A dangerous symptom is ear congestion accompanied by fever, headache, discharge from the ear (purulent or bloody), and foreign body sensation.
Ear congestion does not always indicate a pathological process.
This condition can be caused by water getting into the ear, pressure changes
during air travel or diving to depth.
Sometimes too strong and incorrect blowing of the
nose from two nasal passages at the same time leads to a blocked ear (ears), which is associated with an increase in pressure in the middle chamber of the ear due to a sharp intake of air from the Eustachian tube.
Taking certain medications
(antibiotics, psychotropic substances) has a toxic effect on the ear, causing the development of congestion and hearing loss.
Diseases that can cause ear congestion.
Earwax
blocking the ear canal. Attempting to remove earwax yourself using improvised objects significantly increases the likelihood of pushing the plug deeper into the ear and sticking to the eardrum (this increases the risk of injury to the eardrum, which leads to complete or partial hearing loss). In these cases, the condition of congestion in the ears is accompanied by excruciating pain, noise, dizziness and nausea.
Mycotic, or fungal, infection of the external auditory canal
. Infection with fungi can be complicated by narrowing or blockage of the ear canal with a feeling of fullness in the ears. The spread of fungi in the ear is aggravated by hearing aids, in-ear headphones, and inflammatory diseases of the ear. The main signs of the disease are itching, ear congestion and resulting hearing loss, and increased sound of one’s own voice in the affected ear.
Damage to the external auditory canal and middle ear structures
may be accompanied by hearing loss and congestion. Bleeding and the formation of a blood clot that blocks the ear canal lead to deterioration in sound transmission. In addition, injury to the eardrum is possible during cleaning of the ear canal, a sudden change in pressure, or a strong blow to the outer ear. In this case, sharp pain occurs, which is replaced by congestion, ringing, noise and hearing loss.
Acute inflammatory diseases
accompanied by swelling and sometimes the formation of purulent contents.
They can lead to ear congestion and hearing loss. In particular, with otitis media of the middle ear (tympanitis),
the tympanic cavity and auditory tube are involved in the inflammatory process. Swelling, which narrows the lumen of the auditory tube, and suppuration of the soft tissues cause ear congestion and hearing impairment. As a rule, the infection enters this sterile cavity from the Eustachian tube, which is directly connected to the nasopharynx.
In children of the first and second year of life, acute otitis may occur when breast milk or formula enters the nasopharynx during regurgitation.
In older children, otitis media and congestion can be caused by
inflammation of the adenoids
, the lymphoid tissue responsible for the local immunity of the nasopharynx and closing the openings of the auditory tubes in the nasopharynx. The anatomical proximity of the adenoids and the auditory tube ensures the rapid transition of infection from the nasopharynx to the ears. In addition, enlarged adenoids can block the openings of the auditory tube, which causes a feeling of stuffiness.
Allergic reactions
can also lead to acute inflammation and swelling of the middle ear.
Otitis externa
characterized by inflammation of the external auditory canal. Congestion in the ear in this case occurs due to swelling of the tissues of the ear canal.
If the disease is caused by a foreign body entering the ear canal
, then swelling and congestion are complemented by a picture of severe irritation. The patient complains of severe itching, pain, a feeling of fullness, and heat in the ear area. The pain intensifies with chewing movements.
For furunculosis
In the external auditory canal, the picture of the disease is aggravated by a closed space where the inflammatory process develops. Increasing pain in the ear is complemented by its irradiation to the corresponding half of the head. The patient cannot lie on the painful side. Due to severe swelling of the tissues of the external auditory canal, sound transmission into the affected ear is disrupted, and a feeling of stuffiness occurs.
Among the anatomical and postoperative defects
that cause ear congestion include deviated nasal septum, narrowing of the nasal passage due to hypoplasia of the nasal wings, and stenosis of the external nasal valve.
Impaired nasal breathing leads to frequent runny nose, infection of the nasal sinuses and, as a consequence, to the transition of the inflammatory process to the auditory tube.
Ear congestion in these cases appears on the side of the narrow nasal passage. The same consequences occur after operations in the nose area.
Sensorineural hearing loss
occurs due to damage to any part of the auditory nerve. Most often, this is an irreversible phenomenon, the symptoms of which include imbalance, dizziness, nausea, fullness and noise in the ear, and poor perception of low sounds. The causes of sensorineural hearing loss can be previous infectious and vascular diseases, tumor processes, injuries, and toxic effects of various substances.
Meniere's disease
is a non-purulent disease of the inner ear, which is accompanied by congestion. An increase in the volume of lymph in the labyrinth of the ear leads to increased pressure and attacks of progressive deafness, tinnitus, and sudden dizziness. In most cases, one ear is affected first. The disease begins either with attacks of dizziness or with deterioration of hearing, which is completely restored between attacks. However, after a few years, hearing loss becomes irreversible.
Myofascial pain syndrome, temporomandibular joint diseases
. Patients with myofascial pain syndrome, which is associated with disruption of the masticatory muscles and limited mobility of the lower jaw, may also complain of ear congestion. In addition, the disease is accompanied by headaches and facial pain, difficulty opening the mouth, and clicking in the temporomandibular joint.
The root cause of the syndrome is spasm of the masticatory muscles.
A similar clinical picture is also given by diseases of the joint itself caused by malocclusion. Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels, increased blood pressure
. Congestion in the ears due to damage or narrowing of blood vessels is explained by a deterioration in the blood supply to all tissues, as well as impaired circulation in the area of the inner and middle ear.
Vasomotor rhinitis, or runny nose during pregnancy
occurs under the influence of hormonal changes and is characterized by impaired vascular tone and the release of mucous secretion. With allergic rhinitis, the clinical picture of the disease is almost the same, but the provoking factor is not hormones, but a specific allergen. Swelling of the mucous membrane and narrowing of the nasal passages lead to obstruction of the auditory tube and cause ear congestion.
Tumors in the area of the auditory canal, auditory tube and inner ear
– the most serious cause of ear congestion. Among them should be called cholesteatoma - a tumor-like formation that consists of epidermal cells impregnated with cholesterol. Cholesteatoma is characterized by slow but steady growth. Forming in the middle ear, it can spread to the outer and inner ear, causing congestion and a feeling of heaviness in the ear, purulent discharge, swelling and redness of the auricle.
Which doctors should I contact if I have ear congestion?
If ear congestion occurs, you should contact an otolaryngologist. In the future, you may need to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or allergist.
Diagnosis and examinations for ear congestion
To diagnose the disease that caused ear congestion, a careful questioning of the patient, examination of the outer ear and ear canal to the eardrum, and an audiometric examination are necessary. The infectious nature of the disease is determined on the basis of the clinical picture, otoscopy data and culture of the discharge.
Late dumping syndrome
It is caused by the release of large amounts of insulin in response to high sugar levels. Then, after a few hours, the sugar level drops sharply, and hypoglycemia develops - a lack of glucose. This condition is similar to hypoglycemic coma in diabetics: pallor, cold and clammy sweat, dizziness, trembling, yawning and drowsiness, feeling of hunger. This is a dangerous condition: the blood supply to the heart is disrupted, the blood carries oxygen less well, and tissue oxygen starvation occurs - hypoxia. Possible development of acute heart failure.
In severe forms of dumping syndrome, anorexia and exhaustion may develop.
Other causes of morning sickness
After excluding the above diseases from the list of causes, the following causes can be considered:
- Pregnancy. Intoxication and nausea in the morning often occurs in pregnant women, especially in the early stages. This is a normal reaction of the body to significant changes and hormonal changes. It is very important to completely eliminate medications used to treat the digestive tract during pregnancy. These drugs can have an extremely negative impact on the health of the patient, the unborn child and the course of pregnancy. Therefore, you will have to endure this illness and use folk remedies, but be sure to consult a doctor.
- Migraine. Morning sickness on an empty stomach may precede a severe headache. You will likely also experience a lot of noise and increased sensitivity to smells.
- High blood pressure (hypertension). The problem of morning sickness may be accompanied by headache and dizziness. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk developing this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke.
- Cardiovascular diseases - less often, nausea on an empty stomach appears with heart failure or developing myocardial infarction. If nausea is accompanied by pain, a feeling of heaviness and tightness behind the sternum, numbness or tingling in one half of the body, you should seek medical help as soon as possible, as this may be an incipient myocardial infarction.
- Increased intracranial pressure - nausea and regurgitation in an infant can occur when the pressure inside the ventricles of the brain increases.
What to do
Single cases of dizziness after eating are not dangerous and do not require treatment.
If such a condition is associated with disordered eating, too long gaps between meals, you just need to adjust your diet, try to eat more often and in small portions.
In case of food allergies, it is necessary to identify and exclude from the diet foods that provoke an allergic reaction.
But dumping syndrome requires treatment from a gastroenterologist or abdominal surgeon.
For mild stages of the disease, treatment includes:
- taking medications that normalize digestive processes;
- diet and nutrition;
- elimination of symptoms of pathology;
- taking sedatives;
- physiotherapeutic procedures – electrical stimulation and electrosleep.
If this does not help, surgical treatment is used - gastric surgery.
Survey
Nausea after eating most often indicates the presence of diseases of the digestive system, so the examination is carried out by a gastroenterologist, and the diagnostic search involves a comprehensive study of the morphological and functional characteristics of the patient’s gastrointestinal tract. When making a diagnosis, modern laboratory and instrumental methods are used, of which the most informative are:
- Sonography
. Abdominal ultrasound is prescribed as a screening method for all patients with long-term dyspeptic disorders. Ultrasound examination allows to identify nonspecific signs of ulcerative-destructive and inflammatory processes. If necessary, targeted ultrasound of individual organs is performed. - Gastrointestinal endoscopy
. Endoscopy is the most informative method for diagnosing diseases of the upper digestive tract, which are accompanied by nausea. According to indications, the study is supplemented with a biopsy. If it is necessary to visualize the entire length of the small intestine, video capsule endoscopy is used. - Radiography
. X-ray examination with contrast with a barium mixture is effective in detecting ulcerative-destructive processes in the digestive tract. The method is not specific enough for the diagnosis of inflammatory pathologies, so it is advisable to use it in combination with gastrointestinal endoscopy. - Study of gastric secretion
. Nausea associated with food may indicate disturbances in the acid-producing function of the stomach, so 24-hour pH testing is prescribed. The amount of total and free hydrochloric acid on an empty stomach and after the administration of drugs that stimulate secretion are also assessed. - Stool analysis
. A standard coprogram allows one to suspect malabsorption of food and various inflammatory processes in the intestines, which are accompanied by dyspeptic symptoms. Additionally, bacteriological culture of stool and analysis for helminth eggs are performed to exclude an infectious etiology of the process.
A biochemical blood test is necessary to exclude biliary and hepatic pathologies that cause nausea after eating. If a patient has a general infectious syndrome, specific serological tests are carried out to search for antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms. Intraesophageal manometry is prescribed to assess the motor function of the organ and the coherence of the sphincter apparatus.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs
Is it possible to prevent the disease?
Yes, especially if it manifests itself in a mild form. Here are the doctors' recommendations.
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions. Take your time and chew your food thoroughly.
- Do not drink during or immediately after meals. You can drink half an hour to an hour before and half an hour to an hour after eating.
- Give preference to slow carbohydrates: cereals, pasta, rice, but it is better to limit fast carbohydrates: cakes, pastries, sweets, as well as sweet juices and drinks.
- Vegetables and fruits containing soluble fiber are useful: apples, plums, carrots, beets, cabbage.
- Protein foods: meat, fish, poultry, eggs will also be very useful
- Milk and dairy products can cause an attack, so consuming them is not advisable. You can try using lactose-free milk.
- If your blood pressure drops after eating, it is advisable to lie down for about twenty to half an hour.