What is neurosonography of the newborn brain?
Neurosonography is a method of ultrasound sectoral scanning of the head
the child’s brain through the fontanelle (including in newborns).
Synonyms for the word “ neurosonography ” are “ neurosonography of newborns , neurosonography of the brain , ultrasound neurosonography , transcranial neurosonography , ultrasound of the brain , ultrasound examination of the brain, NSG .”
What does the NSG show?
Neurosonography shows the condition of brain tissue and the circulatory system and gives the specialist the opportunity to assess the size and shape of parts of the brain. Using ultrasound, a specialist determines the condition of the membranes of the child’s brain, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, the state of the vascular system, the degree of formation of brain matter, etc. In addition, ultrasound can track how symmetrical the brain structures are in children, the size of the ventricles of the brain, and assess the development of the cerebellum , detect ischemic areas.
How is neurosonography done?
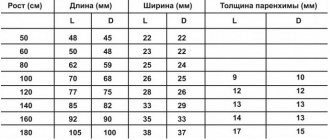
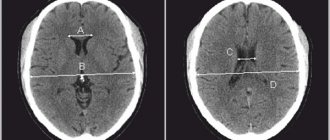
Neurosonography is performed only on a child (1 month, 2 months, 3, 4, 5 months, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 months) whose fontanels or sutures are not closed. The fontanelle is an area on the head that is not covered by bone tissue. Fontanas transmit ultrasound very well. The study is often carried out through the anterior large fontanelle, which is located between the parietal bones and the frontal bone. The foramen magnum is used less frequently; in full-term patients (through a thin bone), the anterolateral fontanel and posterolateral fontanel can be used. By the way, neurosonography can be performed on children even during sleep. Neurosonography is performed at an ultrasound frequency of 5–75 mHz in the coronal and sagittal planes. The study visualizes the ventricular system, periventricular structures, formations of the posterior cranial fossa, middle cranial fossa, anterior cranial fossa, and cerebral vessels (arteries and veins). The bones that form the skull, gyri, sulci of the brain, choroid plexuses of the ventricles and cerebellum have a high echogenic density. The ventricles of the brain containing cerebrospinal fluid, the cavity of the transparent septum, Verge's cavity, and cisterns are anechoic. The brain parenchyma has low echodensity, with the exception of the basal ganglia, which have increased echogenicity.
How is neurosonography performed?
As if having provided for the invention of neurosonography, nature left on the vault of a child’s skull 6 non-ossified areas - fontanelles, which, unlike bones, do not interfere with the passage of ultrasound. Basically, the study is carried out through the large fontanel - a diamond-shaped area of the head in the parietal region, as well as the temporal region. The large fontanel closes by the end of the first year, and in some children by 3-4 months. This is why it is so important to perform neurosonography in early infancy. After the fontanelle closes, neurosonography becomes impossible. Before neurosonography, the skin over the fontanel is lubricated with a special sound-conducting gel: after all, there should be no air between it and the sensor that interrupts the path of ultrasonic waves. Taking into account the age of the child, we try to reduce the examination time to 10 minutes. One of the main advantages of neurosonography is the absence of any special preparation, the examination is carried out both during sleep and during wakefulness, in the presence of parents. If your child is not sleeping or is restless, you can offer him a bottle to drink or distract him with a pacifier. Be sure to show the results of neurosonography to your pediatrician and neurologist. Do not forget that neurosonography is an additional method, and the result is not a diagnosis. In any case, only a pediatric neurologist can establish a final diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Neurosonography is an accurate type of diagnosis
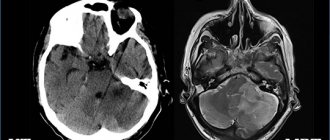
Neurosonography is very important in the diagnosis of pathology in children in the first month of life in identifying various hemorrhages. Both isolated subependymal hemorrhages and hemorrhages in the ventricles of the brain with their spread to the brain parenchyma are well defined. Neurosonography has high sensitivity. Neurosonography is an accurate type of diagnosis. Neurosonography allows you to diagnose focal and multifocal necrosis, foci of periventricular leukomalacia, foci of subcortical leukomalacia.
In the acute phase, ischemic foci in the gray matter of the brain on the echogram are represented by areas of increased echo density. Sarklinik believes that the diagnosis of damage to the thalamus opticus and subcortical nuclei is better determined in the presence of hemorrhagic necrosis. Neurosonography is of great importance in the diagnosis of infectious and inflammatory processes. Neurosonography makes it possible to monitor the development of inflammatory and infectious processes and to promptly identify complications such as hydrocephalus, subdural hygroma, ventricular abscess, and cerebral abscess.
Neurosonography perfectly identifies congenital malformations of the central nervous system, changes in the size, shape, location of the ventricular system, and other anatomical structures of the brain. Using neurosonography, it is possible to diagnose various forms of pathology such as congenital hydrocephalus, Dandy-Walker malformations, holoprosencephaly, aneurysm of the vein of Galen, agenesis of the corpus callosum, Arnold-Chiari syndrome. Neurosonography plays a certain role in the diagnosis of brain tumors. Sonographic signs of tumors are nonspecific. They can manifest themselves in the form of cystic formations against the background of hydrocephalus, or areas of increased echo density. Often the tumors are asymmetrical and are accompanied by displacement of the midline structures of the brain.
Purpose of the study
External factors that are harmless to an adult in the form of various infections, taking certain medications, or household hazards can cause irreparable damage to a fetus or a newly born baby. The brain, which is considered the most vulnerable structure in the human body, is subject to maximum impact. Existing problems in this organ can have very serious complications, which must be prevented by careful diagnosis and timely treatment.
Neurosonography as a diagnostic method is indispensable for the following pathologies:
- congenital abnormalities of brain development;
- neoplasms of various origins;
- brain damage due to impaired blood circulation before childbirth or during labor (hydrocephalus, hemorrhage).
Neurosonography can determine the pathology of the brain of newborns and infants
What does neurosonography show in children? Hypoxic damage to the central nervous system, traumatic damage to the central nervous system, trauma, periventricular edema, increased peripheral vascular resistance, vascular spasm, periventricular leukomalacia, periventricular hemorrhage, cyst (diameter 1, 2, 3 or more cm), pseudocyst, vascular abnormalities, hydrocephalus, hypertensive -hydrocephalic syndrome, hypertensive syndrome, infectious brain lesions (infections), congenital malformations of the brain, central nervous system, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain, subependymal cysts, cysts of the choroid plexus of the brain, expansion of the subarachnoid space, expansion of the external cerebrospinal fluid spaces, hemorrhages in the substance of the brain , hemorrhage into the ventricles (intraventricular hemorrhage, IVH grades 1, 2, 3, 4), cerebral ischemia.
Neurosonography
Neurosonography
- This is an ultrasound examination of the brain in newborns and children in the first year of life. An ultrasound of a newborn's head is performed through the large fontanelle, a section of soft cartilaginous tissue at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones. Upon reaching one year, the fontanel closes (the bones close together). Therefore, at an older age, an ultrasound of the brain is performed through the temporal bone and is called TCD (transcranial Dopplerography).
What does neurosonography of newborns show?
Neurosonography allows you to see the structure of the newborn’s brain; it is used to assess the state of the brain, the structure of the brain matter, and the amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
Neurosonography of newborns helps to identify pathological abnormalities that may occur in a child during intrauterine development and during childbirth. In particular, neurosonography reveals:
- hemorrhages;
- areas experiencing oxygen deficiency (hypoxic damage), including as a result of insufficient blood supply (ischemia);
- swelling;
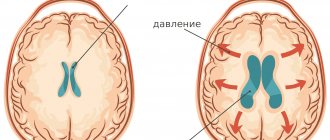
- compression of the brain (as a result of birth trauma);
- malformations of the brain;
- tumors and cysts;
- inflammatory processes;
- consequences of intrauterine infections;
- hydrocephalus is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricular system of the brain.
To make sure that no problems are expected from the brain, you can do neurosonography for your baby as a screening procedure (that is, during a routine examination). This is a completely painless and safe procedure. Developed by Family Doctor specialists specifically for children in the first year of life, the annual program of comprehensive medical care “Solo” involves conducting neurosonography twice (in the first and 12th month).
Indications for neurosonography
Direct indications for neurosonography of newborns are:
- prematurity of the child;
- intrauterine infections such as cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, herpes;
- birth injuries;
- convulsions;
- bulging fontanelles (a sign of increased intracranial pressure).
Neurosonography is also done for children in the first year of life:
- when the head grows too quickly;
- in case of meningitis;
- if there are suspicions of defects of the central nervous system.
Neurosonography Center
Neurosonography centers in Russia necessarily determine the size of the ventricles of the brain (the lateral ventricles may be enlarged), the area of the ventricles, the contours of the ventricles, cerebral vessels, vascular plexuses, and convexital spaces. With pathology, the sizes are reduced or increased. Send us letters with your stories about neurosonography and your beloved children. We will publish them on the medical website sarclinic.ru. You will be able to read patient reviews and discuss all problems.
The sooner the necessary treatment for a child is started, the greater the chance of his recovery.
Photo: (©) Prometeus | Dreamstime.com \ Dreamstock.ru The child depicted in the photo is a model, does not suffer from the diseases described and/or all similarities are excluded.
Related posts:
Enuresis code according to ICD 11, nocturnal or daytime enuresis
What is the proper weight (body weight) and height of a child by month, year: table, norms
Children who involuntarily shout out words, why does the child scream
Why does a child twitch strongly: legs, arms, eyes, body
Which doctor treats enuresis in children? Who to contact if you have enuresis in Russia?
Comments ()
Why is this research necessary?
The baby goes through many tests, both during pregnancy and during childbirth. External factors that are not capable of causing harm to an adult - banal infections, medications, household and professional hazards - can become a disaster for a nascent life. And, naturally, the brain, as the most complex and vulnerable structure of the human body, is most susceptible to these influences. During the first year of a baby’s life, doctors have the opportunity to prevent the consequences that may arise due to certain problems in the brain. The sooner treatment is started, the more likely it is that the child will grow up healthy.