Weather dependent
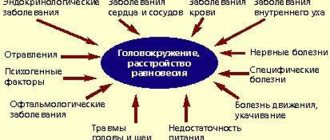
The situation, which does not require serious medical intervention, is explained by sensitivity to atmospheric and climatic changes. It has been noticed that some people react painfully to both solar activity and a decrease in atmospheric pressure. In such situations, they experience a narrowing of vascular tone, which leads to moderate anemia. If at the same time internal pressure tends to increase, heaviness in the head, pain, weakness and weakness occur.
When “flares” occur on the Sun, causing magnetic storms, some people experience blood thickening. Since hemoglobin contains large volumes of iron, when magnetic activity increases, it attracts its own elements, blinding red blood cells. Clots form that block small capillaries, oxygen starvation occurs again, causing a person to feel weak, tired, dizzy and in pain.
Temperature effects on blood vessels are also observed. An increase in temperature affects the dilation of blood vessels, and a cold snap - on the contrary. Improper regulation of this mechanism in vegetative-vascular dystonia leads to a deterioration in well-being. Other unfavorable factors affecting sensations in the head are:
- constant lack of sleep;
- tension of the nervous system when engaged in monotonous work;
- prolonged or uncontrolled use of medications, narcotic drugs;
- drinking alcohol the night before;
- sudden allergic reaction with swelling of brain tissue;
- forced fasting, diets without glucose consumption;
- acclimatization period upon arrival to another area;
- climbing to altitude (altitude sickness);
- high degree of responsibility at work, before an important event;
- head injury.
In most cases, to improve your well-being, it is enough to reconsider your lifestyle, slightly adjust your activity and rest schedule, and balance your diet. If this does not help, and the discomfort increases, you should see a doctor.
Diagnostics
Your doctor will explain why your head feels heavy and feels tense. A diagnostic examination is prescribed taking into account the dominant symptoms. To identify structural changes in brain tissue, examination is carried out in the format of MRI, CT, and ultrasound. X-rays are often taken, due to the need to study the condition of the bone structures of the skull and spinal column. The state of the circulatory system of the brain is determined using Dopplerography and angiography.
A blood test (general, biochemical) shows the functionality of the kidneys and liver, the concentration of glucose, cholesterol in the serum, the rate of coagulation and other characteristics of the blood. The attending physician will tell you how to get rid of heaviness in the head, taking into account the results of a diagnostic examination and other factors (age and general health of the patient, the presence of concomitant pathologies).
Possible diseases
Heavy sensations in the head against the background of increasing insomnia, lethargy, and cloudiness of consciousness may be a consequence of an underlying disease. The most common pathologies leading to such symptoms are:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia. It appears during physical activity, when due to a violation of the vascular regulation mechanism, an outflow of venous blood occurs. In this case, the arterial overflows the blood channels in the skull, which creates a pressing feeling, especially in the occipital area.
- Meniere's disease. Pathology of the inner part of the auditory canal. The inflammatory process in the ear leads to excessive effusion of fluid, which accumulates in the ear labyrinth, putting pressure on brain tissue and nerve endings. Not only hearing suffers, but also coordination.
- Problems with the spine. The thinning of the cartilage layers leads to the fact that the discs of the spinal column compress each other, squeezing the tissues located between them, including nerves and blood vessels. As a result, blood flow to the brain slows down, and hypoxia of varying severity begins.
- Upper respiratory tract diseases. Inflamed, swollen, congested sinuses cause a feeling of something heavy accumulating in the head. Infection or other inflammation of the muscles at the base of the skull has the same effect.
- Diseases of the vascular network. Any vascular disorders lead to damage to brain tissue, since it is the first to suffer from a lack of oxygen. Even slight anemia leads to confusion, weakness, and stupor. Among the serious problems are atherosclerosis, vasculitis, tumor processes in the blood channels, and thromboembolism.
A special place is occupied by severe cancer pathologies, aneurysms, deep cysts in the brain and cervical spine. Any abnormally growing objects lead to compression of neighboring tissues, which is why the first sign is heaviness in the head. If such a condition bothers you systematically, there is a reason to seek medical help.
Causes
The causes of heaviness in the head are often associated with physical and mental fatigue. In this case, the discomfort goes away spontaneously after a long, complete rest. Cloudiness in the head occurs due to an unhealthy lifestyle (abuse of alcohol, drugs, physical activity at night, irregular diet) or due to a pathological process. Common causes of development:
- Lack of sleep, sleep disorder. Often, a feeling of vagueness inside the skull appears after prolonged sleep, which is usually associated with poor rest hygiene or venous stagnation. To prevent discomfort, it is necessary to ventilate the room before going to bed and choose comfortable bedding (pillow, mattress).
- Poor nutrition. A deficiency of important nutrients - vitamins, microelements, protein, healthy fat (olive oil, avocado, sea fish) leads to the feeling that the head is plagued. Disturbances can be triggered by the consumption of foods that cause an allergic reaction.
- Chronic stress. Regular exposure to stress has a negative impact on health, leading to the development of depression, insomnia and discomfort in the skull area.
- Taking pharmaceutical drugs and nutritional supplements. Some medications (anticonvulsants, painkillers, statins, antidepressants, sleeping pills and sedatives, acetylsalicylic acid) provoke the development of fuzzy head syndrome.
- Increased blood pressure levels. Any deviations in blood pressure values from the norm can provoke a feeling that there is cotton wool inside the skull.
- Meniere's disease, vestibular disorders. Pathologies of the vestibular system are one of the likely causes of the feeling of a cloudy head.
- Thyroid dysfunction. Excess and lack of hormones lead to an unpleasant feeling inside the skull.
- Concussion, brain contusion. Suffered TBIs cause a condition where the head is dizzy, there is pressure on the ears and there is a pressing pain in the area of the skull. Disturbances occur in the acute period and can be observed much later than the episode of TBI, transforming into post-traumatic syndrome.
The feeling of a heavy head can occur against the background of inflammatory processes occurring in the respiratory, visual and hearing organs. Pathologies of the heart and vascular system can provoke the appearance of symptoms. Damages to the joints and other structures of the musculoskeletal system are often accompanied by a condition where clouding occurs in the head.
How to understand the reason
In any case, you cannot guess on your own what caused the unpleasant condition. You need to go to the doctor and get checked. At the initial stage, it is enough to consult with a therapist, who, if necessary, will refer you for examination to other specialized specialists. It is impossible to determine the problem by eye, so research manipulations will be prescribed. To do this, carry out the following procedures:
- Laboratory analysis of blood and urine. The inflammatory process, anemia, sugar and cholesterol levels are detected.
- Doppler ultrasound of neck vessels. Shows the condition of the blood channels in this area.
- MRI of the brain. Detects any disturbances occurring inside the skull.
- CT scan of the brain and sinuses. Helps to specifically study the structures of the skull, the cavities inside it, the condition of the mucous membrane, the presence of inflammation and accumulation of fluids.
Tomographic scanning methods are the most informative, since without instrumental intervention they help to see any anomalies of varying complexity in the images. Only through MRI and CT can one recognize a serious disease at an early stage, record possible complications, and plan subsequent treatment.
Daily reasons
Discomfort in the head is not necessarily a consequence of the disease. It is quite possible that yesterday's celebration, albeit with a small dose of red wine or champagne, thus affects your well-being. A lot depends on a person’s image and lifestyle.
Meteor dependence
It has been noted since ancient times that some people are very sensitive to solar activity and changes in atmospheric pressure. When the pressure decreases, people who have problems with vascular tone experience weak oxygen starvation. In such situations, it is not recommended to engage in hard work, it will only aggravate the situation. A cyclone can cause an increase in intracranial pressure, causing the head to become heavy, dizzy, and weakness and vomiting may occur.
Magnetic storms and solar flares cause red blood cells to stick together: hemoglobin contains many iron molecules that are exposed to powerful radiation, which can cause them to stick together. Red blood cell clots impair blood circulation in the thin capillaries of the brain.
Some medications and intoxicating substances (alcohol, narcotics) have a similar effect.
As a result, powerlessness occurs, rapid fatigue when performing even simple work, drowsiness, and the desire to do anything disappears, except perhaps sleep.
Sudden changes in temperature, for example, its rapid increase in the morning after a cold night, affect vascular tone. If there are disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system or other deviations in the mechanism of changes in vascular tone (high temperature causes expansion, and low temperature causes contraction), these processes proceed incorrectly, for example, they slow down.
Other factors that cause discomfort include:
- Total lack of sleep - getting up early and going to bed late. In this case, it is very difficult to get up in the morning, immediately after waking up you feel clouded, your head is heavy and dizzy.
- Doing monotonous work, for example, at a computer, causes tension in the nervous system.
- The next reason is the intake of chemicals: medications, intoxicants.
In case of toxic damage by alcohol or another substance that is poisonous to the body, the brain is primarily affected. Mainly due to impaired blood circulation under the skull, which causes oxygen starvation.
- An allergic reaction that occurs with cerebral edema.
- Fasting, for example, with strict diets. Lack of glucose causes fatigue and headaches, and the brain seems to gain weight.
- Acclimatization is a symptom of changes in the body that occur due to arrival in a new place (often observed in tourists and travelers).
- A heavy head when climbing a mountain is a sign of oxygen starvation.
- Constant nervous tension in representatives of many professions and in people at certain moments (everyone knows that before the arrival of an inspection or failure to meet deadlines, a headache begins).
- A blow to the head, traumatic brain injury in an accident or in athletes. In such a situation, you may feel sick for a long time.
The head becomes like cotton wool or fills with lead in these and similar cases - a consequence of a person’s lifestyle and, in principle, there is nothing to treat here. If you are constantly experiencing pain, you should not refuse to visit a doctor. You may not know everything about yourself.
In most cases, all you need to do is change your regular diet, stop taking medications (with the permission of a specialist or replace them with analogues) or substances that cause discomfort, and engage in active physical labor if you work in an office (walking home, sports). All this plus normal sleep will quickly relieve ailments and unpleasant symptoms. A cold shower is also a good way to cleanse yourself.
Remember that a pill, even if it relieves pain, will definitely not eliminate the cause that causes it.
Diagnostic features
Standard manipulations in the form of ultrasound, analytical tests, and x-rays are carried out in any clinic at the place of treatment, but tomographic scanning will require special conditions. They are not always available in government agencies. To find clinics with the right equipment and trained experts, use our appointment service. Here you can find all the diagnostic centers in the city, which can be compared according to various parameters: reviews, ratings, prices, discounts, location, types of equipment, etc. Choose the services you need, call the service staff, book any procedures on special terms.
Lethargy
Iron deficiency
Diabetes
Atherosclerosis
Stroke
10377 04 May
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Lethargy: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The functioning of the nervous system is based on the reflex arc - the path along which irritation (signal) from the receptor passes to the effector organ. A reflex arc is a set of neural circuits consisting of sensory, intercalary and motor neurons that provide perception of a signal from the outside, conduct it to special centers of the brain, where the received information is analyzed and a response impulse is generated.
Thus, a high speed of impulse conduction and information processing is one of the necessary conditions for adequate speed of functioning of the nervous system.
Due to the fact that the structure of the nervous system is very complex, consisting of many cells connected to each other by nerve processes (nerve fibers), this system is subject to significant influence from the environment. Thus, changes in the composition of the fluid that washes the nerve cells, changes in temperature and other factors can significantly slow down its coordinated work.
Types of retardation
Retardation is manifested by a slowdown in the speed of certain nervous functions. In this case, both isolated changes can be observed (for example, a slowdown in motor activity, inhibition of perception), and complex ones - when all the main functions of the nervous system, including higher mental activity, slow down.
Retardation can develop acutely or gradually.
The more sudden it appears, the more attention must be paid to finding the reasons for its development. Possible reasons for the development of lethargy
There are many reasons for the slowdown of nervous processes, and one of them is
nervous exhaustion
. This term refers to the insufficiency of nerve tissue reserves to perform its functions, which develops during prolonged hard work of the nervous system.
The next condition associated with lethargy is oxygen starvation
central nervous system.
Lack of oxygen may be due to its insufficient supply from the outside (for example, staying in a poorly ventilated room), impaired gas exchange in the lungs due to various bronchopulmonary diseases
, impaired blood supply as a result of damage to the vessels supplying the central nervous system, or as a result of
heart failure
associated with poor blood supply to all organs and tissues.
Also, impaired oxygen delivery develops with anemia
- a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that binds and carries oxygen from the lungs to every cell of our body.
Due to the fact that the nervous system's oxygen needs are high, oxygen deficiency quickly leads to disruption of its functioning.
Another cause of lethargy is a state of
hypoglycemia
- a decrease in blood glucose levels. It is observed when there is insufficient intake of glucose from food, during significant physical exertion (when glucose is predominantly spent by intensively working muscles), and when patients with diabetes mellitus overdose on insulin.
Lethargy also occurs due to toxic damage to the nervous system as a result of cerebral edema.
Diseases that cause lethargy
Among diseases of the cardiovascular system that may be associated with insufficient blood supply to the brain,
atherosclerotic vascular damage
, including against the background
of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart failure
due to
myocardial infarction, myocarditis
and other diseases.
Bronchopulmonary diseases leading to insufficient oxygen saturation of the blood include pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, bronchial asthma
(especially at the time of an attack), etc.
Anemia
may develop due to a disorder of hematopoiesis (for example, iron deficiency anemia), destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia), acute or chronic blood loss.
Hypoglycemia
observed not only in diabetes mellitus, but also in endocrine diseases, such as adrenal insufficiency, insulinoma, long-term severe liver diseases, etc.
Toxic damage to the central nervous system can be caused by the intake of certain toxic substances
from the outside, and by intoxication due to the development
of liver failure
(for example, with cirrhosis of the liver) or
renal failure
.
Intoxication syndrome accompanies most infectious diseases
, as well as many
malignant processes
.
Separately, it is worth noting life-threatening conditions that lead to cerebral edema and are manifested, among other things, by lethargy - these include stroke
, compression of the brain
by an intracranial tumor
,
traumatic brain injury
.
Which doctors should I contact if I feel lethargic?
Due to the fact that the cause of the development of lethargy can be diseases of a variety of organs and systems, if this symptom appears, you should consult a general practitioner, or. These specialists, after establishing the probable cause, can refer the patient to a nephrologist or hepatologist.
Diagnostics and examinations for lethargy
Diagnosis of diseases accompanied by lethargy begins with a survey and examination of the patient. Often this is enough to make a preliminary diagnosis. However, to confirm it, some additional research is necessary:
- a clinical blood test with a leukocyte count, which is necessary primarily to exclude anemia;
Diagnostic methods
Patients with speech disorders need to be carefully assessed, both medically and psychologically. As a rule, several different specialists are involved in the process, such as a speech therapist, a neurologist, a psychiatrist and a psychologist. The patient is visually examined with a history taken, and a series of diagnostic examinations are prescribed. When interviewing the patient, it is necessary to find out whether he has had traumatic brain injuries, neuroinfections and mental illnesses in the past, and whether his heredity is aggravated in this regard. Sometimes urine and blood tests can be informative: they indicate pathologies in a particular organ.
An analysis of the content of pituitary hormones is also important, as is the appointment of cerebral angiography and EEG. MRI and rheoencephalography may also be no less informative. Sometimes a spinal tap helps clarify the diagnosis. All such patients also need to undergo psychiatric tests.
As for speech changes, the level of their pathology and depth is determined by assessing the anatomical features of the organs responsible for voice formation and speech production. The patient's ability to write is tested by asking him dictation and oral reading.
Differential diagnosis of inhibition and the causes that cause it is carried out with dysarthric disorder and stuttering.