What is unsteadiness when walking?
Unstable movements may appear systematically or be present constantly. The clinical picture may worsen due to external stimuli or arise due to the development of inflammatory processes.
Quite often, a person, along with instability in movements, also experiences other unpleasant sensations when walking , signaling a disease that provokes unsteadiness of gait (skidding when walking). Additional manifestations include migraine, loss of orientation in space, numbness of the limbs, a sharp loss of strength, and so on.
Human movement is carried out using muscles, joints and bone structure. And this process is controlled by the cerebellum, organs of vision and vestibular apparatus. The spinal cord conducts impulses that travel to the lower limbs and encourage them to move. After receiving the “command,” the muscles set the entire bone system in motion. If the passage of the impulse is disrupted for some reason, it will not give the correct “command”, and naturally the legs will not move correctly, making the walk shaky and uncertain.
In addition, it staggers when walking and with various problems with the musculoskeletal system . In this case, the legs simply will not be able to carry out “commands” correctly. And if there are problems with the cerebellum, then the “command” itself will be absent.
Important! Before starting therapy, it is imperative to identify the cause of the disorders, since treatment will vary in each specific case.
Disease categories
Based on the above, doctors divide all diseases whose symptoms include staggering into 3 categories.
Category 1 – this includes diseases that are associated with impaired functioning of the musculoskeletal system, diseases of the musculoskeletal structure, joints, and circulatory disorders.
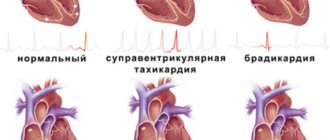
Category 2 – pathology of those areas of the brain that are responsible for coordination of movements and control the functioning of the entire motor system.
Category 3 – psycho-emotional disorders.
1 category
Unsteadiness when walking may occur due to the following reasons:
- spinal injury;
- traumatic brain injury;
- injuries and bruises of muscle tissue in the lower extremities;
- osteochondrosis – when intervertebral discs are affected;
- amyotrophy;
- leg diseases, including foot deformities;
- arthritis;
- damage to cartilage tissue of varying severity;
- violation of bone structure.
Category 1 diseases occur due to injuries, due to improper blood circulation, as a result of which insufficient oxygen and nutrients enter the muscle tissue, the muscles are depleted and are unable to perform their functions. Instability in movements appears, the person’s legs give way, the patient becomes dizzy and staggers when walking, nausea is observed, and the general state of health is unsatisfactory.
2nd category
The 2nd category includes pathologies in the spinal cord and brain, which, during their development, disrupt the proper functioning of the lower extremities. The brain cannot control and send the necessary signals, so the motor processes of the lower extremities become weak.
This happens in the following diseases:
- stroke (hemorrhagic type);
- oncological brain damage;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- purulent formations and inflammation in the brain;
- atherosclerosis;
- neurodegenerative disease, when it occurs against the background of mental complications and hyperkinesis (choreic type);
- dysfunction of the central nervous system;
- congenital anomaly of the structure and location of the cerebellum;
- meningitis;
- Parkinson's disease;
- infection with Treponema pallidum, resulting in damage to the central nervous system;
- inflammation of the inner ear;
- improper use of neurotoxic drugs, resulting in the development of polyneuropathy;
- encephalomyelitis.
With any of the above diseases, not only swaying during movement or gait disturbance is observed, the patient also has a very serious general condition.
3 category
If you stagger when walking, then mental disorders may also be the cause. It could be:
- stress, nervous breakdowns;
- depression, which leads to a depressed state of the whole organism;
- the presence of inexplicable, groundless fears and anxiety;
- neuroses;
- impaired perception of surrounding reality.
Alcohol poisoning
Separately, it is worth considering poisoning with alcohol or other substances.
Quite often you can observe a sharp change in gait, and other movements, after drinking alcohol. After a few minutes of feasting, a healthy person begins to feel a storm. There is an explanation for this.
After alcohol enters the gastrointestinal tract, it is distributed through the blood throughout the body, including muscle tissue and the cerebellum. 20 minutes after consumption, the highest concentration of alcohol in the blood can be observed.
It is known that the intoxicating effect of alcohol is much stronger in women than in men. This is due to the fact that women have more fatty tissues in their bodies, and alcohol does not dissolve in them. All the power of alcohol is directed towards muscle mass, which is why intoxication is more pronounced.
Once alcohol enters the body, its decomposition begins. This releases an active toxic substance – acetaldehyde. It has a detrimental effect on the cerebellum, as a result of which the floor begins to sway under the feet of a drunken person, the gaze becomes cloudy, severe staggering occurs when walking, and the next morning suffers from headache and nausea.
Some relatives or friends, wanting to alleviate the condition of a drunk person, offer medications.
Taking any medications, such as painkillers, at the same time as alcohol is strictly prohibited! The results can be detrimental to your health.
In addition, you can independently help a victim of alcohol poisoning only in the first two stages, that is, with mild or moderate intoxication. The third stage - severe poisoning - should be treated only under the guidance of a doctor. Therefore, if severe poisoning occurs, it is best to call an ambulance.
Elderly age
It is rare to find a person over 60 years of age who does not feel a slight swaying and who does not have “flies” flashing before their eyes. Sometimes older people experience tinnitus and dizziness when walking. Attacks of acute headaches also occur, sometimes even fainting and even falls. But rarely does anyone pay attention to this. It is believed that this is a normal phenomenon, a remnant of age, and no treatment is required.
Meanwhile, an elderly person wants and can live fully and lead a normal lifestyle. You just need to go to a specialist to diagnose the causes of impaired coordination of movements.
One of the predisposing factors is insufficient functioning of the cerebral vascular system. Atherosclerosis appears, that is, a disease from the second category, which affects the coordination of gait.
Very often, due to age, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted.
Affects gait and heart disease. Ischemia can lead to impaired blood circulation in the area of the ear where the balance organ is located. And insufficient blood circulation will lead to disruption of confident movements. Arrhythmia and arterial hypertension will also have a negative effect on the body.
Blood viscosity also affects gait. The flow rate, and therefore the rate of oxygen delivery to all parts of the body, including the cerebellum, depends on it.
Intervertebral hernias, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine - all this will complicate the transmission of signals along the nerve endings to the brain, therefore disturbances in stepping movements are possible.
In addition, sleep is often disturbed with age, and this can lead to diseases of the above-mentioned 3rd category.
There is also such a reason as socio-psychological disadaptation. This is the area of psychosomatics. That is, an elderly person feels insecure, does not see his own importance, he underestimates his physical and psychological capabilities. He develops a feeling of uselessness, fears, phobias, and increased nervousness arise. As a result, the head may become dizzy, it begins to skid when walking, it often becomes dark in the eyes, and the state of health worsens every day. It is imperative to get rid of this condition. It is best to turn to professionals. Otherwise, there may be very serious consequences.
As you can see, there are many reasons for an unsteady gait. And yet, all these factors are not at all a reason to refuse treatment.
If the cause is eliminated, there will be no consequences. That is, life will be full and healthy. Therefore, it is necessary to undergo treatment, regardless of the years lived.
What could be the reasons?
In medicine, there are 3 categories of diseases that can be accompanied by staggering when walking:
- Disturbances in the functioning of the musculoskeletal system - vertebral and craniocerebral injuries, bruises and damage to the muscles of the lower extremities, osteochondrosis, flat feet, arthrosis, muscle atrophy.
- Pathological processes in the brain are damage to the parts that are responsible for coordinating all movements and monitoring the operation of the motor system. For example, hemorrhagic stroke, brain tumors, VSD, inflammatory processes in the brain, malfunction of the central nervous system, atherosclerosis, congenital anomalies of the cerebellum, meningitis, improper use of neurotoxic drugs, as well as the development of polyneuropathy.
- Disorders in the psycho-emotional state - stress, nervous breakdowns, depressive states, panic attacks, neuroses, psycho-neurological disorders. This also includes alcohol poisoning.
The influence of drugs and alcohol on the nervous system is very strong. Once toxic substances are in the body, they quickly penetrate the blood and spread to all tissues and organs. In addition, alcohol in the body begins to decompose, resulting in the formation of acetaldehyde , a toxic substance that has a detrimental effect directly on the cerebellum.
Important! Under no circumstances should you take medications, including painkillers, together with alcohol, as the consequences of this can be completely unpredictable.
Causes
Impaired balance when walking occurs due to inconsistency between muscles that perform the same or opposite functions: flexors - extensors, adductors - abductors, etc. They tense and relax in the wrong order, which interferes with the normal movement of the limbs.
On the other hand, nerve fibers are affected. This is often associated with damage to the central nervous system (CNS). The area of coordination of movements is located in the cerebellum. When some of the cells in this area die, a loss of balance and an unstable gait are observed.
Instability when moving may be due to damage to the vestibular apparatus. It is located in the inner ear and is responsible for maintaining balance. Damage to part of it or pathways leads to incorrect information to the brain about the position of the body in space. Because of this, unsteadiness of gait develops.
Old age and its impact
Quite often, swaying when walking is observed in people over 60 years of age. Such patients feel dizzy, spots appear before their eyes, tinnitus appears , and the patient experiences frequent and severe headaches. In most cases, people attribute such symptoms to age-related changes and do not consult a doctor about it. However, in some cases, such symptoms indicate disturbances in the functioning of the body, which can be controlled with timely consultation with a specialist.
One of the common causes is a malfunction of the heart and blood vessels of the brain. In addition, gait can be affected by increased blood viscosity, injuries and diseases of the spine.
Older people who walk unsteadily may feel disorientated and may develop fears and anxiety. Therefore, you should not delay your visit to the doctor, as the consequences can be very disastrous.