12 April 2021
11785
0
3 out of 5
Neck pain is a very common problem. After all, according to medical statistics, more than 70% of people experience this periodically or regularly. Nevertheless, there are many reasons that can provoke pain of varying intensity in the neck. Most of them lie in diseases of the cervical spine. At the same time, the characteristics of pain, its localization, and the nature of other existing symptoms are important diagnostic signs that help to correctly determine what triggered them and prescribe treatment appropriate to the situation. It is very important to identify the disease causing pain in the neck as early as possible and take measures to eliminate it, since they can cause severe complications, including disability.
Causes of neck pain when turning the head
At home, you can guess the cause of neck pain when you turn your head, but a doctor will make an accurate diagnosis based on the results of the examination. During the examination, it is necessary to indicate exactly in which area the discomfort manifests itself, as well as the conditions under which it appears. The same symptoms may indicate different diseases, each of which requires its own treatment regimen.
Pathologies of the cervical spine
The cervical spine consists of 7 vertebrae and is highly mobile. The bone segments are connected to each other by ligaments, and for shock absorption there are intervertebral discs made of cartilage tissue between them. The processes of the vertebrae form channels for the passage of blood vessels and nerves. The cervical spine is the most vulnerable, since in this area the muscle layer is not strong enough for full protection. During diagnosis, acute and chronic diseases, as well as mechanical damage to the vertebrae and surrounding tissues, can be detected.
Osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of the intervertebral discs. It often appears in old age and is associated with insufficient blood supply and nutrition of cartilage. Fabrics lose elasticity and become less durable. If normally the cartilage layer cushions when walking and when moving the head, then with osteochondrosis this function is performed insufficiently. The disease can also be a consequence of injuries, incorrect posture when walking or while working. Osteochondrosis is manifested by localized pain in the neck, dizziness, and lack of mobility of the affected area. It has a chronic course and develops in several stages:
- decreased elasticity of intervertebral cartilage and its shock-absorbing function;
- reduction of the clearance between adjacent vertebrae, which leads to compression of important nerves and arteries;
- the formation of osteophytes - bone growths that form on the articular surfaces of the vertebrae as a compensatory mechanism to prevent their abrasion during movement;
- pathological immobility of the vertebrae, increasing pain not only during movement, but also at rest, as well as mechanical damage to the nerves and vascular walls.
Acute pain in the neck when turning the head occurs with osteochondrosis of stages 2 and 3. At these stages, irreversible changes begin, the growth of the articular surfaces of the vertebrae. Osteophytes put pressure on the vertebral artery and spinal nerve roots. This leads to sharp pain in a certain position of the head, and then the pain persists even at rest. Treatment is selected individually; in the initial stages, the development of the disease can be stopped without surgery. For this purpose, special exercises, drugs to restore blood circulation and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. If necessary, surgery is prescribed to remove osteophytes.
Protrusions and hernias
A common cause of sharp pain in the neck when turning the head is protrusion and hernia . They represent a protrusion of the intervertebral disc, often in the lateral directions. The pathology may be associated with incorrect posture, curvature of the cervical spine, as well as weakness of muscles and tendons. Protrusions can develop as a result of injuries, including fractures and bruises.
The intervertebral disc is a formation that consists of a strong but elastic outer fibrous membrane and a nucleus pulposus. If the vertebrae place uneven pressure on the cartilage, it begins to protrude in the direction of less resistance. Symptoms are directly related to the stage of protrusion.
- The first stage is associated with the formation of microscopic tears in the fibrous capsule. MRI shows slight protrusions in the lateral direction.
- Second degree – prolapse. Under pressure from the vertebrae, protrusions of intervertebral cartilage are formed, the dimensions of which do not exceed 3 mm.
- At the third stage, protrusions and larger hernias form . They cause acute pain when turning the head, which spreads to the neck, arm, back and shoulder blades.
- The fourth stage is rupture of the fibrous capsule. This is a dangerous condition that requires surgical treatment.
In the first stages, protrusions can be treated conservatively. The doctor prescribes painkillers and drugs to improve the nutrition of cartilage. It is also necessary to perform a daily set of exercises aimed at strengthening the muscles and ligaments of the cervical spine. They allow not only to stop the process, but also to reduce the size of the protrusion. In the third and fourth stages, most patients undergo surgery, during which the adjacent vertebrae are connected and become immobile.
Curvature of the cervical spine
Pain in the neck when tilting the head or turning it to the side often accompanies curvature of the spinal column. In the cervical region, scoliosis (lateral curvature) or lordosis is found - deviation of the axis in the anterior direction. Kyphosis is a backward bend of the spine; it is very rarely diagnosed in the neck area, since this area normally has physiological lordosis. The disease is often detected in childhood or adolescence, during periods of intensive growth. However, in adults its appearance may be associated with injuries, vitamin deficiencies, and weakness of the muscles of the cervical spine.
With the first degree of spinal curvature, a deviation from the normal position is formed by an angle of up to 10 degrees, the second - from 10 to 25, the third - up to 50 and the fourth - more than 50 degrees. Its clinical manifestations depend on the stage of the disease. Mild forms can be corrected with special exercises, correct posture and massage. For third and fourth degree curvature, surgical treatment may be required.
Spondylosis
Spondylosis is an acute or chronic condition in which pathological immobility of adjacent vertebrae is observed. Its causes are injuries, degenerative processes, osteochondrosis and other diseases of the cervical spine. Spondylosis can also be caused by injury. It develops in several stages:
- decreased elasticity of intervertebral discs;
- deposition of calcium salts in soft tissues, including in the fibers of the anterior longitudinal ligament;
- formation of osteophytes;
- in severe forms - fusion of adjacent vertebrae.
With spondylosis, pain occurs at a certain position of the head. They are associated with a mechanical effect on the roots of the spinal nerves, which are located in the damaged area. Surgical treatment consists of removing acute osteophytes or replacing the joint with an implant.
Muscle pain
One of the causes of neck pain when tilting the head forward, backward or to the side is diseases of the muscles of the cervical spine. One of them is myogelosis. Small dense nodules form in the thickness of the muscle tissue, painful when touched. They are small, the largest reaching up to several centimeters in diameter. The disease often occurs in an acute form. Seals prevent normal blood flow through the vessels and the passage of nerve impulses. They cause the following symptoms:
- acute pain in the neck, which intensifies with movement, spreads to the back of the head and shoulders;
- noticeable limitation of mobility of the cervical spine;
- headaches and dizziness;
- nausea and weakness, general deterioration of health.
Common causes of myogelosis are injuries and muscle strains, frequent hypothermia, incorrect posture while walking or working at a monitor. Nodules are easily detected by palpation; the skin over the damaged areas may become red and hot. With timely treatment, the seals disappear, and the mobility of the neck and head is restored.
Cervical migraine
Migraine is a primary headache that occurs in attacks and is chronic. One of its causes is compression of the vertebral artery, which runs in the cervical spine. This can be caused by displacement of the vertebrae, protrusion or hernia, as well as the proliferation of bone tissue and the appearance of osteophytes. Symptoms worsen after a long stay in an uncomfortable position, which puts pressure on the vascular walls. At this time, brain cells receive insufficient amounts of oxygen and nutrients and experience ischemia. Patients present with characteristic symptoms:
- neck pain caused by an underlying disease, which worsens in a certain position;
- soreness of the occipital surface of the head;
- dizziness, nausea, possible fainting due to sudden compression of the artery;
- temporary deterioration of hearing, vision, coordination of movements.
In diseases of the cervical spine, symptoms of classic migraine appear. During diagnosis, it is possible to establish its cause and prescribe treatment that will reduce the manifestations of the underlying disease. Migraine attacks can be controlled by performing special exercises to strengthen the neck muscles, dosing physical activity and monitoring your posture throughout the day.
Other reasons
Neck pain is a common symptom for a large number of diseases. Despite the similar picture, they require an individually selected treatment regimen. During diagnosis, acute and chronic diseases can be detected, including:
- rheumatoid arthritis - an autoimmune inflammation that affects the joints of the cervical spine;
- neoplasms – neurofibromas (benign neoplasms that originate from the nerve sheaths) are more often formed in this area;
- injuries - X-rays reveal dislocations and subluxations of the vertebrae, compression fractures, bruises and muscle strains are also common;
- diseases of the thyroid gland located on the front surface of the neck;
- cold viral diseases.
Neck pain often occurs in healthy people. They develop after a long stay in an uncomfortable position, improper exercise, or sleeping on a surface that is too hard or soft.
Symptomatic sketch
When your neck hurts and you shoot in the head, the obvious symptoms of the disease are indicated not only by inflammatory processes in the cervical lymph nodes above the collarbones, but also by pain in the eyes, attacks of dizziness, and sleep disturbances. Internal diseases can provoke neck pain, each of which is characterized by certain symptoms.
Cervical osteochondrosis. The main symptom is pain. People note that one day the right side of the neck hurts and radiates to the head, another time the left side of the neck hurts and radiates to the head. In this case, the person does not make intense head movements, but the muscles of the back and collar area remain tense. The disease develops slowly over a long period of time. Symptoms may subside and then recur.
Injury. Head contusion, concussion, deformation and destruction of intervertebral discs, damage to ligaments and muscles of the collar area. When turning sharply or bending, the neck hurts greatly and radiates to the head. After a night's sleep or standing for a long time, these symptoms arise with renewed vigor.
Nuchal collar neuralgia. A pinched occipital nerve causes shooting pains. If the pain in the neck on the left or right radiates to the head, then the whole head hurts. Any movement causes severe discomfort, so the patient stands straight and turns his whole body. There is often a feeling of coldness and numbness in the pathological area. The attack may be accompanied by lacrimation and nausea.
Fatigue and stress. Worries, worries, any psycho-emotional stress cause pain in the back of the neck, which radiates to the head. If you follow simple recommendations, the pain goes away (after rest or massage).
Impaired blood circulation. The main reasons are hypertension, smoking, obesity. A sharp increase in pressure in the blood vessels leads to throbbing pain. They appear suddenly. With age, attacks become more frequent. Pressure surges lead to persistent vascular spasms, and blood supply to the brain and neck muscles is disrupted. Excess weight is the cause of many ailments. Hypertension and diabetes are some of the many diseases caused by obesity. If you do not give up your usual but incorrect lifestyle, then pain symptoms will become constant companions.
Diagnostic methods
If you experience neck pain, you should consult a therapist. After the examination, he will refer you for consultation to a doctor of a more narrow specialization. Thus, diseases of the cervical spine are treated by a vertebrologist, diseases of the nerves by a neurologist, damage to bones and soft tissues by a traumatologist. To determine the cause of pain and make an accurate diagnosis, additional examination methods will be required:
- radiography - the pictures will show fractures and dislocations of the vertebrae, signs of osteochondrosis, spondylosis, pathological growth of bone tissue;
- MRI – prescribed for suspected protrusions and hernias, as well as diseases of muscles, ligaments and tendons;
- blood tests to determine symptoms of infectious diseases and inflammatory processes;
- additional tests that will allow you to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis - determination of C-reactive protein, rheumatoid factor.
The Clinical Brain Institute has precise, modern equipment, thanks to which you can quickly obtain the necessary data. Correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment. Complete information about the condition of the cervical spine will indicate which techniques and medications should be used for each patient.
Prevention
To prevent the formation of a cervical hernia in patients at risk, you should adhere to these simple rules:
- Avoid forced, uncomfortable head positions.
- If possible, do neck exercises frequently, especially if your job involves spending a lot of time at the computer.
- Walk and sit straight, do not slouch.
- For rest, use a hard mattress and a small, medium-firm pillow.
- Do not overload the spinal region, regardless of which area the load falls on.
A cervical hernia is a rather dangerous disease; it is difficult to treat. You can count on a positive result using only conservative treatment methods only if the patient promptly seeks help from a specialist. In addition, it should be taken into account that for a cervical hernia larger than 6 mm, surgical intervention is required.
First aid
It is impossible to undergo complex treatment at home. However, there are several ways to reduce pain before consulting a doctor:
- over-the-counter painkillers - Analgin is available in any pharmacy and in your home medicine cabinet;
- massage of the neck and head area - effective for muscle spasms, it can be performed independently;
- warm bath – relaxes muscles, improves blood circulation and relieves spasms.
If the tissues around the painful area are swollen, redness of the skin and an increase in its local temperature are observed - massage and thermal procedures are contraindicated. In this case, it is enough to take a painkiller and make an appointment with a doctor.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Patients who have very severe pain in the cervical spine should provide functional rest for the neck and avoid head movements, especially turning from side to side. To reduce tension in the neck muscles, it is necessary to take regular breaks from working at the computer or machine. To find out the cause of cervicalgia and select treatment, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. Until the diagnosis is verified, it is permissible to take analgesics from the NSAID group to relieve excruciating pain. Independent use of warm compresses is prohibited.
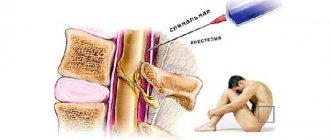
Cervical spine massage
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the cause of the disease and the clinical stage. In the absence of pronounced destructive changes in the spinal column, a combination of drug treatment and physical therapy is sufficient. Physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed after acute pain in the cervical spine subsides; the most effective are acupuncture, transcutaneous electrical stimulation, ultrasound and electromagnetic methods. For chronic pain syndrome, manual therapy is used. Medicines usually used:
- NSAIDs
. They belong to the first line of drugs for the treatment of acute and chronic pain in the spine. Effectively eliminate pain, reduce inflammatory reactions in joints and soft tissues. To minimize side effects, selective COX-2 inhibitors are preferred. - Local anesthetics
. If the spine hurts unbearably in the cervical region, therapeutic blockades are recommended. Anesthetics in combination with glucocorticosteroids are administered as close to the lesion as possible: into the neck muscles, facet joints, and less often, epidural blockades are performed. - Neurotropic vitamins
. To enhance the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of other medications, B vitamins, especially thiamine, are used. The drug inhibits pathological pain impulses and increases the concentration of the most important endogenous analgesic substances. - Anticonvulsants
. These drugs are combined with antidepressants for chronic resistant pain syndrome and psychogenic pain. Additionally, short courses of muscle relaxants are used. For vascular disorders, venotonics are administered.
Surgery
For unstable fractures of the vertebral bodies and arches, surgical reposition of the fragments is indicated with their subsequent stabilization using bone osteosynthesis methods - usually metal plates with transpedicular fixation are installed. For benign spinal tumors, they are removed after preliminary decompression of the brain structures. In the case of spinal osteomyelitis, sequestrectomy is necessary with further restoration of the anatomical integrity of the spinal column.
Surgical treatment methods used for osteochondrosis can be divided into two groups: decompression and stabilization. Decompression surgeries are designed to reduce pressure on the spinal canal and relieve radicular syndrome. For this purpose, laminectomy, endoscopic discectomy, and facetectomy are performed. Stabilizing operations are required when the cervical vertebrae are displaced in the frontal plane and there is a risk of spinal cord damage. Anterior or posterior spinal fusion is performed (fixation of bone structures to ensure their complete immobility).
Treatment methods
Treatment for neck pain when turning the head is selected individually. In most cases, a course of medications is sufficient to eliminate the main cause of discomfort and unpleasant symptoms. Treatment takes place at home, but the patient must periodically visit the doctor for repeated examinations and correction of the regimen. Surgery may be required in advanced cases when conservative methods are not effective enough.
- A course of medications is the basis for treating neck pain. The doctor will prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of tablets, ointments or injections. Painkillers and medications to improve blood circulation may also be required. For osteochondrosis, drugs based on chondroitin and glucosamine are effective for restoring cartilage. Muscle relaxants will relieve muscle tone and reduce compression of nerves and blood vessels.
- Surgeries are prescribed if drug treatment does not help. Minimally invasive removal of hernias, neoplasms, and osteophytes in advanced stages of osteochondrosis is practiced. Joint surgery is performed under the control of an arthroscope - a special device that allows you to visualize the picture through small punctures, without large incisions.
- Additional techniques are required for complex treatment. At home, you need to perform simple exercises to strengthen the muscles of the cervical spine. The doctor may also prescribe wearing an orthopedic collar, physiotherapy sessions and therapeutic massage.
Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute specialize in treating diseases that manifest as neck pain. The effectiveness of the techniques depends, among other things, on the correct implementation of the recommendations. It is important to take prescribed medications on schedule, do exercises, and contact for follow-up consultations on time.
Treatment methods
If neck pain occurs due to diseases of the spine or muscles, treatment will be the same as for similar problems in other areas of the back. Namely - anti-inflammatory tablets and ointments, physiotherapy, massage, and then, in some cases, physical therapy.
For increased excitability and anxiety that accompany neuropathic changes, Pregabalin is often prescribed. Flupirtine works well for muscle strain in the collar area. Finlepsin can perfectly eliminate spasms and convulsions. Any muscle tissue relaxants are also prescribed for neurological diseases. The absence of spasm has a beneficial effect on the nervous and vascular systems. To relieve headaches or neck pain after overwork, you can give preference to a massage with essential oils. Physiotherapy with special devices helps a lot. It is also recommended to rub essential oils into your temples or neck.
Preventing neck pain
Most diseases that cause neck pain when turning the head are chronic. Their development can be stopped if you regularly follow simple prevention rules. Doctors recommend the following measures:
- correct posture in everyday life, as well as while working at the monitor;
- a suitable mattress and pillow - blood circulation should not be impaired during sleep;
- proper nutrition with sufficient vitamins and microelements;
- diet if necessary - excess weight often causes chronic diseases of the spine;
- moderate physical activity.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individual programs for diagnosing and treating neck pain. Here you can get advice from narrow and general doctors, specialists with many years of experience. Modern equipment is used for the examination, which allows you to obtain accurate data. Treatment takes place on an outpatient basis or in a hospital.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 4/5 — 13 votes
Share article on social networks
Main causes of pain
Depending on the nature of origin, the causes of neck pain can be very diverse.
This does not mean at all that the problem appears as a result of natural injuries - back injuries or spinal curvatures. Discomfort at first and painful sensations later - everything can come back to haunt you as a symptom of one of the diseases of the internal organs. Thus, among the most common causes of neck pain that extends to the head are:
- osteochondrosis;
- cervical neuralgia;
- poor blood flow to the cervical and occipital regions;
- injuries;
- infectious diseases;
- cervical migraine;
- myogelosis;
- hypertension;
- spasm of the muscles of the collar zone.
Uncomfortable, incorrect head position when reading or working at the computer leads to overwork of the neck muscles. Muscle spasm as a result of fatigue leads to vasoconstriction and pinched nerves. All this leads to pain in the back of the neck, radiating to the head and back.
How can it bother you?
Neck pain has a number of symptoms that make it possible to suspect a specific disease. Sometimes, based on the patient’s complaints and examination alone, the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment. This is done in order to alleviate the person’s condition; he will still have to undergo examinations to confirm or clarify the doctor’s opinion. For example,
- nagging pain in the neck on the left most likely indicates osteochondrosis or other problems associated with the spine;
- if your neck hurts on the left side, in this place your fingers find a ball, pressing on which is painful, it’s probably an inflamed lymph node, you can’t heat it, you need a therapist;
- when the muscle on the left or back of the neck hurts, and you even feel what it is - a microtrauma, this should go away on its own in 2-3 days;
- if the pain from the neck radiates to other parts of the body - arm, shoulder, shoulder blade -
- when the neck on the left and the head on the left hurt, most likely you need a neurologist: unilateral pain in the head is a likely sign of migraine, and sometimes it spreads to the neck;
- if the pain from the neck clearly radiates to the head on the left, this is also to a neurologist, this is how neuritis of the occipital nerve manifests itself;
- when the neck and shoulder hurt at the same time, and turning the head to the left makes the pain more difficult, this is similar to the symptoms of plexitis, in which the pain is always one-sided, but in this case there is no point in treating the neck, the cause of the disease is in the area of the brachial nerve plexus;
- when it bothers you in the front below, close to the jugular cavity, you need to see a therapist as quickly as possible, this may indicate problems with the thyroid gland;
- if your neck and ear hurt on one side at the same time, it is most likely otitis media, you need a doctor as soon as possible; in extreme cases, an on-duty therapist will do.
A little about unobvious reasons. Pain with cholecystitis may radiate to the neck, and an attack of angina may also occur. Sometimes similar sensations appear after a stroke. There are other diseases in which pain that occurs far from the disturbing part of the body leads to a symptom that is easily confused with osteochondrosis. Therefore, it is better to visit a doctor, otherwise there is a risk of missing a serious or even life-threatening disease.