Epidural anesthesia, also known as “epidural,” is one of the methods of regional anesthesia in which medications are injected into the epidural space of the spine through a catheter. The mechanism of action of epidural anesthesia is associated primarily with the penetration of drugs through the dural couplings into the subarachnoid space, and as a result, blockade of the passage of nerve impulses (including pain) along the radicular nerves and further into the spinal cord. The principle of use is as follows: when a woman is in pain and wants to be relieved, she should receive EA. There is a lot of debate about when to start an epidural. Thus, in the USA they begin to administer analgesia at the very first stage of contractions, and in Canada it is often used already at the full opening of the cervix. The indication for pain relief is any pain in a woman associated with childbirth, regardless of the degree of intensity, the main thing is her desire. Contraindications for epidural analgesia are the presence of a woman with blood problems, septic complications, a tattoo at the puncture site, and other certain physiological conditions. And another very important point: epidural analgesia can only be carried out if the birth is performed by an obstetrician-gynecologist who knows how to conduct childbirth with an epidural. In a number of countries, with the advent of EA, the frequency of cesarean sections increased, since obstetricians simply did not know how to work with it.
So, we figured out the concept of “Epidural anesthesia”. But why do most women have a feeling of fear before a procedure that is aimed at protecting them from pain?
In the animal world, fear is an emotion based on past negative experiences that plays a large role in the survival of an individual. In people, most often, the emergence of fear is associated with the “unknown” and lack of knowledge, as well as with received incorrect information. In fact, according to statistics, there are less than 3% of people who have had negative experiences of complications from regional anesthesia in the past. Others experience fear of the upcoming anesthesia due to negative information received from friends, and most often from social networks and various forums. The Internet is simply replete with various pseudoscientific articles and reposts, written certainly not by anesthesiologists, and perhaps even by people without medical education.
What is epidural anesthesia?
When treating patients, various medications are prescribed. These include painkillers of varying degrees of action. Epidural anesthesia, or epidural, is one of the methods of pain relief in order to eliminate any sensitivity in the patient’s body below the waist. Despite the fact that this method has its obvious and undeniable advantages, some patients complain that their back hurts after epidural anesthesia. Accordingly, questions arise about why this happens, and what needs and can be done to make the discomfort go away faster?
What it is?
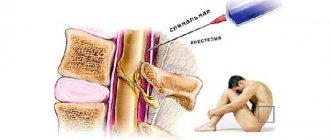
Epidural anesthesia or epidural anesthesia is a method of effective pain relief, during which certain analgesic substances are injected using a thin catheter into the spinal canal area. The substances administered are ketamine, lidocaine and others that have a local effect. The effect of this procedure is simple from a medical point of view - nerve impulses do not reach one of the main centers of the nervous system - the spinal cord. Also, all the patient’s muscles relax – a muscle relaxation effect occurs. In this case, the patient is aware of what is happening, that is, he is fully conscious, but does not experience any unpleasant sensations or even pain.
Epidural anesthesia
This form of pain relief can be used:
- during the birth of a child;
- during caesarean section;
- as an additional method of pain relief during standard anesthesia;
- to eliminate pain after surgery;
- as an analgesic with local action during plastic or urological operations.
Epidural and spinal anesthesia: what is the difference?
The most well-known use of the method is to provide assistance during labor. The pain experienced by a woman during this period is considered one of the most severe variations of the pain syndrome.
The principle of anesthesia
Epidural anesthesia can be performed on any part of the spinal column, depending on the need and the location of the surgical intervention. The spine itself is a complex structure consisting of a large number of vertebrae interconnected through intervertebral discs and a number of other elements. The structure of each vertebra is such that there is a hole in its middle part. A whole series of these holes, “stacked” on top of each other, form a long spinal canal, inside of which the spinal cord is located. In the lumbar region it passes into the spinal cord.
Epidural anesthesia during pregnancy
Table. Methods for determining the venue.
| Method | Description |
| "Hanging Drop" | The needle catheter is inserted into a special interspinous ligament quite deeply. Next, a small drop of the drug or regular saline solution is suspended from it, which will not move when the needle begins to move through the ligaments. But as soon as it reaches the epidural area, the drop will disappear thanks to physics - the effect of negative pressure. The most important thing is that there is no blockage in the needle - the so-called obstruction; in this case, the drop will be drawn into the needle cavity. This method can only be used by anesthesiologists with extensive experience and experience. |
| Loss of resistance | In this case, the catheter is inserted into the same interspinous ligament, then a syringe filled with air or ordinary sodium chloride is attached to it. They cannot be inserted until the tip of the needle reaches the desired epidural space. |
The drug must be injected into the correct place
When is it prescribed?
Before answering the question of what to do if your back hurts after epidural anesthesia, you need to understand what this procedure involves and when it is prescribed. Medications are administered by catheterization (through catheters into existing cavities in the human body) into the space of the spinal cord. The puncture site is also anesthetized so that the patient does not experience any pain when the painkiller is administered. The effect after the administration of medications occurs within 10–15 minutes. Most often, an epidural is prescribed to women in labor - during childbirth or when a caesarean section is scheduled. In such cases, it is important not to harm the fetus, and this method is safe for the baby. In addition to obstetrics, epidurals are prescribed in urology, gynecology, and during surgery in the abdominal cavity or on the pelvic organs.
Contraindications to epidural pain relief
Epidural anesthesia, as mentioned above, is a complex process.
The danger of this procedure lies not only in the fact that the spinal area is affected during medical manipulations. The effect of the drug itself on the body can negatively affect the patient's condition. Some opiates that are added to a primary pain reliever can cause dizziness, nausea, vomiting and sometimes hallucinations. It is strictly forbidden to perform epidural anesthesia if the patient:
- presence of bacteria in the blood (bacteremia);
- the presence of inflammatory diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- lesion or infection of the skin in the area of the puncture;
- heart failure;
- diseases of the central nervous system and spinal cord;
- scoliosis;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- excess weight;
- allergy to anesthetic.
In most cases, even with an intervertebral hernia, epidural anesthesia is allowed. The injection needle is inserted on the other side of the damaged intervertebral discs. This procedure does not affect their condition in any way.
Why does my back hurt after epidural anesthesia?
When the medications stop working, the patient begins a recovery period, which is accompanied by various sensations. Sometimes patients experience back pain after an epidural, and how long it hurts and whether any treatment is needed depends on the type and complexity of the surgery and the resulting complications. The occurrence of pain of varying degrees and localization occurs for various reasons. How quickly does a patient recover after receiving an epidural, and what can happen? Timing and response are individual indicators. The causes of pain are also varied.
Infection
Infection develops where the needle was inserted, for example because mistakes were made during disinfection. In some cases, a problem arises if the catheter is left in the patient's body when additional and longer-term pain relief is required.
Intervertebral hernia
If the pain persists for several months or longer, then most likely the patient has an intervertebral hernia. It is not a contraindication to an epidural, but may be an individual feature that should be taken into account when prescribing this method of pain relief; in any case, careful monitoring of the patient’s condition is required.
Medical errors
Back pain after epidural anesthesia may also have a cause such as medical error. This happens if the doctor touches a bunch of veins when installing a catheter and inserting a needle. This is rare, but patients who take medications to improve blood circulation are at risk (this should be noted in the medical history). Also, when carrying out the necessary manipulations (in the absence of sufficient experience on the part of the doctor), the hernia or ligaments, as well as the roots of nerve fibers, may be damaged. Your back may also hurt after epidural anesthesia for a caesarean section. This happens because the mother’s center of gravity moves, and the body needs time to adjust to a new state and cope with the stress experienced.
Back pain due to complications of regional anesthesia
Complications when following the technique of epidural and spinal anesthesia are quite rare. They may be associated with incorrect determination of indications and contraindications for manipulation, as well as with the exacerbation of pre-existing problems.
- Postpuncture syndrome most often occurs after spinal anesthesia, but can also develop after epidural if the dura mater was damaged during the manipulation. At the same time, through the hole in it, part of the cerebrospinal fluid flows into the epidural space, resulting in the development of liquor hypotension. The main manifestation of post-puncture syndrome is severe headache, especially when standing. Pain in the back usually does not bother patients.
- An epidural hematoma can result from unintentional injury to a vessel during epidural or spinal anesthesia, but most often occurs in patients with reduced blood clotting. That is why regional anesthesia is not necessary in the presence of coagulopathy. In this case, on the first day after the manipulation, the spine and muscles at the injection site begin to ache, then, as the hematoma grows, neurological symptoms associated with compression of the spinal roots may appear: numbness or paresthesia in the legs, muscle weakness, disturbances in urination and defecation, manifestations, similar to cauda equina syndrome. Treatment for this complication should be started as early as possible.
Blood clotting disorders can cause complications such as epidural hematoma
- Cauda equina syndrome can develop as a result of an epidural hematoma or damage to nerve fibers when the technique of spinal anesthesia is violated. In this case, severe pain is felt at the injection site, which spreads along the nerve roots, usually to the leg. In addition, there is urinary retention or urinary incontinence, constipation or, on the contrary, involuntary passage of gas and feces. If clinical signs of cauda equina syndrome appear after regional anesthesia, emergency treatment is required.
- Unintentional damage to the ligaments of the intervertebral joint and muscle spasm as a reaction to manipulation trauma can also cause back pain due to epidural anesthesia. It is rarely strong and long-lasting, and if the load on the spine is rational, it goes away spontaneously. How long the discomfort associated with a ligament injury or muscle spasm can last, and how long the healing will take, depends on compliance with the motor regimen and the level of load on the spine.
Slight pain at the injection site 1-2 days after epidural anesthesia is normal; severe pain combined with numbness or weakness in the legs and other unusual symptoms is a sign of complications requiring urgent treatment.
No matter how many times epidural anesthesia is performed on a patient with a healthy spine, provided the manipulation technique is followed, no problems will arise. But diseases and syndromes that previously existed in a latent form can manifest themselves.
Elimination of pain after the procedure
Normally, the body and body sensitivity are restored a short time after the procedure. If this does not happen, it is recommended to consult a neurologist
who will find out why your back hurts after epidural anesthesia and what to do to relieve the discomfort.
Painkillers
During normal recovery, no painkillers or other medications are required. But if the intensity of the pain is strong enough and lasts a long time, only a doctor can help you choose the right painkillers depending on what the epidural was needed for and why the pain occurred.
Seeing a doctor
If there is inflammation or irritation, then treatment will require taking antibiotics prescribed by a doctor, and in case of an abscess and serious suppuration, treatment by a surgeon is necessary. The doctor can also give valuable recommendations on nutrition - especially for overweight patients or women after childbirth, as well as on physical activity to strengthen the muscle corset. Additionally, a course of vitamins may be prescribed.
Epidural patches
When medications do not help and the post-puncture headache becomes more intense, experts suggest that the patient receive an epidural.
patch. This should be done by an anesthesiologist. A little blood is taken from the patient’s vein; it will act as a kind of filling. Blood is injected in the same way into the spinal space of the spine, where it coagulates and eventually clogs the hole in the tissue. The cerebrospinal fluid stops leaking and the headache stops.
After this procedure, headaches most often disappear within 24 hours. If this does not happen, doctors perform the procedure a second time to achieve the desired effect.
A contraindication to the installation of an epidural patch may be the patient's elevated body temperature. In addition, the patient may experience some serious complications after this procedure:
- infectious processes;
- bleeding;
- disturbances in motor activity of the lower body;
- back pain.
An epidural patch helps only in half of the cases the first time, but a repeated one gives almost 100% effect. After installing the patch, the patient is recommended to lie still for at least 12 hours, and in the first two weeks not to strain or lift anything heavy.
How the treatment method works
Epidural anesthesia can be performed at different levels. For operations on the vessels of the lower extremities, anesthesia is most often performed at the lumbar or thoracic level.
To perform anesthesia, the patient is placed on his side, the puncture site is treated with an antiseptic solution and isolated with sterile material. The patient's legs are brought to the stomach.
The anesthesiologist feels the spinous processes of the vertebrae, administers local anesthesia to the skin at the site of the intended puncture, and then slowly punctures the epidural space with a special needle. After you feel a loss of resistance, the doctor performs a series of tests to make sure that the needle is in the right place. After this, a test dose of the drug is injected into the epidural space. The reaction is monitored. If motor and sensory block occurs quickly, this means that a spinal puncture has been performed. If the tests show that the epidural space is punctured, then a special thin catheter is installed there.
The catheter is fixed with a special plaster and can be used for pain relief both before and after surgery.
Advantages of treatment at the ISC
In our clinic, 100% of surgical interventions on the lower extremities and terminal abdominal aorta are performed using regional anesthesia. 95% of surgical interventions are performed under epidural anesthesia. Epidural anesthesia is also performed after surgical interventions, prolonged postoperative analgesia, and in the preoperative period in patients with critical ischemia of the lower extremities for preoperative preparation. Today, this is the optimal method of anesthesia for operations on the lower extremities and lower abdominal cavity. In addition to anesthesia during operations, epidural anesthesia is used to relieve pain in the legs during critical ischemia. In our clinic, patients with critical ischemia and gangrene are immediately placed with an epidural catheter and given a continuous infusion of anesthetic to completely relieve pain.
Indications and contraindications for the treatment method
Indications:
- Surgical interventions on the chest, abdominal organs, urological, proctological, obstetric and gynecological, operations on the lower extremities.
- Surgical interventions in patients with severe concomitant pathologies (obesity, cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases, impaired liver and kidney function, deformation of the upper respiratory tract), in elderly and senile people, in patients with a “full” stomach.
- Component of combined anesthesia.
- Severe combined skeletal injuries (multiple fractures of the ribs, pelvic bones, lower extremities).
- Postoperative pain relief.
- Component of therapy for pancreatitis, peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, status asthmaticus.
- Fighting chronic pain syndrome.
Contraindications:
Absolute:
- patient refusal;
- skin diseases of the back with pronounced pustular abscesses and formations at the puncture site (injection);
- allergic reaction to local anesthetic;
- severe deformation of the spinal column (for example, Bechterov's disease);
- impaired blood clotting function (coagulopathy);
- clinically significant hypovolemia (dehydration, blood loss);
- cardiac conduction disturbances (AV block, sick sinus syndrome);
Relative:
- developmental anomalies and mild deformation of the spine;
- psychiatric diseases;
- low level of intelligence in the patient;
- treatment with antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants - blood thinning drugs (clopidogrel and its derivatives, warfarin, etc.);
- previous spinal surgeries;
- presence of a tattoo at the puncture site (injection);