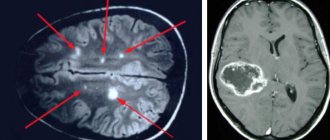
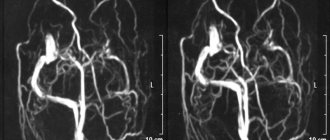
Ultrasound of the child's brain
Ultrasound of the brain in a newborn baby may also be called neurosonography
(NSG). With its help, the specialist receives a two-dimensional image of the structure of the brain, information about the condition of the tissues and head. The method is based on the various properties of tissues to reflect high-frequency sound waves. The procedure does not involve the use of magnetic fields or ionizing radiation, so ultrasound can be used to examine the brain of even newborn children.
When is an ultrasound of the brain prescribed for newborns?
Ultrasound of a newborn’s head is prescribed in a number of cases:
- premature birth (36 weeks or more);
- there are signs of damage to the child’s central nervous system;
- the body weight of the newborn does not exceed 2800 grams;
- bulging fontanel;
- cerebral hernia;
- multiple external developmental defects; • birth injury.
Also, ultrasound of the brain in newborn children is performed after transfer to intensive care, in case of too rapid and protracted labor, in case of complications during the birth process, if the child did not cry immediately after birth. In addition, the examination may be prescribed for other indications, including if specialists suspect an intrauterine infection. From a month to three months, ultrasound of the brain is performed on children if there is a suspicion of neurological diseases. An examination may be required if there is psychomotor retardation, muscle weakness, or seizure activity. To diagnose possible pathologies in the development of a child’s brain, ultrasound of the head is recommended for newborn children from one month to one year of age. It is recommended to carry out several procedures at intervals of a month or more.
Description of the procedure
As a rule, an examination such as an ultrasound of the brain is prescribed for infants or children whose age is no more than 1 year. This is due to the fact that in newborn children the bone structure of the skull, in certain areas of the head, unlike adults, does not fit tightly in relation to each other.
Such places where the connective tissue has not yet had time to transform into a bone structure are called fontanelles. Therefore, in this case, it is not difficult to perform an ultrasound on the baby and obtain detailed examination results. This method of neurosonography is called transfontanelle.
However, it should be noted that in some cases, such diagnostics as ultrasound of the brain can also be used to examine children whose age is more than 1 year. In this case, so-called transcranial neurosonography is performed. It involves conducting an examination directly through the so-called temporal bone of the skull. Transcranial neurosonography is advisable to use when examining children and adolescents whose age does not exceed 17 years.
On a note! Neurosonography is a mandatory procedure. It is prescribed to infants whose age ranges from 1 to 1.5 months. In some cases, it may be prescribed to children aged 3 to 9 months.
Ultrasound of the brain is an absolutely safe and painless procedure, which has no contraindications for use or implementation. This examination method has been actively used in world medicine since the 80s of the last century. To conduct an ultrasound, you do not need to carry out any preliminary preparations. In addition, this examination can be carried out even in cases where the child is asleep.
Types of brain ultrasound for children
In neurosonography, the sensor is located in different areas of the head. Due to its position, there are several types of brain ultrasound for children: transfontanelle
,
transcranial
, combined and examination through bone injuries. Transcranial ultrasonography is performed for children older than one year, since due to overgrowth of the fontanelles, it is necessary to conduct an examination through the temporal or parietal bone. A combined method is used to obtain the most detailed image of the brain from various angles. The examination combines the position of the sensor with a transcranial transfontanelle examination.
Neurosonography
With neurosonography, the examination is carried out through non-ossified areas of the skull - the fontanelles. Their overgrowth occurs by one year, less often by one and a half years, so an ultrasound of the head through the fontanelles is performed on a child up to one year old.
Ultrasound measurements in children: normal
In the study protocol, the diagnostician notes the standard parameters of the organ. Changes in the location, shape, boundaries and size of an anatomical formation indicate possible diseases and developmental abnormalities.
Kidney sizes in children depending on height
The following criteria are considered to be the result indicating the absence of pathology:
- the walls of the blood vessels retain their structure throughout, the lumen is not changed, there are no blood clots;
- parenchymal organs have a homogeneous structure;
- there are no neoplasms, foci of inflammation, cavities or stones;
- the sizes of the studied anatomical formations correspond to the age tabular norms;
- hollow organs without inflammatory exudate, diameter corresponds to age standards;
- no birth defects.
Age norms for the size of the gallbladder in children
The dimensions of the child’s internal structures depend on age and external anthropometric characteristics. There are a number of generally accepted methods for determining ultrasound norms.
Dimensions of the liver (CC - cranio-caudal, PZ - anterior-posterior) of a child depending on height (according to Pykov)
How to prepare your baby for ultrasound diagnostics?
At the ultrasound, parents should bring an extract from the child’s medical record, a referral from the attending physician, and the results of previous examinations. For your baby, you can take disposable diapers and wet wipes.
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal and pelvic organs requires preliminary preparation. It is necessary to take measures to reduce gas formation in the intestines. Flatulence affects the scanning results, reducing the information content of the method.
2-3 days before the procedure, exclude from the baby’s diet:
- legumes (peas, beans, soybeans);
- dishes made from whole milk;
- fresh fruits, vegetables;
- cabbage, turnips in any form;
- confectionery.
The child should not drink carbonated sweet drinks and juices; you can drink water, tea, and compotes. If the baby is breastfed, the mother must comply with the listed restrictions. In case of flatulence, your doctor will help you choose medications (sorbents).
Examination of the child's abdominal cavity
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed on an empty stomach, the last meal is possible 3-8 hours before the procedure (depending on age).
A bowel movement is required before pelvic sonography. The study is carried out with a full bladder, for which 30-60 minutes before the scan the child is offered 0.5-1 liter of clean still water.
Before echocardiography, it is recommended to feed and calm the baby.
Scanning the neck, head, and cerebral structures does not require prior preparation; it is enough to tell the child about the ultrasound procedure. Children are examined in the presence of their parents.
What does the NSG show?
Neurosonography shows the condition of brain tissue and the circulatory system and gives the specialist the opportunity to assess the size and shape of parts of the brain. Using ultrasound, a specialist determines the condition of the membranes of the child’s brain, the amount of cerebrospinal fluid, the state of the vascular system, the degree of formation of brain matter, etc. In addition, ultrasound can track how symmetrical the brain structures are in children, the size of the ventricles of the brain, and assess the development of the cerebellum , detect ischemic areas.
What does neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) show?
As a rule, brain ultrasound is prescribed to children at an early age (up to 6 months). Thanks to this procedure, diseases and pathologies such as:
- Increased intracranial pressure.
- Various developmental anomalies.
- Hydrocephalus.
- Hemorrhage.
- Aneurysm.
- Benign as well as malignant formations.
- Ischemia.
In addition, through ultrasound examination of the cerebral cortex, it is possible to detect the occurrence of various complications, which, as a rule, arise after injuries or infectious diseases. The information obtained, after passing this diagnosis, allows you to make a more accurate diagnosis of the patient and prescribe the most effective course of treatment.
Decoding the result
data of the brain in newborns
are considered in conjunction with what other research methods show. The norm greatly depends on the stage of pregnancy at which the baby was born. Therefore, the results of ultrasound of the brain of newborns require careful decoding and verification with tables of normative indicators. However, ultrasound of the brain has standard indicators common to all children:
- The structure of the ventricles of the brain is homogeneous.
- Stem structures without displacement.
- The convolutions and furrows are clearly visible.
- Symmetry of brain structures.
- The subcortical nuclei and thalamus have medium echogenicity.
Intracranial hematomas
Hematomas can appear as a result of asphyxia during childbirth or intrauterine hypoxia, or due to mechanical impact on the head during childbirth. Hemorrhage is diagnosed by a specialist during examination; ultrasound of the brain confirms the diagnosis in newborns.
Intracranial pressure
A number of diseases, including hydrocephalus, trauma, hemorrhage, tumors and various infections, can lead to increased intracranial pressure. The diagnosis is made based on a set of data; ultrasound of the newborn’s head is performed as an additional examination.
Hydrocephalus
The disease leads to increased intracranial pressure. The child suffers from headaches and gets tired quickly. Without treatment, hydrocephalus leads to delays in physical and mental development. Neurosonography is performed to diagnose the disease as an additional examination.
Ischemia
Ischemia in newborns develops as a result of lack of oxygen during pregnancy or childbirth. In mild cases, the disease leads to excessive excitability or depression in the child. More severe forms are characterized by intracranial hypertension and severe seizures. Severe ischemia leads to cerebral edema and coma. For the health of the baby, it is important to diagnose the disease early and begin treatment. To identify the disease, a study of blood vessels and ultrasound of the newborn’s brain
.
Cysts
Cysts are fluid-filled spherical cavities that arise at the site of death of nervous tissue. Cysts can appear in different areas of the brain as a single tumor or in a group. Ultrasound of the brain is considered the most reliable method for diagnosing such diseases for children under one year of age.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and urinary tract
Performed on all babies at the age of 1 month. Additionally, a study is prescribed for suspected inflammation (usually changes in urine analysis - detection of leukocytes, red blood cells, mucus), injuries to the back and abdomen, pain, and suspected congenital malformations. This study allows us to draw a conclusion about the functioning of the infant’s urinary system, evaluate the structure, shape, location of the kidneys and ureters, as well as the shape, size, volume of the bladder, the condition of its walls, and the volume of residual urine after urination. During the examination, it is possible to draw a conclusion about the functional state of the kidneys and bladder, and find the cause of urination disorders.
Preparing for the study. Preparing for an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder also requires meeting certain conditions. A full bladder is required for a full examination. Therefore, you need to take a bottle of water with you or prepare for breastfeeding before the test. It is quite difficult for a baby to catch the moment of urination, but just in case you should have a “strategic supply” of liquid with you. The approximate amount of liquid is at least 100 ml.