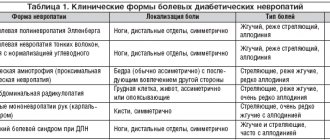
Diagnostics
Questioning the patient, examination, and palpation allow us to determine a list of reasons that can cause pain. To accurately determine the etiology of cervicalgia syndrome, additional examinations are necessary:
- general blood test; blood biochemistry;
- sputum examination;
- Ultrasound of soft tissues of the neck;
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland;
- electromyography;
- Ultrasound scanning of the cervical arteries;
- MRI (CT) angiography of neck vessels;
- MRI (CT) of the cervical spine, with contrast;
- MRI of soft tissues of the neck, with contrast.
The list of examinations is determined individually.
You need to see a doctor as soon as possible. Do not make sudden movements, avoid hypothermia, exercise, and make an appointment with a doctor as soon as possible. This will avoid complications. Consultation with specialists is required: surgeon, vertebrologist, endocrinologist, neurosurgeon, otolaryngologist, dermatologist, oncologist.
Vertebrogenic pain syndrome
Currently, up to 80% of the population of our planet suffer from various diseases of the spine. This is caused by urbanization, low physical activity, changes in diet and quality of nutrition, and deterioration of environmental conditions. In Russia, every 9th person suffers from some kind of spinal disease. Back pain is one of the most common causes of disability in people aged 30-45 years.
Among the numerous forms of joint damage, according to V.K. Velitchenko (2002), the first place is occupied by degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the spine and joints, which affect from 8 to 12% of the population of various countries. However, only 40% of patients seek medical help. Acute pain becomes chronic in a third of patients [5,6]. Women get sick more often. Men have shorter remissions, a higher percentage of those operated on for herniated discs and retirement due to disability. According to statistical studies, pathology of the lumbosacral region accounts for about 30% of the total morbidity, 20-30% of all diseases of the nervous system and more than 80% of diseases of the peripheral nervous system. Every year it is registered in 15-25% of the country's adult population. About 84% of the world's population will experience at least one relatively long-term episode of back pain during their lifetime. A postal survey of 1806 people conducted in Sweden found the following results: 55% of respondents complained of pain lasting more than 3 months, 49% - at least 6 months [22].
Primary vertebrogenic pain is usually associated with degenerative changes in the spine (dorsopathy, spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis). Their development is influenced by genetic predisposition, age, and risk factors. Degenerative-dystrophic changes lead to the appearance of functional blockades and other disorders of the biomechanics of the spinal column. This can provoke diseases of the internal organs segmentally associated with the affected part of the spine. But it should be borne in mind that the internal organs do not have strict segmental innervation. For example, the stomach, liver, kidneys, and pancreas receive innervation from the same celiac plexus. All physiological and pathological reactions are not limited to just one segment, but pass into the zones of neighboring metameres. Due to the fact that spinal pathology causes multilateral disorders of nervous regulation and trophism of various internal organs, it can lead to the development of functional disorders and organic pathology and cause somatic disease [4].
Dorsopathies are the most common cause of vertebrogenic pain. With infectious, oncological, and traumatic lesions of the spine, secondary vertebrogenic pain occurs. More often they are caused by traumatic and infectious (spondylitis) diseases, ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis), less often - tumors and idiopathic spondylopathy (juvenile dorsal kyphosis or Scheuermann-Mau disease. Dorsopathies are a group of diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue, the leading symptom complex of which is pain in the trunk and extremities of non-visceral etiology. This disease is a serious problem all over the world. For example, in the USA, the total losses of the national economy from dorsopathy are estimated at 85-90 billion dollars per year, and the treatment of this disease accounts for up to 80% of health care costs [ 17].
Due to the fact that in clinical practice a general algorithm is often used to treat both acute and chronic pain, the problem of adequately selected therapy for dorsopathies is currently particularly relevant. Moreover, when choosing treatment tactics, it is necessary to take into account that we are talking about a degenerative lesion of the spine, its complex pathogenetic cascade and the time of occurrence of the pathology. Therefore, treatment of patients with dorsopathy should be comprehensive, using medications and non-drug therapy methods. During the acute and interictal periods of the disease, various therapeutic measures are carried out. First of all, it is necessary to take measures aimed at relieving or reducing pain [1,9,23].
In case of acute pain, the patient is advised to remain in bed for 1-3 days. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, and muscle relaxants are also immediately prescribed. To increase the effectiveness of the drug and the speed of onset of pain relief, NSAIDs are best prescribed as intravenous injections [13]. The indication for prescribing anti-ischemic drugs: antioxidants, antihypoxants, vasoactive drugs is the presence of compression syndrome. The issue of using antidepressants is decided individually for each patient [7,12].
Drug treatment of dorsopathies is a complex task that requires deep knowledge of the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of the disease. In addition, the doctor must adhere to algorithms developed taking into account the stage of the process (Fig. 1). When treating acute dorsopathy, significant regression of pain should be expected within 1-2 weeks. The previously existing policy of restricting physical activity up to strict bed rest has now been revised: partial restriction is recommended for moderate pain, bed rest for 1-3 days for intense pain. The patient must be taught how to sit, stand up, walk correctly, and also be prohibited from lifting heavy objects, etc. If there are no results from the therapy within 1-2 weeks, it is necessary to prescribe other drugs in optimal doses. If the pain persists for more than 1 month, this indicates a chronic process or an incorrect diagnosis.
The decision on surgical intervention is made when:
- compression of the cauda equina with lower paraparesis and pelvic disorders;
- increasing paresis;
- severe pain syndrome that is not amenable to conservative treatment.
The basic principles of drug therapy for vertebrogenic back pain include early onset, pain relief, and a combination of pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy. First of all, pathogenetic therapy should be aimed at combating oxidative stress, as well as influencing the microvasculature, improving blood supply to the affected area, and relieving signs of neurogenic inflammation. For this purpose, antioxidant, vasoactive and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used [8,14,15]. To relieve algic manifestations, symptomatic therapy is prescribed. In cases of severe anxiety-depressive disorder, as well as in the presence of chronic pain, the use of antidepressants is indicated.
The complexity of drug therapy in most cases lies in the intricate anatomical and physiological hierarchy of structures involved in the pathological process. On the one hand, this is due to the peculiarities of the structure and functioning of the structures of the lumbosacral plexus. On the other hand, the basic mechanism underlying dorsopathy is a clear correlation between nerve compression and ischemia and the development of oxidative stress [16,18].
An important place in the mechanisms of development of diseases of the peripheral nervous system is occupied by hemodynamic disorders, ischemia, microcirculation disorders, energy exchange disorders in ischemic neurons with a decrease in aerobic energy exchange, ATP metabolism, oxygen and glucose utilization. Correction with vasoactive drugs is required by pathogenetic processes occurring in nerve fibers. To improve microcirculation processes, activate metabolic processes and glycolysis, the following drugs are used: Vesel Due F, trental (pentoxifylline), cavinton (vinpocetine), cortexin.
Oxidative stress is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the activity of antioxidant systems. The resulting imbalance leads to increased production of compounds (neurotransmitters) released by damaged tissues: histamine, serotonin, ATP, leukotrienes, interleukins, prostaglandins, nitric oxide, etc. They lead to the development of neurogenic inflammation, increasing the permeability of the vascular wall, and also promote the release of prostaglandin E2, cytokines and biogenic amines by mast cells and leukocytes, increasing the excitability of nociceptors. Currently, clinical work has appeared on the use of drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood and endothelium-dependent reactions of the vessel wall in patients with compression neuropathies. To reduce the manifestations of oxidative stress, lipoic acid derivatives (octolipene), Mexidol, Actovegin, etc. are successfully used.
Mexidol is a modern domestic drug, the active ingredient of which is ethylmethylhydroxypyridine succinate. It belongs to the group of heteroaromatic antioxidants and antihypoxants and has nootropic and anxiolytic properties. The mechanism of its action is due to its antioxidant and membrane protective effect. It inhibits lipid peroxidation, increases superoxide oxidase activity, increases the lipid-protein ratio, reduces membrane viscosity, and increases its fluidity. The drug modulates the activity of membrane-bound enzymes (calcium-independent phosphodiesterase, adenylate cyclase, acetylcholinesterase), receptor complexes (benzodiazepine, GABA, acetylcholine), which enhances their ability to bind to ligands, helps preserve the structural and functional organization of biomembranes, transport of neurotransmitters and improve synaptic transmission. The range of therapeutic effects of the drug is from 10 to 300 mg/kg. For vertebrogenic pathology, the drug is prescribed 400 mg intramuscularly once a day, a course of 10-15 days, followed by switching to oral administration for 1-3 months.
Actovegin is an antioxidant, which is a deproteinized extract of the blood of young calves, improves the utilization of oxygen and glucose. Under the influence of the drug, the diffusion of oxygen in neuronal structures significantly improves, which leads to a decrease in the severity of secondary trophic disorders. When taking Actovegin, there is also a significant improvement in cerebral and peripheral microcirculation against the background of improved aerobic energy exchange of vascular walls and the release of prostacyclin and nitric oxide. The resulting vasodilation and decrease in peripheral resistance are secondary to the activation of oxygen metabolism of the vascular walls. In case of dorsopathy, it is advisable to prescribe Actovegin in both acute and subacute stages of the disease, especially in the absence of effect from other treatment methods. The drug is administered at a dose of 400-800 mg for 5 days, followed by switching to oral administration. Actovegin can also be used for therapeutic blockades together with an anesthetic.
Cortexin is a peptide drug containing a complex of amino acids, polypeptides, a balanced vitamin and mineral complex. It is produced from the cerebral cortex of calves (pigs). The drug's peptides have a direct and indirect neurotrophic effect on cells. Cortexin, through a system of anti-inflammatory cytokines, improves the neurotrophic supply of nerve fibers and reduces autoimmune aggression, promoting the restoration and growth of axons. For dorsopathies, the drug is prescribed at a dose of 10 mg intramuscularly daily for 10-15 days.
Octolipene (alpha-lipoic acid) is an endogenous antioxidant formed in the body during the oxidative decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids. It helps reduce blood glucose concentrations and increase glycogen content in the liver, as well as overcome insulin resistance. The drug is involved in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, stimulates cholesterol metabolism, and improves liver function. It also has hepatoprotective, hypolipidemic, hypocholesterolemic, hypoglycemic effects, improves neuronal trophism and axonal conduction, and reduces the manifestation of polyneuropathy. Octolipen is taken orally 600 mg (2 capsules) 1 time per day on an empty stomach, 30 minutes before the first meal, without chewing and with a sufficient amount of water. The drug is prescribed in combination with NSAIDs, the course of treatment is 1-3 months.
Cavinton is a drug with a multimodal mechanism of action. The drug inhibits phosphodiesterase, which promotes the accumulation of cAMP in tissues and increases the concentration of ATP. Its distinctive property is the normalization of vascular tone, a positive effect on macro- and microcirculation. Cavinton has a powerful antioxidant effect. It is also an effective angioprotector. It is prescribed to patients with dorsopathy as a means of pathogenetic therapy. Cavinton is prescribed daily intravenously, 2 ml per 200 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution for 10-15 days, followed by switching to oral administration.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are the first choice for pain relief. The mechanism of action of NSAIDs is the inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1,2), a key enzyme in the arachidonic acid metabolic cascade, leading to the synthesis of prostaglandins, prostocyclins and thromboxanes. NSAIDs are widely used in neurological practice, since COX metabolism plays a major role in the induction of pain at the site of inflammation and the transmission of nociceptive impulses to the spinal cord. According to some authors, 300 million patients take them [2,14,19]. All NSAIDs have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects, are able to inhibit the migration of neutrophils to the site of inflammation and platelet aggregation, and also actively bind to serum proteins. Differences in the action of NSAIDs are quantitative, but they determine the severity of the therapeutic effect, tolerability and the presence of side effects in patients. The high gastrotoxicity of NSAIDs, which correlates with the severity of their sanogenetic effect, is associated with indiscriminate inhibition of both isoforms of cyclooxygenase.
Depending on the effect that NSAIDs have on cyclooxygenase, they are currently divided into two groups. Non-selective NSAIDs block both constitutional cyclooxygenase-1, which is associated with the gastrointestinal side effects of these drugs, and inducible cyclooxygenase-2, the formation of which is activated by anti-inflammatory cytokines. Selective drugs act predominantly on cyclooxygenase-2. Non-selective NSAIDs include lornoxicam (Xefocam), ibuprofen, indomethacin; selective CTC inhibitors include meloxicam (Movalis, Artrosan, Mirlox), nimesulide, celecoxib (Celebrex).
Xefocam is a drug that has a pronounced antianginal effect due to a combination of the anti-inflammatory effects of NSAIDs and a strong analgesic effect comparable to opiates. The pharmacokinetics of Xefocam does not differ in patients of different age groups. The effectiveness of oral administration of the drug has been reliably proven according to the following regimen: 1st day – 16 and 8 mg; Days 2-4 – 8 mg 2 times a day, day 5 – 8 mg/day for acute back pain [10].
The analgesic effect of using Xefocam at a dose of 2-16 mg 2 times a day is several times higher than naproxen. For dorsopathy, it is recommended to use the drug in a dose of 16-32 mg. The drug can be administered intramuscularly, intravenously, orally, puncture trigger points, or make therapeutic blockades. The course of treatment is at least 5-7 days with a one-time daily procedure. Medium doses of the drug are as effective as high doses of other NSAIDs. In case of severe pain, on the first day, 16 mg is prescribed IM or IV 2 times a day, then the dose is reduced to 8 mg per day for 3-5 days.
Artrosan (meloxicam) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that has anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic effects. The anti-inflammatory effect of the drug is associated with inhibition of the enzymatic activity of cyclooxygenase-2, which is involved in the biosynthesis of prostaglandins in the area of inflammation [20,21]. To a lesser extent, it acts on cyclooxygenase-1, which is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandin, which protects the mucous membrane of the digestive tract and takes part in the regulation of blood flow in the kidneys. The drug is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, the absolute bioavailability of meloxicam is 89%. Concomitant food intake does not affect absorption. When using the drug orally in doses of 7.5 and 15 mg, its concentrations are proportional to the doses. Equilibrium concentrations are achieved within 3-5 days. The course of treatment is at least 5-7 days with a one-time daily procedure. Artrosan is taken orally with meals once a day or intramuscularly. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, the daily dosage of the drug is 7.5-15 mg/day. The main NSAIDs used in the treatment of back pain are listed in the table.
Main NSAIDs used in the treatment of back pain
Central muscle relaxants play an important role in the complex treatment of back pain, especially in the presence of myofascial syndrome. By reducing pathological hypertonicity, they not only reduce pain and reduce the need for NSAIDs, but also significantly reduce the period of disability. The therapeutic effect of these drugs is due to potentiation of the GABAergic system of the spinal cord, which leads to inhibition of excitatory mediator systems, inhibition of spinal reflexes, and relaxation of muscle hypertonicity [3]. Their analgesic effect is due to the elimination of muscle spasm. Muscle relaxants are used until the pain episode is relieved and then discontinued. Drugs in this group can be prescribed for a period of no more than 7-14 days. The main representatives of the group of muscle relaxants are tolperisone (mydocalm), baclofen, tizanidine (sirdalud).
Mydocalm has moderate adrenergic blocking and weak atropine-like effects, inhibits spinal polysynaptic nociceptive reflexes, due to which it has a direct analgesic effect. The muscle relaxant effect of the drug is realized at the level of peripheral nerves, spinal cord, and brain stem. Unlike other medications, it does not cause dizziness and does not affect the speed of reactions or the ability to drive. For severe muscular-tonic pain syndromes, the drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously slowly at 100 mg twice a day, in other cases 50-150 mg is prescribed orally three times a day, depending on individual need and tolerance.
Sirdalud is an imidosaline derivative and has structural and biochemical similarities to clonidine. The drug affects β2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and spinal cord, due to which it has a muscle relaxant effect. By releasing excitatory neurotransmitters (norepinephrine and aspartate) in the spinal cord and brain, it reduces their effect on receptors, which leads to a decrease in the excitability of α- and β-motoneurons. Tizanidine primarily inhibits polysynaptic reflexes of the spinal cord, which are responsible for muscle hypertonicity, and causes a decrease in the tone of the flexor and extensor muscles, reducing painful muscle spasms. The most common side effects of the drug include dry mouth, dizziness and drowsiness. The drug should be prescribed with caution to elderly people and patients with impaired liver and kidney function. The average dose of sirdalud is 12-24 mg/day. The initial dose of the drug for severe painful muscle spasms is 2 mg in the morning and 4 mg in the evening orally, followed by increasing the dose.
Neuropathic pain in dorsopathy is often of an unusual nature, accompanied by sensory disturbances (hyperesthesia, dysesthesia, allodynia), other neurological disorders or local autonomic dysfunction. This may be due to a restriction in the influx of sensory impulses due to damage to the pathways (deafferentation pain), ectopic spontaneous generation of sensory impulses in damaged neurons, as well as increased sympathetic influences on painful sensory motivation. In order to diagnose the presence of painful neuropathy syndrome, as well as to identify the pathophysiological mechanisms of the development of pain and hyperalgesia, it is necessary to conduct a clinical examination aimed at determining the nature of the pain and identifying various types of hyperalgesia. Knowledge of the mechanisms underlying the development of the pathological process allows us to develop a logical treatment strategy. Anticonvulsants and antidepressants are used in the treatment of neuropathic pain syndrome.
Anticonvulsants are the drugs of choice for the treatment of neuropathic pain. These drugs block sodium channels that generate pathological impulses; stimulate GABAergic activity; act as glutamate antagonists. For the treatment of neuropathic pain, the following drugs are used: carbamazepine at a dose of 400-600 mg/day, phenytoin - 300 mg/day, clonazepam - 4-6 mg/day, valproic acid - 1500-2000 mg/day, lamotrigine - 25-100 mg /day, gabapentin – 1200-3600 mg/day. Average doses of drugs are selected individually in each case.
Tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin reuptake inhibitors enhance descending (serotonergic) inhibitory effects on 5HT receptors at the level of the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. The following drugs are used: amitriptyline – up to 75 mg/day; fluoxetine – 20-40 mg/day; paxil, rexetine – 20 mg/day. In cases of insufficient effectiveness of amitriptyline monotherapy, a higher antinociceptive effect can be achieved by the combined use of amitriptyline (50 mg/day) and anticonvulsants such as clonazepam (4-6 mg/day) or carbamazepine (400-600 mg/day). Tricyclic antidepressants can reduce or eliminate pain regardless of their antidepressant effect.
The basic principles of treatment of psychogenic dorsalgia are the correction of the mental, autonomic and somatic spheres, taking into account the specifics of each specific syndrome and the individual characteristics of the patient. To correct mental disorders, psychotherapy (hypnosis, behavioral and autogenic therapy) is successfully used, focused on the patient’s awareness of the connection between pain and psychogenic factors. The psychotropic drug is selected taking into account the structure of the syndrome of mental disorders. When anxiety-phobic disorders predominate, benzodiazepine anxiolytics (clonazepam, Xanax, etc.) are prescribed, for depressive disorders - antidepressants (amitriptyline, fevarin, Paxil, etc.), for hypochondriacal disorders - antipsychotics (Eglek, Sonapax).
For vegetative disorders, vegetative correctors ( afobazole , grandaxin , atarax ) are prescribed. Afobazole is a derivative of 2-mercaptobenzimidazole, a selective anxiolytic that does not belong to the class of benzodiazepine receptor agonists. The drug has an anxiolytic and mild activating effect, without being hypnosedative or muscle relaxant. With its use, drug dependence does not form and withdrawal syndrome does not develop. On days 5-7 of treatment, a decrease or elimination of anxiety, tension, somatic and autonomic disorders is observed. The maximum effect is achieved by the end of 4 weeks of treatment and persists in the post-therapeutic period, on average 1-2 weeks. For the treatment of vegetative disorders of vertebrogenic nature, the drug is prescribed 10 mg in 3 divided doses during the day. The course of treatment is 2-4 weeks. If necessary, the daily dose of the drug can be increased to 60 mg, and the duration of treatment - up to 3 months.
In the treatment of vertebrogenic pain, not only medications are used, but also manual therapy methods and physiotherapeutic procedures. However, it should be remembered that they can be prescribed only 5-10 days after pain relief. A special role in therapy, mainly for stenosis and arthrosis of the facet joints, is played by chondroprotective drugs, which help inhibit the degenerative process and reduce the likelihood of chronic pain. In neurological practice, preference is given to drugs for parenteral administration (alflutop). Complex treatment traditionally uses vitamin-containing complexes (Ambene, Benfolipen, Combilipen, Milgamma), homeopathic drugs, dehydration therapy, and drugs for local action on the lesion.
In neurology, vitamin B ( thiamine , pyridoxine , cyanocobalamin ) are very widely used [24]. Prospects in the treatment of dorsopathy are associated with the development of new dosage forms of B vitamins - “neurotropic” vitamins that have a specific effect on the function of the nervous system. The biologically active substance of benfotiamine is thiamine diphosphate, which was previously called thiamine pyrophosphate. TDP is a coenzyme of various multienzyme complexes, among which the enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism are of greatest importance for nerve cells. Thiamine-dependent key enzymes play an important role in the oxidative processes of glucose breakdown. By changing the direction of metabolism of intermediate products of glucose breakdown - fructose-6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, benfotiamine prevents the activation of pathogenetic mechanisms. Along with the described effects, thiamine and pyridoxine in combination with cyanocobalamin may have an antinociceptive effect.
Pyrodixal phosphate , as a coenzyme, is involved in the synthesis of serotonin, and thiamine performs an important function in its deposition and transport. It is here that, perhaps, the point of realization of the analgesic effect of pharmacological doses of thiamine and pyridoxine is located. Thiamine, by enhancing energy supply in the form of ATP, supports axoplasmic transport, pyridoxine is involved in the synthesis of transport proteins, and cyanocobalamin ensures the delivery of fatty acids to cell membranes and the myelin sheath. Fat-soluble vitamin B1 preparations have advantages over water-soluble ones.
Benfolipen is a combined multivitamin complex. It contains: benfotiamine (vitamin B1, 100 mg), pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6, 100 mg), cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12, 2 μg). The drug is taken after meals, without chewing and with a small amount of liquid.
Combilipen is a combined multivitamin preparation. The effect of the drug is determined by the properties of the vitamins included in its composition: thiamine hydrochloride (100 mg), pyridoxine hydrochloride (100 mg), cyanocobalamin (1 mg). The drug also contains lidocaine hydrochloride (20 mg). Combilipen is available in ampoules of 2 ml. The maximum clinical effect is achieved when it is prescribed in combination with NSAIDs. In case of severe manifestations of the disease, combilipen is administered intramuscularly, 2 ml daily for 5-7 days, then 2 ml 2-3 times a week for 2 weeks; in mild cases, 2 ml 2-3 times a week for 7-10 days. The duration of the course of injections should not exceed 2 weeks. In the future, for maintenance therapy, it is recommended to take benfolipen 1 tablet 1-3 times a day for a course not exceeding 4 weeks.
The optimal means of influencing the peripheral source of pain - both primary and reflex - are ointment and gel forms of drugs that have anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant effects. These forms of local therapy not only have a targeted effect, but also reduce the need for prescribed medications. When administered locally to the skin, they affect the pathogenetic mechanisms of pain, thereby breaking the “vicious circle”: pain - muscle spasm - pain.
In conclusion, it must be emphasized that effective treatment of vertebrogenic back pain requires not only in-depth knowledge of the pathogenesis and clinical manifestations of the disease, but also a combination of treatment methods and the prescription of drugs from various groups.
Figures and tables are in the appendix
Treatment
The choice of therapy depends on the causes of cervicalgia.
It is imperative to treat the underlying disease. To relieve pain in degenerative processes of the cervical spine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, opioid analgesics, blockades with anesthetics and a corticosteroid drug, and vascular drugs are used. For infectious and purulent processes, antibiotics are prescribed. In case of pathology associated with damage to nerve endings, B vitamins, thioctic acid, vascular drugs, and drugs that improve nerve conduction are added to therapy.
In case of injuries or pathological muscle tension, immobilization of the neck using a Shants collar is necessary. In the absence of contraindications, physiotherapy and balneotherapy are used.
For cervicalgia of vertebrogenic origin, acupuncture, massage, exercise therapy, manual therapy, and hardware traction of the cervical spine are relevant.
If the cause of pain in the cervical spine is degenerative changes in the spine (herniated discs), cysts, abscesses, tumors, surgical treatment may be indicated. Surgery is also necessary for patients who do not have a positive result from conservative therapy.
Vertebrogenic cervicalgia
Often the occurrence of vertebrogenic cervicalgia is accompanied by other diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, vertebral hernia, osteoporosis and some others. To make a final diagnosis, the patient must undergo a series of studies, including: magnetic resonance imaging, radiography and CT. If treatment of the disease is started in a timely manner, a positive result will not take long to appear and the chances of a speedy recovery increase. The chronic form of vertebrogenic cervicalgia is much more difficult to treat with medication, since the situation is complicated by systematic relapses.
Main causes of the disease
It should be noted that the negative impact on the human body of the above-mentioned spinal ailments is not always the cause of the appearance of cervical pain syndrome. Very often, the key factors for the development of the disease are excessive physical stress on the muscles and vertebrae located in the neck. In addition, pain can occur due to hypothermia, infectious infection or osteochondrosis.
Clinical picture
With vertebrogenic cervicalgia, the most “recognizable” symptom is considered to be severe pain of varying degrees of intensity. In this case, the nature of the sensation can be very diverse, starting from mild tingling and ending with prolonged spasms. Other common symptoms of the disease include the following:
- pain in the back of the head;
- presence of noise in the ears;
- feeling of numbness in the upper extremities, including the back of the head.
Diagnosis of the disease
The effectiveness of diagnostics directly depends on the competent performance of clinical tests. Information about the patient collected in the anamnesis is also important. Particular attention should be paid to the time of the first onset of pain. After a thorough examination and interview of the patient, you can move on to other diagnostic procedures: MRI, X-ray examination of the cervical region, CT and some others. Of the well-known methods of functional diagnostics, electroneuromyography is usually used.
Principles of disease treatment
In most cases, proven conservative methods of therapy are used as the main treatment for vertebrogenic cervicalgia. For example, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and pain-blocking drugs are widely used. Also, if necessary, special medications are prescribed to relieve swelling - muscle relaxants to reduce muscle spasms.
There are a number of additional methods that help cope with the disease.
For example, a certain positive effect is achieved from the use of a special neck collar, as well as spinal traction procedures. Of the various preventive methods, doctors primarily give preference to the mandatory use of an orthopedic mattress and pillow, physiotherapeutic procedures and exercises from a course of therapeutic exercises. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Symptoms
The main manifestation of this disease is pain . Cervicalgia is accompanied by a lot of symptoms, but muscular-tonic syndrome is more often observed. In this case, the neck muscles become denser, and if you press on them, the pain intensifies.
Other symptoms include:
- The movement of the head is accompanied by a specific crunching sound.
- Throbbing headache, as well as dizziness.
- Restricted neck mobility.
- When you tilt your head back, fainting occurs.
- Partial loss of vision and hearing.
- The pain spreads to one of the arms and shoulder.
- The gait becomes unsteady.
- The upper limbs become weak.
- Tingling, as well as numbness of the face, hands and back of the head.
- Nausea, but no vomiting.
- When coughing or sneezing, the pain worsens.
Such symptoms are typical for any person, regardless of gender and age . In chronic cervicalgia, the symptoms are less pronounced, in contrast to the acute disease. In case of hypothermia or spinal injury, the pain is intense and severely hinders movement. When the disease occurs against the background of a concomitant disease, the pain is usually mild.
Video: “All causes of neck pain”
Treatment of cervicalgia
As noted above, cervicalgia is a disease that requires consultation and supervision of a specialist. Therefore, if symptoms appear, you should not delay visiting a doctor.
But if it happens that you get sick unexpectedly, and there is no way to get to the nearest medical center, then first aid is provided. Let's consider several ways:
Painkillers
There is no special list, since the drug affects each person differently, but one condition is still met. The medicine should not contain steroids and have a mild anti-inflammatory effect.
It is worth noting that taking painkillers does not imply a long-term program. This may affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Muscle relaxants
Such drugs relieve tension and help relax muscles if pain in the neck is caused by muscle stiffness. It can be a cream based on herbs, or an ointment.
Anesthetics
If gentle exposure does not help, then you can turn to injections. The same novocaine or procaine injected under the skin will temporarily relieve painful sensations, almost completely “freezing” the nerve endings.
The disadvantage of this method of treatment is its short-term effect and does not eliminate the cause of cervicalgia. But it will give you time to seek help.
Neck collar
A special design that fixes the position of the head and prevents muscles from moving, much less making turns. It becomes necessary while the course of treatment is ongoing, and at the same time it will relieve unwanted neck movements.
When choosing a collar you should be careful. It is individual and should not be too tight or, conversely, too spacious.
Traction therapy
In some cases, doctors resort to it. This is a certain set of exercises under the supervision of specialists, when the spine is stretched and space appears between the vertebrae. The muscles are freed and then ready to move.
Physiotherapy
This is a whole program designed to work on the cervical apparatus, relieving stress and tension. It takes into account pain sensations, and exercises are carried out in accordance with them.
Causes of vertebrogenic dorsalgia
The reasons why the disease occurs are quite numerous. They can be associated either directly with spinal problems or appear as a result of various diseases that have arisen in the human body. However, there are several main factors that contribute to the onset of the disease:
- Frequent and prolonged stay in an uncomfortable position
- Various injuries
- Diseases of the joints and internal organs
- Heavy physical activity
- Hypothermia
- Osteochondrosis
- Spondyloarthrosis and other diseases of the spine