Types of damage
Damage to the nerves of the hand is represented by the following groups.
- Complete rupture of a nerve is called neurotmesis. Surgical treatment is indicated. Recovery occurs over months or years depending on the severity of the damage.
- Partial rupture accompanied by various disorders - neuropraxia - occurs with closed injuries. A condition with preserved nerve sensitivity, when the lack of conduction is temporary.
- Neuropathy is a disorder resulting from a fracture, bruise or cut in the hand area.
- A pinched nerve occurs when the patient cannot bend the wrist. The little finger is completely immobilized, the ring finger is partially immobilized, the thumb moves with difficulty. The pain radiates to the little finger.
Nerve damage
Damage to the ulnar nerve primarily manifests as movement disorders. Active flexion, extension and abduction of the 5th and 4th and partly the 3rd fingers is impossible, muscle strength is sharply weakened. Within 1-2 months, atrophy of the interosseous muscles develops, as a result of which the contours of the metacarpal bones begin to stand out sharply on the back of the hand. In the long-term period, a characteristic claw-shaped deformation of the hand occurs. The middle and distal phalanges of the V and IV fingers are in a state of flexion. Opposing the little finger is not possible. On the ulnar side of the hand, sensitivity disorders, secretory and vasomotor disorders are observed.
Damage to the median nerve is accompanied by severe sensory impairment. In addition, already in the initial period, trophic, secretory and vasomotor disorders are clearly visible. The skin of the innervated area is flaky, shiny, cyanotic, dry, smooth and easily wounded. The nails of the I-III fingers are transversely striated, the subcutaneous tissue of the nail phalanges is atrophied. The nature of movement disorders is determined by the level of nerve damage.
Low lesions are accompanied by paralysis of the thenar muscles, high lesions are accompanied by impaired palmar flexion of the hand, pronation of the forearm, extension of the middle phalanges of the third and second fingers, and flexion of the first and third fingers. Opposition and abduction of the first finger is impossible. The muscles gradually atrophy, their fibrous degeneration develops, therefore, if the injury is more than a year old, restoration of their function becomes impossible. A “monkey hand” is formed.
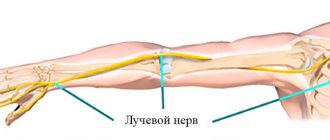
Damage to the radial nerve at the level of the shoulder or axillary region is accompanied by significant motor disturbances. Paralysis of the extensors of the hand and forearm occurs, manifested by the symptom of a drooping or “falling” hand. When the underlying parts are damaged, only sensitivity disorders develop (usually of the hypoesthesia type). The dorsal surface of the radial side of the hand and the phalanges of the I-III fingers suffer.
Damage to the sciatic nerve is manifested by impaired flexion of the lower leg, paralysis of the fingers and foot, loss of sensation along the back of the thigh and almost the entire lower leg (except for the inner surface), as well as loss of the Achilles reflex. Causalgia is possible - excruciating burning pain in the area of innervation of the injured nerve, spreading to the entire limb, and sometimes to the torso. Partial damage to the nerve with loss of functions of its individual branches is often observed.
Damage to the tibial nerve is manifested by loss of the Achilles reflex, impaired sensitivity of the outer edge of the foot, sole and back of the leg. A typical deformity is formed: the foot is extended, the posterior group of muscles of the lower leg is atrophied, the toes are bent, the arch of the foot is deepened, the heel protrudes. Walking on toes, turning the foot inward, and bending the toes and toes are impossible. As in the previous case, causalgia often develops.
Damage to the peroneal nerve is accompanied by paralysis of the extensor muscles of the fingers and toes, as well as the muscles that provide outward rotation of the foot. There are sensory disturbances along the dorsum of the foot and the outer surface of the lower leg. A characteristic gait is formed: the patient raises his shin high, bending the knee strongly, then lowers his leg onto the toe and only then onto the sole. Causalgia and trophic disorders, as a rule, are not expressed, the Achilles reflex is preserved.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, examination using palpation and a series of tests is important.
- Discriminative two-point test - the sensitivity of the branches is checked in turn and the reaction is compared.
- The sensory function of the radial nerve is checked by a discrimination test at two points and pricking the folds of the thumb.
- Motor branches are tested by joint extension.
- The sensitivity of the ulnar nerve is determined on the little finger; to control motor capabilities, the patient spreads his fingers with force.
- Additional tests to analyze ulnar nerve function include ring finger flexion and thumb adduction.
- Motor function of the median nerve is tested by resisting flexion of the wrist and index finger.
- A visual test of the sensitivity of the median nerve is a discrimination test with an attachment in the palm.
Non-drug effects
To normalize metabolic processes and muscle tone, and relieve symptoms, technique (TENS) . After placing the electrodes on the skin, current is applied at different frequencies; sessions are carried out for 20-30 minutes in courses of up to a month.
Other methods of electrotherapy include diadynamic currents , which have an analgesic effect in neuropathies, and darsonvalization, which is characterized by a good trophic effect due to improved blood circulation.
Massage and kinesiotherapy are indicated (certain exercises that normalize muscle tone and tissue trophism), as well as maintaining range of motion in the limbs and allowing patients to feel better.
To restore motor function, magnetic therapy both with stationary devices in hospitals and sanatoriums, and portable ones for home use. During the treatment, trophism improves, tissue hypoxia and pain are eliminated, and restoration of the myelin sheath of nerves is stimulated.
For different types of neuropathies, localized and general magnetic therapy is used, and successes in treatment, namely reduction of symptoms (pain, sensory disturbances), can be achieved at different stages of the disease.
Magnetotherapy has a powerful effect on the body, activating metabolism and blood circulation in general, especially in the area of influence. Repeated courses using an alternating magnetic field, low-frequency pulsed or traveling magnetic field are recommended. Magnetic therapy devices for home use facilitate the treatment of chronic patients with neuropathies, increase adherence to therapy and improve the prognosis of the disease.
They help alleviate the condition of the procedure using infrared irradiation , they reduce paresthesia, improve blood flow through the capillaries.
It is necessary to adhere to a daily routine , proper rest and dosed physical activity, a balanced diet enriched with B vitamins.
When is surgery indicated?
- Impaired sensitivity and movement function.
- Tumors.
- Painful neuromas.
- Compression by scars.
- Damage due to trauma.
- Pain syndrome.
Taking into account the nature of the injury, the method of surgical treatment is selected:
- Excision of scar formations – neurolysis;
- Connecting the nerve sheath and applying a special suture;
- Carrying out plastic surgery of nervous tissue.
During surgical treatment, microsurgical techniques are used to make the comparison as accurate as possible.
Principles of treatment of neuropathy
Complex therapy includes eliminating factors affecting nerve fibers, as well as influencing tissue and stimulating regeneration processes, improving blood circulation in the area of the affected nerves and their conductivity. In order to reduce pain and restore sensitivity, medications, physiotherapeutic treatment and dietary correction, physical therapy and routine measures are used. In the case of neuropathies that have developed against the background of a disease (for example, diabetes), the underlying pathology is treated.
Rehabilitation
The recovery period takes at least six months. First, touch is restored, then sensitivity when touching two points. For recovery, it is important to recognize objects by touch.
Principles of successful rehabilitation:
- Early intervention;
- Reducing the risk of complications;
- Ensuring healing;
- Restoring the functions of the nerve of the hand;
- Using a multi-stakeholder approach.
Restoration of the hand nerve is carried out at the clinic of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, in the department of hand microsurgery. Everything is available here for effective treatment of a nerve rupture in the arm - experienced, highly qualified surgeons work, the most modern microsurgical equipment is used, and the staff is caring.
Registration for a consultation is carried out on the website. You can get the information you are interested in and find out the price of treatment by calling the number provided.
Drug treatment
First of all, high doses of B vitamins have a neurotrophic effect, they help eliminate pain and normalize tissue sensitivity, improve nerve conduction of fibers. Vitamin injections or combined tablet forms of thiamine, cyanocobalamin and riboflavin (B1, B12 and B6) are used. You can supplement the course with products containing vitamins A and E, and ascorbic acid. Such products also have antioxidant properties.
To eliminate pain, non-narcotic analgesics the NSAID , but they have limited effectiveness since there is no point of application for these in this case. For neuropathic pain, other groups of medications are highly effective - antidepressants, anticonvulsants , etc., specific treatment is prescribed by the attending physician. For severe pain, leading to sleep disturbances, depression and disability, blockades or the use of narcotic analgesics are used. The effect of analgesics and NSAIDs can be enhanced by their combination with magnesium and vitamin B6.
In severe cases, therapy with glucocorticoids , and in case of the autoimmune nature of the lesion, also with immunosuppressants . A similar regimen is prescribed strictly individually, only in a hospital setting.
of plasmapheresis are effective , reducing the antigenic load on the body, due to which fewer circulating immune complexes are formed in the vessels and the area of the myelin sheath of the nerves. It is practiced to use a course of immunoglobulin injections in combination with a course of plasmapheresis.
Additionally, drugs are used that improve tissue trophism and thin the blood, vasodilators and venotonics, drugs to normalize neuromuscular conduction and regulators of redox processes in tissues.
With the development of neuropathy due to toxic processes, detoxification therapy and desensitizing treatment , magnesium and calcium preparations are prescribed.
Difficult stages
You shouldn’t even try to cope with such serious damage on your own; call an ambulance. The doctor will apply an immobilizing bandage to the injured limb so that the damaged nerve experiences the least amount of tension. And in the hospital, where the patient must be immediately taken, they will decide whether he needs surgical intervention or whether conservative treatment will be more effective.
Article on the topic
First aid: what to do for a fracture, dislocation and sprain
After the operation, exercise therapy, physiotherapy, massage, reflexology, and an active motor regimen are necessary. All these measures activate blood and lymph circulation, promote restoration of damaged tissue and accelerate wound healing in the affected area.
Therapeutic gymnastics also strengthens muscles and ligaments affected by paralysis, prevents and eliminates muscle tightness.
The main rehabilitation methods that have proven themselves over time are:
- electrical stimulation;
- therapeutic and preventive physical education;
- biofeedback method.
- Anat Baniel method (ABM therapy) based on the Moshe Feldenkrais method.
Regardless of which rehabilitation method the specialist considers most effective in most cases, it must be based on the individual factors of the patient’s disease. In particular, the doctor must take into account the severity of the patient’s illness, his general physical and mental condition, and his emotional mood for rehabilitation.
However, some methods apply to all patients without exception:
- Exercise therapy and massage;
- psychological stimulation;
- exercises to restore memory and speech;
- preventive measures aimed at preventing recurrent disease and complications.
Restoring the functions of movement of the arms and legs cannot be associated only with physical actions. It is necessary to explain to the patient that much depends on his volitional orders to his body. When performing the simplest exercises, it is necessary to mentally pronounce (or out loud, if speech is restored) the movements of the limb, give it orders, and stimulate the brain to carry them out.
Such a pain!
It seems that nerve damage can hardly be confused with something: strong, almost unbearable pain is definitely felt along the nerve trunk, especially when moving and stretching the affected arm or leg, as well as when pressure is applied to the area of the injured nerve.
With other nerve damage, paralysis of an arm or leg and loss of skin sensitivity in certain parts of the body are possible to varying degrees.
Article on the topic Mysterious neurons. Nerve cells are still recovering
In the event of a nerve rupture, the victim develops the so-called causalgic syndrome, described by N. I. Pirogov in his work on military field surgery. In this case, severe pain usually appears after a few days, less often - on the same day or immediately after the injury and intensifies, reaching a maximum 2-3 weeks after nerve damage. The sensations, according to patients, “are reminiscent of applying a piece of red-hot iron that corrodes the skin.” The pain spreads throughout the arm or leg, sometimes radiating very strongly to the palm and fingers, to the area of the sole. Often the pain becomes unbearably cutting, stabbing, acquires a burning sensation and intensifies with any movement, sometimes an unpleasant feeling of dryness is added to it. Patients experience suffering from the slight touch of a dry object to any part of the body, for example, touching with a dry hand, a piece of paper, and constantly wrap the sore limb with a wet towel or keep their hand in a vessel with cold water all the time, and sometimes even wrap themselves in a wet sheet. It comes to the point that patients begin to suffer from any touch to the skin, from light, sound, noise, loud voices, shuffling feet...
Migrating pain with neuritis is usually associated not only with injury, but also with infection. They are sharp, suddenly appearing, intensify with pressure, and radiate to other parts of the body along the nerve trunk.