Patients with persecution mania
Patients suffering from pathology constantly feel a false belief in the continuous surveillance conducted by certain forces. They are confident that such a threat is real. Controlling what is happening requires continuous tension. Obsessive thoughts do not allow patients to rest. Lack of rest and rest wears out the body in a short time. Patients are configured to protect themselves and in this state can be dangerous both to themselves and to others.
In the event of a collision between a non-medic and patients suffering from persecutory delusions, it is recommended not to argue about the presence of personnel who conduct constant surveillance. The best option would be to contact a psychiatrist for advice.
How to behave to others?
First of all, it is necessary to help a sick person understand his problem and convince him to see a psychotherapist. It is very important to find a specialist who will find an approach to such a patient. The success of treatment and the emotional state of the patient largely depend on the level of trust in psychotherapists and psychiatrists.
You should also monitor the intake and dosage of medications prescribed by your doctor.
It is necessary to be patient and try to provide a favorable psycho-emotional atmosphere. There is no need to show excessive anxiety and negative reactions; all these actions encourage retaliatory attacks of aggression.
Relatives of a patient diagnosed with persecution mania should put themselves in the patient’s shoes, so if a person believes that some secret organization wants to kill him, then there is no need to convince him of the opposite.
Persecution mania disease
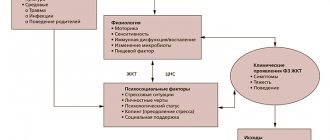
As a disease, persecution mania has not yet been fully studied. Observations made it possible to consider an increased risk of onset in patients in whose family the diagnosis was observed.
As a result of a stressful situation or for other reasons, patients develop persecution mania. Patients feel the constant presence of surveillance. As the patient develops, the body wears out due to the lack of long hours of rest. It is recognized as a manifestation of manic-depressive psychosis, schizophrenia and some other psychiatric diagnoses.
An increased risk of onset of the disease is observed in patients suffering from alcoholism or drug addiction. Often the disease begins against the background of neurological diagnoses. Primarily Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Treatment
There are several ways to get rid of persecution mania. The main thing is that the treatment is comprehensive. Taking medications or psychotherapy alone will not give the desired results.
Psychotherapy
It is carried out in the first stages of the development of the disease. On average, to obtain a sustainable effect you will need from 7 to 20 sessions. Although, if the disease is in the acute stage, treatment may be delayed.
During the session, the doctor’s main task is to prove to the patient that it is the erroneous perception of reality that causes him to experience excessive anxiety and restlessness. In order to correct the situation, a person studies the process of the emergence of certain feelings and emotions, as well as ways to control them.
The psychoanalytic approach has proven to be quite effective in treating persecutory mania. The specialist looks for the reasons for its development in personal conflicts, using transference and projection techniques. Once these conflicts are identified, they are demonstrated to the patient.
Family and art therapy can be added to the listed methods. The latter gives the patient the opportunity to throw out negative emotions through creativity.
Taking medications
Of the medications for persecution mania, the doctor most often prescribes the following groups of drugs:
- antipsychotics to reduce the level of brain arousal;
- anticonvulsants to suppress agitation;
- antipsychotics to inhibit excitation, normalize the mental state;
- antidepressants to improve mood;
- tranquilizers and mood stabilizers to eliminate anxiety and stabilize the general condition.
It is not recommended to take the listed drugs for self-medication, since they have their own indications and contraindications. The dosage, as well as the duration of the course of treatment, is determined by the doctor.
ECT
Electroconvulsive therapy is sometimes used to treat persecutory delusions caused by schizophrenia. It involves the passage of electrical current through the brain. As a result, the structure of the protein changes, which affects the neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system.
This is a rather controversial treatment method, which for a long time was even considered violence against the patient. However, today it is often used in the treatment of complex mental disorders. Contraindications to its implementation are diseases of the cardiovascular system, changes in heart rhythm, diabetes mellitus, metabolic disorders, renal failure, etc.
Pursuit mania in women
The onset of pathology in women is often associated with hormonal changes occurring in the body. This could equally be any resolution of pregnancy (abortion, miscarriage, childbirth), a hormonal surge during adolescence or menopause. There is also a significant role in the onset of pathology when stressful situations arise.
Women who suffer from suspicions of persistent stalking are characterized by increased levels of fear for their health. Often the feeling of being watched extends to family members.
The constant feeling of being watched provokes hysteria. Nervous conditions may cause body temperature to rise, heart rate to increase, and painful symptoms to occur.
Stages of development and immersion in your fictional world
Persecution mania develops gradually in three stages, each of which has its own symptoms and signs:
- The first stage is characterized by the presence of primary signs of the development of paranoia. Closedness, excessive worry, and increased levels of anxiety begin to appear.
- In the second stage, symptoms increase. Behavior becomes more restless, the person is unable to interact with others and adapt to society. Fear becomes a constant companion, and open complaints against others begin.
- At the third stage , uncontrollable signs of aggression begin and severe depression develops. A special category of patients may attempt suicide due to fears and depression. Behavior becomes suspicious and wary. There is a lack of trust in the people around you. There may be a misinterpretation of current events. The patient does unusual things that are completely inconsistent with everyday habits. It should be especially emphasized that all the thoughts of an individual are concentrated on his exceptional personality and the particularity of his significance for society. Also characteristic is the desire for self-isolation, aimed at limiting the influence of the environment.
At the initial stage of development, persecution mania looks quite harmless, but already during this period the disorder prevents a person from living a full life. Living in constant fear and tension, the patient provokes the development of other mental and somatic diseases. It is especially difficult for relatives and other people who surround such a person.
Paranoia (persecution mania)
Persuasive delusions, also called paranoia, can affect men and women. The list of reasons for the onset of pathology states:
- congenital predisposition;
- drug addiction;
- alcoholism;
- injuries leading to brain damage;
- neurological diagnoses, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease;
- other reasons.
Often doctors are unable to associate the onset of a disease with a specific starting point. Regardless of the patient’s gender, the patient may expect the presence of constant surveillance from representatives of large global communities or simply neighbors. Although there is a tendency for the majority of patients to classify their “controllers” as representatives of the authorities, alien civilizations and other large structures and departments.
The diagnosis is often made in patients in the older age group. Especially those who have suffered a stroke suffer from neurological diseases. In this situation, delusional thoughts more often spread to family members and acquaintances, from the point of view of the paranoid, claiming his property and wishing him death.
Causes of mental disorders with paranoia
Delusional ideas in the process of disease formation are closely related to the character and personality of a person. This is not due to the fact that people incorrectly perceive the world around them, but because of their own internal conflict. Patients with paranoia cannot correctly evaluate their own thoughts and ideas, since the value system does not coincide with the real world. They believe that enemies live around them and conspiracies are being woven. As a result of the disease, delirium becomes a symbol of the desire and need to achieve significance in the surrounding society, but at the same time, because of it, it is also impossible to establish contact with society.
From a medical point of view, it has been found that the main cause of health problems such as paranoia is protein-related metabolic disorders in the brain. Various unfavorable situations and incorrect reactions to life circumstances can provoke pathological changes and suspicions. Personality disorder most often occurs due to:
- depression;
- low self-esteem;
- hereditary factor;
- strong feelings;
- feelings of loneliness and physical isolation from society;
- alcohol, drugs and medications;
- Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and other diseases that have negative effects on the brain, for example, epilepsy, stroke, encephalopathy.
Diagnosis carried out by a specialist can reveal the aspects due to which the formation of such unhealthy thinking occurs. Treating paranoia is not easy, because patients in most cases do not trust the doctor and prescribed medications and become aggressive when they are offered help. The patient also classifies a loved one who worries about him as an enemy.
Signs and symptoms of persecutory mania in women
When pathology appears, women become very nervous and wary. They try to constantly monitor what is happening nearby. They may refuse to leave the premises and strive for maximum privacy. Problems arise in communicating with friends and relatives. Patients often leave work and stop social contacts. Suspicions may extend to family members and acquaintances.
Women often begin to stop caring for themselves. Their privacy is being violated. The patient begins to assume a desire to harm her on the part of almost everyone she meets. She may be afraid of cases of violence against her; in defending herself, she can be dangerous to others. Complaints to the police or government agencies are often possible. The complaints are not confirmed.
Patients become difficult in family life. Suspicions may extend to the closest family members, husband, children, parents.
Types of persecutory delusions
Delusional ideas of persecution can have absolutely any content, but scientists still identify several main types of them. The most common special cases of manifestations of delusional ideas in medical practice are:
- Delusion of persecution (in the narrow sense). It seems to the patient that he is being closely monitored. He thinks that someone is watching his every move, wherever he is: at home, on the street, at work, visiting, in public places, etc. He is confident that ill-wishers are infiltrating and installing tracking devices everywhere: in his apartment, entrance, office, elevator, telephone, computer, etc. This type of crazy idea is especially relevant in our time, when information technology is used everywhere and there is a real threat to the security of personal data.
- Delusional relationship. The patient feels increased attention to his person and is confident that everything that happens around him is directly related to his personality. It seems to him that all people want to cause him physical or psychological harm: even when people’s words and actions are neutral or directed at others. For example, when a person enters a store, it seems to him that everyone starts looking at him and discussing his appearance.
- Delirium of influence. The patient is overwhelmed by the idea that he is being affected mentally or physically. With delusions of physical influence, the patient is convinced that someone is influencing him through various devices or devices (for example, chips, rays, lasers, etc.) With delusions of mental influence, the person is convinced that someone is controlling him using various kinds of suggestion (hypnosis, telepathy, witchcraft, etc.). Some patients even believe that they are controlled by God or the devil.
- Delirium of poisoning. The person is convinced that someone is trying to poison him by adding toxic substances to food, water, releasing them into the ventilation or placing them around the apartment, etc.
- Delirium of material damage. It seems to the patient that his ill-wishers are constantly damaging or stealing his personal belongings: from socks to real estate.
- Nonsense of staging. The opinion that everything that is happening around is nothing more than some kind of “conspiracy” against the patient. All the surrounding people participate in the staging, specially adjusting reality in such a way as to somehow ruin a person’s life, kill him, etc.
- Delirium of jealousy . The patient is convinced that his partner is cheating on him: he begins to follow him and collect evidence of his infidelity.
- Nonsense of litigiousness. The patient is sure that his rights have been violated, and constantly applies to various authorities with various kinds of complaints. For example, it seems to him that he was illegally fined or detained, deprived of parental rights, forced to make any payments, etc. (although this may not have actually happened at all).
- Erotic delirium. A person considers himself a victim of erotic claims from others: from unobtrusive advances to accusations of rape [V. Bleicher, 1983].
It is important to note that absolutely all ideas of persecution are devoid of any positive connotation and are strictly negative in nature: the patient does not think that he is being followed because he is interesting or attractive to someone, but is sure that the persecution is always directed against him.
But why do such absurd and illogical ideas arise and develop? Let's figure it out.
Signs and symptoms of persecutory mania in men
In most cases, the syndrome manifests itself in men under the assumption of continuous surveillance. Already in the early stages, the patient tries to isolate himself from the world as much as possible, assuming that everyone he meets could be an enemy.
Men have a hard time with the constant feeling of being watched. Their body wears out quickly. In response to perceived aggression, they may be inclined to attack people, considering them a potential enemy. Constant tension often turns into depression, leading to thoughts of suicide. In a state of seizures, the patient is often dangerous to loved ones and others. In an effort to “save” them from imminent death, an attempt to kill those “being saved” is possible.