Home — For the public
- Map of medical organizations
- Vaccination
- Clinical examination
- Fluorography
- Addresses and opening hours of clinics
- Emergency rooms
- Oncology
- Where to take an HIV test
- Healthy child's office
- Services
- Prevention of CVD
- Disease Prevention
- World Patient Safety Day
- Newspaper "Medical News"
- specialist
- School of Health
— Disease prevention
- HIV infection
- All about vaccination
- All about proper nutrition
- Hepatitis
- Flu
- Dementia
- Schoolchildren's health
- STD
- Tick-borne encephalitis
- Whooping cough
- Measles
- Legionellosis
- Meningococcal infection
- Oncology
- Acute intestinal infection
- Pediculosis
- First aid
- Pneumococcal infection
- Pneumonia
- Prevention of rabies
- Dependency Prevention
- Rotavirus infection
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Injuries
- Tuberculosis
- Tularemia
- Physical activity
- Obstructive pulmonary disease
- Exotic infections
- Ecology
- Why is swimming in ponds dangerous?
— Prevention of addictions
- Prevention of alcoholism
- Smoking prevention
— Smoking prevention — Nicotine: disgusting, pleasant, dangerous
A drop of nicotine not only “kills the horse”, but also helps prevent the development of Alzheimer's disease. A click of a lighter, a few puffs - and after just 7 seconds, the molecules of the substance overcome the blood-brain barrier and begin to act on the brain. The effect of nicotine is not only the appearance of relaxation and high spirits. The substance also affects sleep and wakefulness rhythms, appetite, pain perception, digestion and the cardiovascular system.
Regular smoking leads to the formation of a dependence syndrome and chronic changes in tissues and organs.
Properties of nicotine
What is nicotine? It is an alkaloid - an organic heterocyclic substance consisting of carbon, nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. The group of compounds owes its name to its slightly alkaline chemical properties. Most alkaloids have an effect on the nervous system, among those. What people hear most are caffeine, cocaine, morphine.
According to its physical and organoleptic properties, nicotine is a bitter oily liquid. At certain temperatures it easily mixes with water, their densities are almost the same - about 1 g/cm3.
Nicotine dissolves well in environments with low polarity. This causes its rapid absorption through the skin and the blood-brain barrier. At high pH values, it easily penetrates through mucous membranes.
Where is nicotine found? The alkaloid is isolated from the shoots of plants of the nightshade family (tobacco, tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes). The concentration in tobacco is maximum – up to 14%. Nicotine is synthesized in plant roots, transported and accumulated in leaves. In the human body and warm-blooded animals, the compound breaks down to form safe metabolites.
Basic physiological properties of the “potion”
To understand the problem of nicotine and the brain being incompatible, we need to understand how they interact. This substance is one of the pyridine alkaloids. There is a lot of it in plants that belong to the nightshade family - most of all in individual elements of tobacco (leaves and stems). It is also found in some agricultural plants (tomatoes, eggplants, potatoes), as well as in coca.
After the intake of nicotine, the brain is “reformatted” - pleasant sensations arise:
- euphoria;
- calm;
- relaxation;
- serenity;
- a feeling that previously troubling problems have disappeared.
However, they disappear quite quickly, so a new dose is needed to maintain the “degree” of emotions. But the action consists not only in provoking the desired emotions, but also in pathological changes in various organs. It is due to the effect on the so-called H-cholinergic receptors.
How brain function changes under the influence of nicotine has been thoroughly studied since the 20th century, but people knew about it already several centuries ago. Thus, doctors who served at the royal courts prescribed tobacco to the ruling persons for migraines, which they regularly experienced. Later, the therapeutic effects of tobacco oil, which was obtained by steam distillation, were discovered. It was even used to treat epilepsy - regular attacks of seizures that occur due to overexcitation of the central nervous system.
Smoking has a known detrimental effect on these centers. In fact, there is even greater harm to the structures of the central nervous system if you use tobacco:
- snuff;
- chewing.
How much nicotine is in cigarettes
The range of lethal dose of the substance is from 50 to 100 mg. Recalling the drop of nicotine that killed the horse, toxicologists note that 2-3 drops are enough for a person. A person can get this amount of alkaloid from 1.5 packs of cigarettes.
How much nicotine is contained in 1 cigarette? The tobacco industry produces products of various strengths. The amount of nicotine in them ranges from 0.3 mg to 1.26 mg. For example, one Parliament cigarette can “supply” a smoker with 0.5 mg of nicotine, and a Marlboro “cancer stick” from a red pack can provide a smoker with 1.1 mg.
It is interesting that the strength of products in the line of one manufacturer can be determined solely as a subjective feeling. The filter of so-called light cigarettes has a larger number of perforations than their strong counterparts. This allows the smoker to draw in more air, due to which the concentration of nicotine and other toxic substances in the inhaled air becomes lower, and the taste is not so “rough”.
Another secret of “light” products: such products smolder on their own. The amount of tobacco gradually decreases, even if the person does not puff and just holds the cigarette in his hand.
The very idea of grading cigarettes was associated with an attempt by tobacco corporations to retain consumers: smoking light products was presented as a process of giving up a bad habit. In fact, people increased their daily number of cigarettes because they believed they were getting less tar and nicotine. According to the WHO Framework Convention, the labeling “light” and “soft” on the package is prohibited.
Harm from hookah and electronic cigarettes
Many tobacco lovers, in an attempt to quit smoking, switch to electronic cigarettes (vapes), considering them completely safe for health. This is not entirely true. Such products do not emit combustion products, only vapor, but they are filled with liquid containing a certain proportion of nicotine.
This can be either a fairly high percentage or a minimal one. Any buyer can independently purchase the most suitable liquid. The presence of nicotine in such a liquid still has a slight negative effect on the body of a man or woman.
Today, nicotine-free liquids are available for sale, in which this substance is completely absent, but they contain substances such as propylene glycol and glycerin. When heated, these components have an aggressive effect on the organs of the respiratory system, disrupt the blood circulation process, and provoke an exacerbation of various diseases. It can be concluded that e-cigarettes are also harmful to health.
An alternative to conventional tobacco products is hookah, which has been the subject of controversy for many years. Fans of hookah smoking speak out about its safety:
- Hookah has a more gentle effect on passive smokers, since its vapors do not contain heavy metals and quickly and completely dissolve in the air.
- The product does not contain paper - it is its burning in a cigarette that is harmful, since it contains a large number of carcinogens.
- Before entering the respiratory system, hookah smoke is cleaned and cooled.
But besides the positive, there are also negative sides. Tobacco, which is used to smoke a hookah, contains a small proportion of nicotine, so harm to the body is still caused. In addition, since smoking occurs through inhalation, all harmful substances enter the lowermost parts of the respiratory system. Therefore, hookah cannot be called completely safe.
Smoking tobacco products, electronic cigarettes or hookahs has a detrimental effect on a person’s health and can lead to severe brain diseases. And the longer a smoker is, the higher the likelihood of pathologies such as atherosclerosis or stroke, which can lead to death.
How quickly does nicotine leave the body?
After inhalation, nicotine is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches the brain within a few seconds. The half-life (the time during which the concentration of a substance drops by half) is about 2 hours. Depending on the length of smoking and the method of tobacco use, the rate of intake and metabolism may vary. Information about this helps to understand:
- with what frequency does a person feel the need to “take a drag”;
- how to choose the right therapy to alleviate withdrawal symptoms.
About 30% of the nicotine that enters the body is excreted unchanged, the remaining 70% in the form of non-toxic cotinine. The complete breakdown cycle of nicotine takes about 6-8 hours. When answering the question of how long nicotine is removed from the body, experts give a time frame of 1-2 days.
Interestingly, the name of the cotinine metabolite is an anagram of the word “nicotine.” The substance has an affinity for H-cholinergic receptors, providing a weak anti-anxiety and antipsychotic effect. Its half-life is up to 20 hours. The study of the duration of the last use of medications or smoking is assessed by the presence of cotinine and nicotine in the urine.
How to restore your brain after smoking
The basis of the recovery process is to quit a bad habit. Smoking gradually kills the body; its harmful effects on the brain are too large-scale to be successfully compensated for by one or another method and make smoking harmless. You should consult a neurologist, who, after conducting all the necessary examinations, including hardware examinations, for example, MRI, will make a conclusion about the state of the brain and peripheral nervous system.
What happens after quitting smoking - stages of cleansing and restoring the body hourly and day by day!
The elasticity of blood vessels is restored on its own, and quite quickly - in just three weeks. After this period of time, a sufficient amount of blood begins to flow into the brain to fully supply it with oxygen, and therefore to function. The cells of the brain itself gradually return to normal. But atherosclerotic lesions will have to be dealt with separately with the help of a neurologist, lowering the level of cholesterol in the blood with the help of special drug therapy. The renewal of the nervous impulse system occurs within a month, during which time irritability and nicotine withdrawal will go away.
Nicotine meets receptor
The effect of nicotine on the body is realized through communication with nicotinic cholinergic receptors (or N-cholinergic receptors) and partially with adrenergic receptors.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for the autonomous functioning of internal organs. It consists of 2 parts - sympathetic and parasympathetic. The work of biologically active substances occurs at the level of synapses - places of contact between neurons and neurons or organ cells. Each of them consists of a presynaptic. postsynaptic membranes of cells and the gap between them.
The transmission of impulses in the parasympathetic department is carried out due to the mediator acetylcholine. When it interacts with the presynaptic membrane of the receptor:
- pupils constrict;
- blood pressure decreases;
- heart rate decreases;
- peripheral blood vessels dilate;
- muscle fibers of internal organs contract;
- The secretion of sweat, bronchial, digestive, and lacrimal glands increases.
But the work of acetylcholine is not limited only to the parasympathetic system. The mediator also “puts his hand” to the sympathetic department. By connecting to a receptor on the presynaptic membrane, it has an effect reminiscent of adrenaline. Namely:
- heart rate increases;
- blood pressure increases;
- the concentration of glucose in the blood increases;
- fat breakdown is activated;
- appetite decreases.
Nicotine has a similar structure to the important C-loop of the acetylcholine molecule, but the connection of the alkaloid with the cholinergic receptor is stronger. Chemists claim that its molecule ideally replaces acetylcholine in all parts of the autonomic nervous system. The effect of nicotine on the human body is almost identical and consists of its effect on receptors in various tissues.
"Pros" and cons of the effect of nicotine on brain activity
Often a person continues to smoke because he is sincerely convinced of the benefits of tobacco for the body, in its healing and relaxing effect on the psyche. The most common misconceptions among smokers are:
- Smoking helps keep weight under control by reducing appetite,
- Nicotine has a calming effect on the body and copes better with stress than drugs,
- A cigarette allows you to concentrate,
- Smoking makes it easier to overcome anticipation and successfully cope with boredom.
Only a small proportion of smokers note an almost immediate return of negative emotions almost immediately after finishing a smoke break. Not remembering the normal state of the body, addicts look for the causes of nicotine-induced drowsiness and constant fatigue. Few people think that a temporary increase in concentration and attention ends in increased blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Meanwhile, there are many more negative sides and they are all real. It has been proven that smoking:
- Impairs memory and intelligence
- Leads to a lack of oxygen, slowing down thought processes,
- Violates the psychological and emotional state of a person,
- Causes irritability and inexplicable anger,
- Forms addiction
- Keeps the body in constant tension, aggravates stress,
- Negatively affects the health of others (especially children),
- Increases the risk of serious illness.
Nicotine and the brain
The effect of the alkaloid on the brain is associated with the activation of α4β2 receptors. They make up more than 80% of all H-cholinergic receptors in the central nervous system. Nicotine's affinity for them is so high that even acetylcholine cannot compete with it. These receptors take part in the release of mediators such as dopamine, GABA, and glutamate. This is how smoking improves attention and memory.
The effect of nicotine on the human brain is:
- in stabilizing the emotional background;
- in reducing anxiety;
- in increasing resistance to stress;
- in accelerating the reaction;
- in improving the perception of visual and auditory information.
In addition, the alkaloid activates metabolism in brain tissue and delays cell death. This circumstance formed the basis for clinical studies that have proven the effectiveness of nicotine as a means of preventing atrophic brain lesions (for example, Alzheimer's disease).
The effect of relaxation and increased resistance to stress, for which acetylcholine is responsible, plays a cruel joke in the formation of addiction. Since nicotine binds better to receptors, the body stops producing the mediator on its own. If a person decides to give up cigarettes or, due to various circumstances, cannot satisfy his nicotine hunger immediately, anxiety and irritability appear. Gradually, the addict begins to resort to smoking not in order to feel great, but in order to eliminate discomfort.
Symptoms of physical dependence are due in part to endogenous opioids in the brain. A constant supply of nicotine promotes the release of endorphins and enkephalins, which play an important role in reducing pain.
Nicotine “vigor” and “attractive slimness” are the result of the influence of the alkaloid on a certain group of neurons in the brain. These cells secrete substances that are involved in reducing appetite, breaking down fats and maintaining a high level of activity. When quitting smoking, a person may feel the need for large quantities of food and become lethargic and drowsy.
How does smoking affect the brain?
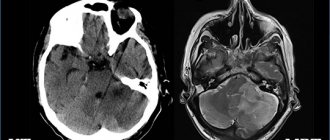
Several years ago in Germany, as part of the fight against smoking, they organized an action: how smoking affects the brain.
One of the exhibits of the action are posters with photographs of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain of a smoker and a non-smoker. You didn't have to be a doctor to see the difference. The feeling that the smoker simply has nothing in his skull! The action was quickly curtailed, and do you know why? Disputes began about the objectivity of the data provided. It doesn't take a visionary to suggest that large cigarette distribution concerns were involved.
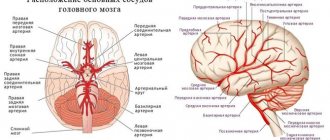
Nicotine and the cardiovascular system
As described earlier, the effect of nicotine on both parts of the autonomic nervous system is realized through changes in the lumen of blood vessels, heart rate, and fluctuations in blood pressure. Arterial spasm, tachycardia and increased pressure are the result of the release of adrenaline. The heart begins to work in emergency mode, pushing blood through narrowed vessels. It is forced to cope with the increased load. If a person smokes continuously, the blood vessels are constantly spasmed.
Nicotine also reduces the level of a substance called prostacyclin, which helps large and small arteries relax after contraction. The blood supply to all organs deteriorates, including the most important ones - the brain and heart. In fact, a smoker lives in a state of hypoxia.
Active and passive smoking destroys the membranes of cells located on the inner surface of blood vessels. Thus, changes in the aortic endothelium are observed even in infants 1 month of age, if their mother does not part with a cigarette. The dangerous effect of nicotine on human blood vessels can lead to sudden death. The risk of acute coronary syndrome in adult passive smokers compared with those isolated from tobacco smoke increases by almost 100%.
Activation of lipolysis and damage to vessel walls accelerate the development of atherosclerosis of any localization.
In addition, nicotine affects the rheological properties of blood. It increases the ability of platelets to stick together. Small clots form in the vessels. Blood viscosity increases, flow rate decreases. The presence of damage to the vascular wall leads to adhesion of formed elements and the formation of wall thrombi.
So the effect of nicotine on the human heart and blood vessels is to increase the risk of developing:
- arterial hypertension;
- coronary heart disease;
- heart attack, stroke;
- gangrene.
Deterioration of memory and intelligence when smoking
Based on reviews from many smokers, one may get the impression that smoking actually improves cognitive (mental) functions, but objective data says the opposite: smoking and the thought process are not compatible.
Along with this, we can cite as an example studies conducted in Europe, which indicate a more rapid loss of intelligence in people who smoke.
But a decline in memory and mental abilities is observed not only in older people. According to an Israeli study conducted among 20-year-old boys, cognitive function also declines among young smokers. The reason for this is hypoxia, which is caused by nicotine through its effect on the transfer of hemoglobin in the blood.
As a result of long-term smoking, concentration of attention decreases, memorization and reproduction of information worsens. It takes about 20% more time to solve logical problems than non-smokers.
The consequences of consuming tobacco smoke also include: excessive irritability, emotional instability, and a tendency to aggression. Smoking can provoke an exacerbation of affective disorders, which ruins the life of both the smoker and those around him.
Meditation
People describe meditative focus as focusing on being moment-to-moment aware of any thoughts, feelings, or bodily sensations without judging or thinking about them. You allow thoughts to come and go like clouds passing in the sky; All that remains is attentiveness and concentration. Scientists wanted to understand what was happening in the brains of the subjects, what exactly caused such rapid changes in the level of attentiveness, mood and fluid intelligence.
A 2010 study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences found that 11 hours of meditation resulted in more intact and efficient white matter in the brain—the wires and cables of the brain. connecting neurons - originating in the anterior part of the cingulate cortex. This gyrus, shaped like the famous upside-down Nike stroke, is located behind our eyebrows, about five centimeters above them, and is closely connected to the prefrontal cortex. It is known to work most intensely during difficult tasks that require cognitive control from us, as well as when we have to exert certain mental efforts, for example in the learning process or when solving relatively complex tasks and problems.
The book is provided by the publishing house Mann, Ivanov and Ferber.
Movement
Over the past ten years, at least four meta-analyses based on formally published studies have come to the same conclusion: physical fitness has a significant effect on cognitive performance. It is curious that all of them have nothing to do with brain gymnastics - in no way. You don't learn anything. You just do walking, swimming, cycling and so on. Just three times a week. But it does result in improved cognitive performance across a wide range of aspects of memory, perception and decision-making. It's amazing what huge results can be achieved with such a small lifestyle change.
Consequences of the negative effects of smoking
All of the above factors contribute to the occurrence of such consequences, when faced with which you need to consult a neurologist:
- significant memory impairment , problems concentrating;
- inhibition in solving certain problems , the difference in solving the same problems by a non-smoker and smokers is approximately 20%;
- decrease in intellectual abilities , the reason for this is a decrease in the activity of brain cells;
- changes in behavior , a person becomes nervous, irritable, and the risk of developing nervous disorders increases.
Of course, smoking negatively affects the ability to regenerate nerve cells and, based on this fact, smoking is strictly prohibited for people with neurological diseases.
The most destructive effect of smoking on blood circulation in the brain is the narrowing of blood vessels in the circulatory system. The narrowing of blood vessels causes oxygen starvation. In turn, due to oxygen starvation, some nerve cells die.
In addition to the above consequences, there is a risk of various types of stroke due to smoking. Disruption of blood vessels due to smoking leads to blockage of blood vessels in the brain. After all, as a result of long-term smoking, the blood vessels have become narrower, which is a favorable condition for the occurrence of blood clots.
There is an option for a fatal type of stroke, in which the vessels themselves are damaged and hemorrhage occurs in the brain. Stroke is a very common cause of death, second only to myocardial infarction, which is also a disease of the circulatory system.