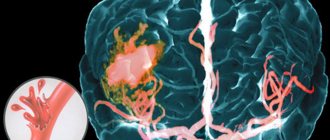
Ischemic stroke is one of the most pressing medical and social problems. Both in the acute period of stroke and after it, patients have swallowing disorders, which requires a special diet. At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors provide treatment and rehabilitation for patients with ischemic stroke. A personal nutritionist will select meals to provide the body with the necessary nutrients.
Causes of changes in metabolism during ischemic stroke
In patients with ischemic stroke, the digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular and urinary systems are most quickly involved in the pathological process, and multiple organ failure develops. During a stroke, the central regulatory organ suffers, which leads to a breakdown of central neurogenic control over the processes occurring in the internal organs.
Metabolic changes during stroke occur both as a result of powerful sympathetic stimulation of hormone release (glucagon, catecholamines, corticosteroids) and under the influence of local mediators. As a result of this reaction, the metabolism changes so that the body can absorb nutrients in the face of severe illness. This allows the mobilization of energy and substrates to support inflammatory and immune responses, as well as tissue regeneration. With ischemic stroke, protein deficiency develops, which ultimately leads to disruption of cell function and structure, as well as organ function.
In conditions of increased metabolism, an important role in the complex intensive care of ischemic stroke belongs to ensuring adequate nutrition using a number of methods other than regular food intake. A significant proportion of patients with ischemic cerebral stroke are unable to eat on their own, which is associated with a decreased level of consciousness or impaired swallowing function. Often the only possible way to deliver nutrients to these patients is artificial nutrition.
What foods should be excluded from the diet?
In order to minimize the risk of stroke, it is better to avoid certain foods. For example, from table salt. Excessive salt consumption can lead to the development of hypertension, one of the complications of which is stroke. People with high blood pressure and older people should reduce their salt intake.
Do not add salt to prepared foods or cook with salt. Healthy spices such as turmeric, black pepper, and basil will diversify the taste of food and make it less bland.
Turmeric is the best care for the brain. Curcumin penetrates directly into brain cells, bypassing the barrier between the circulatory system and the central nervous system.
Beneficial properties of curcumin:
- powerful antioxidant;
- has an anti-inflammatory effect;
- helps improve memory in people with Alzheimer's disease;
- helps new brain cells grow;
- relieves symptoms of depression by increasing serotonin and dopamine levels.
It can be added to food or taken as a dietary supplement.
The effect of curcumin on the body is confirmed by scientific research data, for example, the publication Antidepressant activity of curcumin: involvement of serotonin and dopamine system, Shrinivas K., 2008 states that the use of curcumin reduced symptoms of depression more effectively than the use of antidepressants.
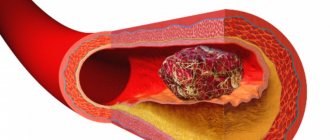
You should also limit the consumption of foods with a high glycemic index (sugar, sweet carbonated drinks, juices, confectionery, ice cream, etc.). They sharply increase blood glucose levels. Their constant use can lead to the development of diabetes, which, in turn, contributes to the development of diseases of the cardiovascular system. These include, among other things, vascular atherosclerosis, a condition that precedes a stroke.
Since the progression of atherosclerosis is associated with increased cholesterol levels, it is necessary to review the structure of the diet and try to avoid eating refined and fatty foods. It’s better not to fry food, but to stew it (with the addition of healthy spices it will be very tasty!), season it not with sunflower oil, but with olive oil, which preserves the health of blood vessels and is included in the healthy Mediterranean diet.
Artificial nutrition for ischemic stroke
Artificial nutrition is carried out enterally (while maintaining, to one degree or another, the movement of nutrients through the gastrointestinal tract) and parenterally.
The main elements of parenteral nutrition are water, sources of nitrogen and energy. As sources of nitrogen, specialists at the Yusupov Hospital use synthetic amino acid mixtures containing adequate and balanced amounts of nonessential and essential amino acids. Of the synthetic amino acid mixtures, the following drugs are most often used:
- azonutril;
- aminosteryl;
- Vamin;
- polyamine;
- Freamin.
The solutions ensure the synthesis of proteins from the administered amino acids, have a pronounced positive effect on protein metabolism, lead to a positive nitrogen balance and stabilization of the patient’s body weight. Amino acid mixtures remove toxins from the body by reducing the concentration of ammonia, which binds to the formation of non-toxic breakdown products.
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital provide the amount of energy needed by patients with ischemic stroke through carbohydrates or a combination of fat emulsions and monosaccharide solutions (lipofundin, intralipid). For enteral nutrition of patients with ischemic stroke at the Yusupov Hospital, polymer or elemental mixtures are used. Polymer mixtures contain fats, proteins and carbohydrates in proportions typical of a normal human diet. They consist of the following ingredients:
- whole protein isolates (milk, soy, meat, eggs);
- partially hydrolyzed starch;
- triglycerides;
- the necessary set of vitamins, micro- and macroelements.
Before absorption, these mixtures undergo enzymatic treatment in the intestines. Elemental mixtures contain:
- amino acids or short peptides;
- dextrose and oligosaccharides;
- essential fatty acids and medium chain triglycerides.
They are administered to patients if it is impossible to use polymer mixtures due to a pronounced decrease in the absorption and digestive functions of the intestine. The Yusupov Hospital also widely uses specific biologically significant elements that purposefully correct metabolic disorders such as:
- glutamine;
- branched amino acids;
- arginine;
- taurine;
- nucleic acids;
- microelements;
- antioxidants;
- vitamins.
In severe ischemic stroke, the inclusion of antioxidants in the enteral nutrition regimen provides better control over the increase in metabolism and reduces the time required for compensation of internal toxicosis. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital for stroke prefer early enteral nutrition as it is more physiological and easier to administer. Early enteral nutrition can solve the problem of “empty intestines.”
The movement of food through the gastrointestinal tract maintains the normal state and composition of the intestinal microflora. By prescribing artificial enteral nutrition to a patient with an ischemic stroke who is unable to feed on his own, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prevent the occurrence of septic complications associated with the penetration of microorganisms from the intestines into the blood.
Diet after a mini-stroke
After an acute cerebrovascular accident, patients need a nutritious diet that ensures the body receives a balanced amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. A necessary component of a healthy diet is a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in the food consumed. After a mini-stroke, it is important to maintain a water regime.
When selecting products from which to prepare dishes, nutritionists recommend giving preference to whole grains or products made from them. After a micro-stroke, you should eat orange and dark green foods, peas and beans. The menu should include a sufficient amount of fresh, frozen or dried fruits and berries every day.
The diet should include low-fat dairy products. To provide the body with protein of animal origin, white poultry meat, veal, and lean fish are best suited. The main sources of fat are nuts and fish. Patients after a mini-stroke should avoid eating lard, margarine, and minimize portions of butter.
Diet after a stroke is aimed at reducing the risk of another attack. When selecting food products, you should pay attention to the following criteria:
- nutritional value (calorie content);
- presence of fat;
- the presence of saturated and trans fats;
- do you have cholesterol?
- content of table salt and fiber.
Limiting your intake of trans fats will reduce blood cholesterol, which is of great importance in cases of brain damage. A diet rich in saturated fats increases cholesterol levels, promotes the development of cardiovascular diseases, and cerebral atherosclerosis. There are many of them in lard, hard cheeses, egg yolks, ice cream, coconut and palm kernel oil. Limiting the consumption of these products is especially important for patients suffering from diabetes mellitus after a microstroke.
What can you eat if you have a stroke: table No. 10
The main question that arises in the process of prevention and recovery from cerebrovascular accidents is what you can eat during a stroke. Most experts agree that the nutrition of patients in this group should be complete and varied, but the diet involves certain restrictions. An excellent example of the dietary diet of stroke patients is the technique developed by Soviet nutritionists, which was called “table No. 10.”
This technique assumes the following principles:
- Caloric content of the diet. The patient's daily caloric intake should be 2500-2600 kcal. Calorie restriction is achieved by reducing the consumption of simple fats and carbohydrates, which contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and blockage of blood vessels, which provokes a stroke.
- Chemical composition of food. The daily ration of the “table No. 10” diet should contain no more than 400 grams of carbohydrates, 90 grams of proteins (55-60% animal) and 70 grams of fat (25-30% vegetable). A restriction on salt consumption is also being introduced, the content of which in the daily diet should not exceed 6-7 grams.
- Method of preparing food. Meat, fish and vegetables are steamed, boiled or baked without the use of fat and with minimal addition of salt and spices.
- Regularity of meals. The patient is recommended to eat 5-6 times a day in small portions, with equal intervals between meals of approximately three hours. The last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime.
- Drinking liquids. The diet introduces a limit on daily fluid intake at 1.2 liters of clean water per day.
The method of therapeutic nutrition “table No. 10” is based on the following principles:
- First meal. The diet recommends preparing vegetarian soups with vegetable broth. Meat, mushroom and fish first courses, as well as soups containing legumes, are completely excluded from the diet. Vegetable soups can contain potatoes, beets, carrots, tomatoes, and various cereals. The serving of the first course should be from 200 to 400 grams.
- Meat, fish, poultry. It is allowed to eat lean meat - beef, veal, chicken, turkey, rabbit, as well as trimmed pork in small quantities. The meat is boiled, baked, or steamed, and also served as aspic. The consumption of fatty meat is excluded - fatty pork, goose and duck meat, offal (liver, kidneys, brains), smoked sausages, as well as any canned food. Lean fish can be prepared by boiling followed by baking or frying. Fatty fish, as well as salted, smoked and dried fish, caviar and any canned fish are completely excluded from the diet.
- Dairy products. If the patient does not have intolerance, low-fat kefir and cottage cheese are allowed. The “table No. 10” food system allows for limited addition of sour cream, cream and cheese to dishes. Salty and fatty cheeses are completely excluded from the diet.
- Eggs. You can eat 1 egg per day, soft-boiled or served as a steamed omelette or baked in the oven. Fried and hard-boiled eggs are completely excluded from the diet.
- Cereals. The diet includes cereals cooked in water or milk in the form of puddings, as well as pasta. Legumes are completely excluded.
- Vegetables and fruits. The following vegetables are allowed to be consumed: potatoes, cauliflower, tomatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, cucumbers, lettuce, as well as parsley and cilantro as a seasoning for food. White cabbage and green peas can be consumed in limited quantities. Vegetables can be cooked by boiling and baking with minimal addition of salt. It is advisable to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables. Salted, pickled and pickled vegetables should be excluded from the diet. It is also recommended to completely avoid eating and adding radishes, spinach, sorrel, garlic, onions and mushrooms to dishes. Ripe fruits, fresh berries and dried fruits can be consumed without restrictions. It is also recommended to introduce into the diet compotes, mousses, jelly, honey and jam with minimal sugar content.
- Beverages. Patients can drink weak tea, vegetable and fruit juices (except grape juice), and rosehip decoction. Natural coffee and cocoa are completely excluded.
Compliance with the above recommendations allows you to avoid the development of atherosclerosis, maintain normal functioning of the cardiovascular system and reduce the risk of stroke. Also, “table No. 10” is one of the options for proper nutrition during the recovery period after an acute vascular crisis.
Why is coffee dangerous after a stroke?
The problem is not the drink itself, but the caffeine it contains. As we already know, this alkaloid can cause increased blood pressure and increased heart rate, and this is contraindicated for those who have suffered a stroke.
So coffee is strictly prohibited during the acute phase of the disease, as well as during medication and physiotherapy. The recovery period is also better spent without the usual drink.
Subsequently, coffee can be returned to the diet. Moreover, according to medical research, the increase in blood pressure under the influence of caffeine occurs more strongly in those who rarely drink coffee. The drink has a much weaker effect on avid coffee drinkers, but in any case, you need to get used to drinking a weak drink. It is highly advisable to dilute it with milk, cream or drink with the addition of lemon. All of these supplements counteract the effects of caffeine, which poses a very serious threat to stroke survivors. Many people try to solve the problem by switching to decaffeinated coffee. This is the wrong way. After all, when processing beans, a small dose of caffeine is still retained in them, so you shouldn’t be fooled - this substance is always present in coffee in varying quantities.
IMPORTANT. Instant coffee is especially prohibited for stroke survivors. The instant powder contains twice as much caffeine as the same amount of ground coffee by weight.
What do the doctor's say?
If the recovery period is successful, then you can ask the attending physician’s permission to drink your favorite drink. If the doctor does not object, then coffee can be returned to the diet. However, with some reservations.
- After completing the recovery period, you can allow yourself one cup a day of weak coffee, diluted with milk or cream. It is better to prepare it from high-grade Arabica beans; they contain much less caffeine than blends with the addition of Robusta.
- You will have to forget about strong coffee forever. Unfortunately, its effect on the body increases the risk of a recurrent stroke, so you will have to exclude it from the diet.
I don’t want to end the article on such a sad note, so we remind all fans of real coffee that recent research into the effects of this drink has revealed the tonic effect that coffee has on the heart muscle. There are also positive results in preventing age-related changes in the brain. Coffee plays a significant role in combating Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Of course, in combination with various types of physical and brain activity.
So be healthy and take care of yourself!