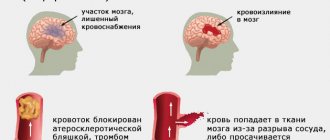
Muscle pain after a stroke, which should be treated immediately, occurs in most patients. Muscle soreness can interfere with the body's recovery. Post-stroke pain can be strategic or thalamic. Strategic pain occurs in the area of the brain that controls sensations, particularly pain, and is caused by spasms. Thalamic pain appears after a stroke in one side of the body several months after the circulatory disorder. Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital, together with rehabilitation specialists, help patients overcome pain and continue to restore lost functions. Patients are treated using modern equipment and innovative techniques to achieve maximum results.
Causes of muscle pain during stroke
In order to begin treatment after a stroke, it is necessary to understand the cause of muscle pain. After a violation of the blood circulation in the brain, hardening of the muscles is often observed; in the absence of rehabilitation measures, they become rigid.
In the human body, some muscles are designed to bend the legs and arms, while others are responsible for straightening the limbs. Normally there is a balance between them. During a stroke, areas of the brain that send nerve impulses to the limbs are damaged, causing some muscles to dominate over others. This imbalance is called contracture, and when it occurs, pain and spasms are observed in the muscles.
Muscle pain after a stroke: treatment
You should not self-medicate for pain in the limbs after a stroke; in this case, you need to consult a neurologist. The doctor is able to accurately determine the causes, taking into account the characteristics of the body, and prescribe comprehensive treatment for post-stroke pain. At the moment pain appears, it is necessary to understand where it is localized and after what actions it appears. Neurologists and rehabilitation specialists recommend that patients monitor their sensations and also record the moments when pain occurs.
In order to begin restoring motor function and pain in the legs after a stroke, you need to contact a neurology clinic and also make an appointment with a rehabilitation specialist. If you do not begin to treat this problem, the muscles may harden and the limbs will not be able to straighten, which will aggravate the condition and slow down the recovery of the body. Treatment of pain syndrome is carried out using physiotherapy, medication, and securing the limbs in a normal position using splints.
Additionally, to relieve spasms and restore motor function, neurologists prescribe physical therapy, laser therapy, magnetic therapy, massage and heat treatment to patients. Pain in the legs after a stroke, the treatment of which is successful with specially selected exercise therapy exercises, can hinder the patient’s recovery.
Traditional methods for relieving pain after a stroke are based on rubbing the limbs with oils; these procedures allow you to restore sensitivity. There is also a known recipe for a special ointment for rubbing, consisting of alcohol and vegetable oil in a ratio of 1:2. Baths made from a decoction of rosehip roots, pine needles, and celandine are effective in solving the problem. Before using these methods, it is important to consult your doctor and determine the presence of contraindications.
Rehabilitation after ischemic stroke
Basic principles
1. Early start of the rehabilitation process - from the first hours of stroke development. At the very beginning, this is primarily:
Correct positioning of affected limbs
To prevent bedsores and the respiratory system, you should lie on both the healthy and paralyzed side. The healthy leg should be straightened, and the paralyzed leg should be brought forward slightly, slightly bent and placed on a pad. Place a pillow under the paralyzed arm.
To lie on the painful side, you should place a pillow under the patient's back to relax the muscles and stabilize him so that he does not roll out of bed. The paralyzed arm should be extended forward. Straighten your arm and place your palm up.
Attention: Do not lie on the paralyzed side for a long time.
The patient can lie with his head elevated for 15-30 minutes 3 times a day, starting from the first day of the disease.
Regularly changing the position of a post-stroke patient in bed
The position of the body in bed should be changed as often as possible. Prolonged pressure on the same areas of the body can lead to the formation of bedsores.
The patient’s position in bed should also be changed to improve bronchial function. If the patient is constantly in the same position, then sputum from some bronchi, under the influence of gravity, flows into the trachea and is coughed up, but from other bronchi, on the contrary, does not flow. And stagnation in any hollow organ leads to its inflammation. Even in the absence of dangerous microorganisms, microbes begin to multiply in the area of stagnation, which leads to pneumonia, which is difficult to cure in a weakened person. Frequent turns in bed help avoid this complication.
Massage
The massage procedure contributes to the overall health of the body, normalization of blood circulation in various parts of the patient’s body, restoration of lost functions or their compensation, normalization of muscle tone, increased joint mobility, elimination of trophic disorders in paralyzed limbs. The pathology of the connection between the muscles of a paralyzed limb and the nervous system leads not only to immobilization of the limb, but also to disruption of tissue nutrition.
Massage after a stroke
Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy)
Exercise therapy is a method of prevention using exercise, often combined with physical therapy and massage.
Exercises for recovery after a stroke
The sooner rehabilitation measures are started, the more lost functions will be restored or compensated.
2. Systematic long-term treatment over many months and sometimes years. Therapy (drug and non-drug) should continue in accordance with the recommendations of the attending physician.
3. Rehabilitation must be comprehensive. It is necessary to combine drug treatment with physical, psychological and speech therapy.
4. Consistency and phasing. At each stage, specific tasks should be set to restore lost functions. After completing the stage, the tasks change as your health improves.
5. Active participation of the patient and his family in the rehabilitation process.
Hyperbaric oxygenation
In diseases when the delivery of oxygen to organs and tissues is disrupted, including ischemic stroke, hypoxia develops - oxygen starvation. The brain is especially sensitive to a lack of oxygen and cannot function normally when it is deficient. In such situations, a modern treatment method, a type of oxygen therapy - hyperbaric oxygenation (HBOT), is used to improve oxygen supply.
Oxygen therapy: treatment and prevention of diseases
Hyperbaric oxygenation is a treatment method using pressure chambers in which the patient breathes an air mixture with an oxygen concentration 5 times higher than normal air. Due to the increased pressure and concentration, oxygen easily and quickly dissolves in the blood and is distributed throughout the body with its current. All tissues of the body are saturated with oxygen, even those in which blood circulation is impaired.
As a result, metabolic processes and blood circulation are improved, the neutralization and removal of waste and harmful substances from the body is accelerated, the functioning of all internal organs is normalized, the body's need for medicinal substances is reduced and their therapeutic effect is enhanced.
In addition, HBO has an anti-edematous effect, promotes the proliferation of blood vessels and restores blood supply to the affected areas of the brain.
Treatment can only be carried out after consultation with a doctor.
Physiotherapy
After a stroke, electromyostimulation, darsonvalization (electrotherapy), faradization (treatment using low-frequency alternating current in pulsed mode), balneotherapy (hydrotherapy), acupuncture, phototherapy and treatment with ionized air are prescribed.
Physiotherapy sessions are held at the Cardiological Sanatorium. The following medical services are also provided: hydrotherapy, inhalations, therapeutic massage, herbal medicine, exercise therapy and drug therapy.
Aromatherapy
The use of the following essential oils is recommended: oil of styrax benzoin, black pepper, eucalyptus, garlic, geranium, ginger, juniper, lemon, tangerine, rosemary, clary sage, thyme.
Oils are used for massage, as bath additives, and to scent the air.
Prevention of muscle pain after stroke
The occurrence of pain after a stroke can be associated with various factors. Neurologists and rehabilitation specialists advise patients to follow recommendations that will prevent the onset of this condition. Measures to prevent muscle pain after a stroke:
- do not take hot baths;
- prefer clothes made from natural materials, do not wear light clothes;
- be in a comfortable position and avoid tightly grouping the body;
- do not put pressure on the affected side;
- use special devices for paralyzed and weakened limbs;
- fix the paralyzed arm while sitting so that the pain localized in the shoulder does not get worse;
- When moving, support from another person is desirable.
If you have pain in the legs after a stroke, it is important to trust treatment to qualified neurologists and rehabilitation specialists. Experienced doctors work at the Yusupov Hospital, which is located in Moscow on Nagornaya Street, and they will select methods for treating post-stroke pain depending on the mechanism of manifestation. Timely consultation with a doctor is the key to the patient’s recovery. You can make an appointment with a doctor and get answers to your questions about stroke treatment and rehabilitation by phone.
Pain after a stroke: how to relieve it?
The appearance of pain after a stroke is associated with damage to the neural connections that transmit information from receptors to the brain. Let's talk about the types of pain and treatment methods
Patients who have suffered a stroke often report pain in the affected part of the body. Sometimes it’s a simple tingling, burning sensation that is easy to come to terms with. Sometimes it is a discomfort that cannot be ignored. And in some cases (6-10%), the pain intensifies so much that it becomes unbearable and significantly worsens the person’s quality of life.
There are two types of pain: central and peripheral. Each of them has its own etiology and characteristics.
Central post-stroke pain
It is neuropathic in nature, that is, painful sensations do not arise as a result of the impact on the affected limb, but due to overexcitation of the nerve cells of the brain. The symptom occurs due to damage to the thalamus, parietal cortex or thalamus opticus. Due to oxygen deficiency in tissues, the process of transmitting information from receptors to the brain is disrupted. He interprets the signals incorrectly: even in the absence of touch or any impact on the injured arm/leg, the person feels pain.
Nervous overexcitation, stress, overwork, and negative emotions aggravate the unpleasant sensations. The patient feels:
- numbness and tingling;
- pain that resembles electric shocks.
Peripheral pain
A stroke provokes a disruption in the transmission of nerve impulses between the limbs and the brain. To restore this function, the brain strengthens impulses, increasing muscle tone. As a result, the person feels pain.
The symptom develops during the period of active rehabilitation - starting 15-20 days after the brain attack. Every time he tries to move his arm or leg, he feels severe discomfort. At the same time, the appearance of such pain after a stroke is considered a good sign - this means that sensitivity is returning to the limb.
Peripheral pain is diagnosed by examining the clinical picture. Laboratory and hardware tests are also carried out: they study the state of the cerebral cortex and determine the foci of damage.
Headache after a stroke - what to do?
According to statistics, about 60% of patients who have suffered a brain attack suffer from headaches. The reasons can be different - from side effects of medications and hypertension to recurrent stroke.
Sometimes the pain takes such a pronounced form that a person loses self-control, becomes aggressive or, conversely, becomes depressed. Therefore, it is very important to undergo studies (MRI and CT) to find out the cause of the headache and choose the right medications to relieve the attack.
Muscle pain
After a stroke, the muscles of the legs/arms are in spasm. This occurs due to damage to the areas of the brain responsible for transmitting nerve impulses for flexion and extension of the limbs. Normally, these functions are balanced, but after a stroke, the muscles responsible for bending the arms and legs may become dominant. These phenomena are called contractures.
With contractures, a person cannot fully control the arm/leg, bend it, or lift it. And all this is accompanied by pain.
The condition requires immediate treatment, because there is a risk of developing an irreversible process when it will no longer be possible to force the extensor muscles of the limbs to function.
My leg hurts after a stroke - what to do?
Joint pain after a brain attack can cause no less discomfort than muscle pain. In addition, it must be differentiated from developing arthritis. In addition to pain, a burning and tingling sensation may be felt in a leg or arm paralyzed after a stroke. When you move your leg or touch clothing/shoes, the discomfort intensifies.
As mentioned above, pain in paretic limbs indicates that the recovery process has begun, and the doctor’s task is to alleviate the patient’s condition during this period.
How to reduce the frequency and severity of pain attacks
Since the causes of pain after a stroke are different, treatment methods also differ:
- Central post-stroke pain. The goal of treatment is to influence the areas of the brain that are responsible for subjective sensations. Here, ordinary analgesics will not help, since the problem is not local, but systemic. The maximum effect will be ensured by the simultaneous use of antidepressants and anticonvulsants. The duration of treatment is from 4 to 8 weeks.
- Peripheral pain. Muscle relaxants are also added to antidepressants and anticonvulsants - drugs that relax the muscles of the paretic limb, thus reducing pain.
- Headache. If they are caused by pressure surges, antihypertensive drugs and blood thinners are used. If the attacks of pain are rare and short-lived, a single dose of paracetamol may be enough. Remember: after a stroke, aspirin is strictly contraindicated.
Folk remedies
In addition to medications, traditional medicine can be used to relieve pain.
- Clover tincture. Recipe: meadow clover inflorescences (1 glass) are placed in a jar (1 liter) and filled with vodka. Leave for two weeks, filter and take 1 tsp. per day after meals. The course of treatment is 3 times for 30 days with a break of 10 days.
- Alcohol ointment. Mix two glasses of unrefined sunflower oil with a glass of vodka. Rub the mixture on the affected limb twice a day. You can use bay oil in the same way.
- Baths with medicinal herbs. Prepare a dry mixture of celandine, pine needles, rose hips, sage (3 cups in total) and pour boiling water in a three-liter jar. Leave for an hour, then strain and pour into a bathtub with bathing water. The course of treatment is 10 procedures.
Please note: all recipes are given for reference; before using them, you should consult your doctor.
Exercise therapy and massage
The rehabilitation complex for patients who have suffered a stroke must include physical therapy. This is a set of movements aimed at developing damaged limbs, relieving muscle spasms and improving joint mobility.
Rehabilitation exercises should be performed regularly (daily) and with sufficient intensity. From time to time it is worth increasing the number of repetitions in order to give a feasible load on the limb. You need to start with 30 repetitions, gradually increasing to 50.
Exercises are performed lying down:
- bend and straighten your arms at the elbows;
- bend your arm at the elbow and then extend it above your head;
- straighten your arms above your head and spread them to the sides;
- alternately bend and straighten the hands;
- clench fists;
- rotate your thumbs;
- extend your arms along your body and then raise them;
- bend and straighten your knees and feet;
- move your feet clockwise and counterclockwise.
Massage is indicated for muscle hypertonicity, which is often observed in patients who have suffered a stroke. It is necessary to influence both the affected and healthy parts of the body at the same time.
Important: you should not start massage immediately after an ischemic stroke - you need to wait at least a week.
The course of procedures is 15 sessions (one per day), after which they take a break and repeat the course one or two more times. If pain in muscles or joints is severe, the procedure should be postponed until the patient feels better.
The intensity of the impact should be minimal at first, with a tendency to increase. The same applies to the duration of the massage session. There should be no pain during the procedure.
Prevention of pain after stroke
It is difficult to prevent the development of pain syndrome, but it is quite possible to reduce the severity of its manifestation. To do this, the patient should not:
- take hot baths;
- allow pressure from clothing, belts, or braces on the affected part of the body;
- walk independently if your legs are not yet strong enough.
While sitting, place a soft pillow/cushion under the affected leg or arm so that it does not hang in the air. If possible, it is necessary to use devices for paretic limbs - bandages, supports, crutches.
_____________________
Pain after a stroke is an unpleasant symptom that worsens the quality of life. It can and should be fought with the help of competent doctors, medications, exercise therapy and massage. The main thing is to support a person during this difficult period, instill in him optimism and confidence in a speedy recovery.