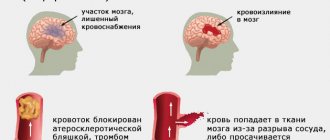
Hemorrhagic stroke is a rupture of cerebral vessels and hemorrhage in brain tissue. Depending on the localization and extent of the process, the prognosis of the disease is determined. Hemorrhagic stroke occurs less frequently than ischemic stroke, but the prognosis of the disease is more unfavorable.
The Yusupov Hospital treats patients with strokes and provides emergency care with the patient being transported to the intensive care unit. In the hospital, the patient will be examined using innovative equipment and will receive effective treatment using minimally invasive neurosurgery methods, the latest developments in the field of stroke treatment, and modern medications. The hospital provides comfortable rooms, dietary meals, and doctors create an individual treatment and rehabilitation program.
Types of hemorrhagic stroke
The effectiveness of stroke treatment depends on timely medical care. In hemorrhagic stroke, symptoms depend on the location of the injury. There are several types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Intraventricular stroke - characterized by rupture of blood vessels and breakthrough of blood into the ventricles of the brain. The brain tissue becomes saturated with blood or hematomas form in the ventricles of the brain. Such a stroke most often ends in the death of the patient on the 2nd or 3rd day.
- Parenchymal stroke - hemorrhage occurs in the substance of the brain, a hematoma can form or the nerve tissues of the brain become saturated with blood, as a result of such a stroke a severe neurological deficit is formed.
- Subarachnoid stroke - hemorrhage occurs in the cavity between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain.
- Mixed hemorrhages - bleeding is accompanied by changes that are characteristic of different types of strokes.
Causes
Hemorrhagic stroke is poorly diagnosed, although the causes and mechanism of its development are well studied. Various factors can provoke the development of hemorrhoidal stroke:
- Hypertension, arterial hypertension.
- Vascular aneurysm.
- Long-term use of anticoagulants.
- Diseases of the brain, spinal cord, cardiovascular system, diabetes.
- Congenital vascular defects.
- Blood diseases.
- Systemic diseases.
- Kidney and liver diseases.
- Alcoholism, drug addiction, tobacco addiction.
- Obesity.
- Stress.
- Hard physical labor.
- Hereditary predisposition.
A persistent increase in blood pressure leads to the formation of fibrinoid-hyaline necrosis of the walls of arterial vessels and can cause rupture of the walls of the aneurysm and the development of bleeding. The hematoma compresses the surrounding brain tissue, causing brain swelling. Blood from ruptured vessels can permeate the nerve tissue of the brain or, under pressure, break into the ventricles of the brain, the subarachnoid space.
Possible causes of the attack
Hemorrhagic stroke has an acute onset. It is difficult to determine its cause, especially in the absence of a history of heart and vascular diseases. Up to 15% of cases remain unrecognized, and in a quarter of patients, hemorrhage begins without a clear cause. During the diagnosis, a rupture of the vessel is noted, and the provoking factor remains the goal of further examinations. This is necessary to prevent further relapses. In general, there are several conditions that can provoke a hemorrhagic stroke:
- chronic increase in blood pressure;
- diabetes;
- lipid metabolism disorders;
- heart and vascular diseases, including atrial fibrillation, stenosis (narrowing) of the carotid arteries, anemia;
- unhealthy lifestyle, bad habits, excess weight.
Arterial hypertension is the most common cause of hemorrhagic stroke. With a chronic increase in pressure, the strength and elasticity of the vascular walls decrease and the properties of the blood change. Patients of the Clinical Brain Institute often complain of pressure surges, but have no idea what consequences this condition can lead to. Rapid blood filling of the vessels causes their rupture with subsequent hemorrhage into the brain tissue.
Metabolic disorders also affect the condition of the vascular walls. One of the most common forms of dyslipidemia (pathologies of fat metabolism) is the accumulation of excess cholesterol. It forms deposits on the walls of the arteries, causing them to become brittle and unable to withstand stress. This condition provokes the development of atherosclerosis, a disease that is accompanied by a decrease in the elasticity of the arteries. This disease is often diagnosed as a precursor to hemorrhagic stroke.
Another pathology that can lead to spontaneous hemorrhages is diabetes mellitus. Frequent fluctuations in blood glucose levels irritate the inner lining of the walls of blood vessels, which causes their fragility. Additional factors, including surges in blood pressure, cause rupture of arteries in any area. If the process is localized in the brain area, it is dangerous with serious complications.
The lifestyle and age of the patient also affect the condition of blood vessels and the chemical composition of the blood. Only with regular physical activity is normal blood circulation possible. Sedentary work, poor diet, alcohol abuse and smoking are the main causes of increased blood viscosity, blood clots, atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases. In such conditions, strokes can occur for no apparent reason, with a slight increase in pressure.
Symptoms of hemorrhagic stroke
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is accompanied by severe headache, vomiting, convulsions may begin, consciousness is impaired, Terson syndrome is observed, and meningeal symptoms appear. Parenchymal stroke is characterized by unexpectedly occurring severe headache, pallor or redness of the face, asymmetry of facial features, impaired coordination of movement, impaired respiratory function, and agitation. Ventricular stroke, the most severe form of the disease, is characterized by rapid deterioration of the patient's condition; bloody vomiting, loss of consciousness, fever, convulsions, and coma may occur. Ventricular stroke most often leads to the death of the patient. In most cases, hemorrhagic stroke occurs during the daytime, and the patient suddenly loses consciousness.
At the first examination, doctors note a change in complexion, high blood pressure, impaired respiratory function, slow pulse, decreased muscle tone, and tendon reflexes. Such symptoms are characteristic of the first hours after a stroke, then an increase in muscle tone and tendon reflexes occurs, the function of the pelvic organs is disrupted, the condition worsens, and the patient may fall into a coma.
Make an appointment
Difference between hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke
Strokes are characterized by the same symptoms, but have different causes of pathology. Hemorrhagic stroke has a more unfavorable prognosis and is characterized by the development of various severe disorders. In ischemic stroke, a favorable prognosis depends on the degree of brain damage. All types of strokes are characterized by the following disorders:
- Loss of speech.
- Paralysis of the body and limbs.
- Impaired sensitivity.
- Visual impairment or complete loss.
- Loss of coordination.
- Partial or complete hearing loss.
- Disorder of the function of the cerebral cortex.
- High blood pressure.
The consequences of a stroke depend on the location and extent of the brain lesion. Hemorrhagic stroke begins acutely, the disease progresses rapidly, and coma may develop within the first minutes or several hours. With hemorrhagic stroke, symptoms appear earlier than with ischemic stroke, they are more pronounced.
Period of return to normal life
Rehabilitation after hemorrhagic stroke is carried out according to plan in medical institutions of various specialties:
- For 1 month, patients are treated in the neurological or neurovascular department of the hospital.
- Then they receive rehabilitation treatment in the rehabilitation department for another 1 month.
After this, doctors evaluate how successful the treatment was. Depending on the preliminary results, the patient is offered different programs for further recovery.
Treatment after a stroke
A patient with a hemorrhagic stroke should receive first aid. The patient is placed on the bed, clothes are unbuttoned to make breathing easier, and a window is opened to allow fresh air to enter. The patient's head should be higher than the body level. The patient should measure blood pressure and pulse, monitor breathing in case of loss of consciousness and, if necessary, carry out resuscitation measures. The main task of doctors in case of hemorrhagic stroke is to stop bleeding, maintain respiratory function, the functioning of the cardiovascular system, and relieve cerebral edema.
In case of extensive hemorrhage in the brain, neurosurgical microtechnical operations are used - the hematoma is removed in order to reduce the pressure on the brain tissue and prevent the development of cerebral edema. Surgery for hemorrhagic stroke is performed strictly according to indications. Painkillers are prescribed to reduce headaches. If the cause of a hemorrhagic stroke was an aneurysm, doctors perform an operation and prescribe hemostatic drugs to stop the bleeding. Often, subarachnoid stroke is accompanied by vasoconstriction (secondary vasospasm) and the development of ischemic stroke. In this case, calcium channel blockers are prescribed to prevent narrowing and spasm of blood vessels.
Consequences
The consequences of a hemorrhagic stroke can bother the patient for the rest of his life. Depending on the severity of the disorders, recovery occurs; the most severe condition is in patients with extensive hemorrhagic stroke. Depending on which hemisphere of the brain is affected, the consequences of cerebral hemorrhage are observed. Hemorrhagic stroke of the right hemisphere of the brain:
- Partial or complete loss of vision.
- Disorders of urination and defecation.
- Paresis or paralysis of the body, decreased sensitivity of the left half of the body.
- Development of mental disorders.
A stroke to the left hemisphere of the brain causes paralysis on the right side of the body. When hemorrhage occurs in the area of the brain stem or cerebellum, loss of sensitivity occurs, the patient cannot swallow or speak, partial or complete loss of hearing in the right ear occurs, vision is impaired, coordination of movements is impaired, the patient cannot make unilateral or bilateral voluntary movements. Often the consequence of a hemorrhagic stroke is dementia (dementia), which develops gradually.
Rehabilitation of hemorrhagic stroke
Rehabilitation of the patient in the first 6-12 months consists of maintaining his vital functions and restoring lost abilities. During this period, when the patient has lost motor functions, the risk of bedsores and congestion increases. The patient is turned several times a day, the position of the body is changed, hygienic procedures are carried out, massage is carried out, the instructor engages in physical therapy exercises with the patient. During this period of time, the patient’s condition is monitored by several doctors - a therapist, a neurologist, a cardiologist and a psychologist. Rehabilitation measures are aimed at improving the patient’s quality of life and restoring lost functions.
What help do people who have had a stroke need?
Rehabilitation after a stroke must be comprehensive, since the consequences of the disease affect all systems and functions of the body. Correcting impairments and restoring lost abilities can take a long time. The timing depends on the type of stroke (ischemic, hemorrhagic), the degree of brain damage, and the age of the patient. Older people, as a rule, need more time to recover, since cell renewal is slower than in youth, and existing chronic heart and vascular diseases make treatment difficult.
At different stages of rehabilitation treatment the following are used:
- Drug therapy using drugs that improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in the brain.
- Therapeutic exercises to stimulate physical activity. Properly selected exercises compensate for the inactivity of dead nerve cells.
- Classic and acupressure massage that improves muscle tone.
- Social adaptation. After a stroke, many patients have to relearn how to walk, talk, coordinate movements, and care for themselves. At this stage, professional help from doctors and support from loved ones are very important. Psychologists help you get comfortable faster and avoid stress.
- Nutrition correction. For successful recovery, you need a balanced diet that excludes heavy foods (fatty, smoked, sweet, etc.). The menu should include fruits, cereals, vegetables, and lean meat. To establish the correct diet, the help of a nutritionist may be necessary.
For mild to moderate disorders, the patient may remain at home with regular medical supervision. In severe forms, it is advisable for the patient to remain in a hospital under the constant supervision of doctors.
Forecast
The prognosis for hemorrhagic stroke depends on the severity of brain damage and the time of seeking first aid. If the stroke was not extensive and did not affect the vital centers of the brain, timely assistance was provided - there is a chance to return to normal life. It is impossible to predict the patient’s life expectancy - the prognosis depends on many factors:
- Patient's age.
- Severity of brain damage.
- Concomitant diseases.
According to statistics, more than 30% of patients die within a few weeks after a stroke, more than half of patients die within a year, and more than 60% of patients become disabled. No more than 20% of patients can recover completely within a few years.
Effective rehabilitation programs have been developed and tested at the Yusupov Hospital. The recovery process after a hemorrhagic stroke is unpredictable, lengthy and difficult. You can get advice on the treatment and rehabilitation of a patient by calling the hospital.
Make an appointment
Rehabilitation and prognosis
It is impossible to recover quickly after a stroke. This process begins once the patient is stabilized and can continue for many years. Doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute are confident that no two cases of hemorrhagic stroke are absolutely identical, so an individual program must be developed for each patient. It will include medication support, as well as sessions with specialists and at home. It is important to gradually restore motor, speech and social function, self-care skills, as well as the patient’s intellectual abilities. Rehabilitation includes simple exercises that must be performed daily, constantly becoming more complex. The process can be lengthy—many patients are unable to get up and move independently for the first few years after a stroke. However, fine motor skills and the ability to care for oneself improve within the first months. It is also worth contacting specialists in therapeutic massage and rehabilitation physical education - such activities significantly speed up the recovery process.
Hemorrhagic stroke is a dangerous condition, the prognosis of which largely depends on the speed of medical care. It is worth understanding that full rehabilitation of the patient is possible only if the doctors’ orders are followed, independent work and the support of loved ones. Specialists at the Clinical Brain Institute are ready to develop an individual program for each person who has suffered a stroke, as well as examine them throughout the entire rehabilitation period.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 4 votes
Share article on social networks