What is intercostal neuralgia?
Neuralgia of the intercostal nerves is pain of a different nature that occurs due to various etiological factors. It is more often observed in adult men and women over 30-35 years of age. Symptoms of neuralgia may appear suddenly on one or both sides of the chest, along one or more intercostal nerves. The disease has an ICD code - M.79.2.
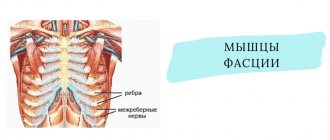
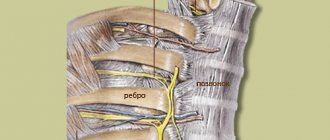
To understand what intercostal neuralgia is, you should understand the anatomical features of the thoracic nerves. There are 12 pairs in total. Each intercostal nerve contains motor, sensory and sympathetic fibers. It originates from the anterior roots of the spinal cord of the thoracic spine, passes along the lower edge of each rib, reaching the sternum. The parietal pleura covers the nerve fibers on top.
Thoracic nerves transmit impulses to the skin, the musculo-ligamentous apparatus of the chest and the anterior wall of the abdomen, partly the pleura and peritoneum, and the mammary glands. Sensitive fibers of neighboring nerve trunks actively interact with each other, creating cross innervation.
How to distinguish intercostal neuralgia from heart disease?
If neuralgia has acute symptoms in the thoracic region on the left side, differential diagnosis with heart disease must be carried out. You should not look for the cause of the pain syndrome on your own. Thoracalgia on the left side should always be a reason to consult a doctor.
Heart pain and symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left have distinctive features:
| Intercostal acute neuralgia on the left: typical symptoms | Cardiovascular diseases: characteristic manifestations |
| The pain intensifies with forced breathing, coughing, sneezing, laughing, physical exertion and movement, but does not change with fast walking and excitement. | The pain does not change its intensity with a deep breath or muscle tension, but intensifies with cardio exercise (fast walking, running, climbing stairs). |
| Chest neuralgia is not relieved by taking nitroglycerin | With angina pectoris, the pain attack goes away within 3-5 minutes after using nitroglycerin. With myocardial infarction, severe pain cannot be relieved with medications. In this case, you should immediately call an ambulance. |
| Normal pulse and blood pressure are determined | Changes in heart rate and blood pressure |
| Pain increases with palpation of the ribs and spaces between them | The intensity of pain does not change when palpating the intercostal spaces |
| Painful symptoms on the left “go” along the nerve or are encircling in nature | Pain is localized behind the sternum or in the projection of the heart |
Symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left and right should also be differentiated from other diseases (pleurisy, pneumonia, thoracic aortic aneurysm, pericarditis, acute pancreatitis and others). If there is severe pain in the chest, only a doctor can determine exactly what it is - neuralgia or another pathology.
How to distinguish
To distinguish heart pain from neuralgia and other pathologies that are successfully masked by cardialgia, it is necessary to take into account the following factors:
- duration;
- localization and depth;
- provocative factors;
- drugs to relieve symptoms.
When trying to determine the cause, I always pay attention to the accompanying signs. This allows you to fairly accurately diagnose the disease, even at the stage of a preliminary survey, before using additional research methods.
Angina pectoris lasts 3-20 minutes, and a heart attack is characterized by a long-lasting attack (the same pain is observed with myocardial inflammation, pericarditis and aneurysm). Suffering of varying intensity and duration is observed with pinched nerves and myositis.
It is necessary to determine the depth and localization of pain. In case of cardiac pathology or vascular problems, it is internal, as if going outward. Superficial sensations are characteristic of neuralgia and muscle inflammation. In this case, it is possible to distinguish pinching from pain in the heart using palpation.
Provoking factors for the development of IHD are psycho-emotional stress or physical overload. The latter factor can also provoke an exacerbation of osteochondrosis and hernia. Myositis occurs against the background of general inflammation, hypothermia or intoxication.
If the attack is relieved by sublingual nitroglycerin, then angina pectoris should be suspected. For a heart attack, acute aneurysm or thromboembolism, this action will not have a significant effect; in this case, only narcotic analgesics, which are administered to the patient immediately after admission to the department, will help. To distinguish intercostal neuralgia from cardiac pain, you should know that the first pathology can be easily eliminated with the help of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the use of muscle relaxants, but cardiac problems cannot be solved in this way.
Causes of intercostal neuralgia and risk factors
Intercostal neuralgia can develop for a variety of reasons. Among them are:
- injuries to the thoracic nerves, chest and spine;
- surgical interventions, long-term immobilization of a person in a certain position;
- poisoning with chemicals, prolonged use of medications;
- congenital developmental anomalies, hereditary diseases;
- infectious processes (shingles, tuberculosis, brucellosis and others);
- some neurological diseases, such as radiculitis and multiple sclerosis;
- diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, deforming spondylosis, herniated intervertebral discs);
- compression of nerve branches in the bone-connective sheaths, for example, in the presence of scar changes, benign or malignant neoplasms;
- immunodeficiency (HIV infection, cancer, etc.);
- allergic reactions;
- diabetes;
- various metabolic disorders in nervous tissue and its hypoxia;
- lack of B vitamins in the body;
- alcohol abuse;
- osteoporosis;
- pathology of nearby anatomical structures (aorta, lungs, pleura);
- various systemic diseases (atherosclerosis, rheumatism, anemia, thyrotoxicosis, etc.).
More often, chest neuralgia appears due to several causes. Therefore, it is typical for older patients with vascular, degenerative and metabolic disorders. Sometimes symptoms of neuralgia appear after excessive physical activity, sudden movements or prolonged stay in one position. They can also occur after hypothermia or severe stress.
More often, intercostal neuralgia is observed on the left or right; less often, there is a bilateral lesion. In most cases, the pathogenesis is based on muscle spasm, leading to compression of nerve fibers. Pain occurs in response to nerve damage.
In children, signs of intercostal neuralgia are rare. When they appear, parents should definitely show the child to the doctor, as this may be a signal of the presence of a serious pathology. The doctor will determine the possible causes and explain how to cure intercostal neuralgia in this case.
Diseases that cause burning in the chest
Only a doctor who has everything necessary for diagnosis can identify the cause of a burning sensation in the chest in the middle, right or left. You should not engage in self-diagnosis, as it is fraught with the risk of complications.
| Diseases | Triggering factors |
| Hearts | Sharp pain and burning in the chest near the heart may be a sign of a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. This occurs with the following diseases:
|
| Liver | Experts identify a number of diseases of the liver and biliary tract, the symptoms of which are manifested by a burning sensation in the sternum. These include:
Other clinical manifestations of the above diseases are as follows:
|
| Gastrointestinal tract | A phenomenon such as heartburn always leads to a burning sensation and pain symptoms due to irritation of the walls of the esophagus by gastric juice. As for diseases, one of the symptoms of which is a burning sensation in the chest, they are as follows:
|
| Intercostal neuralgia | It is a pain syndrome that develops as a result of damage to the intercostal nerves due to various reasons, ranging from compression to infection or intoxication. This syndrome is a sign that the patient has diseases of the organs of the chest wall, mediastinum, and spinal cord. Clinical manifestations are as follows:
|
| Pneumonia | Acute inflammatory infectious lesion of the lungs, which can be lobar or focal. Symptoms of the first include a cough, a sharp increase in temperature, burning and pain in the sternum, and weakness. As for the second, its onset is hardly noticeable; it appears after acute respiratory diseases. Clinical manifestations in addition to pain on inspiration, shortness of breath, cyanosis, wet cough. |
| Scoliosis | Persistent sideways curvature of the spinal column relative to its axis. A burning sensation in the chest occurs due to the fact that with this disease, abrasion of the intervertebral discs and compression of the nerve endings occurs, which provokes serious discomfort. |
| Intercostal myositis | Inflammatory processes of skeletal muscles located between the ribs. On palpation, pain symptoms appear along the entire intercostal space. Experts identify three pain points: the spinal column, the sternum and its lateral surface. In addition, there is swelling of the affected part, redness or, conversely, paleness of the skin, sore throat, cough and headache. |
Forms of the disease
Chest neuralgia can be primary (an independent pathology) and secondary (a symptom of another disease). There are also radicular and reflex forms of the disease. In the first case, symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left and right arise due to irritation of the spinal roots. The second type of pathology occurs due to a negative effect on peripheral receptors.
In addition, clinicians distinguish the following types of thoracic neuralgia:
- musculoskeletal;
- vertebrogenic;
- spicy;
- chronic;
- right-sided;
- left-handed;
- psychogenic;
- during pregnancy.
Intercostal neuralgia of a certain type has its own characteristic symptoms and treatment features.
Symptoms of neuralgia on the right and left
Any neuralgia, including intercostal neuralgia, is primarily pain. Painful sensations can be of a different nature (aching, dull, sharp, piercing, burning) and have different intensity. Sometimes the pain is so severe that it forces a person to take a forced position and sharply limit physical activity. Intercostal neuralgia, which has pronounced symptoms, is described by patients as a lumbago or electric current discharge running from the spine to the sternum.
Thoracalgia often begins gradually, with a tingling sensation in the intercostal spaces, then acquires pronounced intensity. Less often it occurs suddenly. The pain can radiate to the scapula, epigastric area, heart, arm and lower back. Sometimes it takes on an encircling character. It intensifies with changes in body position, movements, coughing and deep breathing.
As a rule, painful attacks are constantly repeated, lasting from a few seconds to 2-3 minutes. Therefore, treatment of acute intercostal neuralgia on the right and left, first of all, always begins with the elimination of pain.
In addition to thoracalgia, a person may be bothered by characteristic local signs caused by the influence of sympathetic, sensory and motor nerve fibers. Intercostal neuralgia, depending on the damage to a particular nerve, will have characteristic symptoms on the right, left or both sides of the chest:
- impaired sensitivity, crawling sensation, numbness, tingling;
- muscle twitching;
- increased sweating;
- change in skin color.
If chest neuralgia appears against the background of a herpes infection, it may be accompanied by skin rashes. The latter appear 2-4 days after the onset of thoracalgia. Elements of the rash are located on the skin of the intercostal space in the form of small pink spots, which then turn into vesicles and then into crusts. Subsequently, traces of pigmentation may remain on the skin.
Diagnosis of intercostal neuralgia
Make an appointment Shpigel Anna Yakovlevna Neurologist, massage therapist 33 years of experience. The specialist receives: - newborn children and schoolchildren - adults - athletes Reviews from patients Consultation from 3000 rubles.
Acute intercostal neuralgia is a reason to contact a competent, qualified neurologist. Since symptoms in adults with damage to the thoracic nerves can be disguised as other diseases, the patient must undergo a comprehensive examination to exclude possible pathology. The doctor must conduct a survey and examination.
The person’s posture is noteworthy when he leans towards the healthy side, so as not to provoke a painful attack. Palpation of the chest reveals pain. Trigger points are identified at the lower edge of the rib, where the affected nerve passes. If neuralgia affects several nerve branches, which often happens, this leads to a decrease or complete loss of sensitivity in the corresponding area of the body.
First of all, the doctor must distinguish the symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left from cardiovascular pathology. For this purpose, the patient undergoes an ECG. If indicated, a cardiologist is consulted. In order to correctly diagnose and treat intercostal neuralgia, the doctor also excludes diseases of the respiratory system, digestive tract, musculoskeletal system, infectious processes and other diseases. He may prescribe a number of additional tests (laboratory tests, x-ray of the lungs, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, MRI of the spine, etc.).
Thoracic neuralgia is an indication for electroneurography. This method allows you to determine the condition of nerve fibers by assessing their structure and functionality.
Chest neuralgia can be a manifestation of benign and malignant tumors. It is often the first symptom of a herniated disc and degenerative changes in the spine. Therefore, early identification of its causes is considered an important task for the neurologist and the patient.
Physiological causes of burning in the chest
Experts identify a number of initiating factors for such a phenomenon as a burning sensation in the chest. The most common of these is poor diet, including fatty, spicy, salty foods, carbonated water and fast food, along with frequent overeating or eating food before bed.
The above leads to the contents of the stomach entering the esophagus, where it irritates the mucous membrane, which causes discomfort. They are accompanied by nausea, heartburn and belching, as well as bloating. In order to exclude this, it is enough to change your diet by minimizing the above-mentioned foods, optimizing portion sizes and eliminating the consumption of food before bedtime.
The same can be said about excessive consumption of coffee and alcoholic beverages, as well as smoking. All of them can cause a burning sensation in the chest, which will stop as soon as their consumption is reduced to a reasonable limit. It is important to understand that it is not the norm and its appearance is a reason to visit a doctor.
A number of reasons are associated with diseases of the cardiovascular system, characterized by the inability of blood vessels to provide the heart with a sufficient volume of oxygen. This occurs with ischemia, which is manifested by a local decrease in blood supply due to narrowing or blockage of the arteries, due to which the most important organ of the human body suffers.
Do not forget about neurological factors, when a burning sensation occurs due to compression or damage to the nerve ending or in stressful situations, with neuropsychiatric disorders. In addition, it can be caused by pathological conditions characterized by damage to the bronchial mucosa or trachea.
How to treat intercostal neuralgia?
Treatment of any neuralgia, including intercostal neuralgia, is aimed at eliminating the clinical manifestations and causes of the disease. Therapy includes a whole range of activities. If a patient is diagnosed with neuralgia, you can find out how to treat it from the specialists of our clinic. The doctor will select the optimal therapeutic course, taking into account the characteristics of the disease and the individual characteristics of the person.
As a rule, intercostal neuralgia requires long-term treatment and further measures to prevent painful attacks. The doctor prescribes specific methods of therapy, determines the duration of each course, and gives his recommendations on lifestyle and regimen. The treatment plan may include:
- painkillers;
- etiotropic therapy aimed at combating the underlying disease;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- neurotropic drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- osteopathy;
- massage;
- Exercise therapy.
The doctor always chooses how to treat neuralgia, based on the clinical picture, the stage of the process, the results of diagnostic examinations and the individual characteristics of the patient.
The nature of pain in neuralgia
Pain in neuralgia occurs as a result of spasm of the intercostal muscles or due to pinched nerve endings in the spinal column.
In the latter case, the problem may be an exacerbation of osteochondrosis, the appearance of a hernia or protrusion. The following symptoms are typical for this type of pain:
- Most often, the pain is severe, but it can also manifest itself in the form of some discomfort.
- It intensifies after changes in body position (bending, turning), as well as during coughing or sneezing.
- Manifests itself as constant or paroxysmal.
- The sensations are burning, stabbing, pressing.
- Duration – from 1-2 hours to several days or more.
- Even a slight touch to the intercostal spaces or at paravertebral points makes the pain unbearable.
- Irradiation is observed in the arm, back, neck, and left anterior chest. It is this symptom that often leads to a false interpretation of the cause of the disease, as it resembles a heart attack.
- The skin along the pinched nerve changes sensitivity. Paresthesia (distorted sensation) is observed in the form of burning, crawling, tingling. Sometimes a person complains of numbness in the affected area.
- The attack is often accompanied by sweating, paleness, and muscle spasms. The latter symptom is caused by impaired blood flow in the area and irritation. The local temperature drops and the body area becomes cool.
All of the above symptoms can occur simultaneously. But sometimes only one or two signs appear. The degree of their severity depends on the sensitivity threshold and other individual characteristics.
Is osteopathy effective for intercostal neuralgia?
The causes of neuralgia in the rib area can be different. However, in many cases, a pinched nerve is caused by the consequences of various injuries a person has received in the past. The capabilities of fine diagnostics using hands make it possible to identify and eliminate these disorders, which leads to the elimination of compression of the nerve and the restoration of its normal blood supply. As a result, inflammation and its integral companion – pain – go away. Osteopathy shows high effectiveness in the treatment of both unilateral and bilateral intercostal neuralgia.
Possible complications and consequences
Any neuralgia, in particular intercostal neuralgia, that does not respond to treatment, may be a sign of a serious illness. Most of the complications that arise with thoracalgia are precisely a manifestation of the underlying pathology, which worsens against the background of constant pain.
Chest neuralgia itself, with a long-term severe course, can provoke the development of a hypertensive crisis or an attack of angina (less often, myocardial infarction). Severe, constant pain affects a person’s physical and mental state in different ways. Often severe symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left or right significantly complicate the patient’s life. He sleeps poorly, is nervous, cannot move normally and do his usual work.
Pain in the intercostal spaces does not allow the patient to perform full breathing movements, which leads to a decrease in oxygen supply to the body and the development of hypoxia. Sometimes neuralgia is accompanied by such debilitating pain that it contributes to emotional exhaustion, and this is a serious complication, since this condition causes depression.
Expert advice
If severe pressing pain appears in the chest area, I recommend that a person adhere to the following tactics:
- calm down and take a position in which some relief is felt;
- stop any active movements;
- take Aspirin and put a Nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue;
- in the case where a history of angina pectoris was diagnosed, during a prolonged attack, continue to use sublingual nitrates every 15-20 minutes;
- Call an ambulance and, before it appears, try to determine the nature of the sensation (dependence on breathing, posture, movement).
It is very important to tell the doctor what preceded the attack, after which it began, and what measures were taken to eliminate it.
Neuralgia during pregnancy
If intercostal neuralgia appears in a pregnant woman, how to diagnose it and how to treat it is decided by a neurologist together with a gynecologist. Therapy is selected taking into account possible negative effects on the fetus. Self-medication in this situation is considered unacceptable, as this can have a negative impact on the health of the expectant mother and child.
To prevent chest neuralgia from appearing during pregnancy, it is advisable to follow preventive measures. If a woman has previously had attacks of thoracalgia, then at the stage of preconception preparation she should visit a neurologist and osteopath. The doctor will conduct a diagnosis, and then the neurologist will give a number of recommendations on how to treat intercostal neuralgia. An osteopath will identify possible causes of neuralgia and conduct a treatment session aimed at eliminating them.
Forecast and prevention of intercostal neuralgia
In most patients, intercostal neuralgia can be completely cured. If thoracalgia occurs against the background of a herpetic infection, relapses are possible.
If adequate treatment of neuralgia does not bring the desired result, a more “deep” diagnosis is carried out to search for the possible cause of this condition. First of all, spinal hernias, benign and malignant tumors are excluded.
To prevent neuralgia of the intercostal branches from recurring, and its symptoms in adults to manifest themselves less painfully, doctors recommend the following preventive measures:
- follow the canons of a healthy lifestyle: give the body adequate physical activity, eat right, actively relax in the fresh air, give up bad habits, etc.;
- maintain normal functioning of the immune system;
- monitor posture and spinal health;
- promptly treat chronic diseases and infectious processes;
- if possible, visit the pool and harden yourself;
- undergo preventive examinations on time;
- undergo regular scheduled examinations by an osteopath approximately once every six months.
If a person has previously had thoracic neuralgia, he should not be overcooled, be in a draft, expose the body to excessive physical stress, perform sudden movements or remain in an uncomfortable position for a long time. In addition, it is necessary to eliminate or minimize as much as possible stress and any unfavorable factors that can cause symptoms of intercostal neuralgia on the left, right or both sides.
Did you like the article? Add the site to your browser bookmarks
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Tingling in the heart is usually provoked by psycho-emotional factors, so it is advisable to use light herbal sedatives. To get rid of signs of neurosis, it is necessary to normalize your daily routine and diet, increase physical activity and time spent in the fresh air. If a person is diagnosed with coronary artery disease, to eliminate the stabbing pain, you need to take fast-acting vasodilators prescribed by your doctor.
Conservative therapy
Tingling rarely reaches such intensity that there is a threat of painful shock and emergency measures are required. The main thing in treatment is the elimination of the etiological factor. After successful treatment of the existing disease, the tingling in the heart disappears. The drug treatment regimen is selected individually according to the type of pathological process. The following drugs are used:
- Sedatives
. Medicines that act on the central nervous system are effective for cardioneuroses. They quickly stabilize the psycho-emotional background and eliminate increased anxiety. To eliminate neurotic disorders, their long-term use is required. - Muscle relaxants
. The drugs are widely recommended to combat pain caused by neuralgia and osteochondrosis. They affect peripheral nerve endings and reduce painful muscle tension. - Antiarrhythmic medications
. To normalize heart rhythm, cardiologists use 4 classes of medications. Medicines are selected taking into account the nature and severity of the arrhythmia, the presence of concomitant diseases of the cardiovascular system. - Anti-inflammatory drugs
. Medicines from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated for myocarditis and other infectious processes, joint diseases. If therapy is insufficiently effective, glucocorticoids are prescribed.
For the targeted action of medications for neuralgia and joint damage, the electrophoresis technique is effective. To reduce tingling and pain of neurological origin, physiotherapeutic treatment is carried out - laser therapy, UHF, magnetic therapy. For neuroses, individual and group sessions with a psychotherapist are required.