Pinchuk Elena Anatolyevna
Deputy chief physician for medical work, kmn, neurologist, doctor of physical and rehabilitation medicine
Maltseva Marina Arnoldovna
Head of the consultation department - neurologist, specialist in the field of extrapyramidal pathologies, doctor of the highest category
Kritskaya Olga Pavlovna
Neurologist, highest category
The term stroke is understood as an acute disorder of cerebral circulation with a persistent decrease or complete loss of certain body functions. A stroke can be a focal stroke (micro-stroke) or extensive, in which paresis can occur, most often of one half of the body. A condition in which a person experiences weakness or complete lack of movement in the left or right half of the body is called hemiparesis. Paralysis of the left side or paralysis of the right side during a stroke often occurs as a result of rupture of a cerebral artery, if qualified help is not sought in a timely manner.
Etiopathogenesis
The main mechanism for the development of paralysis is stroke - damage to the artery with blood escaping beyond the vascular bed. As a result, a hematoma is formed, which gradually grows and compresses the brain tissue. Vital neurons die, loss of function is noted, control of skeletal and smooth muscles decreases, and sensitivity disappears.
This condition is predisposed to:
- Eating disorders – the main role is played by a lack of calcium in the diet, which strengthens the walls of the arteries. In these cases, cardiologists repeat “where it’s thin, that’s where it breaks.” Weakened brain vessels that are prone to damage can cause a stroke;
- Hypertension – the situation is aggravated by increased blood pressure, which can damage weakened blood vessels. In older people, there is a lack of calcium, which can cause artery rupture;
- Compounded heredity - according to recent studies, there is a predisposition to vascular diseases, especially hypertension and strokes. The mechanism has not been fully studied; insufficiency of the neurohumoral mechanism and weakness of the vascular wall are assumed;
- Obesity - this condition is accompanied by a lack of minerals, an increase in blood pressure, which increases the likelihood of developing a stroke with subsequent paralysis;
- Cardiovascular diseases - valve malformations, heart failure, atherosclerosis and thrombosis predispose to cerebral hemorrhage;
- Endocrine diseases - diabetes comes first, leading to hypertension and hemorrhages. Sometimes the causes are hypothyroidism, pathologies of the adrenal cortex;
- Bad habits - nicotine weakens the walls of arteries and increases cholesterol levels in the blood. Natural alcohol in minimal dosages is useful, but an excess of surrogate or drunkenness often ends in stroke and paralysis.
The listed factors can provoke both left and right paralysis. According to statistics, the latter option is observed more often, which increases the patient’s chances of survival due to timely diagnosis.
Types of paralysis
After a stroke, the doctor’s main task is to determine the presence of paralysis and its type. All hemorrhages on the right and left sides are divided into two categories:
- Peripheral paralysis is the most favorable variant of the disease, characterized by partial loss of function. The patient's motor neurons are damaged, which leads to loss of sensitivity and a decrease in complex and purposeful movements.
- Central paralysis - indicates hemorrhage in the motor areas, as a result of which the right arm and leg are completely amputated. Such patients are unable to care for themselves and there is a high risk of disability.
Kinds
Neurology defines two types of stroke with paralysis of the right side:
- Ischemic stroke. Occurs due to blockage of cerebral vessels by atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots. In the area of circulatory arrest, a focus of brain tissue necrosis occurs. The severity of subsequent paralysis and the ability of the central nervous system to compensate for lost functions depend on its location and size. The disease most often threatens hypertensive patients, diabetics, smokers and anyone with high cholesterol, thrombophlebitis, blood thickening, or problems with heart rhythm. Attacks of tachycardia or atrial fibrillation can provoke the formation of blood clots in the heart cavity, which enter the brain vessels with the blood flow. This type of stroke develops over 2-3 days or longer, so it has specific diagnostic features.
- Hemorrhagic stroke. It is characterized by a rupture of the vascular wall and a breakthrough of blood into the brain tissue, which dies from ischemia. It is provoked by a hypertensive crisis, specific aggregate states of the blood, diseases that cause pathological changes in the structure of blood vessels. Hemorrhagic stroke develops rapidly, quickly causing a coma in the patient. This diagnosis entails the most severe consequences.
The practice of neurology shows that strokes with paralysis of the right side are easier and the consequences are eliminated faster. This is explained by the fact that ischemic stroke more clearly manifests the onset of the disease with characteristic signs. Additional time is provided to recognize the illness and transport the patient to a medical facility. The earlier therapeutic actions are started, the less severe the consequences will be. Neurologists call this the stroke race.
Expert opinion
Author: Ekaterina Dmitrievna Abramova
Neurologist, director of the chronic pain clinic
According to the Federal State Statistics Service, stroke ranks second in the structure of mortality. This is a dangerous neurological disease, the incidence of which is increasing every year. Statistics show that acute cerebrovascular accident occurs in every third person per 1000 population. Stroke in 60% of cases leads to disability. Due to severe complications, 10% of patients completely lose the ability to self-care. The appearance of persistent paralysis is associated with extensive brain damage.
A stroke requires immediate diagnosis and correct treatment. At the Yusupov Hospital, examinations are carried out using the latest medical equipment: CT, MRI. Thanks to them, it is possible to accurately determine the location of the pathological focus. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital develop an individual treatment and rehabilitation plan for each patient. The drugs are selected in accordance with the latest European recommendations for the treatment of strokes. Conservative treatment can be supplemented with surgical intervention if indicated. In addition, to speed up recovery, physiotherapy and a course of physical therapy are prescribed.
Types of paralysis on the right side
According to the nature and localization of vascular accidents, the types and subtypes of paralysis are classified:
Central paralysis
It develops when the areas of the brain and spinal cord responsible for the function of movement and the state of the neuromuscular complex are damaged. Characterized by specific spastic reactions. With the central form of paralysis, all muscles are affected, which are in constant tension, and when calm they show clonus - rhythmic twitching, mainly in the area of the knees and feet. In many areas, diagnostic reflexes are absent or weakened. Hypertonicity of the muscles causes their painful tightening with a high degree of resistance. This causes painful contractures due to stretching of the tendons. With tension, tremor of the affected limb is often observed. There is a weakening of the facial muscles and articulation disorders. These markers indicate in which part of the brain the pathological focus is located, which subsequently determines the place where restorative measures need to be carried out.
Peripheral paralysis
With this type of stroke, a decrease or absence of neurological reflexes develops. The tone in the muscles is not determined, they atrophy, decrease in mass, patients lose the ability to move, self-care and generally do any activity. The main task is to restore the conduction pathways of impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the neuromuscular system. By the nature of the pathological symptoms and the areas of their location, it is possible to determine which segments of the central nervous system are out of order. For example, damage to the anterior horns of the spinal cord in the region of the 6-7 cervical and first thoracic vertebrae causes peripheral paralysis of the arm. In the lumbar region there is paralysis of the leg. There is atrophy of small muscles - facial, oculomotor, sublingual, laryngeal, tracheal muscles. Accordingly, the process negatively affects the ability to swallow, vision, breathing, etc.
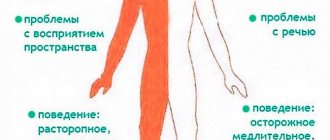
Signs of right-sided paralysis
If there was a stroke in the left hemisphere, the patient’s right side of the body is affected, the muscles of the limbs are paralyzed and there is no speech. These are the main differences between this condition. Patients also develop the following symptoms:
- Common symptoms are headache, nausea, vomiting and weakness. They appear in the first few days and are considered the body’s response to damage to brain neurons;
- Loss of movement - with central paralysis, the right limbs are flaccid, there is no sensitivity, the patient cannot perform any actions with the right arm and leg. If peripheral neurons are affected, the patient experiences tremor, and some movements are difficult on the same side;
- Reduced memory – there are difficulties in remembering sentences; in severe cases, it is difficult for a person to repeat individual words;
- Paresis of the right facial nerve - this branch innervates all facial muscles on its side. In the absence of control, the muscles relax, the patient’s corner of the mouth and lower eyelid “hang”;
- Spontaneous contractions of some skeletal muscles on the right - usually the arm is bent at the elbow joint, the leg is straightened, and inward rotation of the foot is noted.
The listed symptoms are observed a few minutes after hemorrhage. As health deteriorates, the patient develops stress, accompanied by depression and difficulties in communication.
Symptoms
The signs of the onset of an illness are beyond doubt; not only doctors, but also ordinary people should know them in order to help their loved ones, acquaintances, or just a person on the street who has become ill in time. You should call the emergency room immediately if you experience the following symptoms:
- Sudden loss of speech (or when it becomes slurred);
- Inability to move an arm or leg;
- Inability to smile (the right side of the mouth sags);
- drooping eyelid;
- State of stupefaction, spatial and temporal disorientation, the patient complains of “mess in the head”;
- Severe headache with vomiting, dizziness;
- The extended right leg turns the foot inward;
- The right arm is bent and pressed towards the body.
Consequences of right-sided paralysis
In severe cases, right-sided lesions lead to irreversible complications that develop as a result of massive hemorrhage or violation of treatment rules. We list the most common conditions:
- paralysis of both arms and legs;
- lifelong speech dysfunction;
- disturbance of thinking, memorization, social behavior;
- the appearance of bedsores;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases against the background of reduced physical activity;
- enuresis and fecal continence disorders.
The main task of the doctor is to create conditions that ensure full recovery after a stroke on the right side, which will minimize the development of complications.
Treatment
Thanks to the efforts of healthcare organizers, the system of stroke treatment in Russia has undergone positive changes. It has become the norm to transport patients with suspected cerebral circulatory disorders to an intensive care bed or neurosurgeon's table within three hours. There are 24-hour vascular centers in all major cities. Specialized structures like the Moscow Yusupov Hospital, which have invaluable experience in treating and rehabilitating the most complex neurological diseases, received support.
Treatment for stroke, when the right side is paralyzed, begins in the intensive care unit, where patients are hospitalized urgently. The treatment regimen provides for the normalization of blood circulation in the brain, restoration of respiratory and swallowing functions, and elimination of the threat of convulsive phenomena. The fight against cerebral edema, the normalization of the body’s water and electrolyte balance, and the metabolic processes of the central nervous system are being actively carried out.
The treatment regimen for hemorrhagic stroke with paralysis of the right side is somewhat different. In this case, drugs that eliminate thromboembolism come to the fore. If treatment is started on time, the blood clot is destroyed and impaired blood flow is restored. Thanks to modern medications, it is often possible to completely avoid the consequences of a stroke.
The patient's condition requires normalization of homeostasis, a decrease in the degree of permeability of the vascular walls and the formation of plasmin.
In some cases, blood clots from brain vessels are removed surgically in neurosurgery departments.
Drug therapy
Subsequent treatment occurs with the help of drugs: neuroprotectors, antiplatelet agents, anticoagulants, thrombolytics, defibrinizing enzymes, antihypertensive drugs. The composition and duration of medication may be varied by your doctor. But several drugs must be taken for life to prevent stroke.
Lifestyle
Stroke is a disease in which a person must start life in new conditions. Most people find it difficult to accept their condition, so deep depression is as dangerous a complication as the physical manifestations. Already in the first stages of recovery, much attention is paid to this aspect. Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital - neurodefectologists, neuropsychologists, occupational therapists, rehabilitation specialists, working with patients in groups and individually, help them overcome a depressed, anxious state, gain confidence in their abilities to overcome the disease, and follow the rules of a healthy lifestyle. These are changes in the principles of nutrition with a predominance of vegetable and dairy products, reasonable physical activity, giving up bad habits, training the functions of the nervous, muscular, and cardiovascular systems.
The scientific, material and technical base of the Yusupov Hospital allows patients to undergo rehabilitation procedures using modern equipment that meets European standards. And the friendly, optimistic attitude of rehabilitators helps make sure that the simulator is as important and necessary as the pill.
The cause of the disease was lifestyle. It becomes a means of overcoming it.
Right side massage
Recovery after a stroke with paralysis of the right side with the help of massage begins on the 20th day of illness. This is an average date; the severity of the patient’s condition, age, concomitant diseases, etc. are taken into account.
The first massage sessions begin with gentle stroking of the limbs, back and neck muscles. The intensity of the effect increases from session to session, the massage therapist’s actions are aimed at restoring normal blood circulation and sensitivity in the affected part of the body. If the treatment is well tolerated, a course of manual therapy is subsequently prescribed, which demonstrates good results in a short time. A course of physical therapy, physiotherapeutic, kinesiotherapeutic procedures, and acupuncture to restore limb mobility is recommended.
The Yusupov Hospital has a full range of rehabilitation equipment, including innovative ones, and a staff of highly qualified specialists who are proficient in modern techniques and types of massage and physical therapy. Their efforts, led by the country's best neurologists, are helping people recover from stroke paralysis.
Drug therapy
If the right side is paralyzed due to a stroke, you should start with drug therapy. The drugs of choice are:
- Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants (Curantil, Warfarin) - thin the blood and improve its passage through the arteries. The use of these drugs is effective for atherosclerosis, thrombosis or vascular spasms;
- Diuretics (Hypothiazide, Veroshpiron) – remove excess fluid, prevent cerebral edema and hypertensive crisis;
- Antispasmodics (Papaverine, Vincamine) - relax blood vessels and improve blood circulation;
- Agnioprotectors (Parmidin, Alprostan) – have a beneficial effect on the arteries, preventing the development of spasms;
- Nootropics (Piracetam, Actovegin) - improve brain function. They are taken for a long time, including the rehabilitation period.
The doctor prescribes medications based on the patient’s condition. In severe cases, a complete list is written out, and daily blood pressure monitoring is carried out.
Diet
Diet is necessary to improve blood circulation and maintain immune resistance. A well-chosen table should contain everything necessary for the regeneration of damaged tissues, but not overload the weakened body.
The basic rules for the diet are as follows:
- exclusion of smoked and fatty foods;
- meat can only be eaten with the approval of a doctor, in small portions and pureed. The menu includes only lean varieties;
- enrich your diet with vegetables and fruits;
- exclude coffee, strong tea, soda and alcohol;
- food should be fractional, in small portions.
For seriously ill patients, the menu is prepared by a nutritionist, taking into account the state of the body and the necessary energy costs.
Massage
This method is aimed at preventing bedsores and is used from the first days of paralysis. The right side of the body is warmed up, after which blood circulation and tissue trophism are improved, and mobility in the joints is restored.
To eliminate the effects of paralysis, a standard warm-up includes:
- stroking - from the periphery, along the blood flow;
- rubbing – carried out more intensively, similar to the previous method;
- vibration movements – in the area of soft tissues;
- The procedure ends with stroking.
To prevent new bedsores from arising, it is recommended to massage daily, regularly change the patient’s position and rub the skin with alcohol (if there are no wounds).
Visit to a speech therapist
To restore speech, daily training is required, which will be supervised by a specialist. The patient is given homework, including systematic exercises.
The objectives of such therapy are:
- restoration of oral speech;
- rehabilitation of writing;
- normalization of speech memory.
It is very important that a person not only learns to speak, but also understands the speech of others. Experts recommend that patients not isolate themselves, but constantly contact people.
Mechanisms of recovery after stroke
The adaptive mechanism of recovery after a stroke consists of changing the balance between the processes of excitation and inhibition. The earliest changes are observed in and around the damaged area. After some time, they begin in the opposite, unaffected hemisphere. There, one week after the stroke, increased excitability is recorded.
At the moment when brain activity on the opposite side increases, motor functions begin to be restored. As studies have shown, motor functions after a stroke in the cerebral hemisphere can be restored without restoring the function of the subcortical region of the affected hemisphere.
The balance of excitation and inhibition also changes in the subacute and chronic phases of stroke. In order for a person to perform simple movements, additional connections are activated that are inactive in healthy individuals. Subsequently, the motor and premotor zones are disinhibited and activated. After some time, areas of the cerebral cortex that were not previously involved in the motor circles are activated: the posterior parietal and prefrontal cortex, as well as the insular region.
The success of restoration of lost motor functions depends on the degree of damage to the pathways and the possibility of activation of the psilateral corticospinal pathways. Recovery is impossible in completely destroyed tissues; it occurs in ischemic areas.
Restoration of lost motor functions can be ensured by partial preservation of neurons near the lesion. In the early phase, structural changes occur, which play the most important role in the restoration of motor functions: collateral sprouting and the formation of new synapses (synaptogenesis).
Subsequently, the restoration of motor functions occurs due to synaptic plasticity in cortical connections. From 2-3 weeks after a stroke, collateral sprouting begins to occur. On the 18th day after an acute cerebrovascular accident, an increased number of dendrites can be seen in the collateral cortex.
Reorganization of corticomotor centers after a stroke occurs quite quickly. During the first month, plastic restructuring of the motor cortex occurs. On the fifth day after the stroke, processes of functional reorganization begin in the nearby unaffected motor cortex. They occur faster in the case of training the affected limb.
Reorganization of the motor cortex occurs 2-4 months after a stroke.
If rehabilitation measures are sufficient and started in a timely manner, then recovery occurs more quickly. With intense load on a paretic limb, excitability increases in the affected hemisphere. These positive changes persist six months after the stroke.