Patients who have suffered a stroke involuntarily wonder how serious their injury is and whether it depends on the side of the lesion.
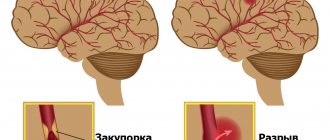
The following types of stroke changes are distinguished:
- Hemorrhagic (bleeding).
- Ischemic (changes due to blockage of the bloodstream by a thrombus).
- Mixed (a combination of thrombosis and vessel rupture).
The main damaging factor in any type is a direct disruption of the blood supply. It occurs due to damage to a vessel that supplies a certain part of the brain. Depending on what functions it is responsible for, certain disorders will develop.
General cerebral symptoms appear regardless of the location of the damaged area.
These include:
- severe headache;
- disturbance of consciousness, from transient to comatose;
- disturbance of orientation in time and space;
- convulsive syndrome, motor agitation.
Differences in focal symptoms
A stroke on the right side of the brain causes paralysis or paresis in the left side of the body, which is caused by the crossing of nerve pathways in the brain. In other words, the hemispheres control the motor work of muscles on the opposite side. In turn, a left-sided stroke causes disturbances in the right side of the body.
In addition to controlling voluntary movements, various centers are distributed in the hemispheres, which are responsible for different functions. Therefore, determining the side of damage is not a difficult task for specialists.
Since the center of speech and writing is located in the left hemisphere, a left-sided stroke is accompanied by a violation of speech activity. A person loses the ability to both read and write text (language deficit).
A stroke on the right side leads to a disruption in the perception of oneself and the surrounding space. There is a shortage of memory for established actions.
Damage to the midline structures – brainstem and cerebellum – is also important.
Helpful information
Stroke is a fairly common disease, especially among older people. Stroke occurs annually, according to statistics, in 20-30 out of every 10,000 people. Among the causes of death, stroke ranks third after diseases such as heart disease and malignant tumors.
A stroke is an acute cerebrovascular accident that occurs due to blockage or rupture of a cerebral vessel and leads to damage to brain cells. There are two main forms of stroke:
hemorrhagic stroke, the cause of which is the rupture of a vessel with hemorrhage into the brain tissue.
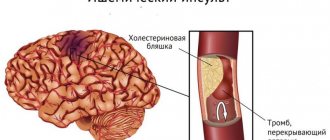
ischemic stroke, the cause of which is acute blockage of a cerebral artery by a thrombus or embolus, as a result of which the part of the brain that was supplied with blood by this artery ceases to receive oxygen and dies.
In both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes, those vessels that suffer (clog or rupture) are primarily those that contain atherosclerotic plaques or whose walls are already damaged as a result of repeated increases in blood pressure.
Damage or death of areas of brain tissue during acute cerebrovascular accident leads to the development of symptoms, the nature of which depends on the location and size of the lesion. The brain consists of two hemispheres - left and right. In this case, the left hemisphere controls the work of the right half of the body, and the right hemisphere controls the work of the left half of the body. Therefore, a stroke that occurs in the right hemisphere leads to disorders in the left half of the body and vice versa. The most common disorders resulting from a stroke include paralysis of the muscles of the arm and leg on the side opposite to the localization of the lesion, decreased skin sensitivity in the same area, and speech disorders (impaired ability to pronounce words and phrases or understand someone else’s speech). Possible changes in vision, dizziness, difficulty swallowing, etc.
Risk factors for stroke:
1. Arterial hypertension. The risk of stroke in patients with blood pressure more than 160/95 mm. rt. Art. increases approximately four times compared to persons with normal blood pressure, and with blood pressure more than 200/115 mm Hg. Art. - 10 times.
2. Heart diseases. The most significant risk factor for ischemic stroke is atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), as well as the presence of coronary artery disease and heart failure.
3. Diabetes mellitus. Patients with this disease more often have lipid metabolism disorders, arterial hypertension and various manifestations of atherosclerosis.
4. TIA or minor stroke (with complete restoration of impaired functions already in the first three weeks of the disease). The risk of developing ischemic stroke in patients with TIA is about 4-5% per year.
5. Smoking. Doubles the risk of stroke. Accelerates the development of atherosclerosis of the carotid and coronary arteries. Quitting smoking leads to a reduced risk of stroke after 2-4 years.
6. Age. For example, at 80 years of age the risk of ischemic stroke is 30 times greater than at 50 years of age.
7. Oral contraceptives. Drugs containing more than 50 mg of estrogen significantly increase the risk of stroke, especially in combination with smoking and increased blood pressure.
Stroke Prevention
Stroke prevention comes down to controlling risk factors.
1. First of all, you should follow all the doctor’s recommendations for taking medications if you suffer from hypertension, diabetes mellitus, heart pain, palpitations, or shortness of breath.
2. Quit drinking and smoking.
3. Exercise. A sedentary lifestyle is very typical for middle-aged and elderly people. Low physical activity contributes to the progressive deterioration of the cardiovascular system and also leads to obesity. The optimal form of physical activity is walking, preferably two to three times a day, non-stress sports games (table tennis, billiards, etc.), swimming in the pool.
4. Dieting.
Wheat bread made from second-grade flour, grain bread, bran bread, rye bread;
Vegetarian vegetable, cereal, cabbage soup, beet soup;
Lean varieties of beef, veal, pork, boiled or baked chicken;
All types of fish;
Reduced fat dairy products;
eggs (up to 3 eggs per week);
cereals, vegetables, fruits.
If you have high blood pressure, you need to limit your salt intake to 3-5g per day, do not add salt to your food, and it is advisable to completely avoid salty foods (various canned foods, sausages). Limiting the consumption of animal fats (lard, fatty meats, sausage, ham, butter, sour cream) is necessary to reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, which in turn slows down the development of vascular atherosclerosis. Animal fats are replaced with vegetable fats (sunflower, corn, olive oil instead of butter) 1/3-1/2 of the total amount of fats, and also eat fish more often (up to 3 times a week). It is not recommended to abuse foods that contain large amounts of cholesterol (liver, eggs); it is advisable to eat no more than three eggs per week. Coffee also increases cholesterol levels, so it is better to prefer tea.
5. Patients with increased body weight are advised to lose weight, primarily by eliminating excess easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, white bread, confectionery) from their diet. In this case, you should eat grain bread, bran, peeled, rye, rich in dietary fiber. It is recommended to eat frequently, but in small portions (4-5 times a day).
What is the danger?
The danger of a stroke lies not in the side of the lesion, but in the vastness of the focus involved in the process of ischemia or hemorrhage. The speed of providing first aid is of great importance: the sooner it is provided, the better the patient’s prognosis for replenishment of lost functions and recovery. The best results are obtained by timely and comprehensive organization of restoration procedures, which are developed in each individual case and complement each other.
The Center for Progressive Medicine “Doctor Pozvonkov” has in its arsenal all the necessary techniques for the multidirectional restoration of a person’s lost motor, sensory, speech and mnestic capabilities. All patients who have suffered a stroke require full rehabilitation, regardless of the location of the lesion. Coordinated interactions with doctors significantly reduce the percentage of disability among victims.
Methods
The randomized trial, conducted in 9 countries, included 11,093 patients with acute stroke (85% of cases were ischemic in nature). The patients were divided into 2 groups: in a completely supine position or in a sitting position with the head raised at least 30 degrees. This body position was established immediately after hospitalization and maintained for 24 hours.
The primary end point was the degree of disability at 90 days, determined by the modified Rankin scale (sum of points from 0 to 6 points, where a higher score reflects a more severe degree of disability, 6 points corresponds to death).
Functions of the left hemisphere
The left hemisphere of the brain is responsible for logical thinking and speech abilities.
Thanks to it, people can read, write, remember numbers, letters, names and dates.
This hemisphere is responsible for analysis and logic.
They perceive all facts, recognize numbers and mathematical symbols. The left hemisphere understands only the literal meaning of spoken words. Also here, control is exercised over the opposite side of the body - the right. That is, the left hemisphere is responsible for raising the right hand, and vice versa.
Causes
- Critical pressure;
- Tendency to develop blood clots;
- Diabetes mellitus or obesity;
- High cholesterol;
- VSD;
- Chronic smoking or alcohol abuse;
- Arrhythmia;
- Frequent stress and depression.
These factors are the most common reasons why left-sided brain strokes most often occur. You need to better monitor your health and the course of diseases that can lead to the most unfavorable consequences. It is necessary to constantly monitor your blood pressure, experience less stress, etc.
results
The average period between the onset of stroke symptoms and the initiation of posturing was 14 hours (range 5 to 35 hours).
- Patients in the supine group were less likely than patients in the sitting group to maintain this position at 24 hours (87% vs. 95%, P<0.001).
- There were no significant differences between groups in the incidence of disability at 90 days of follow-up (odds ratio, 1.01; 95% CI, 0.92-1.10; P=0.84).
- Mortality at 90 days was 7.3% in the supine group and 7.4% in the sitting group (P=0.83).
- There were no statistically significant differences between groups in the incidence of serious adverse events, including pneumonia.
Recovery and rehabilitation
The effectiveness of a patient’s recovery after a stroke on the left side of the brain largely depends on how quickly first aid was provided. Recovery from a stroke is quite possible at any age, the main thing is good care and compliance with all the doctor’s instructions and recommendations.
After discharge from the hospital, the patient is under the supervision of a neurologist. It is also necessary to take some medications to strengthen the body. All these drugs are prescribed by a doctor depending on the condition.
Physiotherapy
Physical education and breathing exercises for recovery also play a big role. After a stroke of the left hemisphere of the brain, patients can study independently or with the help of loved ones and relatives. It also depends on how strong the body is. At first, it is advisable to monitor the patient’s activities and help him with them.
Speech restoration
Moral support is also very important here.
It is necessary to communicate more with the patient, ask him questions so that he can answer.
If speech functions have not been restored after treatment, then you need to invite a speech therapist to the patient so that he can work with him and re-teach him to speak and think well.
Hirudotherapy
Hirudotherapy is often used in the prevention of recurrent stroke and recovery . This therapeutic method , including hirudin (an anticoagulant), enters the blood It helps dissolve blood clots and improve blood circulation. Usually leeches are placed behind the ears or in the tailbone area.
Massotherapy
To restore motor activity of the right side of the body, the patient is given a therapeutic massage. It is necessary to carry it out for 5 minutes at first, then increase the time to 30 minutes. The massage should be performed by a specially invited massage therapist who knows all the necessary nuances and basics of therapeutic massage after a stroke. Massage helps thin the blood, reduce tone, and prevent bedsores.
Special diet
Not least important is a special diet with a reduced amount of cholesterol, which causes blockage of blood vessels and the appearance of plaques, which subsequently leads to the formation of blood clots.
Food products that can be eaten: citrus fruits, spinach, mustard, berries, nuts, corn, vegetables, dried fruits, tomato paste, fruits, wheat bran, sea fish, seaweed, freshly squeezed juices, etc.
Products that need to be excluded from the diet: smoked, salted, canned, fatty and rich broths, sausages and frankfurters, milk and everything made from it, sweets and flour products, processed foods, fast food, soda, ice cream, strong tea and coffee, semolina, etc.
Doctors advise eating foods that contain vitamin E. You can also take this vitamin in tablets. It reduces the risk of recurrent stroke.
Getting rid of bad habits
It’s hard to get rid of bad habits, but it’s necessary for your health.
After a stroke, the patient is prohibited from drinking alcohol and smoking.
Not only family and friends should control this, but the patient himself needs to realize the significance of this step for his own health.