“Angel child” is what children are sometimes called when they have been given a terrible diagnosis that sounds like a death sentence - cerebral palsy. Cerebral palsy. Yes, these kids will never become like their peers. They will not happily jump through puddles, rush headlong on a bicycle and ask endless “why?” But this will not make them less dear and beloved to their parents! What could be more terrible for them than the suffering of their little blood? But you can’t give up and fall into despondency and depression! After all, it depends on the parents and loved ones how much such a child can adapt to life in society and how successful the child’s development will be - physical and mental. Only through the efforts of loved ones will there be hope for reducing pain and developing motor functions. And to fight the enemy, you need to know him by sight.
So, what is “cerebral palsy”? Why “children’s” - after all, adults also suffer from it? What types of cerebral palsy can there be? How common is this diagnosis? What are the causes of cerebral palsy and its consequences? Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of cerebral palsy? Is cerebral palsy inherited? Is it possible to become infected with this disease? What should you pay attention to so as not to miss the first manifestations of cerebral palsy?
Which children are at risk? And, of course, the questions that most concern parents are: is cerebral palsy curable and what can be done to help a sick child and alleviate his condition? You will learn about all this by reading the article. And, most importantly, you will understand in which direction you need to move and what to do so that the child begins to crawl, walk, hear you and speak. Indeed, even in the most severe cases, progress in sensory and motor functions is possible, which significantly improves the child’s development and quality of life.
The term cerebral palsy is used to describe a group of chronic conditions that affect motor and muscle activity with impaired coordination of movements.
The cause of cerebral palsy is damage to one or more parts of the brain either during fetal development, or during (or immediately after) childbirth, or during infancy/infancy. This usually occurs during a complicated pregnancy, which is a harbinger of premature birth.
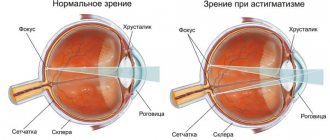
The word “cerebral” means “cerebral” (from the Latin word “cerebrum” - “brain”), and the word “paralysis” (from the Greek “paralysis” - “relaxation”) defines insufficient (low) physical activity. Cerebral palsy itself does not progress, because... does not give relapses. However, during the course of treatment, the patient’s condition may improve, worsen, or remain unchanged.
Cerebral palsy is not a hereditary disease . They can never become infected or get sick. Although cerebral palsy cannot be cured (it is not “curable” in the generally accepted sense), constant training and therapy can lead to improvement of the condition.
Story
In 1860 English surgeon William Little first published the results of his observations of children who, after suffering a birth injury, developed paralysis of the limbs. The children's condition did not improve or worsen as they grew: problems with the grasping reflex, crawling and walking remained. Signs of such lesions in children have long been called “Little’s disease”; they are now known as “spastic diplegia”. Little suggested that these lesions were caused by oxygen deprivation (hypoxia) during childbirth. However, in 1897, the famous psychiatrist Sigmund Freud, noting that children with cerebral palsy often suffered from mental retardation, visual perception disorders and epileptic-type seizures, suggested that the cause of such deeper brain lesions was rooted in the pathology of the infant’s brain development at an earlier age. period of life - during the period of fetal development in the womb.
Despite this assumption by Freud, until the 1960s of this century, it was widely believed among doctors and scientists that the main cause of cerebral palsy was complications during childbirth. But in 1980, after analyzing data from national studies of more than 35,000 cases of newborns with signs of cerebral palsy, scientists were amazed that complications due to birth trauma were less than 10%. In most cases, the causes of cerebral palsy have not been identified. And from then on, extensive research began on the perinatal period of life: from the 28th week of intrauterine life of the fetus to the 7th day of the newborn’s life.
Consequences of cerebral palsy
Characteristic features of cerebral palsy are disturbances in motor activity, the muscular sphere is especially affected - there is a lack of coordination of movements. Depending on the extent and location of areas of brain damage, one or more forms of muscle pathology may occur^
- muscle tension or spasticity;
- involuntary movements;
- disturbance of gait and degree of mobility.
The following pathological phenomena may also occur:
- abnormality of sensation and perception;
- decreased vision, hearing and speech impairment;
- epilepsy;
- impaired mental function.
Other problems include difficulty eating, decreased urinary and bowel control, breathing problems due to poor posture, bedsores and learning difficulties.
Causes of cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy can be caused by most factors that impair brain development. The main reason is insufficient oxygen supply to the brain - hypoxia (intrauterine or in a newborn). The supply of oxygen can be interrupted by premature separation of the placenta from the walls of the uterus, malpresentation of the fetus, prolonged or rapid labor, and impaired circulation in the umbilical cord.
Premature birth, prematurity, low birth weight, RH factor or group incompatibility of the blood of the fetus and mother according to the A-B-O system, infection of the mother with rubella measles or other viral diseases during early pregnancy - and microorganisms attack the central nervous system of the fetus - all these are also risk factors.
In the USA, in particular, all research is aimed at studying the two main causes of cerebral palsy: rubella measles and incompatibility of the blood of the fetus and mother.
So, the main causes of cerebral palsy are associated with the development of pregnancy and childbirth , and these conditions are not inherited: and such paralysis is often called congenital cerebral palsy (associated with intrauterine pathology or the process of childbirth). A less common type is acquired cerebral palsy , usually developing before the age of two (traumatic brain injuries due to accidents or brain infections).
Diagnosis of hemiparetic form of cerebral palsy
Specialists conduct a neurological examination using metameter techniques. During communication with parents, a symptomatic picture is collected. Obstetric history is important, that is, information about how pregnancy and childbirth went. For example, the fact that the mother used drugs is helpful for considering the version with the hemiparetic form of cerebral palsy.
In addition, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- MRI of the brain;
- vision and hearing tests;
- Ultrasound of head and neck vessels;
- CT.
Types of Cerebral Palsy
There are three main types of cerebral palsy:
- Spastic - the patient has great stiffness and difficulty moving: 70-80% of patients;
- Athetoid (athetoid), or dyskinetic - the presence of involuntary, uncontrolled movements (hyperkinesis): 10-20% of patients;
- Ataxic (ataxic) - imbalance, the presence of deep-seated mental deviations: 5-10% of patients.
A mixed type (from the above) is possible. There are other types of cerebral palsy, although they are rare.
Can cerebral palsy be prevented?
Yes. Currently, the chances that make it possible to prevent the occurrence of cerebral palsy have increased: testing and monitoring the health of the mother during pregnancy. First of all, the definition of the RH factor. If Rh is negative, immunization must be carried out within 72 hours after birth (or at the end of pregnancy), which will prevent the adverse consequences of blood incompatibility in a subsequent pregnancy. If the woman has not been immunized, the consequences of blood incompatibility in the newborn can be prevented by an exchange transfusion of blood in the child.
If a newborn is diagnosed with jaundice, he is subjected to light therapy in the infant feeding department. There are other methods to prevent premature birth. These measures reduce the likelihood of viral diseases and other viral infections in pregnant women. The birth of sick children is greatly influenced by increased radiation and the use of drugs and other medications by pregnant women.
To prevent the possible birth of a sick child, it is necessary to monitor patients with diabetes mellitus, anemia (anemia), and control over the rational nutrition of pregnant women. Great importance should be given to creating favorable conditions for the birth of a healthy child. The assistance of highly qualified specialists in the prenatal period is necessary, and newborns should also be protected from accidents and injuries.
Cerebral palsy hemiparetic form: treatment
In order to improve motor capabilities, massage, physiotherapy (if there are no cramps), and therapeutic exercises are prescribed. These treatment methods have a positive effect on spasticity, gait, endurance, and stability.
Attention is paid to eliminating intellectual retardation, if any. Children read books, learn poems, and are involved in discussions of certain events. The prognosis for mental abilities is favorable if the right approach is taken. Such children learn much better than, for example, patients with double hemiplegia . To improve the effect, drugs are used that saturate the brain with oxygen and improve metabolism.
Metameric treatment methods are effective. Their essence is a local effect on the affected areas. The main method is injection. A small amount of the drug, which consists of amino acids and nerve cells, is injected under the skin. The injection method is complemented by metameric acupressure and metameric pharmaceutical massage. These activities help improve the condition of the affected limbs, regenerate the nervous system and improve brain function.
The metameric treatment method is effective only when individual therapy is developed by an experienced specialist. In this case, the prognosis is favorable. Among the advantages of the technique, it is worth noting its versatility. With its help, it is possible to treat patients with both hemiparetic form and, for example, spastic and atonic-astatic forms.
In short, the hemiparetic form of cerebral palsy is not a death sentence. Treatment requires a lot of effort from the child and his loved ones, but with the right approach, the negative manifestations of the disease can be reduced to a minimum.
Can cerebral palsy be cured?
In this case, it is better to talk about “care” or “caring attitude” towards a disabled person, “the ability to provide assistance”, than about “treatment”; this means creating conditions for the child to maximize his potential as he grows and develops. And you need to start as early as possible - with early diagnosis of a baby with signs of developmental delay (or disorder), because Identifying the disease early in life can improve the child’s health. Recovery programs should begin as early as possible.
Such programs include various activities for the child^
- his training;
- speech and hearing development classes;
- conducting classes aimed at the child’s social adaptation;
- classes on the development of the emotional sphere.
Such “management” programs should include monitoring the child’s movements, learning, speech, hearing, social and emotional development. Through various programs, physical therapists, therapists, teachers, nurses, social workers and other professionals help both the family and the child. (Using appropriate medications, surgery, orthopedic devices, etc., to improve neuromuscular coordination and eliminate or prevent dysfunction).
When people with disabilities become adults, they need support from services such as:
- personal assistance service,
- long-term therapy
- vocational and special training,
- independent living services,
- consulting,
- transportation,
- implementation of leisure and recreation programs,
- employment services - everything you need for development.
People with cerebral palsy can go to school, have a job, get married, support a family, and live in their own home. Most people with cerebral palsy need help to first gain independence and the opportunity to take an active part in society.
Treatment of cerebral palsy
It is not possible to completely cure cerebral palsy. But with timely measures and the right attitude of parents and teachers, the child is able to achieve great success in self-care and acquisition of skills.
Treatment objectives:
- Encourage the child to develop self-care skills, movement and proper movements of the whole body.
- Prevent the appearance of incorrect postures, contractures and curvature of the spine.
- Create conditions for the full development of speech and the formation of psycho-emotional activity.
The treatment of children with cerebral palsy is determined by a specialist, since many factors must be taken into account: the form of cerebral palsy, its severity, the preservation of other skills, the level of intellectual development, the child’s age and concomitant diseases.
How many people have cerebral palsy?
Some statistics:
Cerebral palsy is the most common cause of childhood disability, among which the first place is diseases of the nervous system. Cerebral palsy is the second most common neurological disorder in childhood; The first is mental retardation in children. In third place are congenital anomalies.
Latest publications in an international scientific research journal:
Evolutionary medicine and child neurology and the Research Foundation of Cerebral Palsy Associations (UCPA, USA) provide insight into the statistics of the birth of children suffering from cerebral palsy.
Among children with normal birth weight who become disabled due to cerebral palsy:
- approximately 70% became disabled due to factors that occurred before birth (prenatal period),
- about 20% - due to factors that appeared either during childbirth (perinatal period) or immediately after birth (the first four weeks of life),
- 10% - due to factors that appeared during the first two years of life (postnatal period)
Among low birth weight (or premature) children in whom cerebral palsy is the cause of disability: the incidence is approximately 0.7 per 1000 live births;
There is still no certainty as to when the brain damage occurred:
- did cerebral lesions occur during embryonic development?
- or due to the use of neonatological techniques for preserving the baby?
- Have cerebral lesions occurred during or after birth in infants with “vulnerable” (“easily injured”) brains?
According to the Research Foundation of Cerebral Palsy Associations (UCPA), there are approximately 550,000 people with the disease in the United States and 9,750 children and newborns are diagnosed with the disease each year. Of these, 1.2-1.5 thousand are preschool children. The number of births of patients with signs of cerebral palsy in the United States has increased by 25% over ten years: from 1.5 to 1.8. per 1000 babies born alive in 1990. up to 2.0 - 2.5 infants with this pathology in 2000. Currently in the United States there are from 550 to 760 thousand disabled people with cerebral palsy, which is 2.8 people per 1000 population.
In Moscow, according to Professor E.G. Sologubov, there is an increase in the incidence of cerebral palsy: over 20 years (from 1967 to 1987), the number of births per 1000 children increased from 1.71 to 1.88 in 1992 in Russia there were 62 thousand, and in the territory of the former USSR - 122 thousand patients with Cerebral palsy (patients under 15 years of age were taken into account). the frequency of occurrence in 2001 was (according to various sources) 5.0-6.0 per 1000 newborns
It should be noted that statistical data on the number of patients with cerebral palsy in the USSR were not available, and even the few statistical data tended to be underestimated.
In Moscow there are approximately 10 thousand disabled people with consequences of cerebral palsy, half of them are children. In the Moscow region - about 5 thousand people. Based on the frequency of births of children with signs of cerebral palsy (5.0-6.0 per 1000), it can be assumed that there are at least 1.5 million such disabled people in Russia. There are no exact data on the number of disabled people with consequences of cerebral palsy in Russia.
In terms of severity, one of the most common lesions now associated with new views of cerebral palsy is spasticity of one or more limbs.
It turns out that muscle spasticity of the limbs at the birth of a normal-weight baby is caused by lesions that dominate the prenatal period; and at the birth of premature babies and children with low weight, spasticity of the limbs is caused by lesions that dominate in the perinatal (from the 28th week of intrauterine life of the fetus to the 7th day of the newborn’s life) and neonatal periods of the newborn.
The rehabilitation center should teach parents
– A child was born, different from the usual one. How to make sure that mom is not left alone with the problem? She doesn't know who to contact. How to make it have a clear action plan?
– I will tell you from the experience of our region. Our mother alone will never be left with this problem, thanks to the fact that there are certain administrative and organizational steps in the work of our medical community.
For example, a child is born with a problem, but how do you know whether this child will have cerebral palsy or a child who simply has some problems?
Before the age of one to one and a half years, a specialist has no right to talk about such a diagnosis, because there is a certain resource for restoring nervous tissue.
We cannot even imagine what level of movement this will be. There may be a problem, but no one can say at what level.
But there is a risk group: if the child was born premature, or full-term, but with a lower body weight than expected, if the child suffered some kind of infection in utero, or after birth he suffered some kind of infection that seriously affects the structure of the brain, for example, meningitis, it can also be a hemolytic disease, according to the A0 system, according to the Rh factor.
We will immediately learn about such children in Tyumen. Having discharged children at risk home, we determine their route; these children must come to us at the state rehabilitation center. Moreover, any mother, if she sees that something is wrong, can contact our center, absolutely free of charge, with a referral.
A commission of doctors at the center, including neurologists, determines whether the child has a problem or whether there is no need to worry. Sometimes we ourselves cannot immediately say whether there will be further problems to some extent, so these children are invited again - in three months. So we observe a risk group from birth.
It happens, of course, that a mother comes for the first time when the child is already a year old. The child has a motor delay, and she says: “Well, maybe it will go away on its own, but the neighbor had the same thing, everything was fine afterwards.” Looking for excuses for himself.
– What is the role of parents in the process of rehabilitation of a child with cerebral palsy?
– It is believed that the most important thing on which the rehabilitation of cerebral palsy is based is movement therapy. It is clear that movement occupies a very important place in life, and a child who has motor problems must engage in movement every day.
But no amount of healthcare will ever be enough to keep children physically active 365 days a year. Parents correctly understand that they need to work with their child constantly, but they think that this should be done by some kind of instructor or physiotherapist. They are looking for more and more rehabilitation courses. Public health care can offer therapy only 1-2 times a year, and parents turn to everyone, including deputies and foundations: “We need a course here, a course here.”
We must change this worldview. The specialist must show how to do this, teach the parents, and the parent must continue the lessons. When a child masters some more advanced movement, the specialist gives new tasks. This is why there is a rehabilitation center, where a specialist tells parents what and how to do.
– Was this the original setting of yours?
- No. And we had a period when we sent children for “treatment,” for example, to Israel. But we understood perfectly well that there was not enough money to send all the children somewhere from the regions. Over time, we came to the conclusion that we need to create something here. Now there is such a trend - the money of the region should remain in the region. This is right.
I have been working at (the official name is the State Autonomous Institution "Children's Psychoneurological Treatment and Rehabilitation Center" - editor's note) since 1992, as a deputy chief physician since 2001. All my scientific activities were devoted to methods of working with cerebral palsy, so here we were able to organize a medical selection committee, when three times a week we see, and children of Tyumen and the region come to us with any problems - orthopedic, neurological, psychopathology, and we select the optimal one rehabilitation route for this child, taking into account the factors that we talked about earlier.
Comments
This study is confirmed by similar data in the USA, Germany, and Russia. It is clear that special attention needs to be paid to when brain damage occurs, what are the risk factors that put the infant's health at risk, and what are the most common consequences of cerebral palsy. As the likelihood of cerebral disorders increases due to the increasing number of surviving premature infants, studying the causes of low birth weight and premature birth is becoming a priority in research.
Cerebral palsy - how to deal with it?
This disease can occur for various reasons, the main one being maternal diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, heart defects, endocrine system defects - hyperthyroidism, hyperandrogenism. Throughout their pregnancy, which is often pathological or premature, such women “sit” on hormones.
By the way, prematurity is also a risk factor. Cerebral palsy is very common in twins, with one baby being born healthy, and the other developing cerebral palsy over time. The cause of the development of this disease can also be abortions in the mother, which lead to low placentation (fixation of the placenta) and, as a consequence, chronic intrauterine hypoxia of the fetus. Sometimes a pregnant woman’s too young or, conversely, too mature age plays a role.
with toxoplasmosis, enterovirus infection, hepatitis, herpes, cytomegalovirus, chlamydia, etc. during pregnancy.
As you know, child development has its own norms:
- at 3 months the baby should be able to hold his head up,
- at 4-5 months - roll over from back to stomach and back,
- at 6 months - sit down,
- at 8-9 months (but no later than one year and three months) - walk with a support,
- per year - speak 8-10 words (“mom”, “dad”),
- at one and a half years - speak 20-30 words,
- at two years old phrasal speech (“Mama give”) should appear.
- Mom should worry if the child “does not reach” the norm. Any delay in motor development is also a risk factor for developing the disease.
The diagnosis of cerebral palsy is not always made immediately after birth . The disease can occur under different “masks” - syndromes of muscle hypertonicity, dystonia, hypotension, and increased neuro-reflex excitability. Children with such diseases need regular medical examinations, both from an orthopedist and a speech therapist. Cerebral palsy must be treated at the moment the pathology forms. And, most importantly, don’t miss it.
The main methods of treating cerebral palsy are physical therapy, medications and massage. It is advisable to have the massage done by a specialist. Parents themselves should not do this. The procedure scheme is selected individually. At the same time, they try to restore the balance between the muscles - flexors and extensors, inconsistency in the work of which leads to delayed development and incorrect postures.
It is advisable to start massage no earlier than 1.5 months, since at an earlier age the cause of the pathology is not entirely clear.
There are many types of massage: classical, segmental, acupressure, according to Manakov, cryomassage.
The treatment complex also includes running on a treadmill with a mirror hanging in front of it, which allows the child to see himself and correct his movements. Kids ride on a special bicycle, with their arms, legs and back fixed. For those who move poorly, there are special walkers. And trampolines help develop the vestibular apparatus.
Such children enjoy splashing in the pool. This procedure is called balneotherapy. In water, their body weight changes, and they are not afraid to take a step. Paradoxically, some babies first learn to swim and then walk. Those who cannot walk yet get into the pool using a lift. Bathing is complemented by a very effective and pleasant hydromassage.
Many children suffering from cerebral palsy are prescribed mud therapy. Dirt has a general reflex chemical effect and stimulates nerve endings. Warm mud is a good remedy for hypertension. Electrophoresis helps relieve muscle spasticity (tension) in cerebral palsy, and magnetic therapy is used to improve vascular regulation. An integral part of treatment is physiotherapy and paraffin therapy.
And now - a very important detail that parents should definitely know about. A child with cerebral palsy needs to be shown to a speech therapist. Delayed motor development is often accompanied by a slowdown in mental and speech development. With hypertonicity, even the baby’s tongue is in good shape. This prevents the child from speaking, so speech therapy massage and a course of drug therapy may be required.
The course of treatment is carried out every six months and lasts on average 35-40 sessions.
Since cerebral palsy is a neurological pathology, it is also treated with nootropic drugs that stimulate mental activity, which are prescribed by the attending physician.
One of the syndromes of cerebral palsy is increased intracranial pressure, which can be reduced by massage, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis. To improve blood flow, the doctor prescribes special vascular medications.
If cerebral palsy is not treated in time, in addition to muscle deformation, orthopedic deformation may appear - kyphosis and kyphoscoliosis of the spine, hip dysplasia, flat feet. When treating such diseases, it is necessary to apply orthopedic splints and spacers, wear orthopedic splints and splints, and be sure to wear orthopedic shoes. A reclinator is used to straighten the spine. With dysplasia, dislocations and subluxations often occur, which requires surgical intervention. Surgery is also necessary for persistent orthopedic deformities.
Symptoms and classification of cerebral palsy
Symptoms characteristic of cerebral palsy are, first of all, motor disorders, as well as: intellectual and behavioral disorders, epilepsy and other paroxysmal disorders, visual and hearing impairments, speech disorders (dysarthria) and nutrition.
In Russia, the classification of forms of cerebral palsy by Doctor of Medical Sciences, neurologist Ksenia Aleksandrovna Semenova, which took into account the development of not only motor, but also intellectual, psycho-speech and emotional spheres, is considered generally accepted: spastic diplegia; double hemiplegia; spastic hemiplegia; atonic-astatic form; ataxic form; hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy.
Spastic diplegia is the most common form of cerebral palsy. It is characterized by motor disturbances in the upper or lower extremities, with the legs being more affected. Spastic diplegia is detected in children already in the first months of life. The extensor tone is increased, the legs are extended, and the tendon reflexes are high. Children begin to sit and walk at a later age.
High muscle tone contributes to the development of contractures in the joints of the legs. Hypertonicity of the adductor muscles of the thigh is characteristic, causing crossing of the legs in some patients.
Double hemiplegia is the most severe form of cerebral palsy, all tonic reflexes with muscle rigidity are expressed, that is, there are disturbances in all extremities - often more in the arms than in the legs. Swallowing disturbances, significant disturbances or absence of speech are detected. Speech disorders are severe and manifest themselves according to the principle of anarthria (lack of speech).
The straightening reflexes of the trunk and balance reactions are almost undeveloped. Children cannot hold their heads up, do not sit, do not stand, do not walk. They show an excessive reaction to sound stimuli - they shudder sharply, make chaotic movements.
At the medical center at the Marfo-Mariinsky Convent. Photo by Deacon Andrei Radkevich
Delayed mental development associated with primary brain damage is aggravated by severe immobility and the inability to contact children of their own age. In 90% of cases, mental retardation is noted, in 60% - convulsions.
This form of cerebral palsy is often combined with microcephaly and minor developmental anomalies, which indicates pathology in the prenatal period. Double hemiplegia is diagnosed already in the neonatal period. The lives of these children depend on their immediate environment. The prognosis for the child's motor, speech and mental development is unfavorable.
Spastic hemiplegia is characterized by movement disorders predominantly on one side. This is due to damage to one hemisphere of the brain.
Bacterial meningitis or viral encephalitis (especially herpetic) suffered at an early age leads to vasculitis, the formation of venous thrombosis, parenchymal necrosis in the brain, which is clinically manifested by a long period of repeated focal seizures and the development of hemiplegia.
The atonic-astatic form of cerebral palsy is associated with damage to the frontal lobes of the brain and fronto-cerebellar tracts. In the clinical picture, pronounced muscle hypotonia comes to the fore; children cannot hold their heads, sit, stand, or walk for a long time. Reactions of straightening and balance are sometimes absent until two or three years of age. Independent walking is possible, but it is quite late. The gait is unsteady, with legs widely spaced.
The incidence of intellectual deficit and speech disorders is high - up to 90% of cases, which complicates the social adaptation of such children. It is believed that many hereditary diseases and syndromes that are difficult to diagnose can be hidden under the mask of the atonic-astatic form of cerebral palsy.
The atactic form is 10-15% of all cases of cerebral palsy. In the first months of life, the child experiences muscle hypotonia and delayed motor development, which gives rise to a preliminary diagnosis of “floppy child” syndrome. As motor skills and hand manipulations develop, incoordination, dysmetria, trunk ataxia, and intention tremor of the hands become apparent. Ataxia increases with standing and walking.
The hyperkinetic form of cerebral palsy is characterized by predominant damage to the structures of the striopallidal system (subcortical parts of the brain). Muscle tone is variable, often fluctuating between hypotension and normotension, and intermittent spasms are observed. Children's movements are awkward and accompanied by excessive motor reactions.
Mental development suffers less than with other types. With mental arousal and a change in the position of the limbs, a sharp topical contraction of the muscles occurs with a pathological setting of the arm segments to contracture or deformation. Patients are characterized by an “pretentious” posture, which impedes the ability of the hand to grip and other purposeful actions.
At the medical center at the Marfo-Mariinsky Convent. Photo by Deacon Andrei Radkevich