Symptoms of cerebral aneurysm
A small protrusion of blood vessels (less than 11-12 cm) has virtually no symptoms. The patient experiences discomfort only when the protrusion of the cerebral arteries has increased in size.
| Type of intervention | Price |
| Endovascular embolization of cerebral aneurysm | 450,000 - 600,000 rub. |
Medium (12-26 mm) and large (from 26 mm) aneurysms are characterized by a number of symptoms.
Among them:
- deterioration of hearing and vision,
- pupil dilation,
- partial numbness of the facial muscles.
Pronounced symptoms of brain damage appear when an aneurysm ruptures.
The patient experiences:
- nausea,
- acute pain in the temples, occipital and frontal parts of the head.
Often the patient cannot speak or swallow. When an aneurysm ruptures, the functioning of the vestibular apparatus is disrupted and vital functions of the body are lost. In addition, spasms and convulsions occur. The patient may fall into a coma. These symptoms are also associated with brain damage.
Important!
Treatment of an aneurysm through surgery should not be delayed. It should be understood that the pathology is very dangerous. The patient can die at any minute. It is extremely difficult to save him, especially if there is no way to quickly get medical help.
If you are diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm, you should immediately contact a specialist for treatment.
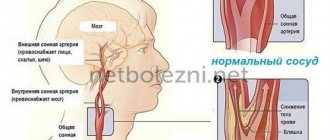
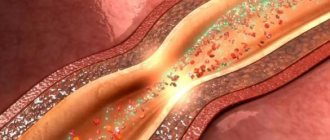
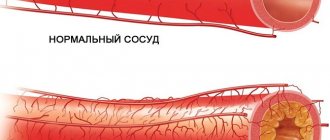
Cerebral aneurysm is a dangerous disease in which cerebral circulation is disrupted. With this deviation, a section of an artery (large vessel) bulges outward, forming a sac of blood. This sac puts pressure on the nerves and nearby vessels, causing neurological spectrum disorders.
Symptoms of an aneurysm
Symptoms of a cerebral aneurysm include:
- nausea/vomiting
- sudden deterioration of vision,
- fear of light,
- double vision,
- numbness of a part of the body (usually on 1 side),
- headaches (attacks, similar to migraines),
- hearing impairment,
- speech problems.
Also, special attention is paid to squint, sharp noises in the ears, severe dilation of the pupils, drooping of the upper eyelid, cloudy vision before the eyes, and sudden weakness in the lower extremities.
Congenital aneurysms are rare. Typically, cerebral aneurysms are acquired diseases caused by high blood pressure, trauma, tumors, atherosclerosis, genetic, autoimmune and other diseases.
It is important to remember that when an aneurysm ruptures, the patient experiences sharp, severe pain. In this case, prompt medical attention is needed - seek help immediately! Unfortunately, this disease cannot be treated with medications; the most promising method of treatment is surgery. The drugs only slightly reduce the risk of aneurysm rupture and are used as a temporary remedy to remove critical factors.
If signs of an aneurysm are detected, to confirm or refute the diagnosis, a medical examination by a neurologist or neurosurgeon is necessary, who will prescribe a diagnosis - MSCT or MRI of the head. When the diagnosis is confirmed, the patient must be observed by a neurosurgeon, because Even small aneurysms can rupture and lead to irreversible neurological damage.
Once a patient has been diagnosed with a cerebral aneurysm, different types of treatment may be prescribed:
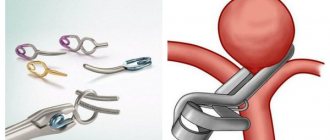
- Open surgery (aneurysm clipping).
- Endovascular surgery (aneurysm embolization). The operation is performed inside the vessels through a small puncture in the skin.
The worst consequence of an aneurysm is its rupture! The death rate from aneurysm rupture is more than 50%. In other cases, severe neurological disorders occur.
|
Federal centers accept all citizens of the Russian Federation for treatment, regardless of their place of registration. Operations are carried out within the framework of state guarantees, which means they are free for all residents of Russia.
Even during a pandemic, federal centers continue to work in a “clean” zone, providing timely planned care to all patients.
Among these are the Russian Ministry of Health. Doctors of the vascular center perform complex operations in a hospital setting to embolize aneurysms using the endovascular method (inside the vessels), and the neurosurgical department performs clipping of aneurysms. The low invasiveness of the method allows patients to recover in the shortest possible time and return to their usual rhythm of life.
For consultation with vascular surgeons, call: +7926 686 19 58.
Risk group. Danger of aneurysm
An aneurysm is a disease of the arteries of the brain that is found in various people, regardless of age.
The risk group includes:
- smoking,
- alcohol abusers,
- patients with hypertension, hereditary vascular pathologies.
The insidiousness of an aneurysm is that in the early stages the symptoms of brain damage are almost invisible. It is not easy to notice them, especially for a constantly busy person. At the same time, a relatively small number of people undergo comprehensive examinations of the brain and blood vessels.
Many patients do not pay attention to headaches and nausea. Usually these conditions are associated with chronic fatigue and age.
Important! 25% of patients suffering from protrusion of the wall of a cerebral vessel die.
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Aneurysm rupture: consequences
When cerebral aneurysms rupture, blood can flow into the meningeal spaces of the brain (actually subarachnoid hemorrhage), blood can flow into the brain tissue and/or inside the ventricles of the brain. Thus, rupture of cerebral aneurysms can occur as a hemorrhagic stroke.
With all anatomical forms of hemorrhage, occlusion of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways may occur with the development of acute occlusive hydrocephalus and brain dislocation. After intracerebral hemorrhage, cerebral edema develops. Due to the breakdown of blood and the reaction of brain tissue to blood breakdown products, inflammation and necrosis of brain tissue occurs. Thus, the damaged areas of the brain stop working and, accordingly, the parts of the body controlled by this area of the brain will not work.
The subarachnoid hemorrhage that occurs when a rupture occurs can have a number of complications:
- Recurrent aneurysm rupture
- Cerebral vasospasm
- More than half of all patients develop cerebral ischemia. In 15-17% of cases this leads to death.
- Internal hydrocephalus, caused by occlusion of the cerebrospinal fluid ducts, is observed in 1/4 of the patients.
After rupture of cerebral aneurysms, people may experience complications characteristic of both hemorrhagic stroke and ischemic stroke:
- Movement problems, weakness or paralysis – this can lead to difficulty moving, walking and coordinating. Movement problems on one side of the body are called hemiparesis or hemiplegia.
- Swallowing disorder . Violation of the act of swallowing can lead to food and liquid entering not into the esophagus, but into the windpipe and lungs, thereby becoming the cause of severe pneumonia. Swallowing problems can also lead to constipation and dehydration.
- Speech Impairment. Impaired reproduction and understanding of speech, including difficulties in reading, writing, and counting, occur as a result of damage to the left hemisphere of the brain.
- Problems of perception. With normal vision, a person is not able to understand what he sees. Perceptual impairments make it difficult for a person to use everyday objects. For example, a person cannot take a glass and pour water into it and then drink it.
- Cognitive impairment. The ability to mentally perceive and process external information is impaired. Clear and logical thinking is impaired, memory deteriorates, and the ability to learn, make decisions and plan ahead is lost.
- Behavioral disorders. Aggression, delayed reactions, fearfulness, emotional instability, and disorganization may appear.
- Disorders of urination and defecation. Bowel or bladder difficulties (urinary incontinence or retention, fecal incontinence) can be caused by a number of different problems after a stroke.
- Psychological disorders. Sudden mood swings, depression, irritability, reasonless laughter or crying. Depression is a very common problem in people who have suffered a stroke and is often accompanied by loss of appetite, unreasonable laughter or crying, insomnia, low self-esteem and increased feelings of anxiety...
- Epilepsy develops in 7-20% of people who have had a stroke.
- Pain syndrome. After a stroke, a small number of people develop painful attacks in the form of burning, shooting, throbbing pains that are not relieved by painkillers.
Treatment of pathology
Emergency treatment for patients with a ruptured brain aneurysm includes restoring deteriorating breathing and reducing intracranial pressure.
There are 2 main treatment options.
They allow you to fasten the intracranial protrusion of cerebral vessels.
- Surgical clipping.
- Endovascular embolization.
If possible, treatment is given within the first 24 hours after bleeding to close the ruptured aneurysm and reduce the risk of recurrences that affect the blood vessels.
Let's consider the features of both methods.
How is the treatment carried out?
After local anesthesia, the doctor inserts a hollow plastic tube (catheter) into the femoral artery and advances it, using angiography, to the site of the aneurysm. Using a guide catheter, coils of platinum wire or small latex beads are passed through the catheter and inserted into the aneurysm. They fill the aneurysm sac, cutting it off from circulation, causing the formation of a blood clot (thrombus) that completely seals the aneurysm cavity. The softness of platinum allows the coil to conform to the fancy shape of the bag. To fill it completely, an average of 5-6 spirals are required.
The average duration of the procedure is 1-2 hours.
When the neck of the aneurysm is too wide, it is sometimes necessary to place a stent in the main vessel to hold the coils inside the sac. Because the stent acts as a barrier between the aneurysm and the mother vessel, it is very unlikely that coils will protrude from it.
Surgical clipping
The goal of the intervention is to apply a special clip to the neck of the aneurysm. This allows you to exclude it from the general bloodstream without blocking a normal vessel. If the aneurysm cannot be clipped, alternative techniques are used (wrapping, tripping, etc.).
Important! The operation to clip the cerebral vessels is performed with craniotomy. Microsurgical techniques are used to carry out the intervention. This allows you to free the aneurysm (its neck) from the feeding vessels. Complications after surgery arise from a previous rupture. Eliminating all its consequences is not so easy. When treating unruptured aneurysms, complications occur less frequently (in 4-10% of cases).
Request a call back Get a free consultation
Cost of surgery to remove a cerebral aneurysm in Germany
Prices for regular diagnostics in Germany, rehabilitation and recovery after removal of an aneurysm are calculated based on the patient’s condition at the time of contacting the Nordwest clinic. You can consult a doctor to identify an aneurysm by signing up for a video consultation. The acute course of the disease requires immediate hospitalization. Patient relationship managers will provide you with assistance in organizing your treatment as soon as you contact them and go through all the stages of interaction. They will also be able to advise you how much the operation costs to prevent complications in the form of rupture or stroke if the diagnosis has already been established.
Embolization
This technique has become widespread in the last 15 years. It allows you to exclude the damaged vessel from the cerebral circulatory system without opening the skull. A special catheter is inserted through one of the veins or arteries. It moves through the circulatory system until it reaches the aneurysm. After this, using special instruments, the vessel is disconnected from blood circulation.
Embolization is the least traumatic way to eliminate aneurysms. That is why it has become widespread. Efficiency and advantages of treating cerebral aneurysm using modern endovascular techniques Embolization is a method that has proven to be highly effective.
That is why it is often used to disconnect a cerebral vessel from the circulatory system when:
- Inaccessibility of the aneurysm.
- Risk of serious complications with direct intervention.
- Carrying out operations on elderly people.
- Treatment of patients in serious condition.
Intervention is also prescribed when the aneurysm cannot be clipped.
Over the past few years, a large number of interventions have been performed. Moreover, surgery on cerebral vessels was prescribed even for gigantic aneurysms. The majority of patients did not require a long stay in the intensive care unit and were discharged from the clinic within 2-3 days.
There was no damage to any major healthy cerebral vessel. Thanks to this, patients were able to lead a normal life and did not experience any restrictions.
In some patients, the aneurysm was not completely excluded from the bloodstream during one intervention. In this case, another operation was performed. Repeated intervention on the cerebral vessels did not lead to a worsening of the patient's condition.
Main advantages of the method
- Low probability of need for repeated interventions. The operation is performed a second time in approximately 1 case out of 300.
- Possibilities for intervention to stop a cerebral vessel in patients who are contraindicated for extensive surgical clipping.
- Short duration of the procedure. Usually the operation takes no more than 2-3 hours.
- Opportunities for full recovery of health. An aneurysm will not bother you.
5. Immediate improvement. After intervention on a cerebral vessel, patients recover as quickly as possible. Moreover, embolization of cerebral vessels does not prevent them from leading a normal life.
Rehabilitation
An integral and no less important stage of treatment is rehabilitation after cerebral aneurysms. Only with a professional approach to the recovery process is it possible to significantly increase the results of complex treatment and return the patient to human life. This approach was developed by German specialists who have unique experience in neurorehabilitation and accept patients from all over the world.
To receive professional advice on the treatment of cerebral aneurysm in Germany, call us at: +49 228 972 723 72 or write to Email here
Technique of operations to remove aneurysms
The main types of interventions on vascular malformations of the brain are:
- Removal of aneurysm using open access;
- Endovascular technique.
Treatment of aneurysm during trepanation
The effectiveness of open operations reaches 98%; they are performed when the aneurysm is sufficiently accessible and in case of rupture. The patient is given general anesthesia, the surgeon performs a craniotomy, cuts the dura mater, and looks for the entire aneurysm or the site of its rupture. Next, you need to turn off the malformation from the general bloodstream. This is usually done with the help of a metal clip, reminiscent of a clothespin, which is placed on the vessel feeding the aneurysm and blocks the flow of blood through it.
After “switching off” the aneurysm, the dura mater is sutured, the bone flap is placed in place, and sutures are placed on the skin flap. In case of severe cerebral edema, decompression trepanation is possible, leaving an open bone window until the edema subsides and does not threaten displacement of the stem structures. The bone fragment is temporarily placed in the abdominal tissue to maintain viability, and then returned to its place.
aneurysm clipping
Open brain surgery can cause tissue damage and neurological disorders later, so it is important to proceed with extreme caution. In the presence of hemorrhage, clots and liquid blood are removed from the skull, and when it penetrates into the ventricular system, the brain cavities are drained.
After clipping the aneurysm, it is important to assess the preservation of blood flow through the healthy vessels of the brain even before the surgical wound is sutured. For this purpose, intraoperative Doppler ultrasound with a microsensor is used. If the blood flow is normal, then the operation can be considered successful and completed.
Video: open clipping of an internal carotid artery aneurysm
Endovascular treatment
Minimally invasive interventions include endovasal treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Indications for it are:
- Deep and inaccessible location of the vascular tangle;
- The proximity of vital structures, which makes open surgery very dangerous;
- Senile age and concomitant pathology that prevent general anesthesia and trepanation;
- Ineffectiveness of clipping during trepanation.
endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms
Access during endovascular surgery is carried out through the femoral artery, into which a catheter is inserted, delivering a detachable balloon or special coils to the abnormal vessels, causing the cessation of blood flow in the formation. Stents can also be used to block the aneurysm, but ensure unimpeded blood flow through the brain.
First, the largest coil is installed into the lumen of the aneurysm, then the cavity is filled with smaller ones, which cause thrombosis and shut off the aneurysm from the bloodstream. If the neck of the feeding vessel is wide, the installation of spirals is complemented by stenting.
A type of endovascular treatment is embolization of aneurysm vessels, when their walls are glued together using alcohol, surgical gel, and special compounds. Several of these procedures may be required to repair an aneurysm.
When performing operations on cerebral vessels, an operating microscope, a special table with a fixing bracket, and endoscopic and microsurgical techniques are used. The state of blood flow is monitored by ultrasound microsensors.