Postural instability is a syndrome in which there are difficulties in maintaining balance in a certain position or when changing positions. Quite often, postural instability is observed with the development of paralysis and Parkinson's disease, although the development of postural instability as an independent disease is not excluded. The syndrome develops as a result of disorders in the brain: damage to the basal ganglia, brain stem, frontal lobes. Postural instability is characterized by an unsteady gait and a tendency to fall. In severe cases, patients are unable to stand or sit on their own.
Treatment of postural instability is successfully performed at the Yusupov Hospital. Qualified neurologists and psychotherapists use high-tech equipment and modern methods for treating diseases of the nervous system in their work, which allows them to obtain the most favorable results.
Treatment of anxiety-phobic disorders in Samara
Anxiety-phobic disorder (other names - obsessive-phobic disorder, obsessional neurosis, obsessive-phobic neurosis) is a neurotic disorder that causes phobias, obsessive (obsessive) states, sudden fears and thoughts. Obsessive states torment the patient, but he cannot get rid of them without outside help.
Treatment
Psychopharmacotherapy in combination with psychotherapy is effective. Pharmacological effects are aimed at uniform relief of psychopathological manifestations (anxiety, depression, asthenia, psychosomatic manifestations, phobias). The activity of the autonomic system is stabilized, senesto-hypochondriacal inclusions are eliminated. Groups of drugs and their combinations are used:
- Tranquilizers to reduce the severity of anxiety, normalize sleep, relieve panic attacks. Anticonvulsant, muscle-relaxing tranquilizers are prescribed in short courses, lasting from 2 to 4 weeks. The reason is the side effects - decreased cognitive capabilities, drowsiness, withdrawal syndrome.
- Antidepressants have a cumulative effect, so the prescription is prescribed over a long course. Drugs are necessary to increase the pain threshold (in the presence of pain), to improve mood and appetite. Antidepressants do not cause withdrawal symptoms and have a favorable tolerability spectrum.
- Beta-blockers are prescribed to patients with severe somatic symptoms. The drugs normalize blood pressure, eliminate arrhythmias, and normalize sweating. Beta blockers are effective in relieving tremors and weakness.
- Drugs from the neuroleptic-antipsychotic group are rarely prescribed in small dosages.
When treating neuroses and depression, the patient’s condition turns out to be especially suicidal during the period when, as a result of treatment, motor retardation decreases, and other depressive symptoms remain at the same level. In the absence of supervision and adequate treatment, suicide attempts tend to be repeated.
Brief cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in combination with medication has been proven to be effective. CBT helps patients learn to monitor their own anxious fears and sad thoughts. Through working with a psychotherapist, a person learns to adequately evaluate his thoughts. Methods of transforming negative thinking into positive ones are practiced. Psychotherapy helps develop relaxation skills, muscle and mental relaxation. The effect becomes noticeable after 14-20 (depending on the severity of the condition) sessions.
Recovery can be brought closer by attending training sessions. There are psychotherapeutic trainings aimed at awareness of anxiety. The patient is asked to keep notes indicating a specific time, describing the content and duration of disturbing thoughts and fears. The training helps to develop problem-solving behavior skills.
Psychotherapy is a scientifically proven way to get rid of anxiety and depressive disorder without subsequent relapses. However, psychotherapy will not be effective for people with certain characterological characteristics: gross negativism, rigidity, lack of reflection skills, low interpersonal sensitivity. Psychotherapy will not help a patient who receives secondary benefit from an illness and has no desire to get well.
Physical therapy is another complementary treatment modality. Therapeutic massage sessions, mastering self-massage skills, attending electromassage and electrosleep sessions are useful.
Obsessive-phobic disorder: risk group
People with certain qualities are predisposed to anxiety-phobic disorder: anxiety, low self-esteem, pedantry. At risk are perfectionists who constantly evaluate their activities and accompany them with a detailed mental algorithm, as well as psychasthenics who are prone to suspiciousness and excessive introspection.
It is extremely rare that anxiety-phobic disorder is found in people who tend to shift responsibility for what is happening to others, who do not spare others in order to achieve their goals, or who are aggressive.
The gender of a person does not matter for the statistics of the disease, but a certain age (teenagers and young adults, as well as the age preceding menopause) increases the risk of its development.
How does HPD (hysterical personality disorder) manifest?
One of the important clinical indicators of the presence of hysteroidal personality disorder is the desire to constantly be in the center of attention along with high self-esteem. Such individuals usually lead a bright, dramatic and charismatic lifestyle, trying to be in the center of events. They also always try to flirt with new acquaintances, who sometimes take this for attempts at romantic acquaintance or flirtation. In part, this is true. But hysterical personality disorder manifests itself equally in both single people and people with families. Therefore, the active development of this disorder can negatively affect family relationships.
One of the characteristic signs for people with HPD is the desire to dress flamboyantly and provocatively. But all the emotions of such individuals are greatly exaggerated. They behave quite feignedly, without realizing it themselves. It’s one thing when it comes to the pretense of public people for the public, and another thing is a characteristic hysterical disorder even in everyday life, when this is inappropriate. Often, excessively challenging behavior has a negative impact on work and family. Being overly dramatic and charismatic with an employer increases misunderstandings, which can get a person fired. Omissions may also appear in the family. For example, a spouse may not recognize hysterical personality disorder, mistaking challenging behavior for inappropriate behavior, disrespect and frivolity.
If you have this disorder, you should be careful about being overly influenced by authority figures and trends. Deviation in the form of HPD implies excessive gullibility and following fashion trends. Because of this, such individuals can often change friends, place of residence, gadgets, cars, and even jobs.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of anxiety-phobic disorder include:
- Panic attacks are a sudden strong fear of danger, death, causing autonomic disorders in the patient: dizziness, fainting, nausea, lack of air, tachycardia.
- Agoraphobia – fear of public places, crowds, the street.
- Hypochondriacal phobias are fear of the possibility of illness, intense search for symptoms, panic and confidence in the inevitability of illness at the slightest detection.
- Social phobias – fear of being evaluated by other people, fear of close attention from others.
- Other phobias: fear of heights, touching, confined spaces, elements, certain situations.
For a person prone to phobias to manifest them, it is enough to remember and imagine similar situations or a previous attack. Phobias tend to develop: embarrassment during speeches in front of the public or management, with the aggravation of obsessive states, is transformed into a fear of ordinary communication with well-known people.
Agoraphobia: postural phobic instability
Postural instability occurs as a result of the development of a phobia in a person. Agoraphobia is a fear of open spaces and crowds of people. With this mental disorder, the following fears arise:
- fear of a large number of people,
- fear of an unusual situation appearing in public,
- fear when walking through a large square or street,
- fear of visiting public places that cannot be left unnoticed (theaters, restaurants, public transport).
Agoraphobia is usually associated with a fear of public embarrassment in the event of a panic attack. Since a panic attack usually occurs spontaneously, constantly waiting for it to occur makes the situation worse. A person is afraid to leave his comfort zone and avoids situations that can cause a feeling of fear. During a panic attack, a person with agoraphobia may develop postural phobic instability. Its characteristics will be:
- absence of objective reasons for imbalance, dizziness and instability when walking;
- dizziness develops during attacks of fear, while a person may lose touch with reality and experience short-term swaying;
- An attack of postural instability occurs in certain situations associated with a phobia.
In a person with agoraphobia, the number of situations that lead to postural instability gradually increases. As a result, there is a growing desire to exclude such situations in life, resulting in isolation and detachment. People with agoraphobia may not leave their home for weeks or even years. Postural phobic instability is more associated with emotional distress than with physical brain disorders.
Course of obsessive-phobic neurosis
There are several variants of the course of anxiety-phobic disorder:
1) attacks of panic attacks, as a rule, are not accompanied by manifestations of other phobias;
2) a combination of panic attacks and persistent agoraphobia, while in the manifestation of panic attacks, strong fear prevails over the physical manifestations of the phobia. A person can take extreme measures (a complete change of activity, moving, changing contacts) to level out the possibility of new panic attacks;
3) vegetative manifestations of panic attacks prevail over the severity of fear and subsequently provoke attacks of hypochondriacal phobias.
Diagnostics
Even doctors often confuse anxiety-depressive disorder with neurocirculatory dystonia (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
The reason is that the somatic symptoms of neurosis are similar to VSD. The result of an incorrect diagnosis is incorrect and ineffective treatment. Therefore, if you suspect neurosis with complaints, it is better to consult a psychiatrist or psychotherapist, rather than a general practitioner. Anxiety disorder is more difficult to diagnose than depression. The reason is that the list of diagnostic criteria is rather “erased”, not clear, built according to the method of exclusion. At the first consultation, the psychiatrist collects anamnesis, asks the patient questions about his well-being, and inquires about the presence of mental pathologies in relatives. During the diagnosis, the patient undergoes a series of questionnaires. The Zung scale and the Beck test indicate the presence of signs of depression. The Hamilton and Montgomery-Asberg scales reveal the level of severity and neglect of a depressive state.
A general blood and urine test is needed in order to exclude somatic pathologies of an inflammatory, immunological and hormonal nature. It is advisable to use instrumental examination methods.
Electroneuromyography is prescribed for muscle pain syndrome to assess the condition of peripheral nerves and muscles. An EEG is needed to refute epilepsy, since some of its symptoms overlap with manifestations of neurosis. MRI of the brain allows you to see the organic causes of the disease and assess the state of blood flow. Electrocardiography is prescribed in case of frequent attacks of suffocation, feeling of pressure in the chest area. The method helps to exclude cardiovascular pathologies.
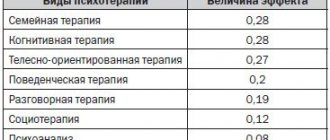
Psychotherapy in the treatment of obsessive-phobic neurosis
The activities of a psychologist in the treatment of anxiety-phobic disorder and manifestations of phobias are aimed, first of all, at reducing and completely eliminating anxiety, as well as at correcting behavior. Patients are taught relaxation and behavioral habits that exclude avoidance of certain situations. Psycho-emotional support therapy is used, as well as behavioral therapy, during which the patient learns not to succumb to fear in certain situations. Rational psychotherapy is also used, which includes an explanation of the course of the disease, forming the patient’s understanding and awareness of his illness, which will allow him not to succumb to its manifestations.
You can make an appointment with a psychologist by phone + 7 (846) 333-66-22.
How is hysterical personality disorder diagnosed?
To diagnose this mental disorder, clinical criteria are used. A patient with this diagnosis must have the following symptoms:
- Excessive need for attention;
— Emotionality and charisma even when it looks ridiculous and stupid;
— Blindly following fashion trends and having idols;
— Superficial and feigned emotions;
- Excessively impulsive manner of speech and attempts to constantly be the center of attention of groups of people or individuals;
- Easy suggestibility.
Clinical picture and course
A characteristic feature of the disease is the occurrence in persons prone to obsessions of complaints of dizziness and balance disorders in the absence of objective signs of vestibular disorders (during otoneurological examination, electronystagmography with caloric test and stabilography) or other conditions that explain the complaints. The feeling of instability occurs in bursts while standing or walking, is provoked by certain circumstances or occurs spontaneously and, sometimes, is accompanied by anxiety. The absence of a provoking factor or anxiety makes patients and the doctors treating them doubt the psychogenic nature of the disease.
Patients with phobic postural dizziness initially have a certain personality type: they are prone to obsessive states, introspection and strive for constant self-control. In most cases, these are ambitious people who place high demands on themselves, are extremely irritable and impressionable.
Such patients rarely go straight to a psychiatrist. Usually they go to a specialist, trying to find an organic disease. Most neurologists and otolaryngologists also do not immediately think about the possible psychogenic nature of dizziness in their patients, and therefore the disease remains undiagnosed for a long time (an average of 3 years, according to an analysis of 154 cases; Huppert et al, 1995). The diagnosis is made only after repeated visits to different specialists, useless laboratory and instrumental studies and unsuccessful attempts to treat either “vertebrogenic dizziness” or “vertebrobasilar insufficiency”. A prospective psychiatric study confirmed that phobic postural vertigo is a distinct disorder that can be clearly differentiated from panic disorder with or without agoraphobia (Kapfhanuner et al., 1997).
Phobic postural dizziness affects adults. The peak incidence occurs between 20 and 50 years; and in this age group, phobic postural dizziness is the most common cause of dizziness (Strupp et al., 2003). Men and women get sick equally often. Without treatment, the disease progresses, and the patient, trying to avoid situations that provoke dizziness, gradually stops leaving the house unaccompanied.