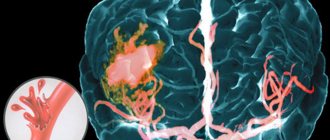
Loss of speech during a stroke is a common complication of a dangerous disease that occurs in every third patient who has suffered an attack. This condition is called aphasia: the patient cannot express his thoughts, has difficulty speaking on simple topics, and cannot even name simple objects. You can often regain lost skills if you enroll in a rehabilitation center after a stroke and undergo recovery under the supervision of experienced doctors.
The prognosis largely depends on the severity of hemorrhage or ischemia, but even with a mild form of stroke, rehabilitation requires concentration on the part of the patient and supervision by a doctor. The doctor must identify aphasia and prescribe a rehabilitation program.
How to recognize aphasia?
Lack of speech after a stroke does not always mean a complete loss of speaking skills. A person may confuse words, letters, sounds, stutter, and try to use the simplest expressions. When a stroke occurs, the speech motor analyzer is affected, phonetics when speaking, as well as syntax, grammar and vocabulary when writing words may suffer. In severe cases, the patient completely loses writing skills.
Speech impairment during a stroke in a patient can be determined by the following signs:
- similar sounds or words are confused;
- there is a violation in the construction of even simple sentences;
- there is an inability to correctly construct a sentence (for example, instead of “I’ll take the bus to the dacha,” a person says “I’ll take the bus to the dacha”);
- stuttering and frequent repetition of the same words are noted;
- obscene language is used.
The last sign often causes anxiety among relatives - even well-mannered and intelligent people often begin to swear after an attack. Scientists explain this by the fact that obscene language is considered one of the most ancient and simplest pronunciations, and therefore settles in the subconscious of every person.
Sometimes dysarthria is observed - the quality of pronunciation of sounds suffers. The intonation changes, the voice may become dull or nasal. In severe cases, there is complete loss of speech during a stroke.
How long does it take to recover speech after a stroke?
The period of speech restoration, as a rule, begins 7-10 days after the stroke (possibly if the patient is in a stable condition). But sometimes there are situations when the patient is not able to start working with a speech therapist after 3-4 weeks. In any case, recovery should begin no later than after 6-8 weeks, otherwise it will be much more difficult to restore impaired functions.
Speech restoration as part of a rehabilitation program after a stroke is quite slow. Depending on the form of aphasia and the severity of the clinical case, it can take several weeks or even months. It often happens that articulation returns to the patient in spurts: for a long time, the exercises do not bring positive results, but one day the speech improves noticeably.
It is problematic to provide an accurate forecast for the timing of speech restoration in advance (individual for each patient). Rehabilitation is a strictly gradual and step-by-step process. The duration of all stages is individual for each patient: for some it takes several weeks, while for others it takes up to a year. As practice shows, in most patients, speech abilities noticeably improve 3-4 months after regular classes. However, the entire recovery period takes from 3 to 5 years.
What types of aphasia are there?
Speech impairment can be different; this condition depends on which centers were damaged during ischemia or hemorrhage. Each Broca's area is responsible for its activity; based on the presence of specific signs, doctors determine the severity of the attack.
Types of speech impairment in stroke:
- if the patient cannot name specific objects, optical-mnestic aphasia is diagnosed - the patient usually says “what they write with” instead of the word “pen”;
- if conversational perception is impaired with preserved hearing, sensory aphasia is diagnosed;
- when the patient cannot repeat a word or phrase that is spoken to him, he suffers from an acoustic-mnestic form;
- If a person cannot speak words, but understands everything and can pronounce syllables and letters, motor aphasia is diagnosed.
What are the types of speech disorders in stroke?
When a blood vessel ruptures in the brain, speech functions are first affected. With hemorrhage, various disorders appear (difficulty in understanding one’s own speech, inability to form words). In addition to aphasia, there are other types of disorders - dysarthria and dyspraxia.
Features of aphasia
It is characterized by deterioration of speech functions against the background of damage to speech centers in the brain. It is divided into complete (when there is no speech at all) and partial. Also, there are 6 forms, including:
- Motor. It can be afferent and efferent. With afferent, a person has difficulty maintaining an articulatory posture. Many people lack instinctive speech. With efferent, difficulties arise with the assimilation and reproduction of the motor program. Speech is characterized by rearrangement of sounds and syllables.
- Sensory. With this form, Wernicke's center, localized in the temporal lobe, is affected. As a result, a person loses the ability to understand speech, but conversational function is preserved. Sometimes visual function deteriorates.
- Dynamic. It is characterized by difficulty or complete absence of the possibility of active expression. The person is unable to pronounce long sentences and has great difficulty constructing phrases. During a conversation, speech patterns dominate.
- Acoustic-mnestic. The main clinical manifestation is difficulty retaining recently acquired information in memory. There are patients who cannot repeat a phrase of several words after a speech therapist. It is difficult for them to name the objects around them, because they simply do not remember their names.
- Semantic. Patients do not perceive complex speech formulations. Many people have difficulty solving problems that contain complex syntactic structures. Patients with this form read very slowly.
- Total. This is the most severe form, which is characterized by a complete absence of speech (due to damage to many speech areas of the brain). Most patients do not even recognize their closest relatives. This form requires a long recovery.
Features of dysarthria
With dysarthria, the mobility of the speech organs is limited, which makes articulation difficult. As a rule, in adults the disease does not lead to the collapse of the speech system. It is often accompanied by problems with swallowing and breathing. In more than 70% of cases, it occurs as a result of a stroke. The main signs of dysarthria include:
- difficulties in the mobility of articulation organs;
- disturbances in fluency of speech (constant hesitation);
- unintelligible and slurred speech;
- problems with speech rate (slow or accelerated);
- monotony of intonation (monotonous speech);
- grimaces;
- changes in voice timbre.
There are several forms of dysarthria: bulbar, pseudobulbar, cerebellar, subcortical and cortical. Each of them is associated with a specific location of brain damage. To restore speech, the help of a speech therapist is required. He conducts diagnostics to identify which aspects of speech are impaired and draws up an individual therapy program.
Features of articulatory dyspraxia
Articulatory dyspraxia is a disorder in which the facial muscles maintain the normal tone of the body, but the movements and coordination required to produce sounds are impaired (pronunciation is slurred). There are problems remembering the next movement in a sequence, which causes a lot of inconvenience in everyday life.
People with dyspraxia may speak continuously and repetitively. Ensuring content and consistency in language is often very difficult. Speech is often unclear and tempo and tone cannot be fully controlled. For treatment, an integrated approach is used.
Rehabilitation
As soon as a speech disorder after a stroke is diagnosed, doctors develop a rehabilitation program: how to restore it and return the patient’s social life skills. The speech therapist determines which skills are impaired and develops an individual program, conducts training and gives homework. Here, success largely depends not only on the quality of rehabilitation, but also on the efforts and determination of the patient himself.
The program may include:
- reading short sentences with the doctor;
- learning standard phrases with gradual expansion of the vocabulary;
- reasoning about the functional significance of objects;
- as recovery progresses, more complex word forms are used;
- at the end the patient retells the sentences in his own words.
Each speech therapist has his own peculiarities of treating speech impairment during a stroke - the doctor tries to use effective techniques that bring results. It is better to contact trusted and qualified doctors who will help you gain conversational and social skills.
Our rehabilitation center provides a comprehensive program for the recovery of patients with speech impairment after a stroke. We try to select an effective program and monitor the rehabilitation process.
Speech therapy after stroke: what can you expect?
27.11.2019
As a result of brain damage caused by a stroke, 30 percent of patients develop a speech disorder. Although this is common in stroke, it is important to emphasize that it can develop as a consequence of other neurological diseases.
Who cares about post-stroke speech disorder?
Part of the speech disorder is an articulation disorder (dysarthria), which, in addition to retained speech skills, means difficulty producing sound . In this case, the content of the speech remains unchanged, but is difficult to understand, which may even increase to the point of incomprehensibility. Another large group includes the so-called aphasia , that is, various manifestations and levels of speech learning and understanding that are not necessarily associated with difficulty in articulation.
During trauma, complex brain and networks involved in language impair speech , as well as reading and writing, in addition to retained intelligence. However, due to the complexity of language fields, impairment in the use of conceptual systems can lead to loss of prior intellectual abilities.
What is aphasia?
Although the areas of the brain that play an important role in organizing speech (depending on the guarantee) are primarily located in the left hemisphere, a more precise term is the dominant hemisphere, which, regardless of laterality, refers to the hemisphere in which the speech fields are located. Aphasia is typically a symptom of the dominant hemisphere.
Characteristics of the degree of damage to speech fields in the dominant hemisphere and the nerve pathways that connect them, the location of damage
Speech impairment may be mild ( speech ), and in the worst case, complete absence of speech . Difficulty of speech (difficulty in choosing words and concepts) makes speech obscene or incomprehensible, loses continuity, and in addition to searching for words, repetitions appear with difficult-to-read content. Speech impairment naturally also impairs writing and reading skills. Speech comprehension is primarily impaired by understanding. This may create an impression of confusion and it may be difficult for the professional to make a correct diagnosis.
What are the rehabilitation options?
Treatment of aphasia requires an interdisciplinary approach, meaning it is a task that involves several professions and requires comprehensive expertise in treatment and rehabilitation . The rate of return of lost language skills largely depends on the rehabilitation .
Neuropsychology
The task of the clinically qualified and clinical psychologist begins with the assessment of the speech . It is very important to create the right conditions at this stage, as you need a timely, calm test situation and the patience to examine patients who have difficulty communicating in order to establish an appropriate diagnostic relationship. The work is helped by aids such as tests, which subsequently play an important role in speech . Difficulties in conversation that are not perceived by the patient but manifest as a burden to the environment present a particular challenge.
What to ask your therapist?
- What did the health checks show?
- Can you write down important points in therapy so you can take care of yourself later?
- What will therapy ?
- Are there other treatments that may work?
- How can I involve my family in therapy ?
- How long will the therapy ?
- How do we know when we have reached the end of therapy ?
- Is there something I can do after completing therapy ?
Music therapy
Speech reconstruction, or music therapy , is a method that uses music as a tool for treatment and rehabilitation . The quiet melodies you listen to can reveal deeply etched elements of childhood that interfere with the language in childhood. Music also releases positive mental energies, helping the healing process.
Group therapy
A group therapy improves functional communication. The group also has a strong motivational factor for further individual treatment and can also help with social isolation caused by speech . speech impaired people often make the patient's environment ignorant of his/her communication area and capabilities. The shared experience of those who face similar difficulties is very helpful in overcoming these obstacles.
Speech therapist
If necessary, you can also see a speech therapist , who is usually available through a home care service.
What might healing depend on?
Improvement in aphasia depends on age, gender, location of brain injury, patient intent, motivation, and the form and intensity of aphasia .
Early onset of traumatic brain injury is important. Rehabilitation for women tends to be faster, and pre-disease tongue use is also an important factor. During speech therapy , one third of patients improve significantly, 1/3 only moderately, and the remaining 1/3 do not change significantly. In the first year after speech , spontaneous improvement is also a major factor, which is most pronounced in the first 3 months. Speech therapy in the first half of the year is most effective, but after that therapy is of great importance. It is important to emphasize that rehabilitation can take years.
How can family help?
Tasks that can be done at home are an important part of speech therapy . This requires collaboration between patients and their families. Speech therapy should not be limited to the therapeutic activities of a specialist, and the key to improvement is self-employment.
It is important that family members help the speaker in a timely and appropriate manner. Over-help is a barrier to development, as is lack of therapy . For example, during release, the initial (yes-no) questions that need to be addressed may gradually lead to more complex dialogue.
Speech therapy is a challenging task, and for patients with aphasia , communication is exhausting. This should be taken into account during rehabilitation by introducing joint recreation programs.
Published in Defectology Premium Clinic
How to restore the ability to speak in an adult after losing it?
How long it takes for speech function to recover depends on how severely the brain was damaged.
Therefore, in some patients, the ability to speak is restored quite quickly (within a few weeks or months), while in others it takes years, and it is difficult to predict how long it will take. To restore patients who have suffered a stroke, the following types of rehabilitation are used:
- Drug therapy.
- Classes with a speech therapist.
- Physiotherapy.
- Massage.
- Surgical intervention.
Medicines
During rehabilitation after a stroke, the doctor prescribes several groups of drugs to the patient that help reduce side effects, improve the condition and help the patient quickly return to their normal lifestyle:
- Muscle relaxants.
- Antidepressants.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Antiplatelet agents.
Muscle relaxants
On a note. In the third month after a stroke, the patient may develop muscle hypertonicity, which greatly slows down the rehabilitation process.
Then muscle relaxants are prescribed that can reduce excessive muscle tone. The best muscle relaxants for stroke:
- Sirdalud (cost in Moscow from 227, in St. Petersburg from 176).
- Tizalud (cost in Moscow from 160, in St. Petersburg from 125 rubles).
Antidepressant series drugs
Almost 80% of patients suffer from depression after a stroke, which slows down the recovery process. In this case, antidepressants are prescribed. The best antidepressants for stroke:
- Nortriptyline (cost in Moscow from 990, in St. Petersburg from 1,000 rubles).
- Paxil (cost in Moscow from 650, in St. Petersburg from 660 rubles).
Anticonvulsants
When seizures occur, anticonvulsants are prescribed, but they should be taken with caution, as this group of drugs can cause side effects. The best anticonvulsants for stroke:
- Finlepsin (cost in Moscow from 215, in St. Petersburg from 193 rubles).
- Convulex (cost in Moscow from 116, in St. Petersburg from 135 rubles).
Antiplatelet agents
If after a stroke the patient’s blood becomes more viscous, this slows down the recovery of brain tissue. In this case, the help of antiplatelet agents is required to prevent the formation of blood clots. The best antiplatelet drugs for stroke:
- Reopoliglyukin (cost in Moscow from 102, in St. Petersburg from 110 rubles).
- Clopidogrel (cost in Moscow from 226, in St. Petersburg from 205 rubles).
Important! Any medications should be prescribed only by the attending physician. Do not self-prescribe medications, otherwise this can only worsen the patient’s condition.
Medication alone does not provide much benefit, but it does help progress recovery when used with other types of therapy, such as speech therapy and physical therapy.
- How exactly does speech restoration proceed after a stroke?
Classes with a speech therapist
At the first lesson, the speech therapist draws up a plan for each patient individually. The following exercises are required:
- Reading tongue twisters.
- Drawing.
- Mimic and speech therapy massage.
If all the specialist’s recommendations are carefully followed, about 20-30% of patients with moderate and severe speech disorders begin to speak normally by the time they are discharged from the hospital. Classes can also be held at home. The exercise program must be combined with medications, physical therapy and other types of rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy
This type of rehabilitation stimulates muscle recovery and helps to achieve better results from classes with a speech therapist and from taking medications.
- Magnetotherapy. This procedure stimulates all processes in the brain, and also improves the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems. A rather painful method, but it is considered one of the most effective. The patient's condition improves after 2-3 weeks.
- Dorsanval. Prescribed for poor blood supply to the brain and limbs. After a whole course of procedures, which is at least 5-7 sessions that take place over 2-3 weeks, the patient’s condition improves significantly.
Massage
Therapeutic massage for stroke significantly improves blood supply to the affected tissues, which increases the flow of oxygen and other nutrients to them. In addition, massage helps relieve muscle and psychological tension. A therapeutic massage course usually consists of 10 sessions , but can be adjusted individually for each patient.
Note! A massage course can only be conducted by a qualified specialist with a medical education.
Surgery
A method such as surgery is resorted to in extreme cases, when other methods do not improve the patient’s condition and cannot restore lost speech. To restore speech, a neurosurgical operation is performed, which creates additional connections between healthy tissues and vessels in the speech area of the brain, without affecting the damaged areas.
Classification
For ease of use in practical medicine, there is a special classification of aphasias, based on the systematization of manifested disorders in accordance with the lost function and the affected area of the brain.
The following types of aphasia are distinguished:
- Efferent motor aphasia manifests itself when Broca’s area is damaged, and the patient develops articulatory speech defects or apraxia;
- Afferent motor aphasia develops with damage to the postcentral sulcus. The main disorder in this form is a kinetic speech disorder or severe difficulty in speech function associated with the formation of specific sounds;
- Acoustic-gnostic, with damage to Wernicke's area. Characterized by loss of phonemic hearing. A person with this form ceases to adequately perceive the interlocutor’s speech;
- Acoustic-mnestic, with this form, Wernicke’s area is also affected, and the manifestation is a violation of the visual representation of an object and loss of auditory memory;
- Amnestic-semantic, with damage to the posterior temporal parts of the brain. Understanding of complex grammatical structures is impaired, simple speech is not affected;
- Dynamic, manifests itself when the posterior areas of the frontal lobes are damaged. It manifests itself as a violation of the utterance program, which leads to both a violation of speech perception and a violation of its formation.