Borderline personality disorder (BPD) is a mental pathology that previously belonged to the group of psychopathy. Persons suffering from this disorder have instability of emotions, impulsive actions, and a tendency to anxious experiences. The behavior of patients is marked by attacks of anger, conflict, idealization of events and actions of other people, alternating with their subsequent denial and devaluation. This pathology is stable in its manifestations. Psychiatrists identify it in childhood, adolescence and young adulthood. The violation makes itself felt throughout a person’s life. The development of the disease is facilitated by the characteristics of a person’s mental type, external factors, and excesses in family upbringing. Our Leto clinic has all the necessary conditions for identifying pathology, its drug treatment and psychotherapy.
Features of BPD
The symptoms of the disorder become the cause of partial and complete desocialization of patients. The pathology is detected in approximately 2% of the population and is often combined with other mental problems. Very often, clients are diagnosed with concomitant addiction to psychoactive substances. The quality of life of patients is reduced due to the emphasis on their own failures, loneliness, and lack of fulfillment. People with this disease naturally become depressed. They often exhibit suicidal tendencies. To save patients from the disease, doctors at our medical center use the most effective medications and psychotherapeutic technologies.
Personality disorder: symptoms and signs
Manifestations of the disease affect all areas of the personality: primarily emotional and volitional, in addition, thinking, style of behavior and communication in society. There is no ability to flexibly adjust and adapt to changes in everyday life. Such people are unable to realistically perceive themselves and others and establish friendly relations with them. But these are only general symptoms; more specific clinical manifestations depend on the form of the disease.
Paranoid (paranoid) form
Characterized by constant suspicion, mistrust, and a tendency to shift responsibility for actions and decisions made. People with this type of disease often feel constantly offended, relegated to the background, and betrayed.
They are full of prejudices, but at the same time they are 100% convinced of their own objectivity and rationality. From the outside, their behavior seems devoid of emotion and lacks a sense of humor. All aspects related to power are highly valued, the rest is only contemptible.
Important! Sometimes this type of illness is a harbinger of the manifestation of schizophrenia, therefore, special attention is paid to the diagnostic examination and treatment of such patients at the Cordia clinic.
Schizoid type
The main feature of people with this type of illness is withdrawal and inability to establish long-term and emotional interpersonal relationships. They prefer work that is not associated with close communication or social interaction, while they are little concerned about the prestige or financial component of the profession, and easily tolerate monotonous activities. The ability to experience pleasure and experience both physical and emotional pain is often reduced. Paradoxically, coldness in communication is often combined with a reverent attitude towards animals and admiration for some inanimate objects (architectural structures, objects of art).
Characterized by an obsession with a healthy lifestyle (passion for specific and extraordinary diets, sports). But at the same time, the risk of developing alcoholism or drug addiction in attempts to have fun is quite high. Patients are indifferent to the opinions of others, incapable of empathy, there is no impulsiveness - only cold calculation.
Dissocial form of pathology
Typically, the desire to obtain pleasure and enjoyment, while avoiding any work and stress.
From an early age, they are characterized by deceit, running away from home, a specific, asocial circle of friends, theft, fights, drugs, and alcohol. Patients constantly manipulate others, resorting to blackmail, threats of suicide, and complaints of poor health.
They are not at all concerned about the consequences of their actions; their explanations look naive and infantile. Thinking disorders are usually absent; rather, on the contrary, the intellect is well developed.
Emotionally unstable type
- Impulsive (aggressive) personality disorder. Characterized by episodes of loss of self-control with attacks on others, damage to furniture, breaking dishes, etc. The level of aggression clearly does not correspond to the situation. The attack begins abruptly, ends very quickly, after which the person regrets what happened.
- Borderline (mixed) personality disorder. Symptoms combine manifestations of neurosis, psychosis, and schizophrenia. Typically there is a violation of the perception of one’s own identity, which provokes demonstrative attempts at suicide, a feverish search for communication with a demand for devotion and support.
Hysterical variant of the course of the disease
The main feature is attracting attention to oneself through defiant behavior, exaggerated display of emotions, manipulation (tears, reproaches, attacks of anger and irritability). Sexual attractiveness is emphasized separately, but impotence is typical for men with a similar illness, and anorgasmia is typical for women. They note self-centeredness, the desire to satisfy their own needs, and neglect of the needs of others.
Anankastny (obsessive-compulsive) form
The person is focused on correctness, ordering, regulation, neatness. He lacks a sense of humor, spontaneity in actions, initiative, and is indecisive. In interpersonal relationships, incapable of compromise, intolerant.
Anxious subtype
Patients have extremely low self-esteem, but they are constantly in search of new social contacts. However, they always need guarantees of a positive attitude and lack of criticism. Any deviation from the “ideal” they represent causes fear and is perceived as betrayal. Behavior is characterized by stiffness, unnaturalness, and excessive modesty.
Other types of personality disorders
- Dependent. The desire to find a person who could solve the patient’s problems and help him get out of difficult life situations is clearly expressed.
- Narcissistic, characterized by an exaggeration of one's own importance. Patients cannot tolerate criticism, responding to it with open aggression.
- Passive-aggressive, characterized by constant internal resistance to leadership and loved ones. Feeling internal tension and rage, patients are constantly irritated and dissatisfied, as they cannot fight back or express their dissatisfaction or desires.
- Association disorder. Against the background of acceleration of associative processes, a rapid change of thoughts of the patient and inhibition of the speech apparatus are observed. This leads to difficulties communicating with other people. It is difficult for a person to concentrate on one thing, it is difficult to express his own opinion on this or that issue, in a conversation he constantly jumps from topic to topic.
Does your relative have a mental disorder?
Refuses hospitalization? Are you afraid that he will harm himself and others? Call or request a free consultation.
URGENT CONSULTATION
The doctor will arrive within 1 hour . We'll take you to the hospital ourselves. Emergency hospitalization - around the clock!
What Causes Borderline Personality Disorder?
The disease develops as a result of exposure to a complex of factors.
Most often, the violation is provoked by:
Family predisposition.- Accentuations of individuals with low self-esteem.
- Tendency towards pessimism.
- Low stress resistance.
- Lack of parental care.
- Negative experiences of communicating with adults with inappropriate behavior.
- Excessive control over the child’s personality, prohibitions, excessive demands.
- Experiencing mental trauma in childhood, loss of loved ones, psychophysical violence.
Psychiatrists at our clinic noticed that this pathology occurs more often in women than in men.
Complications without treatment
Timely contact with a specialist in a psychiatric department improves the prognosis of recovery. Ignoring the clinical manifestations of the disease leads to its aggravation and acquisition of a chronic form.
Among the negative consequences are:
- lack of opportunity to build personal and business relationships with partners;
- constant thoughts of suicide, which will sooner or later be realized;
- chronic depression, lack of interest in the outside world;
- social isolation, secluded lifestyle;
- lack of desire to leave the house.
Borderline personality disorder develops in childhood. It is very important to take some preventive measures to prevent the manifestation of the disease. Among them are:
- visiting a specialist in critical situations (divorce of parents or death of a loved one);
- allowing the child to express his own emotions, even if they are negative;
- exclusion of physical, emotional, sexual violence;
- providing conditions for full communication with significant adults;
- creating an atmosphere in which it is comfortable to live and study;
- building a trusting relationship in which the child can freely share his problems.
The duration of therapy is determined by several factors:
- features of relationships with loved ones;
- age;
- the primary source of the disease;
- willingness to undergo long-term therapy;
- level of personal, professional, social development.
Biochemical disorders in the brain and their impact on the psyche
With psychopathization, increased activity of the limbic part of the central nervous system is detected. As a result of emotional overload, a pronounced fluctuation in the level of neurotransmitters is observed in the body. These disruptions aggravate pathological neuropsychic reactions and cause a stress response. The autonomic nervous system is involved in the process. In patients with mental problems, neurological symptoms are additionally formed. Against this background, physiological and social maladaptation develops.
How do borderline mental personality disorders manifest?
The initial symptoms of deviations attract attention in childhood.
In children and adolescents, doctors identify:
- Frequent episodes of restless behavior.
- Instability and impulsiveness of mental reactions.
- Inadequate response to external stimuli.
These signs are not specific to the disease. Therefore, the diagnosis cannot be established immediately. In most cases, the disorder finally develops by the age of 25.
In patients it is determined:
Fear of loneliness. Patients against this background often become dependent on other people. But in most cases, “attachment” is soon replaced by disappointment and devaluation of the existing relationship.- Tension in communication with loved ones, excessive demands, capriciousness.
- Strengthening and more frequent signs of impulsive behavior.
- Desocialization, accompanied by a desire for promiscuous sex life, frequent changes of partners, and the use of alcohol and drugs.
- Ennui.
- Loss of the ability to control your emotions, which leads to frequent quarrels and fights.
- Suicidal tendencies.
A number of patients suffer from overeating and senseless waste of money. If you do not pay attention to the patient and do not treat him, then the symptoms of the disease worsen over time.
Clinical manifestations are supplemented by:
- Transient paranoid ideas.
- Dissociation (splitting) of personality.
- Partial or complete social maladaptation.
Clients become isolated in their experiences, experience constant fears of loneliness, cannot solve everyday problems, and become completely dependent on others. They develop a “bad person” complex with the idea that they will be used for bad purposes. Trying to restrain his emotions, a person increasingly loses control over himself. As a result, even a small person has excessively inflated and impossible demands on himself. This reveals suspicion, distrust of people, and fear that they will be used for bad purposes. Trying to restrain his emotions, a person increasingly loses control over himself. As a result of even a small force, an external stimulus, a request, can become an unconscious impetus for an inadequate mental reaction. The course of the disease is cyclical. The deterioration of the condition is replaced by a period of stability. This becomes the reason that patients stop receiving treatment and lose confidence in psychiatrists and psychologists, considering them unable to help.
Borderline mental disorders are often combined with:
- Panic attacks.
- Generalized anxiety disorder.
- Neuroses.
- Bipolar disorder.
General information about the disease
Borderline personality disorder is a form of psychopathy that significantly impairs the quality of life. A person suffering from it cannot build long-term relationships with partners, he has no friends, and adaptation to new conditions is extremely difficult. Conflict situations are aggravated by a lack of self-control. The patient is unable to monitor his reactions and control his own impulses in behavior.
The disease is diagnosed in approximately 3% of patients with mental disorders, 10% of them die by suicide. The first symptoms of BPD appear in adolescence, and the trigger is not necessarily stress. The development of mental illness can occur gradually. At first, it often remains invisible to others.
The inner world of such patients is very poor; they often describe their state as empty, “de-energized,” devoid of energy and strength. Borderline personality disorder is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent worries over minor issues;
- emotional instability;
- impulsiveness in decision making;
- internal experiences;
- inability to master basic communication skills.
Frustrated attempts to realize oneself in the profession and society aggravate the situation. Against the background of constant dissatisfaction with oneself, depression develops. Drug and alcohol addiction occurs. First, with the help of third-party stimulants, such patients try to relieve internal pain. Unnoticed, they become involved, exhibiting extreme forms of alcoholism and drug addiction.
How to get treatment at the Leto clinic
Our center's telephone number is 8(969)060-93-93 . Call us, we work around the clock and seven days a week. The registrar will make an appointment with a specialist at a convenient time. You can get to us either by public or by your own transport. If necessary, you can call a consultant to your home. Both diagnosis and treatment are carried out in anonymity.
During hospitalization, clients are offered a choice of ward classes:
- Standard (2-3-4 seats).
- Comfortable, designed for two people.
- VIP, equipped for one patient.
Questions about the cost of stay and the price of individual procedures can be discussed by phone with the operator.
What is included in the treatment course
Before helping a patient with BPD, psychiatrists at our clinic draw up a treatment plan. It takes into account all the individual characteristics of a person, the degree of his desocialization. For initial forms, outpatient psychotherapeutic treatment is quite acceptable. In situations with advanced symptoms, hospitalization is recommended. In the hospital, patients are given drug therapy.
Experts prescribe:
- Tranquilizers that relieve phobic feelings.
- Neuroleptics that have a positive effect in severe affective disorders.
- Antidepressants that eliminate depression.
Correction of mental disorders requires the use of psychotherapy methods.
Our doctors use:
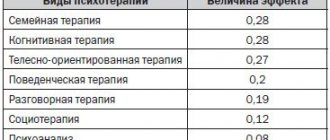
Cognitive-behavioral method of healing the psyche.- Rational individual and group psychotherapy.
- Hypnosis.
- Training in self-correction and self-control skills, auto-training.
Psychologists are involved in the healing and rehabilitation process. After completion of the course of therapy, we recommend continued observation. For recovery and prevention of relapses, it is necessary to undergo periodic preventive and consulting conversations with a psychotherapist.
Treatment of borderline disorder in Moscow
Therapy for this disease is based on a combination of conservative methods and the latest techniques with medications. All patients require courses of psychotherapy, as well as the use of medications with a specific spectrum of action. Cognitive behavioral therapy has proven itself well, helping to restore the adaptive potential of the psyche.
The specialist works in the following areas:
- rethinking the patient’s lifestyle;
- a detailed discussion of his problems, aspirations, desires;
- developing skills to control one’s behavior and spontaneously arising emotions;
- formation of protective mechanisms that will help in time to get rid of stress and anxiety;
- developing skills of constructive communication with other people.
Consultations can be individual or group. Communication with a psychologist in a confidential environment helps to relax, understand and acknowledge your condition. The second option involves the participation of friends, relatives, and other significant persons in the program. The specialist teaches all participants how to avoid conflict situations. Individual indicators of the course of the disease include the use of drugs from the following groups:
- antidepressants;
- neuroleptics;
- tranquilizers.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
How to live with borderline personality disorder
A person with this pathology should be attentive to his psychophysical state. As soon as there is a suspicion of a return of painful symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist. Therefore, we recommend that if your symptoms worsen, you immediately contact our Leto mental health center by phone at 8(969)060-93-93 and make an appointment. This should be done as soon as possible. It is much easier to stop the disease at the very beginning than at its peak. Against the background of pronounced clinical signs, eliminating them can be very difficult. We do not advise “wandering and rushing” from one specialist to another with the question: how to treat yourself and with what. To relieve painful symptoms, you will need to be patient. The prognosis will always be positive if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Questions and answers
Can borderline disorder be treated at home?
No. Such mental disorders are treated in a hospital setting. The patient can cause physical harm to the life and health of others, as well as to himself. Therefore, he needs hospitalization.
Is it possible to get rid of BPD using folk remedies?
No, using questionable drugs will only worsen the situation. Any medications are used after prior consultation with a doctor.