Causes of Memory Loss
- Certain injuries and pathologies of the brain - these include, for example, cancer, traumatic brain injury, stroke;
- Disruption of certain systems of the human body;
- Negative factors - sleep problems, stress, lifestyle changes, increased brain load, incl. for memory;
- Addictions – alcohol, nicotine, drugs, systematic use of sedatives;
- Age-related changes that reduce memory function.
Questions and answers
At what age does amnesia most often occur?
Typically, amnestic syndrome appears in people after 65 years of age due to senile changes in the brain. In other age groups, amnesia can occur after trauma, severe intoxication, or as a result of severe psycho-emotional shocks.
Is it possible to restore memory without taking medications?
Even with a regressing form of the disease of organic origin, certain groups of drugs may be required to restore memory in full. They will help normalize metabolic processes and restore bioelectric impulses. If amnesia appears after stress, then in mild cases, competent psychotherapy will be sufficient.
Diseases that cause memory problems
Memory impairment often appears as a result or symptom of various diseases. They are often caused by traumatic brain injuries. People who receive them note memory impairment, the degree of which directly depends on the severity of the injury. Traumatic brain injuries can lead to various types of amnesia - retrograde or anterograde. The patient may not remember either the moment of injury or the period preceding it. Sometimes memory loss is combined with the appearance of hallucinations and false memories.
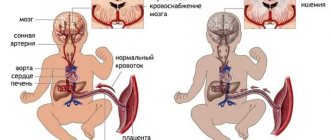
The most common causes of memory problems include disruption of normal cerebral circulation. Atherosclerosis of blood vessels leads to a decrease in blood flow in all parts of the brain, and this often provokes an acute cerebral circulatory disorder. A stroke developing in one of the brain zones cuts off the blood flow to it. This leads to impaired brain activity and memory loss. Similar symptoms also occur if a person suffers from diabetes.
It's a different story with diseases that are transmitted genetically, including Alzheimer's disease. It cannot be cured, but competent therapy and care slow down the development of the disease, minimize the consequences and reduce the risk of complications.
Memory also becomes worse due to diseases of the thyroid gland, leading to iodine deficiency in the human body. This is accompanied by a tendency to obesity, apathy, depression, excessive irritability, and swelling of muscle tissue. You can avoid such manifestations if you choose the right diet, which includes frequent consumption of iodine-containing foods, as well as persimmons, seafood, seaweed, hard cheese, and nuts. The diet also includes a variety of dairy products.
But forgetfulness is not always a pathology of memory, because quite often a person consciously tries to forget difficult life situations, negative events, and tragedies from memory. In this way, the body protects its psyche and reason. If a person throws out the negative things that happened to him from his memory, then this phenomenon is called repression; he believes that certain events did not happen - denial, and if he chooses another object to displace negative emotions - replacement. Suppressed and forgotten negative emotions that have not found a way out often turn into prolonged depression and neuroses.
1.Different types of memory disorders
If you suffer from memory lapses, you are not alone. The speed of our brain begins to decline after the age of 20, this is especially noticeable under high loads. There are many different types of memory disorders that can affect you. We will try to consider the most common of them.
Memory losses
How many times have you found your car keys all over the house or forgotten the name of someone you know? These are ordinary memory lapses. Some doctors believe this is even more true of attention disorders. After all, the older we get, the more difficult it is for us to divide attention between several tasks. If there are too many thoughts that need to be kept in mind at the same time, then our brain simply “turns off the lights.”
Research shows that the frontal lobes of the brain in older adults are more vulnerable to aging than any other organ, and as a result, they are more prone to memory loss.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Symptoms indicating memory impairment
Memory bells that should alert you:
- forgetfulness, manifested in everyday matters;
- difficulty focusing on a specific object;
- problems with learning and remembering information, with its reproduction;
- disruption of the thought process, loss of logical connections, loss of mental acuity;
- confusion and uncertainty;
- autism, social maladjustment;
- foggy consciousness.
Often, memory problems begin against the background of deteriorating general health. However, they can be combined:
- with headaches;
- with pressure surges;
- with hand tremors;
- with muscle spasms;
- with dizziness;
- with a decrease in visual acuity.
If, in the presence of 2-3 of the above problems, memory has decreased, you should urgently seek medical help, since these symptoms signal rapidly developing brain pathologies.
How does alcohol affect our memory?
When the feeling of deceptive euphoria due to prolonged alcohol consumption in a person passes, temporary changes in the brain of an organic and cognitive-psychic nature occur.
Alcoholic drinks have a detrimental effect on memory - they literally protect a person from what is happening to him at the present time, and selectively. In other words, a person who drank the night before remembers some things, but not everything. For comparison, it is worth noting that in a sober state, memory records everything - both good and bad. Alcohol displaces negative thoughts, replacing them with positive, but deceptive ones.
The action of ethanol also affects perception, which changes greatly, namely, it ceases to perceive all the details of what is happening. What comes to the fore is what a person desires within himself, what he would be happy about. This leads to the splitting of the present into two planes, one of which projects what is desired and joyful, the second one disappears for a while. A drunk person focuses his attention on one thing and is able to talk only about this all evening. Accordingly, his memory is filled only with this information and often with fragments.
How do organic brain disorders affect memory?
The issue of the relationship between alcohol and memory has long been considered among scientists. The loss of memory, according to many, occurs as a result of the destruction of brain cells. When the regeneration process is stopped, nerve cells die and, as a result, memory function stops working. According to foreign scientists, ethanol destroys neural connections in the brain, not neurons.
What disorders occur in the brain?
The hippocampus is a part of the brain that controls the storage and memorization of incoming information. It has a paired structure and is located on both sides of the head in the temple area. Long- and short-term memory is modified from signals from the cerebral cortex through nerve cells in the hippocampus, where they are recoded. When a person drinks alcohol, neurons in this region become isolated from neurons in other parts of the brain. As a result, a drunk person does not retain information even in the current memory.
When ethanol is ingested, certain neurons trigger the process of producing steroids. They block communication between neuron cells of the hippocampus and the cerebral cortex. The impulse reserve of the nerve cell weakens in other neurons and later stops altogether. It is noteworthy that cognitive processes, including memory function, occur as a result of potential maintenance by the cell. Otherwise, memory loss after drinking is inevitable.
Features of alcohol poisoning
Ethanol is considered a highly toxic substance. If a person has previously consumed alcohol, memory loss may be due to severe brain poisoning. Under the influence of alcohol, synoptic transmission changes, as does the direction of neuron functioning. In special cases, hallucinations are possible .
Features of oxygen starvation
The human brain must receive appropriate nutrition. This process occurs through blood. It is logical that when ethanol enters its composition, a number of changes occur. As a result, blood cells initially move more quickly through the vessels. However, later the water balance is disturbed, and the red blood cells cease to be negatively charged (they participate in the process of repelling blood cells from each other). This ensures the accumulation of blood cells , as well as their connection. Further, the chain of changes due to intoxication in the human body does not stop. The following processes take place inside:
- rupture of the blood cell membrane;
- gluing of hemoglobin into lumps due to the ingress of components included in the membrane into the vascular cavity;
- compaction of small vessels of the brain;
- blood clot formation.
Such changes will lead to a lack of blood access to the brain and its subsequent hypoxia, while the death of nerve cells is observed. Missing neurons negatively impact brain function and memory. A person who drank the day before experiences atherosclerotic memory loss.
Of course, alcohol “cleanses” the already weakened body of all vitamins – C, B6.
How a neurologist treats memory
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to understand what disease caused the problem. Medicines should be used only those prescribed by your attending physician; self-medication is unacceptable. It is optimal to undergo a complete diagnosis of brain activity, vascular health, and electroneuromyography.
It should be remembered that rapid memory deterioration in itself is not a disease; this symptom only warns of the emergence of a more serious disease that needs to be diagnosed and therapeutic or radical treatment begun. This will help restore the previous quality of life, prevent the patient from separating from society and deteriorating adaptive functions. When memory impairment is detected, nootropic drugs are usually prescribed.
Classification
Depending on the degree of memory loss, amnesia can be complete or partial. In the first case, a person cannot remember anything from a period of his life, and in the second, he observes vague fragments of events. There is also selective or local amnesia, when the patient loses only a specific skill. This condition is characteristic of psychogenic disorders. According to the time of forgetting, this deviation can be:
- retrograde in the absence of memory for everything that happened before the onset of the disease;
- anterograde, when everything that happens after the first signs of the disorder is forgotten;
- combined (combines retrograde and anterograde amnesia);
- fixation – forgetting what is currently happening, usually lasts for 2-5 minutes.
The type of course of amnestic syndrome can be:
- regressing with gradual recovery;
- stationary, in the absence of positive dynamics and without signs of deterioration, forgetting usually applies only to a certain situation;
- progressive – gradual loss of memory up to its complete loss.
There is also retarded memory loss, when a person’s events are erased some time after stress, acute psychosis or traumatic injury. Immediately after regaining consciousness, he talks about what happened, but later forgetting sets in.
How to improve memory. Recommendations from the Neuroscience Center
If you observe alarming symptoms in yourself or in people close to you, indicating memory problems similar to those indicated above, then you need to go to an appointment with a neurologist, neuropsychologist or therapist and undergo a series of special diagnostic tests. If you want to immediately start fighting an undesirable phenomenon before receiving the doctors’ verdict, then take action - start training your memory.
Here are some exercises to improve memory:
- If possible, perform your usual tasks with your eyes closed, from memory;
- If you are a left-handed person, do everyday tasks with your right hand, if you are right-handed, then with your left. Try this rule, for example, writing, ironing clothes, drawing, etc. – You will soon feel a positive result;
- learn Braille, which is used by blind people when reading, or learn sign language - this is useful for memory and can be useful in life;
- type texts on the keyboard with both hands, using all fingers;
- do some handicrafts - start embroidering or knitting;
- learn foreign languages and speak them more;
- try to distinguish the denomination of coins blindly, feeling them with your hands.
In addition, expand your range of interests, read more, visit places and institutions you have not been to before, go to plays and performances, walk in parks, meet and communicate with people, make new friends.
Perform the recommended exercises, follow the listed rules, take care of your health, and your memory will not fail you until old age!
Where can you improve your memory in St. Petersburg
Where should you go if it becomes clear that memory impairment is affecting your quality of life and you urgently need to take action? Why did my memory deteriorate? A specialist neurologist at our Center for Neurology, Professor Zhulev, can answer these questions.
Make an appointment with a doctor using the phone number listed on the website. If you notice that your ability to remember dates, faces and other data has sharply deteriorated, then you need to undergo an examination and identify the reasons. Don't let your health take its course. If memory has sharply deteriorated, then this is a signal from the body about problems that have arisen, and the sooner the doctor diagnoses them, the better.
We are located in the Central district of St. Petersburg, the work schedule and map can be found in the Contacts section.
Content:
- Why memory disappears: causes of amnesia in alcohol addiction.
- How alcohol affects memory.
- Memory restoration after alcoholism.
Serious cognitive disorders and neurometabolic disorders are frequent “companions” of alcoholism. According to statistics, specific brain lesions are noted in 75% of addicts, and almost always such pathological changes negatively affect the processes of memorizing and analyzing information. At first, alcoholic memory lapses are episodic: a person does not remember events that occurred while intoxicated. But as addiction progresses, intellectual abilities noticeably decrease: personality degradation begins, which often ends in alcoholic dementia.