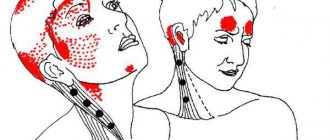
Why does cervical migraine occur?
Cervical migraine syndrome occurs due to several factors. Conventionally, they can be divided into two categories:
- Those related to problems in the vertebrae.
- Those that do not relate to vertebral lesions.
Nonvertebrates:
- Pathologies of the structure of the spinal artery, which are present from birth.
- Affected vessels.
- Anomalies in the location of blood vessels.
- Myositis.
Causes related to the vertebra:
- Pathologies of the vertebral structure.
- Vertebral deviations due to injury.
- Osteochondrosis of the vertebrae.
- Unstable functioning of the cervical vertebrae.
- Problems whose consequences are difficult to determine.
Migraine stages
Migraine attacks occur in several stages. Among them:
- Prodrome. In other words, harbingers of headaches. The occurrence of these symptoms is observed in 50% of patients suffering from migraine. Pathological signs include irritability, emotional lability, weakness, thirst, swelling, muscle tension in the neck and back of the head. These symptoms may occur several hours or days before the attack.
- Migraine aura. This is a set of neurological symptoms that occur immediately before a migraine attack. In accordance with this, violations are distinguished:
- visual (flashes or colored lines, loss of areas of vision;
- motor;
- sensitive (numbness, tingling);
- speech.
The intensity of the listed migraine symptoms gradually increases. The duration of a migraine aura can be 1 hour.
- Stage of headache. Signs of a migraine are an intense headache that appears on one side (less often bilateral). Its severity increases even with moderate physical activity. A migraine attack is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and increased sensitivity to light and sounds. The duration of headache without appropriate therapy can reach 3 days.
- Postdrome. The stage that occurs after the headache has subsided. Symptoms of postdrome include pale skin, yawning, irritability, and fatigue. These symptoms of migraine may persist for 2 days.
Symptoms of cervical migraine
The main sign that you have a cervical migraine is unbearable pain in the head area. But also when:
- The pain lasts all the time or occurs intermittently.
- The pain becomes unbearable, brings agony and constantly pulsates.
- During attacks, the eyes, bridge of the nose, or ears and forehead begin to hurt.
- A feeling of pain also appears with any touch.
- When you turn your head, you feel terrible discomfort.
- There is a ringing in the ears that pulsates along with the heartbeat.
- Dizziness, vomiting and nausea are common.
- There are problems with hearing and vision.
- A lump appears in the throat and swallowing is impaired.
- The body becomes hot, or vice versa, it makes you shiver.
These are the main problems that occur with cervical migraine.
Modern concept of migraine treatment
Ineffective treatment of migraine attacks is one of the common problems that can lead to the development of drug-induced (overuse) headaches in patients, an increase in the number of ambulance calls, visits to medical institutions and the number of hospitalizations. Selecting a drug that is effective in the treatment of migraine attacks is one of the key elements in the successful treatment of patients. [1]. The drug Relpax® meets this goal. Since it was absent from the pharmaceutical market for a long time, visitors stopped being interested in its availability in pharmacies. Currently, front desk workers can, as part of pharmaceutical information, convey good news to visitors requesting anti-migraine drugs - about the return of the drug Relpax® to Russia. (+ link to Relpax microsite, the approved layout of which is attached in Related Pieces)
Migraine is a neurological disease characterized by periodic or regular attacks of headache, often unilateral. It occurs in 14% of the world's population and women are more affected by it [2,4]. The incidence of migraine in the Russian Federation significantly exceeds global indicators and amounts to 20.8%. However, only 25% of patients consulted a doctor about their condition [1]. Meanwhile, in 2006, the European Federation of Neurological Societies created standards for the treatment of migraine. A serious approach to stopping migraine attacks is due to the fact that migraine is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including stroke. The goal of migraine therapy is to reduce the intensity and frequency of attacks, reduce the amount of painkillers taken, and improve the quality of life of patients [3,4].
Treatment
After diagnostics and other additional examinations, neurologists offer the following methods of therapy:
- Use of anti-inflammatory and pain relievers.
- Prescribing medications that can improve blood circulation.
- Consumption of vitamin B complexes.
- Drugs to protect nerve cells from hypoxia.
- Sometimes cervical massages and special physical exercises are used.
- Severe cases require surgery.
Posterior cervical sympathetic Barre syndrome can be cured if you promptly consult a competent specialist and complete a full course of treatment. If the situation is advanced, then you can simply relieve the pain. Prevention of this disease is considered to be strengthening the back muscles, correct posture, avoiding spinal injuries and proper nutrition.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 8 votes
Share article on social networks
Diagnosis of migraine
The diagnosis is made in the presence of typical complaints and a characteristic medical history. At the initial consultation, the neurologist conducts a thorough survey. During this, the time of onset and frequency of headaches, the duration of symptoms, accompanying symptoms, and the presence of hereditary burden are determined. In addition, the doctor needs to clarify the medications that relieve pain, if any. Additional methods for diagnosing migraine are:
- REG (rheoencephalography);
- EEG (electroencephalogram);
- Ultrasound doppler scanning (ultrasound duplex scanning of cerebral vessels).
They are prescribed only if a symptomatic migraine is suspected. Otherwise, the above methods have no diagnostic value, since they do not reflect any specific changes.
When making a diagnosis, it is recommended to rely on diagnostic criteria. Let's consider the criteria characteristic of the 2 most common forms of migraine - with and without aura.
- With aura:
- the presence of at least 2 attacks that meet diagnostic criteria;
- presence of at least two symptoms and the following:
- visual disturbances or unilateral sensory impairment;
- one of the clinical signs of aura develops within at least 5 minutes;
- The duration of each symptom is at least 5 minutes.
- headache is not associated with other disorders;
- headache is accompanied by at least one of the following symptoms:
- visual (reversible visual impairment, flickering spots or stripes);
- sensitive (tingling, numbness);
- speech (reversible speech disorders).
- Without aura:
- the presence of at least 5 attacks that meet diagnostic criteria;
- the average duration of headache is 4-72 hours;
- headache is accompanied by at least one of the following symptoms:
- vomit;
- nausea;
- hypersensitivity to light;
- hypersensitivity to sounds.
- headache is not associated with other causes;
- headache is characterized by at least two of the following:
- one-sided;
- pulsating;
- intense;
- worsens with physical activity.
Main reasons
Migraine with focal neurological symptoms can be caused by PA-vertebral artery syndrome. They, in turn, are located along the spinal column and pass through the canals, which are formed by the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. At the base of the brain stem, the vessel merges into an artery, which branches and at the same time supplies blood to the hemispheres. The cause of the pathology may be nothing more than cervical osteochondrosis. Migraine with focal neurological symptoms can be accompanied by a number of symptoms.
- Paresis of the limbs, which can be partial or complete;
- Nausea;
- Vomiting and dizziness;
- Hearing loss and decreased vision;
- Impaired coordination of movements;
- Amnesia.
A patient suffering from such a disease may experience intense pain that begins in the back of the head and spreads to the parietal region - to the forehead, temples, and neck. During this disease, when turning the head, a crunching or burning sensation may occur.
Headaches that occur in neurology are usually caused by severe compression of the occipital nerves; the pain itself has a shooting character. They can spread along the location of the nerves, and are also distinguished by the fact that they continue for a long time and constantly. If competent treatment is prescribed, it should bring the desired result, but often this does not happen.
Seizures usually limit the patient’s ability to work and take him out of his usual routine of life. There are several main types of migraine with focal neurological symptoms - pharyngeal, facial, hemiplegic. The first is diagnosed less frequently than the others, and the second is represented by pain in the face, which affects overall well-being. The latter type of migraine is quite difficult to detect and diagnose; for this, a specialist must collect all the necessary data and make a diagnosis.
Clinical Brain Institute Rating: 5/5 — 1 votes
Share article on social networks
Prevention of migraine recurrence
Prevention of relapse is indicated for patients suffering from chronic and frequent episodic migraines. This type of therapy adheres to the following goals:
- reduction in the number and severity of migraine symptoms;
- reducing the frequency of using medications to relieve headaches;
- improving quality of life.
Indications for prescribing preventive therapy are:
- presence of migraine attacks at least 3 times a month;
- duration of headache for at least 3 days;
- symptoms cause disorientation;
- concomitant conditions that reduce quality of life (depression, dyssomnia);
- risk of developing permanent neurological symptoms.
The duration of the therapeutic course for migraine is selected on an individual basis. Preventive therapy involves long-term use of medications. On average it takes from 2 to 6 months. In this way, it is possible to minimize the number of migraine exacerbations. For the purpose of prevention, the following drugs are used:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- anticonvulsants;
- antidepressants;
- calcium channel blockers;
- beta blockers.
Migraine treatment begins with minimal doses. If ineffective, the dosage can be gradually increased. This way, the risk of side effects is minimized. It is recommended to start migraine prevention with monotherapy. If there is no therapeutic effect within 2-3 months, the drug can be replaced or enhanced with another drug. When choosing a drug, it is necessary to take into account the presence of concomitant conditions.