Causes of migraine in women
Migraine is a chronic neurological disease. Refers to angiocephalgia (headache of vascular origin). It manifests itself as periodic or regular attacks of severe throbbing headaches, usually in one half of the head.
According to clinical studies of the World Health Organization, women are susceptible to the disease 4 times more often than men. This is due to the peculiarities of the functioning of the reproductive system and hormonal fluctuations.
Migraine often occurs in adolescence; 20-30% of patients aged 20-25 years suffer from pronounced manifestations of the disease.
The causes of the disease are not fully understood. Failures in the regulation of vascular wall tone can occur at any period of life against the background of changes in brain activity, autonomic vascular disorders, and hormonal imbalance. Lack of physical activity, obesity, chronic stress, unbalanced diet, smoking and alcohol abuse, hormonal changes - a number of factors can cause migraines and provoke an attack. The disease can be hereditary, with maternal transmission.
At risk are residents of megacities, patients with diabetes mellitus and endocrine disorders.
The following factors can trigger a migraine attack:
- stress;
- weather dependence;
- hormonal changes associated with the menstrual cycle (ovulation, PMS, menopause);
- overwork, mental and physical;
- taking certain medications, incl. oral contraceptives;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- excess/lack of sleep.
Triggering factors include:
- substances with a pungent odor;
- tight hairstyles and hats;
- excessive consumption of carbonated drinks and caffeine-containing products;
- certain food products (chocolate, citrus fruits, legumes, fast food, cheeses, fatty and smoked foods);
- alcohol;
- change of time zones.
Clinical manifestations
The symptoms of the disease are difficult to describe; patients cannot convey in words all the sequential sensations that arise. Anyone who has not experienced the manifestations of migraine will not be able to fully understand the clinical picture of the disease.
The description of the pathological process includes the following features:
- The attack begins with painful sensations on the right or left side of the head. Initially, the discomfort affects the temporal lobe, but can move to the eye or back of the head.
- Pain can vary in severity, from mild to severe. Some patients report pulsating shocks, others mention sharp, dagger-like impacts.
- The appearance of attacks of nausea and muscle discomfort are considered standard symptoms.
- Men may experience involuntary lacrimation, rhinitis, and a rush of blood to a certain part of the body.
A standard attack lasts from 4 hours to one day. It occurs in the evening or night hours, before the onset the patient experiences irritability, weakness, loss of appetite or complete refusal to eat.
In some patients, a standard migraine is accompanied by an aura - visual changes. They see spots, crooked lines before their eyes; optical illusion is combined with loss of sensitivity in one of the parts of the body: lower or upper limb, half of the face. The aura occurs for 10-60 minutes and is a harbinger of an imminent attack.
Migraine symptoms and types
Manifestations of migraine in women can occur episodically, with a frequency of 1-2 times a month. In some cases, there is a clear connection with periods of menstruation.
The disease has characteristic symptoms:
- severe headache lasting from several hours to several days;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- tactile touch intolerance;
- increased pain during mental and physical activity.
The headache is unilateral, less often bilateral. Sometimes it is localized in the eye or temporal region, spreading to the neck area. At the beginning of the attack, the pain is dull, with gradual intensification and pulsation. External irritants (bright lights, loud sounds, strong odors) contribute to increased pain.
In about a third of patients, characteristic warning signs are observed before the onset of an attack:
- anxiety;
- panic attacks;
- depressed mood, its sudden changes;
- decreased performance;
- chills;
- yawn;
- drowsiness and apathy;
- dizziness.
About an hour before the onset of an attack, visual disturbances may occur: flashes of light, double outlines of objects, luminous zigzags, spots or dots. Less commonly, there is a feeling of numbness in the limbs or transient speech disturbances (the so-called migraine aura).
The attack ends with a long, heavy sleep.
The symptoms and causes of migraine in women are individual, appear in various combinations and can differ significantly in patients of different ages.
The most common types of migraines are:
Classic or migraine with aura
The attack is preceded by auditory hallucinations, disturbances of smell and vision.
No aura
The attack occurs without warning, with a painful headache in one part of the head.
With an aura without a headache
There is only an aura and additional symptoms, no headache.
Aphasic
At the peak of the attack, temporary speech disorders are noted.
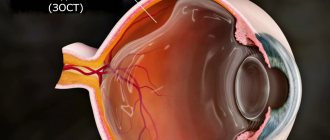
Ophthalmic
Pregnant women are mainly susceptible due to stress, overexertion, and disruption of their daily routine. A distinctive feature is temporary visual disturbances (flashes, sparks, spots, distortion of the size of objects).
Basilar
Manifests itself in the form of a pronounced aura with hearing loss, dizziness, and fainting. May provoke the development of ischemic stroke.
Cervical migraine
Dysfunction of the arteries located in the cervical spine leads to oxygen starvation of the brain. A characteristic symptom is a dull throbbing pain in the back of the head.
Menstrual
Associated with hormonal fluctuations that occur in the female body during the menstrual cycle. Pain and accompanying symptoms develop 2 days before the onset of menstrual bleeding or within three days after its completion.
How to treat the disease?
If migraines are infrequent, don't last long, and aren't too painful, you may not need treatment. If they occur frequently and affect your ability to perform daily activities or enjoy life, you should consider treatment.
There is no cure for migraines, but treatment can help control symptoms. Treatment for silent migraine is the same as treatment for migraine with headache.
The following over-the-counter medications may help treat acute migraine symptoms:
- aspirin
- ibuprofen
- naproxen
- acetaminophen
While caffeine can cause migraines, it can also help relieve acute migraine symptoms. Some people think that drinking a cup of coffee or taking Excedrin, which contains caffeine, helps. If your migraine is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, your doctor may prescribe anti-nausea medications.
If you experience migraines frequently, you may be advised to take preventative medications. These include cardiovascular drugs - beta blockers, including propranolol and metoprolol. Another option is calcium channel blockers such as verapamil and diltiazem. Your doctor may also prescribe tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline or nortriptyline.
Some migraine treatments have side effects. For this reason, some people try alternative treatments before prescribing medications. Alternative options may include:
- BOS
- massage therapy
- behavior therapy
- acupuncture
These treatments are often effective in combating the stress that may be causing it. They can also ease flare-ups.
Migraine during pregnancy
Predisposition to the development of migraines during pregnancy is associated with hormonal changes. It occurs both with an aura and without previous signals. Attacks are accompanied by nausea, less often vomiting, sensitivity to external stimuli (light, loud sounds, noises, smells).
Seizures without aura tend to decrease in frequency and duration as labor approaches.
Migraine with aura is characterized by a stable course. Against the background of the disease, blood circulation in the placenta may deteriorate. In rare cases, headaches provoke the development of fetal brain hypoxia. Attacks deplete the expectant mother’s body, which necessitates treatment. When contacting certified medical centers with experienced specialists, treatment is successful.
By the second trimester, positive dynamics are observed - the intensity and duration of paroxysms decreases. By the third trimester, there is an improvement in well-being in 50-80% of cases.
Features of migraine
Before you figure out how to treat migraine in men, you should understand the characteristics of the disease and how it manifests itself. As a rule, attacks are recognized by a previous condition, called aura by doctors.
The aura is accompanied by visual disturbances, anxiety, nausea, and general dysfunction of the body. It can last from half an hour to an hour, then the symptoms regress and the attack occurs directly.
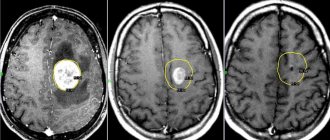
Complications of migraine are a series of severe attacks, the climax of which is a migraine stroke.
Migraine prevention
How to get rid of migraine? Is it possible to beat migraines? Medicines only relieve symptoms, but do not prevent the development of an attack. However, migraine medications and some medications (anticonvulsants, beta blockers) can be taken regularly, daily, regardless of the presence of symptoms. In such cases, the purpose of prescribing the drug is to prevent pain.
To get rid of migraines, you need to follow several rules.
This is keeping a diary, where you need to record the date and time of the onset of the attack, symptoms and provoking situations. Thanks to this, you will soon understand what causes your headache. There are also mobile applications developed for this purpose.
Regular physical activity and an active lifestyle, normalization of sleep also prevent headaches.
Diet and migraines: A diet rich in tyramine (tyramine is found in aged cheeses, processed meats, olives), alcohol, chocolate, coffee, and overeating can trigger headaches. Therefore, it is rational to avoid these foods. Vitamin B2 supplementation may reduce the frequency and severity of migraine attacks
What is migraine
Migraine is a neurological disease that causes severe unilateral headaches.
Another name for the disease is hemicrania. Migraine sufferers often describe it as a severe, throbbing, paroxysmal headache on one side, accompanied by nausea, vomiting and increased sensitivity to light and sound.
Statistics
Migraines affect a large proportion of the population (1 in 5 women and 1 in 15 men suffer from chronic headaches). On average, 14% of Europeans suffer from the disease. The incidence in Russia exceeds the world average; according to various studies, it is 15.9-20.8%.
Migraines are more common in young people under the age of 20.
Although on average women are more likely to get migraines, boys are more likely to get migraines in childhood. In middle age, the severity of the disease reaches its peak, but over time, after 60 years, its course becomes easier.
Causes of migraine in old age
- depression, chronic stress, anxiety;
- muscle tone associated with neurological diseases;
- hypertension;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs;
- bad habits.
An elderly person can suppress the symptoms of a migraine with painkillers, but this will only relieve him of the pain for a certain period of time. In old age, migraines are chronic, which means that painful headaches will return again and again. Meanwhile, migraine is dangerous for older people due to severe complications such as Alzheimer's disease, the development of cardiovascular diseases and stroke.
Elderly people who have smoking habits are at particular risk of getting a stroke. Tesham Montagne, MD, of the Miller School of Medicine in Miami, spent 11 years following older adults aged 68 years. Her research suggests that older smokers have a 3 times higher risk of stroke than non-smokers.
Scientists from the University of Waterloo (Canada), observing older people with migraines, found that 51 out of 679 people developed Alzheimer's disease in just 5 years. That is why it is extremely important not to start the disease, but to diagnose it and begin treatment.