Amino acid deficiency
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, including the neurotransmitters responsible for transmitting nerve impulses in the brain. With an imbalance of amino acids, sleep disturbances, mood swings, and a lowered pain threshold often occur—even with minimal exposure, the pain is perceived as very acute.
A lack of tryptophan, a precursor of serotonin (“the hormone of joy”), provokes a depressive state, and a deficiency of tyrosine or phenylalanine is fraught with severe mood swings.
Amino acid testing is performed as part of any metabolic evaluation, including chronic conditions with unclear diagnosis and/or difficult to treat.
Amino acids in the blood, 12 indicators (test code 99-10-112).
Mild obsessive-compulsive disorder
For mild obsessive-compulsive disorder (obsessive-compulsive disorder), psychotherapeutic help is recommended first.
For OCD, methods such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), EMDR therapy, short-term strategic psychotherapy, and hypnotherapy have shown high effectiveness. If necessary, treatment can be supplemented with drug therapy. The Yale-Brown test for obsessive-compulsive disorder has a high degree of reliability, but cannot serve as a basic tool for determining neurotic disorder (OCD). You should consult a psychiatrist for diagnosis and treatment if necessary.
Elevated cortisol levels
The hormone cortisol is produced by the adrenal glands. Against the background of stress, its value in the blood can increase to pathological values, which immediately affects the state of the nervous system. In case of excess, cortisol can cause conditions including panic attacks, leading to increased irritability, anxiety, and aggression.
Cortisol (test code 33-20-001);
Steroid profile of 24-hour urine includes 17-ketosteroids (test code 95-86-601).
Neurosis test
Author of the material:
Inna Trofimova
writer, psychologist, gestalt therapist
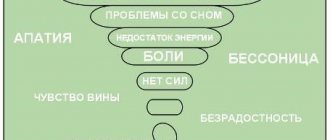
The fast pace of life, haste, constant competition, frequent stressful situations, and the inability to control one’s emotions lead to internal psychological conflicts and exhaustion of the nervous system. All together this becomes an excellent basis for the development of neuroses. They also cause problems with new situations in life and do not allow you to move forward freely. This is why their treatment and prevention are so important. The test for neurosis will determine the presence of this disorder and tell you what to do next.
1. Do you have a strange feeling as if you are backed into a corner and have nowhere to run?
2. How long does your psychological discomfort last?
3. Do you have sleep problems such as insomnia, frequent nightmares, difficulty falling asleep, short shallow sleep with frequent waking up?
4. Do you feel dizzy, your vision becomes dark, your gait becomes unstable, and your movements become less precise?
5. Do you experience stiffness, tension, or discomfort when communicating, especially with unfamiliar people?
6. Have you become more vulnerable, whiny, or touchy in the last few weeks or months?
7. Has your work capacity, efficiency and duration decreased?
8. Do you often feel that your emotional state is rather depressed, sad, apathetic? Do you have sudden mood swings for no apparent reason?
9. Do you experience unreasonable anxiety or panic?
10. Have you noticed that you have become sensitive to even the smallest troubles, although you previously experienced them calmly?
11. Has your sex life faded into the background, desire has decreased and you don’t have the strength for all this?
12. Do you have problems with appetite (increased or lost appetite, strong feeling of hunger against the background of rapid satiety)?
13. Lately have you been feeling lethargic, weak, drowsy, tired for no particular reason?
14. Do you often get colds and feel low energy?
15. Have you become more sensitive to bright lights, loud sounds, strong smells, sudden movements?
16. Do you have causeless attacks of shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, pressure surges, tremors, or it’s unclear where problems started in the toilet?
17. Do you feel that you sometimes lack determination and confidence?
18. Have you recently had more frequent headaches, heart or muscle pain, or discomfort in the stomach or intestines?
19. Have you become a more irritable person lately?
20. Does your psychological discomfort increase in specific situations, and not on its own? Can you predict in advance a situation in which you will feel uneasy?
Additional Information:
- Test for mental disorders
- Social phobia test
- Mental test
- Test for split personality
- Paranoia test
- Test for signs of autism
- Suicide test
- Panic attack test
- Alcoholism test
Indigestion
Well-being and good mood are associated with the functioning of the digestive system. A decrease in the absorption of essential nutrients - proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins - affects the balance of amino acids and glucose, which leads to a deterioration in mood and provokes a depressive state. Imbalance of microflora in the intestines also affects the emotional background.
General analysis of stool (coprogram, research code 84-84-003);
Profile “Gastropanel” (research code 99-20-303) and/or profile “Gastropanel extended” (research code 99-20-304);
Stool culture for dysbacteriosis (test code 71-84-300).
Moderate obsessive-compulsive disorder
The prognosis for the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder without appropriate therapy is unfavorable.
An important element of the treatment of OCD is psychotherapeutic assistance (cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), EMDR therapy, short-term strategic psychotherapy, hypnotherapy). Psychotherapy must be combined with medications prescribed by a psychiatrist (antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications). The Yale-Brown test for obsessive-compulsive disorder has a high degree of reliability, but cannot serve as a basic tool for determining neurotic disorder (OCD). You should consult a psychiatrist for diagnosis and treatment if necessary.
Intoxication
The presence of heavy metals (mercury, lead, cadmium, aluminum) in the body causes organic brain damage and provokes the development of severe mental disorders. With their deficiency or excess, macroelements that the body needs can also have a toxic effect. For example, magnesium deficiency causes constant fatigue, decreased cognitive function, insomnia, and irritability. In order to determine the level of metals in the body, you can have your hair analyzed.
Comprehensive hair analysis for the presence of heavy metals and microelements, 23 indicators (test code 99-50-100).
Obsessive-compulsive disorder. Yale-Brown test
The Yale-Brown technique is a common test used for preliminary self-diagnosis of obsessive-compulsive disorder (obsessive-compulsive disorder).
Living with OCD is extremely difficult. Performing obsessive actions (rituals) in order to reduce emotional stress takes more and more time, and anxiety absorbs all thoughts, interfering with normal functioning. The patient remains critical of the manifestations of the disorder, he is able to comprehend the absurdity of his behavior, but the level of anxiety caused by obsessive thoughts is too high.
The most common symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder are:
- excessive perfectionism, desire for strict order, symmetry
- fears of becoming infected or poisoned, unjustified disgust
- inability to make a choice even in minor situations
- incessant thoughts about turning off electrical appliances, etc.
You have already taken the test before. You can't start it again.
The test is loading...
You must log in or register in order to begin the test.
You must complete the following tests to start this one:
results
Time is over
Categories
- No category 0%
Changes in glucose and insulin levels
To maintain stable functioning of the central nervous system, a sufficient amount of glucose is required. Fluctuations in blood sugar levels, especially in diabetics, aggravate depression. People with hypoglycemia (sugar levels below normal) are at higher risk of developing depression. Insulin promotes the transfer of tryptophan and stimulates the synthesis of serotonin, the “hormone of joy.” To identify violations, CITILAB conducts glucose and insulin testing and calculates the HOMA index.
Assessment of insulin resistance: glucose (fasting), insulin (fasting), calculation of the HOMA-IR index (test code 99-00-860)
Severe obsessive-compulsive disorder
The prognosis for the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder without appropriate therapy is unfavorable.
Most likely, you need to take medications (antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications), which are prescribed by a psychiatrist. Also an extremely important element in the treatment of OCD is psychotherapeutic assistance (cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), EMDR therapy, short-term strategic psychotherapy, hypnotherapy). Psychotherapy must be combined with drug treatment.
The Yale-Brown test for obsessive-compulsive disorder has a high degree of reliability, but cannot serve as a basic tool for determining neurotic disorder (OCD). You should consult a psychiatrist for diagnosis and treatment if necessary.
Fatty acid deficiency
Deficiency of fatty acids aggravates symptoms of depression, especially in pregnant women, women in labor, patients with multiple sclerosis and people who abuse alcohol. Fatty acids ensure stable cell functioning and maintain the required energy level. With a lack of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, emotional instability appears, brain function and cardiovascular system deteriorate.
Unsaturated fatty acids omega-3 and omega-6 in the blood, complex analysis (test code 99-10-117).
Be healthy!
Author:
Baktyshev Alexey Ilyich, General Practitioner (family doctor), Ultrasound Doctor, Chief Physician
Extremely severe obsessive-compulsive disorder
The prognosis for the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder without appropriate therapy is unfavorable.
Most likely, you need to take medications (antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications), which are prescribed by a psychiatrist. Also an extremely important element in the treatment of OCD is psychotherapeutic assistance (cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), EMDR therapy, short-term strategic psychotherapy, hypnotherapy). Psychotherapy must be combined with drug treatment.
The Yale-Brown test for obsessive-compulsive disorder has a high degree of reliability, but cannot serve as a basic tool for determining neurotic disorder (OCD). You should consult a psychiatrist for diagnosis and treatment if necessary.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- With answer
- With a viewing mark
- Task 1 of 10
1.
The total duration of your obsessive thoughts (obsessions) during the day is:
- Task 2 of 10
2.
The degree of disruption to daily life due to intrusive thoughts:
- Task 3 of 10
3.
Level of psychological discomfort due to obsessive thoughts:
- Task 4 of 10
4.
Resistance to obsessions:
- Task 5 of 10
5.
Degree of control over obsessions:
- Task 6 of 10
6.
Your duration of obsessive actions, rituals (compulsions) during the day:
- Task 7 of 10
7.
Degree of disruption to daily life:
- Task 8 of 10
8.
Level of psychological discomfort:
- Task 9 of 10
9.
Resistance to compulsions:
- Task 10 out of 10