Electroencephalography is a neurophysiological method for recording the total electrical activity of the brain. In modern practice, a computer encephalograph, which is an analog-to-digital converter, is used to record EEG. Its purpose is to record and continuously graphically display the state of bioelectrical activity of the brain. Activity is recorded using electrodes that are commutated (connected) to the encephalograph according to certain rules. Depending on the type of study, different types of electrodes are used (scalp, invasive, for the internal cavities of the skull, etc.). A separate electrode records relatively local cortical activity, so the study uses a fairly large number of electrodes placed on a convex according to the system defined by the International Society of Neurophysiology. Since the state of bioelectrical activity depends on the functional state of the brain and changes rapidly with external stimulation, one of the important conditions is strict adherence to standard research conditions. A typical clinical EEG study includes several successive stages of recording both spontaneous (background) activity and the results of a battery of standard stress tests. The final chord is the analysis of the research results and the formation of a clinical conclusion, which is based on a specific algorithm.
Thus, EEG not only requires special technical equipment, but also has a detailed research methodology. Competent execution of EEG is based on strict adherence to the methodology. This ensures comparability of results obtained both over time in one subject and by different specialists.
Conditions for conducting an EEG
Ideally, the study should be performed in a special room - an EEG chamber. This room, along with light and sound insulation, must have another fundamental feature - shielding from external electromagnetic influences. The influence of interference, primarily network interference, is minimized. The meaning of shielding goes back to the Faraday cage: inside this shielded space, the field voltage tends to zero. Modern analog-digital equipment has a great ability to selectively reject certain frequency ranges, primarily the range of network electricity with a frequency of 50 + 5 Hz. As a result, in modern practice, the tendency to use an EEG cabinet has become firmly established, in which the conditions of sensory deprivation are maintained, but the room is no longer shielded.
Safety precautions
Grounding is the “holy of holies” of electrophysiology.
The patient must be grounded through the appropriate channel of the encephalograph!
Safety requirements require the use of grounded outlets. This grounding is called “protective”. If the EEG cabinet has a protective ground, then, as a rule, no additional measures are required when working with analog-digital systems.
In some cases (for example, an X-ray unit is connected to the protective grounding loop), it may be necessary to equip the EEG room with a separate working grounding loop. If necessary, to eliminate (reduce) electrical interference, the patient's chair (bed) can be connected to a working grounding bus. For electrical safety reasons, the patient should not connect to the bus!
Additional devices for EEG
To achieve a state of calm wakefulness during the examination, either special chairs with a headrest or a couch are used on which the patient lies lying down. The need for muscle relaxation, in addition to ensuring maximum emotional peace of the subject, is determined by the fact that tension in the muscles of the head and neck is accompanied by the appearance of electromyogram artifacts.
To perform photostimulation and phonostimulation, the encephalograph is equipped with appropriate additional devices.
The photostimulator can be a block of LED lamps or glasses with LEDs built into the frame. Photostimulation is carried out by pulses with a duration of 50 μs. The pulse repetition rate can be set arbitrarily - from 1 to 30-40 Hz. As a rule, white flashes are used. For special studies, chromatic flashes (red, blue, green) can be used. When using a photostimulation unit, its tripod should be installed so that the photostimulator is located strictly along the line of sight at a distance of 20-25 cm from the eyes of the subject.
A single-speaker phonostimulator is mounted behind the back of a chair, which is believed to provide simultaneous binaural stimulation. With separate binaural stimulation, the speakers are installed at an equal distance and at the same angle to the subject’s head, unless, of course, special studies are carried out on the lateralization of functions.
What is the essence of the EEG procedure?
An electroencephalogram records electrical signals from brain cells and allows us to identify epilepsy, trauma, neoplasms, inflammatory processes, and changes in blood vessels. Pathology is indicated by disturbances in the electrical activity of neurons, which are recorded using special sensors placed on the patient’s head.
Using an electroencephalogram, the doctor can:
- analyze the performance of the brain;
- identify foci of pathologies;
- assess the nature and extent of damage;
- confirm or clarify the diagnosis;
- monitor the effectiveness of the treatment.
If your child has been prescribed an EEG
If your child has been prescribed an EEG
Sometimes a child is prescribed electroencephalography (EEG) - what kind of study is this and why it is needed, how it is carried out, says a neurologist at the Medical
Electroencephalography (EEG) is the main method for studying the functioning of the brain and assessing its functioning. EEG allows us to identify changes in brain function in various neurological disorders, consequences of birth injuries, and hypoxia. Also, indications for an EEG are: delays in speech or psychomotor development, emotional disturbances, injuries, brain diseases.
The main elements of the central nervous system, which includes the brain, are nerve cells - neurons. They have the property of conducting and generating electrical impulses, these impulses are recorded by a device - an electroencephalograph. We can say that the electroencephalogram is a reflection of the functioning of the brain.
To conduct an EEG, you wear a special mesh cap with electrodes that record electrical impulses from the brain. Under this cap, the baby's skin is treated with a neutral gel (as for ultrasound diagnostics) or an alcohol solution in order to remove the air layer. The procedure does not cause any discomfort and is completely safe. But the child may be frightened by the preparation process. Young children, who still find it difficult to explain what will happen, usually actively resist the doctor’s actions; parents need to be prepared for this. It’s good if you can come to the study together, mom and dad. In some exceptional cases, when it is necessary to conduct a study, but it is impossible to persuade the child to put on a hat and sit quietly for a while, you even have to resort to swaddling.
The duration of the study is 25-30 minutes, of which the main time is spent preparing the child, the procedure itself is 5-7 minutes. It is important that during the procedure the child behaves calmly and does not cry. The time for the procedure should be chosen so that the child is not hungry or tired. The most convenient time for testing for infants is immediately after feeding. If the child is worried, they pause so that the mother can feed him and calm him down.
Older children need to be prepared for the examination in advance by talking about what will happen and presenting it in the form of a game. The task of parents is to interest and set the child in a positive mood. You can take a new interesting toy or tablet with you, although the results will be more informative if you can persuade the child to sit quietly and the study is carried out with his eyes closed.
Electroencephalography is a harmless diagnostic method; it can be done on children of any age, as many times as necessary. This is important because sometimes it is necessary to look at the results of studies over time in order to assess how the condition is changing and how effective the treatment is.
A conclusion based on the results of the study is made by a neurologist, usually the next day after the procedure. The diagnosis is made not only according to EEG data, but on the basis of a comprehensive examination, including examination, assessment of reactions, laboratory tests and other studies. An EEG helps the doctor get an objective picture and, if necessary, prescribe appropriate treatment.
In what cases is EEG prescribed?
After a conversation with the patient and studying the medical history, the specialist decides to prescribe encephalography. Typically, indications for an EEG are frequent headaches, sleep problems, fainting, fatigue and chronic fatigue.
Deterioration in well-being may be a sign of disorders in the functioning of the brain. The above ailments often arise due to:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head;
- inflammatory processes in meningitis and encephalitis;
- endocrine disorders;
- malignant or benign neoplasms.
For patients suffering from epilepsy who have undergone neurosurgical interventions and head injuries, EEG monitoring is mandatory.
EEG for autism: to do or not
Children with autism are usually prescribed EEG by neurologists for the following reasons:
- as an aid in the diagnosis of epilepsy accompanied by seizures (epilepsy may be associated with autism in early childhood and adolescence);
- to check for problems with dementia;
- when studying sleep disorders;
- to monitor brain activity during sleep or wakefulness.
Research shows that epilepsy is most often associated with autism.
How to prepare for an electroencephalograph examination?
Monitoring the electrical activity of the brain does not require complex training. During the examination, it is important to simply follow the doctor's instructions and remain calm. Flashes of light and noise are part of the procedure.
Three days before the examination, it is recommended to stop taking tranquilizers, anticonvulsants and sedatives. 24 hours before the examination, do not drink tea, coffee, energy drinks, or eat chocolate. The day before monitoring, wash your hair. Have a snack an hour before the examination. Before starting, loosen your hair and remove metal jewelry.
What is usually revealed during the study
The method helps to carry out differential diagnosis with a wide range of diseases. As a presumptive diagnosis, a number of diseases with similar symptoms and epilepsy (focal, temporal, frontal, parietal, etc.) can be indicated.
One of the objectives of the study is to collect indicators, decipher them and exclude the following diseases that have similar symptoms to epilepsy, but are reflected differently on the electroencephalogram:
- apnea;
- Yactation;
- hyperekplexia;
- syncope;
- parasomnias;
- paroxysmal dizziness;
- childhood periodic syndromes, infant motor stereotypies, physiological infant behavior, infantile masturbation;
- extrapyramidal disorders;
- cardiogenic pathologies;
- Fergeman's syndrome, etc.
Regular EEG video monitoring is required during patient treatment to analyze the effectiveness of the measures taken. Since the study has no contraindications and does not have a negative impact on patients, it can be carried out with any regularity. The only contraindications may be intolerance caused by an individual psychological attitude to the procedure, and some scalp diseases.
How is an EEG performed?
The examination takes place in several stages.
Preparatory stage
- the patient enters the office, protected from light and sound;
- an encephalograph “cap” consisting of special sensors is put on it;
- The sensor wires are connected to a device that records the bioelectric impulses of the brain.
Diagnostic stage
- the encephalograph transmits data to the monitor in the form of a graph;
- the power of electric fields and its distribution in different parts of the brain are recorded;
- Functional tests are carried out: the patient is asked to blink, look at flashes of light, breathe less often or deeper, listen to a sharp sound.
Final stage
- the electrodes are removed from the patient;
- print out the results.
Common advantages and disadvantages of the presented method
EEG video monitoring allows:
- assess the functional state of the brain using an electroencephalogram and accompanying human behavior using video;
- register epileptic diagnosis during an attack;
- identify the area where the attack began;
- make a diagnosis with a high degree of probability;
- determine the nature of the disease in patients with unclear attacks.
The method has no contraindications, can be performed an unlimited number of times and is highly informative. EEG video monitoring is one of the most useful tests in neurology for detecting epilepsy.
The disadvantages of the method include the daily duration and possible tediousness for children, but they are completely covered by the information content of the study.
How long does the electroencephalogram procedure take?
A regular encephalogram (routine EEG or diagnosis of a paroxysmal state) takes from 20 to 30 minutes.
During the examination, a number of tests are carried out:
- rhythmic photostimulation;
- hyperventilation;
- load in the form of slow blinking.
If it is necessary to evaluate certain brain functions, the specialist adds additional tests, which he informs the patient about in advance. Such tests include:
- clenching your fingers into a fist;
- being in the dark;
- sleep deprivation for a certain period;
- night sleep monitoring.
General description of the study
Electroencephalogram + video is an additional research method that helps confirm the diagnosis of epilepsy and determine the form it has taken. It is applicable to an adult, neonatal or preterm infant to assess the severity of encephalopathy.
The purpose of the method is to record a paroxysmal event on the electroencephalogram and study it for differential diagnosis with similar conditions (parasomnia, stereotypy, cardiogenic pathologies, etc.). Many convulsive conditions have manifestations similar to epileptic ones, and EEG video monitoring helps to recognize their non-epileptic nature on the electroencephalogram and avoid expensive treatment with side effects.
Several types of EEG video monitoring are used in neurology:
- hourly;
- daytime - lasts 4-6 hours, suitable for monitoring treatment or studying brain activity in a young child (requires a period of sleep during it);
- night - lasts 9-12 hours, for example, from 21.00 to 6.00, records night attacks;
- daily - carried out with intensive functional tests and special tests;
- ten days - helps to record several attacks (it may turn out that they have different localization and origin) and examine the period between them.
Daytime EEG video monitoring is carried out when attacks occur mainly during the daytime, or to monitor treatment. Nighttime is prescribed if daytime sleep is impossible due to personal characteristics, and attacks occur only during sleep.
During the study, it is imperative to fall asleep, since in the first and second phases of sleep, epileptic activity increases, and the likelihood of noticing it or the attack itself on the electroencephalogram increases.
The result of the diagnosis is an electroencephalogram and a video recording all the patient’s movements. The study is carried out in the ward. The patient should behave normally and try to relax. Drugs that induce sleep are not used, but the drugs that the patient usually takes during treatment are not canceled and are used as usual.
Interpretation of survey results
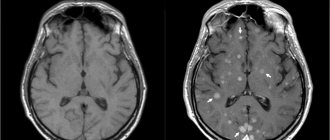
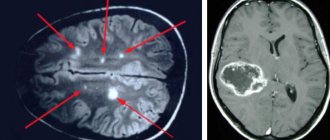
Even a qualified specialist is not always able to accurately name the cause of the patient’s poor health and immediately make a diagnosis. The doctor may be alerted to focal changes on the EEG. In this case, magnetic resonance imaging will be required to exclude a tumor or cyst.
When you contact a medical doctor, you will be able to undergo all examinations as quickly as possible, without delaying your visit to specialists.
If you need to do an EEG of the brain and you want to do it using modern expert-class equipment and in the shortest possible time, call the phone number listed on the website or leave a request in the feedback form.
Medical staff will answer your questions and conduct all necessary examinations within one business day. Let's take care of your health together!
Who is prescribed such a study?
EEG video monitoring is intended for diagnosing diseases in patients with seizures, a child in the neonatal period, and a premature baby. The method shows the epileptic or non-epileptic nature of seizures, their type (focal, generalized), specific features, form of epilepsy, localization of seizures.
EEG video monitoring is prescribed for:
- suddenly appeared and previously absent convulsive attacks;
- paroxysmal states, the origin of which is unknown;
- behavioral and cognitive disorders in children that progress over time;
- preparation for anticonvulsant therapy or surgery (if anatomical causes of epilepsy are detected), monitoring therapy.
Other reasons for using this method in neurology: before discontinuation of AEDs, in intensive care conditions - establishing the type of coma and diagnosing brain death.
It is recommended to consult a doctor in case of convulsive attacks of unknown origin, disorders of consciousness (including during the period before menstruation), fainting, sleep disturbances, headaches, dizziness, speech delay, and decreased cognitive functions.
Decoding EEG indicators in an adult
In order to decipher the EEG and provide accurate results, without missing any of the smallest manifestations in the recording, neurophysiologists take into account all the important points that may affect the indicators being studied, such as:
- patient's age;
- the presence of certain diseases;
- possible contraindications.
After collecting all the EEG data and processing it, the functional diagnostics doctor conducts an analysis and generates a final conclusion, which he provides for making a further decision on the choice of therapy method. Any disturbance in activity may be a sign of diseases caused by certain factors.
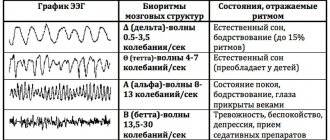
EEG disorders are considered:
- constant fixation of the alpha rhythm in the frontal lobe;
- constant violation of wave sinusoidality;
- presence of frequency dispersion;
- exceeding the difference between the hemispheres by up to 35%;
- amplitude below 25 μV and above 95 μV.
The presence of violations of this indicator indicates possible asymmetry of the hemispheres. This may be the result of malignant neoplasms or cerebral circulatory disorders (ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke). A high frequency indicates traumatic brain injury or brain damage.
If a high amplitude of the delta rhythm is detected, the neurophysiologist can assume the presence of a space-occupying tumor in the brain. Inflated values of the theta and delta rhythm, which are recorded in the occipital region, indicate impaired circulatory function, inhibition and a delay in the development of the child.