According to statistics, depression develops less often in men than in women, but its manifestations can be more dangerous. Men in a depressed state often make attempts to commit suicide, and, unfortunately, these attempts are usually realized.
In order to prevent the death of a loved one, a woman needs to be especially attentive to him during difficult periods of life. Why does the disease develop, how to deal with it, and what to do if a man shows signs of a depressive disorder? , a psychiatrist and psychotherapist at the MEDSI clinic on Leninsky Prospekt, spoke about this .
Symptoms of depression in men
Psychiatry does not divide depression into male and female. This condition manifests itself equally in all people, regardless of gender and age. Signs of depressive disorders are formulated by the international classification of diseases. And if you notice one or more of them in a loved one, you should be wary.
It’s worth paying attention if a man has stopped enjoying those things that gave him pleasure before. For example, he happily went fishing, but now he refuses to do it. Or if he is increasingly in a bad, depressed mood, he tries to leave the house as little as possible, and in his free time he prefers not to get out of bed.
In addition to the external signs of depression in a man, there are also internal ones. “Boys don’t cry” - this is how men are raised in modern society. But precisely because of this, all the internal experiences that torment a person and increase melancholy are not brought out. Men are not used to discussing problems with their wives and girlfriends. And with depression, multiple negative thoughts may arise:
- about personal or professional insolvency;
- about the lack of prospects in life;
- feeling of guilt.
Against this background, attention decreases and intellectual functions deteriorate. The person becomes distracted and cannot remember important information or concentrate on important work. There is also a decrease in sexual desire for the spouse, sleep is disturbed, and appetite usually decreases.
pixabay.com/
My husband has depression: what to do?
It is important to understand that a man himself will never admit that he has depression. Therefore, at her first, the wife and all her close circle should show activity. The ideal option is to immediately consult a psychiatrist.
For minor symptoms of depressive disorder, the following may help:
- distraction from everyday problems with a family vacation or trip;
- involvement in active participation in public and family affairs;
- refusal to reproach and/or ignore;
- encouragement, gratitude for doing even a small thing, raising a man’s self-esteem;
- creating a friendly atmosphere in the house;
- new positive emotions;
- involvement in the sports world (regular participation in sports).
It is necessary to convey to your spouse that it is impossible to insure against depression. But the following will help reduce its manifestations:
- Discussion of the problem - you should not withdraw into yourself. Discussing your worries with someone close to you reduces your fears by half.
- Physical exercise - any physical exercise stimulates the production of “happiness hormones”.
- Taking part in the lives of loved ones - interest and activity in family life or in your close circle distracts from your own experiences.
- Hobby - a hobby allows you to spend your free time to your advantage.
If all these measures do not help, do everything in your power to get your husband to see a psychiatrist.
Causes of the disease
These manifestations become a “marker” of processes that occur inside the body. Scientists have not yet figured out the causes of depressive disorders, but they agree that dozens of biologically active substances in the body are involved in them.
Clinical depression in men is not just a bad mood. This is a disease that affects the hormonal and immune systems, but mostly affects the functioning of the brain, as it disrupts the production of neurotransmitters responsible for emotions, reaction speed and performance.
Some external “push” usually leads to the development of depression:
- problems at work;
- dismissal;
- dissatisfaction with personal relationships;
- lack of career growth and financial well-being.
At different ages, the reasons may be different, but the processes occurring in the body of a man at 30 years old with depression do not differ from those at 40 and 50 years old. An external push triggers a cascade of biochemical reactions in the body, and it is not always possible to stop them on your own, without the help of a specialist.
pixabay.com/
Test for symptoms of depression in men
Psychiatrists diagnose the disease and determine its severity. It is difficult to make a diagnosis on your own, as well as to develop treatment tactics. Despite the fact that there are enough tests on the Internet for diagnosing depressive conditions and various scales, this method alone is not enough to clarify the diagnosis.
“In psychiatry, a diagnosis is established based on a person’s current mental state, life history and examination using tests,” comments psychiatrist Christina Wirth. “A diagnosis can only be made based on a combination of factors.”
At the appointment, the specialist evaluates the person’s behavior, clarifies the life history, causes and duration of the depressive state, and offers to fill out a test as an additional diagnostic method.
For self-completion, the patient uses the Aaron Beck test, where you need to select answers from groups of statements based on your condition over the past week. Another well-known test for diagnosing depression is the Hamilton Scale; it is completed by a doctor based on a professional assessment of the patient’s condition and behavior. This test is not suitable for self-diagnosis.
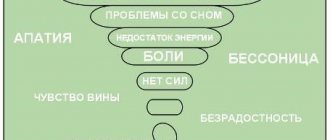
Depression symptoms
For each person, signs of depression can manifest themselves differently, it all depends on the stage and form of the pathology. Symptoms occur at different levels, affecting all aspects of the emotional sphere and behavioral reactions of the patient.
Emotional manifestation:
- deep depression is accompanied by a loss of the ability to experience simple human feelings (anger, joy, surprise, fear);
- there is no interest in surrounding events and people;
- those activities that previously evoked pleasant emotions are of no interest to the patient at all;
- a person is dissatisfied with himself, his appearance;
- lack of self-confidence, low self-esteem;
- constant feeling of guilt, even if the objective reason for this is not determined;
- the patient often blames himself for everything, without necessarily saying it out loud;
- increased irritability, nervousness;
- depressed and depressed mood;
- often falls into despair;
- the patient is characterized by melancholy and suffering;
- the feeling of internal tension increases;
- a subconscious expectation of trouble arises;
- increased anxiety even in the absence of any reason.
Fears about the health of loved ones are constantly present in depressed patients. They understand that they cannot do or change anything in this situation. Anxiety is also associated with fears of appearing stupid or ineffective in the eyes of the public. Going to a psychiatric clinic is the first step on the path to recovery.
The manifestation of the disease at the physical level is expressed in the following:
- sleep disturbance (constant daytime sleepiness or insomnia);
- complete loss of appetite or uncontrolled eating;
- decreased libido, sexual needs cease to interest the patient;
- disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (constipation or diarrhea);
- increased fatigue and chronic fatigue;
- decreased energy level, exhaustion, feeling of lack of strength.
Even with ordinary physical or intellectual stress, general weakness of the body, unpleasant sensations in the body and pain of varying intensity occur.
Behavioral symptoms of depression:
- it is impossible to involve a person in any activity that involves the implementation of a certain algorithm of actions;
- he refuses entertainment;
- There is a tendency towards solitude and avoidance of social contacts.
A depressed state can change the intensity of cognitive processes:
- there are difficulties when trying to concentrate on any subject;
- concentration suffers;
- the patient experiences problems if he needs to make some decision and cannot rationally “weigh” the risks;
- he constantly doubts whether he is doing the right thing, turning over the situation in his head, and in the end he never comes to a definite opinion;
- constantly thinks about his own helplessness, insignificance for others;
- thinking is slow, which is very noticeable to others;
- in severe cases, thoughts of suicide occur, and the likelihood of committing it is high.
If there are two or more symptoms from this list, and they are observed in the patient for 2 weeks or more, the doctor may diagnose depression. The selection of effective treatment depends on which type of disorder the patient has:
- Dysthymia.
This is a mild variant of the disease, which begins in adolescence and is formed against the background of intrapersonal conflicts, problems with parents, and constantly changing hormonal levels. People around him believe that this is a manifestation of a difficult character; such a person is called a melancholic or a pessimist.
- Depressive episode.
This condition arose in the patient for the first time in his life; it did not have time to develop into a severe form. A short-term but memorable case of total sadness, exhaustion, lack of interest in everything that was happening.
- Bipolar affective disorder.
Characterized by alternating moments of bad mood and pathological joy, the patient’s life is constantly between these two poles. He seems to float on the waves of mood, constantly moving from one peak of emotions to another.
- Recurrent depressive disorder.
These episodes recur every few years, after which they may go away on their own. The pathology must be treated in a psychiatric center for a long time with the help of psychotherapy and periodic courses of medications.
How can a man get out of depression on his own?
Despite the fact that depression was included in the international classification of diseases quite a long time ago and was recognized by the world medical community as a dangerous disorder, many people, especially in Russia, still do not take it seriously.
They think it will go away on its own, compare it to laziness, or accuse a person suffering from a depressive disorder of being spineless and irresponsible. And this is a huge risk, since without proper help, mental problems will only get worse. And against their background, the accompanying “responses” of the body will develop.
pixabay.com/Pexels
“Since depression is based on an imbalance of bioactive substances, hormones and even the immune system, it increases the risk of dangerous diseases,” says Christina Wirth. “Against a background of depression, the risk of cardiovascular diseases and infectious diseases increases.”
It is important to take into account that you can get out of depression on your own only if it developed against the background of a problematic situation and at some point the problem was resolved. This improves a man’s emotional state and helps him regain his zest for life. If the problem is “prolonged”, depression develops over a long time, and it becomes impossible to get rid of it on your own.
After all, physiological processes are added to the psychological disorder, hormonal imbalance occurs, and the production of neurotransmitters in the brain is disrupted. And to correct the condition, the help of a specialist is needed. Otherwise, improvements may be temporarily observed against the background of the disease, but depression will regularly return and intensify for no apparent reason.
“Self-healing is possible with mild depression,” comments the doctor. — The maximum you can do on your own is to find psychological literature, self-help manuals, read them, try to work with yourself. But there must be a will for this, there must be faith in one’s own strength, and the aid itself must be professional.”
pixabay.com/
Depression causes
According to statistics, about 90% of diagnoses are made to people who are in a state of chronic stress or experiencing acute psychological trauma. The body cannot cope with this influence of external factors on its own, the psyche fails, depressive episodes are a kind of defensive reaction.
Conditions arising due to severe psychological trauma are considered reactive. They can be triggered by the following events in the patient’s life:
- disability due to health and absence of serious illnesses;
- detection of a malignant tumor;
- conflicts at work, constant tension in relationships with colleagues;
- serious illness of a close relative;
- death of a loved one;
- divorce from your beloved spouse;
- retirement;
- rapid decline in financial levels;
- moving to another city and other factors that can be a real shock for a person.
Depression is not always formed on the basis of negative events. Sometimes the disease occurs when an important life goal is achieved, when a person experiences great success. The patient gets what he wanted. He suddenly loses the meaning of life, he no longer needs to make every effort for a specific result. The situation is aggravated if there are no other life goals at this moment.
A separate category includes depressive neurosis, which develops against a background of constant stress. In this case, it is not always possible to establish the specific cause that became the trigger for the pathology. The patient describes his life as a chain of constantly recurring failures that haunt him every day.
A depressive state of the psychogenic type is more typical for women, while older people suffer from the disease more often than young people. In our society, there are two extreme poles of financial well-being - poverty and wealth. This social scale causes a person to feel dissatisfied with himself if he constantly approaches the first category.
Additional provoking factors will be:
- pessimistic outlook on life;
- low self-esteem, constant self-flagellation;
- loss of parents, loved ones, friends;
- emotional violence against a person;
- physical aggression that the child experienced at an early age;
- predisposition to drug addiction and alcoholism;
- lack of support from others, their indifference towards the person.
Each of these factors in itself is not dangerous; if desired, a person can easily ignore it or seek help from a psychotherapist. If there are several of them, the situation becomes more complicated, the experiences become more intense and acute. In this case, drug treatment may be required.
For example, in a teenager, the period of growing up is associated with intensive growth of all organs and systems; pregnancy and menopause in women are accompanied by hormonal storms. This is fertile ground for the development of a melancholic mood and ever-increasing dissatisfaction with oneself. During these periods, experiences take on a negative connotation; the world around often seems hostile and indifferent.
Organic brain lesions, as well as physical diseases, are classified into a separate category. Cerebrovascular accidents, strokes and heart attacks, traumatic brain injuries, coronary heart disease, and stomach ulcers are also among the sources of depression listed by experts. Against the backdrop of the development of such diseases, depression manifests itself clearly and clearly.