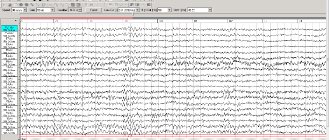
Our center performs EEG (electroencephalogram of the brain), including a full neurological protocol and with sleep deprivation. The study allows you to diagnose pathology in the functioning of the vascular system of the brain and nervous system. The interpretation of the study results is carried out by the doctor immediately after the completion of the EEG, and does not take more than 15–20 minutes.
In particular, the method allows you to determine:
- epileptic activity characteristic of different lobes of the brain;
- probable cause provoking panic attacks and loss of consciousness;
- location of pathological foci in certain lobes of the brain;
- the degree of change in the electrical activity of the brain before attacks.
Also, an electroencephalogram of the brain allows you to find the cause of neurology in a person (is it a functional disorder or caused by an organic lesion), assess how effective treatment and rehabilitation are - then an EEG is done 3 times: before treatment, during therapy and after its completion.
| Service | Price |
| Electroencephalogram (EEG) | 2000 |
| EEG with sleep deprivation | 4000 |
| Urgent EEG interpretation | 300 |
Our address: St. Petersburg, st. Marata, house 78.
Our phone: +7 (812) 385-55-82.
Opening hours: from 9:00 to 21:00.
We work by appointment.
EEG is performed on modern medical equipment that meets international (ISO) and European certification - Mitsar and Neurosoft.
When is it necessary to do an EEG?
Before doing an electroencephalogram, the doctor examines the patient and listens to complaints. The basis for the study may be:
- sleep disorders - for example, insomnia;
- frequent awakenings and sleepwalking;
- frequent attacks of dizziness and fainting;
- fatigue and feeling tired;
- headaches that occur for no reason.
Even a seemingly insignificant deterioration in a person’s well-being may indicate irreversible negative processes in the GM. Based on this, it is extremely important to do an EEG in the following cases:
- vascular diseases of the cervical region of the head;
- VSD;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- post-stroke condition;
- speech delays;
- logoneurosis;
- autism;
- inflammation of the brain;
- hormonal disorders;
- suspicion of cancer.
Brain EEG is mandatory for patients with TBI, epilepsy, or who have undergone neurosurgery.
VEM procedure
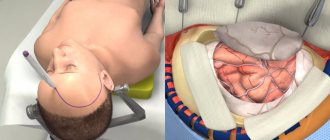
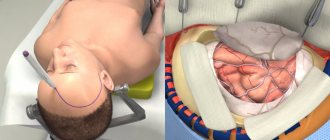
Video EEG is a completely harmless and painless study. To carry it out, small electrodes are applied to the patient's head and secured to it using a soft rubber cap. The electrodes are connected via wires to an electroencephalograph, which amplifies the electrical signals of brain cells received from them by 100 thousand times. Wall-mounted video cameras provide constant monitoring of patient behavior. The EEG and video signal are transmitted to the control room, where the EEG curve, after digital processing, is sent to a video monitor. EEG and video recordings are shown simultaneously in real time and recorded on digital media for subsequent processing.
During the examination, the patient lies or sits in a comfortable diagnostic chair, relaxed, with his eyes closed. Usually, when taking an EEG, so-called functional tests (photostimulation and hyperventilation) are performed, which are provocative loads on the brain through bright flashing light and increased respiratory activity.
In our center, two wards operate around the clock, where both daytime and nighttime Video-EEG monitoring is carried out. During daytime VEM, the patient has the opportunity to read, listen to the radio, play board games, eat, etc. within the premises where Video-EEG monitoring is carried out. To conduct night VEMs, each room has a sleeping place for the patient and, if necessary, for an accompanying person.
In our center, in addition to daytime and nighttime VEM, you can do any type of routine EEG. Long-term electroencephalography (30 minutes, 1 hour) is performed on high-tech equipment taking into account modern standards in neurology and epileptology, which also increases the information content of this method. Parallel video recording is possible.
How is an electroencephalogram performed?
According to global practice, EEG of the brain in St. Petersburg is carried out using an encephalograph. It includes a processing unit, a monitor and a set of electrodes mounted in a rubber “cap” worn on the head. EEG is carried out in a compact room, protected from light and noise from outside. The procedure is quick and consists of several stages.
Preparation
First, the subject chooses a comfortable position - reclining or sitting. Next, you put on a cap with electrodes that record the electronic activity of the brain.
Study
During an EEG of the brain, the device reads data from the electrodes, forming a graph based on it that is displayed on the monitor. In some cases, a series of functional tests is carried out: the subject must blink, look at flashes of light, change the breathing rhythm, listen to certain sounds.
Completion of the study
At this stage, the electrodes are removed, the results of the study are printed, and a transcript is made.
Duration of the study
An electroencephalogram in St. Petersburg lasts depending on the need for functional tests and the area of the brain being studied. On average, an EEG is performed in 20–30 minutes using:
- rhythmic photostimulation of various frequencies;
- hyperventilation (the subject will have to breathe deeply and rarely);
- loads in the format of slow blinking (opening and closing the eyes on command).
In addition, at this time, functional changes that occur covertly are detected.
EEG video monitoring day and night: in what cases is it prescribed?
Night EEG monitoring is prescribed by a neurologist in cases where attacks occur only at night or the patient cannot fall asleep during the day. Carrying out a diagnostic study is relevant if differential diagnosis of an epileptic convulsive condition is necessary, which cannot be determined by any other method.
Application of electroencelograph in neurology
The electroencephalograph is used in medicine to diagnose various neurological pathologies. When carrying out monitoring, the reaction of the cerebral cortex to external and internal stimuli is observed. The nervous system is examined. Using this device, it is determined how correctly the brain works and whether there are any disorders.
If the electroencephalograph detects abnormalities, pathology is detected, after which an accurate diagnosis is established. During monitoring, the form of epilepsy, Alzheimer's disease and degenerative changes in the brain are determined. With the help of such diagnostics, treatment is monitored. Doctors determine whether changes have appeared in the patient’s body after treatment.
EEG monitoring is prescribed to a patient who has the following symptoms or complaints:
- disturbed sleep (constant drowsiness during the day or insomnia, nightmares);
- fainting conditions;
- regular headaches;
- tinnitus, stuffy ears;
- epileptic seizures;
- emotional stress, mood swings.
In addition, EEG is performed in the following cases:
- determination of the form of epilepsy;
- differential diagnosis of paroxysmal conditions (presence of non-epileptic seizures, including: nervous tic, psychogenic attack, panic attack, night terror, “sleepwalking”).
The type of epileptic seizures, which are focal and generalized, is specified. A patient examination may be ordered before surgery. Monitoring monitors the effectiveness of antiepileptic therapy. The issue of stopping or replacing certain antiepileptic drugs is often decided.
What kind of video-EEG monitoring will be prescribed - night or day?
The differences between the studies are the duration of the study and the time of day at which video-EEG monitoring is carried out. Below is detailed information about the diagnostic test, its advantages and disadvantages.
Both the night and day methods clarify the nature of the attacks and the form of epilepsy. Differential diagnosis of epilepsy also determines other non-epileptic seizures, including: metabolic disorders, psychogenic and cardiogenic seizures, disturbed behavior during sleep. The study determines the risk of developing recurrent convulsive conditions.
According to epileptologists, the increased duration of the study increases the information content. The decision on the duration of the diagnosis is made by the attending physician.
Routine EEG
Primary diagnosis reveals paroxysmal disorders in the brain. In this case, various stress tests are performed, including photostimulation and hyperventilation. Photostimulation allows you to visualize the brain and nervous system's response to flashing LEDs. Hyperventilation, in turn, tests the body for formed breathing of a specific frequency.
The advantages of the study include its short duration. The minimum monitoring duration is 30 minutes, which is suitable for examining small children or busy people. A significant disadvantage of routine EEG is the minimal information content. This diagnostic method is not enough to establish a diagnosis and determine the etiology of the disease.
EEG monitoring with deprivation (lack of sleep)
- Video-EEG monitoring, in addition to recording while awake, must necessarily include recording during sleep. During an overnight study, this usually does not cause difficulties.
- For daytime research, preparation is required - the so-called. sleep deprivation: on the eve of the study, it is advisable to significantly reduce the duration of night sleep (go to bed later than the usual bedtime by at least 2 hours and get up in the morning also earlier than the usual time of rising by at least 2 hours).
- It is very important to prevent your child from dozing off in transport on the way to the study.
Long-term EEG monitoring with daytime sleep recording
The examination is carried out on an outpatient basis. The patient is in the clinic from 5 to 12 hours. The duration of the study depends on the indications and prescriptions of the attending physician. The visualized results of the study are quite informative, which is a significant advantage. The doctor identifies brain disorders and other pathologies. The downside is that not all people can fall asleep during the daytime. The cost of the study depends on the duration.
EEG monitoring of night sleep
Most patients are indicated for overnight monitoring. The study provides the most informative results, showing the state of the brain during wakefulness, in a state of drowsiness and night sleep, and at the moment of awakening. The duration of the study varies from 10 hours or more. EEG monitoring is carried out in stationary conditions.
The advantage of the study is that it is informative, which allows the doctor to make an accurate conclusion. During the examination, even specific disorders are recognized that cannot be detected during routine EEG.
Daily EEG monitoring
The 24-hour examination is called Holter EEG monitoring. The study is carried out in stationary conditions. Duration ranges from 18 hours or more. A cap with electrodes is placed on the patient's head. The wires are connected to a holter receiver, which is attached to the patient's body. The study is carried out in a state of normal functioning. The patient's condition is determined when exposed to natural stimuli. Such violations occur to a person in everyday life.
Multi-day EEG monitoring
A diagnostic study of the cerebral cortex is carried out using a Holter EEG device, which records the study on a memory card. Recording stores data that records brain activity at different moments. Additionally, EMG and ECG sensors are installed. The patient's snoring, breathing, and chest condition are recorded. Video recording is being carried out. The patient's physical condition and EEG indicators are compared.
Full monitoring of the state of the brain is carried out. It is possible to conduct the study at home rather than in a hospital, which eliminates the psychogenic factor. According to medical professionals, preference is given to overnight or 24-hour monitoring. The diagnostic technique depends on the patient’s condition and the presence of complaints. If fainting occurs during the daytime, daytime monitoring is performed.
Additional Information:
- Preparation for video-EEG monitoring
- How is video-EEG monitoring performed?
EEG with sleep deprivation
EEG with sleep deprivation is a type of electroencephalography in which sleep time is limited or interrupted multiple times at night followed by falling asleep. This is used in cases where the patient’s EEG in a normal state does not reveal pathology in brain activity. This type of study is 30% more accurate than traditional EEG and is more effective in relation to the following types of pathologies:
- epilepsy;
- episyndromes;
- syncope;
- sleep disorders;
- insomnia;
- sleepwalking and dream-talking.
EEG with sleep deprivation can last from 1.5 to 3 hours.
What you need to know about preparing for an EEG
To do an EEG in St. Petersburg, the patient does not need to prepare for a long time. The main thing is to strictly follow a number of recommendations necessary to obtain reliable results:
- Avoid taking anticonvulsants, sedatives or stimulants at least 3-4 days before the procedure;
- limit your consumption of tea, coffee, chocolate and energy drinks;
- eat a heavy meal 2 hours before the EEG, since hunger and a decrease in blood sugar against its background distorts the diagnostic results;
- When conducting an EEG during sleep, the night before the study, you are prohibited from sleeping.
The patient's head must be washed and free of cosmetics, the hair must be dry, and if it is long, it must be loose. Metal jewelry must be removed. The patient should be calm and not react to sounds or flashes of light. An electroencephalogram of the brain must be carried out during periods of mental calm - any experiences, nervous shocks and breakdowns a few days before the study should be excluded.
What is cerebral electroencephalography (EEG)?
Bioelectric activity of the brain can be recorded using electrodes placed on the surface of the patient's head. This study was called electroencephalography, abbreviated EEG (electro- + Greek encephalos - brain + Greek grapho - writing).
The set of visual curves (patterns or patterns) obtained during an electroencephalographic study is called an electroencephalogram (EEG)
. This diagnostic neurophysiological technique makes it possible to understand whether the brain is functioning normally or whether it has paroxysmal and/or pathological activity.
Electroencephalography is used as an additional diagnostic method for a wide range of diseases of the central nervous system, endocrine pathology, and even for diseases of internal organs (for example, for differential diagnostic purposes, for bronchial asthma and diabetes mellitus).
This method is widely used when conducting initial and periodic medical examinations in certain types of professions associated with a high risk of occupational injuries (aviation, railway transport, road transport, etc.).
For epilepsy and epileptic syndromes, EEG is
the main method of functional diagnosis.