Price list Doctors clinic
Echoencephalography or Echo-EG of the head is an ultrasound diagnostic method that is used to identify pathological processes and changes in the structure of the brain. It is based on the ability of tissues to reflect ultrasonic waves and has almost no contraindications due to safety. The method demonstrates indirect signs of pathological changes.
The examination takes no more than 15-20 minutes, does not cause pain or discomfort, which makes it popular when examining young patients. Quite rarely used in adult neurological practice.
Indications for Echo-EG
A therapist, neurologist or other specialist can refer you for echoencephalography for the purpose of primary diagnosis in cases of brain diseases or suspicion of them. One of the important reasons for the procedure is emergency cases (including TBI) that threaten a person’s life. The examination allows you to detect the following changes and disorders:
- volumetric brain lesions;
- foci of hemorrhage, intracranial hematomas;
- abscesses, purulent inflammation of tissues;
- indirect signs of intracranial hypertension;
- indirect signs of hydrocephalus.
Using echo-EG of the head, it is possible to assess the dynamics of treatment. Thus, the following symptoms and conditions may be the basis for the procedure:
- previous injuries and bruises, suspected concussion, hematomas, etc.;
- attacks of nausea not caused by pathology of the digestive system;
- dizziness, repeated fainting;
- noise in ears;
- decreased performance;
- paresthesia, tingling in the upper or lower extremities;
- sleep disorders: drowsiness, intermittent, superficial sleep, nightmares, etc.;
- frequent headaches;
- neurological reactions: enuresis, stuttering, tics, automatisms, etc.
The procedure can be prescribed for already identified diseases as a tool for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment. It can be repeated the required number of times without restrictions, unlike radiographic diagnostic methods. Echo-EG of the head can be performed after surgical interventions. In this case, it is important to wait for the skin to heal and then begin the study.
Echoencephalography can be the first diagnostic step and precede studies such as CT and MRI. In other cases, Echo-EG replaces these methods and serves as the only diagnostic method, for example, if there are contraindications to other examination tools.
Why do children need an EEG?
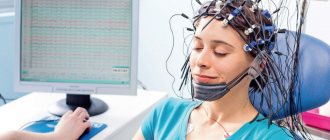
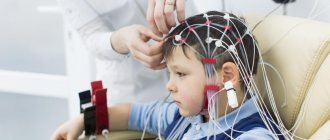
Electroencephalography is a research method that allows you to assess the functional state of the brain. The essence of this method is to record electrical activity from the cerebral cortex using electrodes that are installed in certain areas on the surface of the head. This method allows us to assess the functioning of the central nervous system, identify any disturbances, characterize them and identify the degree of disturbance.
Indications for this research method are:
- various forms of epilepsy. EEG allows you to track the dynamics of the disease and monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment;
- various convulsive syndromes;
- respiratory attacks in a child;
- delayed speech and psycho-speech development of the baby, mental disorders;
- headaches, dizziness of unknown etiology;
- children with organic damage to the central nervous system, with cerebral palsy, with autism;
- sleep and memory disturbances, if parents notice a deterioration in their child’s performance at school;
- children with enuresis, logoneurosis;
- cerebrovascular accidents, including traumatic brain injuries and the consequences of these injuries;
- inflammatory process caused by neuroinfections;
- neoplasms – tumors, abscesses, hematomas;
- panic attacks in children;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- neurocirculatory distances and encephalopathy.
These and many other disorders in the functioning of the central nervous system are an indication for electroencephalography in a child.
Order of conduct
No special preparation is required for echoencephalography. You can lead your usual lifestyle, there are no restrictions on diet or medication.
The procedure is performed in a lying or sitting position. It is important to keep the head still, so when examining the child, parents can be present in person and help the baby not move. A special gel is applied to the scalp to improve the conductivity of the ultrasound signal, then the doctor installs the sensors.
Depending on the tasks, a specialist can install one sensor or use two located on both sides of the head. The result of this diagnostic method is a graphic image that shows whether the midline structures of the brain are displaced or whether there is an expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces.
Echo-EG of the brain: what is it and why do it?
EchoEG of the brain is a highly effective innovative diagnostic technique. Its implementation is based on the ability of organ tissue to reflect ultrasonic waves.
This examination is prescribed to assess the condition of the textures of the substance, identify their displacement, establish the existence of anomalies, as well as the degree of their severity.
The scan is performed non-invasively and is completely painless. Its essence is the delivery of high-frequency electrical impulses to special plates attached to the head of the subject. Impulses are transmitted to tissue. The signal is reflected from them as from natural obstacles, and the information is recorded by the device.
Based on the results of the study, a graph is obtained on the screen - an echoencephalogram.
Some areas and tissues of the brain reflect the signal differently, and therefore produce different data on the monitor. That is why, thanks to this property of Head Echo, every structure and area of the brain, the condition of blood vessels, and pressure levels are assessed.
Indications for testing
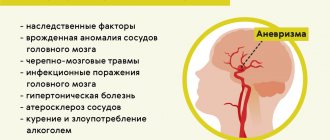
The reason for referring a patient for echoencephaloscopy may be suspicion of the following pathological processes:
- benign tumor and cancer,
- tuberculosis, coronary disease, ischemic stroke,
- blood flow disturbance,
- hemorrhage,
- organ abscess,
- edema.
A referral for a head echo is given when the patient experiences similar symptoms:
- intense, constant migraines,
- disorientation,
- sudden loss of consciousness,
- persistently high intracranial pressure,
- signs of pre-stroke and stroke,
- shortness of breath, inability to take a deep breath,
- sleep disturbance,
- stuttering, athetosis,
- loss of strength, loss of attentiveness,
- nausea,
- humming and ringing in the ears.
The examination is prescribed after traumatic brain injuries, when defects of the cervical vertebrae are detected.
With the support of Echo-EG of the brain, the effect of the prescribed treatment is assessed and the patient’s condition is assessed.
How to prepare
There is no need to prepare for the study at all. Echoencephalography is not prohibited during pregnancy and lactation; echoEG is not dangerous at any age.
Before the examination, it is only important to wash your hair, and you can go to the diagnostic room.
If the patient is taking medications, it is necessary to consult a doctor, since some medications must be stopped several days before the examination.
When performing an EEG on young children, it is necessary to have parents present who will hold the child’s head and will always be able to calm the baby down. Before diagnosis, the baby should be fed so that he does not get hungry or cry.
What does the Head Echo show?
Echo-EG (or -ES) allows you to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis and monitor the dynamics of pathological processes, and therefore the method is widely used in neurology, surgery, therapy and other areas of medicine.
The technique reveals:
- cystic, tumor neoplasms, foreign bodies, abscesses,
- pathology of the central nervous system (CNS),
- dysfunction of the ventricles of the brain,
- tissue heterogeneity, hematomas.
The essence of the study
The human brain plays a major role in the functioning of the entire nervous system. A slight malfunction in the functioning of this organ can lead to disturbances in the coordination of the human body. A thorough examination will help identify the causes of the disease.
Echoencephalography of the brain is a reliable and accessible method of research presented in medicine. The procedure is absolutely painless. It can be done at any age.
Not everyone has an idea about the features of this examination method and where it is carried out. Many people are interested in how this procedure is done and what are the indications for diagnostics.
Echo EG is practically no different from ultrasound (ultrasound). Echoencephalography of the brain or echoencephaloscopy (EchoES) is based on the reflection of ultrasonic waves from the tissues of human organs.
Sensors installed on the patient's head transmit waves to each other, which are reflected from the surface and internal structures of the brain. These waves are converted into an electrical signal, which is recorded by a specialist in the form of an image or diagram on the screen. This method gives an accurate picture of the condition and pathologies of the brain.
Electroencephalography allows you to learn about vascular diseases and the causes of improper cerebral circulation. The method helps to assess the lumen and tone of the veins.
A head echo is a non-invasive type of examination, so it is often used to quickly establish a diagnosis in an emergency. This examination should not be confused with the echocardiography procedure, which is used in heart studies.
The use of echoencephalography in childhood
The procedure is completely painless. This is the main advantage of EchoEG. The research process is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations or discomfort. This makes this type of examination convenient for diagnosing various pathologies in a child.
Echoencephalography is used in children with the following disorders:
- to assess the degree of hydrocephalus of the brain;
- with significant sleep disorders;
- with nervous tics;
- with delays in speech and physical development;
- with muscle hypertonicity;
- with urinary incontinence;
- for bruises and concussions.
In children under one and a half years old, it is possible to make a more accurate and complete diagnosis of all parts of the brain, since before this age the fontanel has not yet completely healed.
Also, to identify malfunctions in the brain in children, the EEG (encephalogram) method is used. This study captures biological neural currents and helps identify the causes of epilepsy in brain activity.
Where can I make an Echo Head?
This type of disease testing is offered by specialized clinics in many Russian cities. The study is prescribed by a neurologist.
Doctors have been using echo EG for many years. This is the only method of brain research that has no contraindications. It allows you to identify pathologies when magnetic resonance or computed tomography are unavailable for one reason or another. The procedure does not cause discomfort and there are no side effects after it. The only drawback of this diagnostic method is that it does not detect small pathologies, unlike CT or MRI, which help diagnose the disease in the early stages.
What is the essence of the procedure
Echoeg is based on ultrasonic waves, which, upon reaching the tissues, are reflected and recorded by sensors. Sensor plates are placed on the patient's head. They form ultrasound, spreading to the structures of the brain and skull. When the signal reaches the interface between the brain and the skull, or between the ventricle and the medulla, it undergoes echolocation and is reflected back. The returned waves are recorded by sensors, and an image of the structures appears on the computer screen. An echoencephalogram is a picture that shows reflected waves.
In the human body, each tissue has its own acoustic resistance: it reacts differently to ultrasonic waves. For example, dense bone tissue produces one type of reflected signal, while tumors and cysts produce another. Echoencephaloscopy is based on this property of tissues, thanks to which the diagnostician determines healthy and diseased areas of the brain and skull.
The examination of the skull and brain is carried out using ultrasound with a frequency of 2 to 20 MHz. This is too little to potentially cause harm to the body of a child and an adult. Ultrasound energy is too low to somehow change the state of a biological object.
The impulse is formed in the following successive stages:
- Initial complex. The frequency of the sent wave is determined.
- M-echo. Echo is the main signal formed during the passage of dense and liquid structures.
- Ultimate complex. The signal bounces off the bony wall of the skull on the opposite side.
- Lateral signal. This is the difference between the sent signal of the first sensor and the received signal in the second.
Echo examination of the brain has several negative aspects:
- In comparison with modern methods (MRI, neurosonography) it has a low diagnostic value.
- Shows only a ready-made picture of the disease, without the possibility of establishing its cause.